Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2 Skema
Cargado por
Cikgu Faizal100%(1)100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
827 vistas12 páginasSumber : http://eeumchem.wordpress.com/
Manfaatkan sebaik2nya Percubaan Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 untuk membantu peningkatan optimum pencapaian calon dalam peperiksaan SPM 2014
Selamat berjaya Calon SPM 2014
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoSumber : http://eeumchem.wordpress.com/
Manfaatkan sebaik2nya Percubaan Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 untuk membantu peningkatan optimum pencapaian calon dalam peperiksaan SPM 2014
Selamat berjaya Calon SPM 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
100%(1)100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
827 vistas12 páginasTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2 Skema
Cargado por
Cikgu FaizalSumber : http://eeumchem.wordpress.com/
Manfaatkan sebaik2nya Percubaan Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 untuk membantu peningkatan optimum pencapaian calon dalam peperiksaan SPM 2014
Selamat berjaya Calon SPM 2014
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 12
1
PERATURAN PEMARKAHAN (Kertas 2)
Num. Scoring Criteria Marks
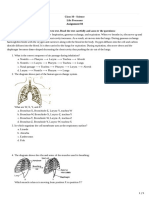
1(a)(i) Able to name the cell
Answer: Animal cell
1
1
1(a)(ii) Able to state the reason of the answer in (a)(i)
Answer:
Has no cell wall // has no vacuole // has no chloroplast // has
centrioles
1
1
1(a)(iii) Able to label structure Q, R and S
Answer:
Q: mitochondria
R: Golgi apparatus
S: Rough ER
1
1
1
3
1(b)(i) Able to state the function of organelle contain structure P
Answer:
Control all cell activities // contain genetic materials
1
1
1(b)(ii) Able to state the component of structure P
Answer: DNA
1
1
1(b)(iii) Able to name the parts labeled X, Y and Z
Answer:
X: phosphate group
Y: Pentose sugar
Z: Nitrogenous base
1
1
1
3
1(c)(i) Able to name cell T
Answer: Mesophyll palisade cell
1
1
1(c)(ii) Able to state why cell T has a large number of organelle R
Answer:
Process and modify protein into enzyme (to carry out photosynthesis)
1
1
TOTAL
12
2
NUM
SCORING CRITERIA
MARKS
2(a)(i) Able to state the condition of the red blood cells after being
immersed in
Solution P: Crenation / shrink / shrivel
Solution Q:Haemolysis / swell and burst
1
1
2
2(a)(ii) Able to name the type of solution R in which the red blood cells are
immersed.
Solution R is Isotonic solution.
1
1
2(a)(iii) Able to explain the answers given in a(ii)
P1:The cell retains its normal shape.
P2:The water diffuses in and out of the cells at equal rate by
osmosis
P3:Solution R has the same osmotic concentration as the
cytoplasmic fluid in the red blood cells
1
1
1
3
2(b) Able to explain why vinegar is suitable to be used as the natural
preservative for the preservation of garlic.
F1: Vinegar has a low pH/acidic
E1: Vinegar diffuses into the tissues of the garlic
E2: The tissues of the garlic becomes acidic
E3: The low pH prevents the growth of microorganisms in
garlics
E4: The garlic can be preserved to last longer
F any 2E
1
1
1
1
1
3
2(c) Able to explain the condition of the plant in Diagram 2.2 after one
week .
F: The plant wilt
E1: The cells become flaccid/plasmolysed//both the vacuole the
vacuole and cytoplasm shrink//the plasma membrane of the
root cells pull away from the cell wall.
E2:Water molecules diffuse out from the cell sap of the root
hair cell by osmosis
E3:(the remaining) soil water becomes hypertonic to the cell
sap of the root hair cell as the soil dries out.
F any 2E
1
1
1
1
3
TOTAL
12
3
Num SCORING CRITERIA MARK
3(a) Able to state number of chromosomes in the cell
Answer: 6 chromosomes
1
1m
3(b) Able to draw one daughter cell of mitosis and meiosis
Answer:
(i) mitosis
Number of chromosomes are 6
Same pattern and same size of chromosomes as parent cell
(ii) meiosis
Number of chromosomes are 3
Pattern and size of chromosomes is different compare to parent cell
1
1
1
1
2m
2m
3(c) Able to explain why the chromosomes numbers are different
Suggested Answer:
In mitosis:
- (During anaphase) chromosome / sister chromatids separated and
move to the opposite poles (cause the number of chromosome in
daughter cell remain the same)
In meiosis:
- (During anaphase I) homologous chromosomes separated and move
to the oppoeite poles (cause the number of chromosome in daughter
cell become half form the parent cell)
1
1
2m
3(d) Able to explain one difference of importance of mitosis and meiosis
Suggested Answer:
F1: Mitosis produce no variation, while meiosis produce variation
P1: caused by crossing over during Prophase I in meiosis
1
1
2m
3(e) Able to explain why buffalo is white colour
Answer:
P1: albino buffaloes caused by gene mutation which control the
production of skin pigmentation
P2: in autosomes
P2: controlled by recessive alleles
P3: skin cells unable to synthesis (melanin) pigment // no (melanin)
pigment
Any 3
1
1
1
1
3 m
Total 12
4
Num Mark Scheme Mark
4(a) Able to name corectly R dan S
Answer:
R : Tendon
S : Ball and socket joint
1
1
2
4(b) Able to explain the function of X muscle, Y muscle and R in
action to straighten the arm
Suggested answer:
F : Muscle X and muscle Y act as an antogonistic pair
P1 : Muscle Y / triseps contract while muscle X / biseps was
relaxes
P2 : to transfer the force by tendon / R tissue to the bone
P3: (Tendon is inelastic and tough) pulled the ulna bone
downward (and caused the forearm is straighten)
1
1
1
1
Max
3
4 (c) Able to explain why muscle work in pairs to produced movement
Suggested answer:
F: The muscle can only contract / pull out
P: It has to be extended back to it original lenght (to contract
again) by the contraction of another muscle
1
1
2
4 (d) Able to state the importance of skeletal part in movement
Suggested answer:
P1: provides surface area for muscle attachment
P2: form the joints that enable the bone to move and allowing
movement
P3: support the body / forearm weight
1
1
1
Max
2
4( e ) Able to explain what happened if the tissue R torn
Suggested answer :
F: the forearm cannot bend / straightens
P1: when the muscle X or Y contract
P2: the pulling force (produced by contraction of muscle) is not
transmit to the radius / ulna
1
1
1
3
Jumlah
12
5
Num Mark Scheme Mark
5(a)(i) Able to name the machine
Answer: Dialysis machine
1
1
5(a)(ii) Able to explain the function of the machine
Suggested answer:
P1: During haemodialysis, patients blood is pumped out from artery
in the arm and flow into dialysis machine
P2: the blood flow through semipermeable tube in the machine
P3: blood has higher concentration of urea and salts
P4: urea and salts diffuse out through the semipermeable tube into
dialysis fluid
P5: dialysis fluid contain lower concentration of urea and salts
compare to the blood
P6: the blood is returned back in the body through vein in the same
arm
P7: concentration of urea and salts in the blood // blood osmotic
pressure back to normal range
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
3
5(b)(i) Able to state the effect of salts to the formation of urine
Answer: Volume of urine is less and concentrated
1
1
5(b)(ii) Able to explain the answer in (b)(i)
Suggested answer:
P1: salted sup tulang cause the blood osmotic pressure increase
P2: more ADH secretes by pituitary gland
P3: wall of nephron in kidneys become more permeable to water
P4: more water reabsorb into blood capillary by osmosis
1
1
1
1
Max
3
5(c)(i) Able to label the structure
Notes:
3 labels correct
2 labels correct
1 label correct
2
1
0
2
5(c)(ii) Able to explain why there is no glucose and amino acids in urine
Suggested answer:
P1: all glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed into blood capillary
P2: at proximal convoluted tubules
1
1
2
Total
12
6
NUM. MARK SCHEME MARKS
6(a)(i) Able to name the organs that are involved in the processing of food P
correctly.
Answer:
Mouth / Oral cavity
Duodenum
Ileum / Small intestine
1
1
1
3
6(a)(ii) Able to explain the processes which occur to the food P until it can be
used by body cells.
Sample answer:
P1 Food P rich in starch
P2 (In oral cavity) saliva contains enzyme salivary amylase
P3 To hydrolysis starch to maltose //
P4 Duodenum receive pancreatic amylase from pancreas
P6 Pancreatic amylase completes the digestion of starch to maltose //
P7 (In ileum) intestinal juice contains maltase (erepsin, sucrase,
lactase)
P8 (Maltase) hydrolysis maltose to glucose //
P9 Glucose diffuse into the epithelial cells and absorbed into the
capillaries (villus)
P10 Capillaries drain glucose into hepatic portal vein, which leads to the
liver
P11 Glucose is distributed throughout the body by the circulatory system
P12 (When the glucose molecules reach the cells) glucose are oxidised
to release energy (during cellular respiration)
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
7
Salivary amylase
Starch + (Water) Maltose
Pancreatic amylase
Starch + (Water ) Maltose
Maltase
Maltose + Water Glucose
7
6(b) Able to explain the role of organ R in assimilation of nutrients in foods P.
Answer:
F (At the end of the digestive process) Food P are hydrolysed /
digested into glucose (at ileum)
P1 Excess glucose is converted into glycogen
P2 stored in the liver
P3 (When the blood sugar level falls) the stored glycogen is converted
back to glucose
P4 (When the glycogen stored in the liver is full) excess glucose is
converted into lipid (by liver)
1
1
1
1
1
5
6(c) Able to explain how the gastric bypass surgery can reduce excessive
weight problems
Sample answers:
F: (Due to the stomach becomes too small) the patient has less appetite
P1: reduce food intake
P2: reducing the absorption of nutrients (from digested food)
P3: causing the system in body takes energy from fat (in the body as a
substitute for food that is often taken)
P4: leading to weight loss
1
1
1
1
1
Max
5
TOTAL MARKS 20
No Mark Scheme Mark
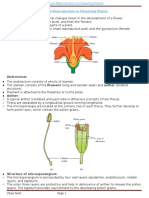
7(a) Able to explain the development of pollen based on the diagram above.
Suggested answer:
E1: pollen mother cell ( diploid) undergo meiosis I
E2: 2 cell stage of pollen cell (haploid) is form
E3: 2 cell stage undergo meiosis II
E4: tetrad stage is form
E5: after the secretion of cell wall, the pollen is form
1
1
1
1
1
1
max
4
7(b) Able to explain the process of double fertilisation occurs in the plant.
Suggested answer:
E1- The pollen tube grows down the style towards the ovule
E2- The sugar solution (sucrose) secreted by the stigma stimulates
the pollen grain to germinate and form a pollen tube
E3- The generative nucleus divides by mitosis to form two male
gamete nuclei
E4- The male gamete nuclei move down the pollen tube led by the
tube nucleus
1
1
1
1
8
E5- When the pollen tube reaches the ovary, it penetrates the
ovule through the micropyle
E6- The tube nucleus degenerates, leaving a clear passage for the
male nuclei to enter the embryo sac
E7- Double fertilization occurs in the ovule. One male nucleus fuses
with the egg nucleus to form a diploid zygote(2n)
E8- The other male nucleus fuses with the two polar nuclei to form a
triploid nucleus(3n)
1
1
1
1
Max
6
7(c) Able to explain the process of secondary growth in plant
Suggested answer:
F1:Vascular cambium divides actively radially
E1:forming cambium ring/ intervascular cambium
F2:Cambium cells divides tangently,
E2:cell in the outside differentiate to form secondary phloem
E3:while the inner cell differentiate to form secondary xylem
E4:primary xylem pushed towards the pith
E5:and primary phloem pushed towards the epidermis
E6:the walls of secondary xylem will be thickened with lignin
E7:this give tissues mechanical strength to support the plant
E8:the tissues outside become increasingly compressed
E9:the circumference/ diameter increased caused the epidermis to be
stretched
E10:the ruptured epidermis will be replaced by cork as a result of the
activity of cork cambium
F3:cork cambium divides tangently
E11:form secondary cortex/inner cell and cork/ outer cell
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
max
6
7(d) Able to explain the important of secondary growth in plant.
Suggested answer:
P1: Increase the diameters of the plant stems and roots for additional
mechanical support
P2: Produces secondary xylem called wood to support and strengthen the
growing plant
P3: Produces more secondary phloem and secondary xylem to
accommodate the increase in demand for water, mineral and organic
nutrient
P4: produced new phloem and xylem tissues to replace old and damaged
ones
P5: Produces a thick and tough bark which reduces evaporation of water
from the surface of stem, also protects the plant against of insect and
parasite fungi
P6: Increase the opportunities to produce seeds and propagate as plant that
undergo secondary growth live longer
P7: produce large quantities of fruit for local consumption and export
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
4
TOTAL 20
9
NUM SCORING CRITERIA MARKS
8(a) Able to explain the used of microorganism S and T in the field of
biotechnology
Sampel answer:
Microorganism S fungi / yeast
Uses Explanation
E1 Producing wine Fermentation of glucose (grape
juice) by yeast produces etahanol
E2 Making of bread Respiration of yeast produces carbon
dioxide which causes bread dough to
rise
E3 Producing beer Yeast is added to maltose to produce
alcohol
E4 Producing citric
acid
Break down maize starch into citric
acid
Any 2
Microorganism T bacteria
Uses Explanation
E5 Treatment of
industrial wastes
Anaerobes bacteria are used to break
down / converted industrial wastes
into non-poisonous materials
E6 Making yogurt Bacteria (Lactobacillius bulgaricus)
used to break down lactose into
lactic acid
E7 Producing vinegar
from alcohol
Bacteria (Acetobacter sp) is used to
change alcohol into acetic acid
(vinegar)
Any 2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2 m
2m
8(b) Able to explain the used of biotechnology in the waste treatment
process
Sampel answer:
P1 - rich in organic matters, bacteria / microorganism
P2 - the sewage is decomposed by aerobic bacteria
P3 - in the presence of oxygen
P4 - (Decomposed sewage /sludge) settled to the bottom of the
pond
P5 - Fermentation takes place (at sedimentation tanks)
P6 - Using anaerobic bacteria
P7 - Produce methane / carbon dioxide / minerals
P8 - Digested sludge used as fertilisers
Any 6
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
6 m
10
8(c) Able to explain the characteristics, transmission of microorganism
Q and prevention from spreading
Sampel answer:
The characteristics of living things:-
C1 - ability to reproduce
C2 - the presence of nucleic acids
The characteristics of non-living things:-
C3 - do not respire
C4 - Do not feed
C5 - Do not excrete
C6 - Can be crystallised Any 2
Transmission of Microorganism Q
T1 - microorganism Q is virus HIV
T2 - enters the body through the transfer of body fluids / blood /
semen / vagina fluids
T3 - from infected pregnant mother to the foetus (across the
placenta) // from infected mother to the baby by breast
feeding
T4 - contaminated needles used to inject drugs / for tattoo
T5 - unprotected sex with infected person
Prevention disease from spreading
P1 - type of disease : AIDS
P2 - blood produces used should be treated to detect the virus
P3 - people who have sex with different partners must wear a
condom to reduce the risk of infection // do not have sex
with any individual whose background / correct health status
is unknown // royalty to one sex-partners only // do not have
sex with homosexual person
P4 - do not share (contaminated) needles / syringes
Note
- Characteristics
- At least one from C1 to C2; one from C3to C6
- Maximum four C only
- Transmission and Prevention
- At least two T and two P
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
10M
TOTAL
20
11
NO SCORING CRITERIA MARKS
9 (a)(i)
9(a)(ii)
Able to state the example of continuous variation and
discontinuous variation and the difference of continuous
variation and discontinuous variation
Sample answer:
Example of continuous variation: Height or weight
Example of discontinuous variation: ABO blood group
Differences:
Continuous variation Discontinuous variation
Graf distribution shows a
normal distribution
Graf distribution shows a
discrete distribution
The characters are
quantitative / can be
measured and graded
(from one extreme to the
other)
The characters are
qualitative / cannot be
measured and graded
(from one extreme to the
other)
Exhibits a spectrum of
phenotypes with
intermediate character
Exhibits a few distinctive
phenotypes with no
intermediate character
Influenced by
environmental factors
Is not Influenced by
environmental factors
Two or more genes control
the same character
A single genes determines
the differences in the traits
of the character
The phenotype is usually
controlled by many pair of
alleles
The phenotype is
controlled by a pair of
alleles
Able to state the importance of variation to organism
Sample answer:
P1: variation provided better adaptation for organism to survive
in the changing environment
P2: variation are essential to the survival of species / to survive
more successfully
P3: variation be able to organism explore a new habitat
P4: to ensure organism survival from predator
Any 3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
Max 5
3
12
9(b) Able to explain how genetic factors cause the variation among
the organism
Sample answer:
F1: meiosis
P1: produce varies gamete with different genetic content
P2: through homologous chromosomes random assortment
during metaphase I
F2: crossing over
P3: two homologous chromosomes are paired up / synapsis
during prophase I
P3: crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids at the
chiasma
P4: chromatids break and rejoin in such a way that segments of
chromatids are exchange // causing a genetic recombination
P5: genes in the chromosomes is altered and gametes with
various combinations of chromosomes are produced
F3: Fertilization
P6: random fertilization between sperm and ovum
P7: produce zygote with varies genetic material
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Max
10
JUMLAH 20
También podría gustarte
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisDe EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers HomeostasisCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Necropsy Guide for Dogs, Cats, and Small MammalsDe EverandNecropsy Guide for Dogs, Cats, and Small MammalsSean P. McDonoughCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Scheme Bio Paper 2 2011Documento12 páginasScheme Bio Paper 2 2011Hafiq IkhwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Answer Scheme Paper 2 Form 5Documento15 páginasAnswer Scheme Paper 2 Form 5Azam NoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 BioDocumento9 páginasSkema Jawapan Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2012 Biogomathi24Aún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 2Documento13 páginasSkema Jawapan Kertas 2zulhariszan abd mananAún no hay calificaciones
- Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyDocumento102 páginasModule SBP Perfect Score SPM 2011 BiologyKen Yew PiongAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFDocumento43 páginasModul Biologi 2016 t5 Skema PDFIsmaliza IshakAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Kertas 2Documento9 páginasSkema Kertas 2Sitinorsyahidah Jantan100% (1)
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaDocumento14 páginasTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaDocumento14 páginasTrial Spm-Bio k2 SkemaFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Biology Paper 123 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM Del JsuDocumento43 páginasSkema Biology Paper 123 Trial SPM 2013 MRSM Del JsuAhmad Imran Idzqandar100% (2)
- Skema Biologi Kertas 2 PPC 2014Documento10 páginasSkema Biologi Kertas 2 PPC 2014arissaamanyAún no hay calificaciones
- Biologi K2 JawapanDocumento14 páginasBiologi K2 JawapanShou ZhengAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Perak 2016 p2 SkemaDocumento15 páginasTrial Perak 2016 p2 SkemaHaw AHAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Sac PDFDocumento24 páginasSkema Sac PDFNoridaAnisAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaDocumento65 páginasModul Biologi 2016 t4 SkemaIsmaliza IshakAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Pppa Bio k2Documento12 páginasSkema Pppa Bio k2Tavamani MuniandyAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K2Documento18 páginasTrial SBP SPM 2013 Biology SKEMA K2Cikgu Faizal60% (5)
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 6Documento28 páginasNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 6REJEEAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 K2 SKEMADocumento9 páginasTrial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 K2 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Skema Jawapan Biologi Percubaan SPM 2008: Structured Question: No. 1Documento13 páginasSkema Jawapan Biologi Percubaan SPM 2008: Structured Question: No. 1afifasolehahAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Jawapan Percubaan SPM Biologi 2012 Negeri SembilanDocumento26 páginasSkema Jawapan Percubaan SPM Biologi 2012 Negeri Sembilanhazwani_motorola100% (4)
- Worksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Documento2 páginasWorksheet 4 On Transportation (Circulatory System)Naruto UzumakiAún no hay calificaciones
- 4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015Documento22 páginas4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015zulkarnain100% (1)
- Modul Bio SBP 2011 AnsDocumento23 páginasModul Bio SBP 2011 AnsAlan WangAún no hay calificaciones
- Question BankDocumento105 páginasQuestion BankIcy HurricaneAún no hay calificaciones
- 2011 SBP Bio SkemaDocumento33 páginas2011 SBP Bio SkemaChe ShazuandyAún no hay calificaciones
- 4551 BIO - Skema Kertas 1 & 2 & 3Documento19 páginas4551 BIO - Skema Kertas 1 & 2 & 3Yeow Pow ChooAún no hay calificaciones
- S4 QQK L1 NJ 49 Xs ZQGJ HKBDocumento28 páginasS4 QQK L1 NJ 49 Xs ZQGJ HKBLakhwinder RaundAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Documento11 páginasBio P2 Skema PP SPM 2016Ismaliza IshakAún no hay calificaciones
- Sulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbDocumento17 páginasSulit 4551/2: Reject: Provide Reject: AbsorbYatihanna MrodiAún no hay calificaciones
- Answer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Documento0 páginasAnswer Ramalan Biology SPM 2013Thuran NathanAún no hay calificaciones
- NCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesDocumento26 páginasNCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelAún no hay calificaciones
- Ans Paper 2 SelangorDocumento12 páginasAns Paper 2 SelangorRozaini OthmanAún no hay calificaciones
- XAPlus 2016 Answer MiauDocumento24 páginasXAPlus 2016 Answer MiauzulkarnainAún no hay calificaciones
- Jawapan BioDocumento9 páginasJawapan BioJesus SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Sci Lifeprocesses As03Documento5 páginas10 Sci Lifeprocesses As03Rudraksh Infra ConsultantsAún no hay calificaciones
- Ps - Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - EseiDocumento43 páginasPs - Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - EseiNadira Bt IsmailAún no hay calificaciones
- 17 Moz@C: (40 Marks) Answer Only Two Question From This SectionDocumento4 páginas17 Moz@C: (40 Marks) Answer Only Two Question From This SectionazszahAún no hay calificaciones
- Mark Scheme, BIOLOGY Paper 2, Trial SBP 2007: AnswerDocumento14 páginasMark Scheme, BIOLOGY Paper 2, Trial SBP 2007: Answerhuixin1017Aún no hay calificaciones
- Confidential: ATP SynthetaseDocumento5 páginasConfidential: ATP SynthetaseazszahAún no hay calificaciones
- Cbse - X - Biology - PT-1 - April 2023 Key)Documento9 páginasCbse - X - Biology - PT-1 - April 2023 Key)LAZED YT GAMINGAún no hay calificaciones
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDocumento12 páginasThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- Class X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesDocumento2 páginasClass X Additional Homework On Life ProcessesBornil Bikash BhuyanAún no hay calificaciones
- Life Processes-Question BankDocumento9 páginasLife Processes-Question Bankkfjg47zq26Aún no hay calificaciones
- (Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014Documento12 páginas(Spmsoalan) Skema Biologi K2 Terengganu 2014zaihassniAún no hay calificaciones
- X - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 MarksDocumento11 páginasX - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 Marksvalliammai thiagarajanAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology T4 2013 JWPDocumento4 páginasBiology T4 2013 JWPShirmei WangAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Sci Lifeprocesses As04Documento5 páginas10 Sci Lifeprocesses As04Rudraksh Infra ConsultantsAún no hay calificaciones
- Life Processes 1695198606892Documento38 páginasLife Processes 1695198606892TuikmcAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Sci Lifeprocesses As02Documento5 páginas10 Sci Lifeprocesses As02Rudraksh Infra ConsultantsAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem of The DayDocumento28 páginasProblem of The Dayibyakubu2016Aún no hay calificaciones
- British Biology Olympiad 2013: Time Allowed 1Documento25 páginasBritish Biology Olympiad 2013: Time Allowed 1Malvina YuanAún no hay calificaciones
- NCERT Chapter - 11 - Transportation - in - Animals - and - PlantsDocumento5 páginasNCERT Chapter - 11 - Transportation - in - Animals - and - PlantsrmurthyAún no hay calificaciones
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsDe EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In PlantsAún no hay calificaciones
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesDe EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsDe EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (12)
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K3 SkemaDocumento8 páginasTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K3 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K3 Skema Soalan 2Documento3 páginasTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K3 Skema Soalan 2Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaDocumento5 páginasModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2 SkemaDocumento10 páginasTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K3 Skema Soalan 1Documento7 páginasTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K3 Skema Soalan 1Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial MRSM Kimia SPM 2014 K1 K2 K3 No SkemaDocumento78 páginasTrial MRSM Kimia SPM 2014 K1 K2 K3 No SkemaCikgu Faizal56% (16)
- Modul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014Documento21 páginasModul Analisis Fizik Merbau Miri SPM 2014Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaDocumento14 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K3 Skema Modul 2Documento3 páginasTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K3 Skema Modul 2Cikgu Faizal50% (2)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2Documento15 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2Cikgu Faizal0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K1 Set 2Documento34 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K1 Set 2Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Documento5 páginasTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Skema Modul 2Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3Documento14 páginasTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics Skema K1 K2 K3NgauHWAún no hay calificaciones
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 1Documento21 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 1Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Documento20 páginasModul Kimia SPM A+ 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (6)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2 SkemaDocumento7 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 2 SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K1 Set 2 SkemaDocumento7 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K1 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K1 Set 1 SkemaDocumento7 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K1 Set 1 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K3 SkemaDocumento11 páginasTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 1 SkemaDocumento6 páginasJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 English K2 Set 1 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Add Math SPM 2014 Modul Melaka GemilangDocumento65 páginasAdd Math SPM 2014 Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu Faizal71% (7)
- Modul Perfect Score - SPM 2014 EnglishDocumento52 páginasModul Perfect Score - SPM 2014 EnglishSyapie Nasir MAún no hay calificaciones
- Jawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraDocumento63 páginasJawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- JUJ Pahang 2014 Biology SPM K3 Set 1 SkemaDocumento15 páginasJUJ Pahang 2014 Biology SPM K3 Set 1 SkemaCikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- K2 Fizik Percubaan Terengganu 2014Documento27 páginasK2 Fizik Percubaan Terengganu 2014Panitia Fizik BASISAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K3Documento16 páginasTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K3Cikgu FaizalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaDocumento16 páginasTrial Terengganu SPM 2014 Physics K1 K2 K3 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Trial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaDocumento14 páginasTrial Kedah 2014 SPM Biologi K2 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K1 No SkemaDocumento48 páginasTrial MRSM SPM 2014 Physics K1 No SkemaCikgu Faizal50% (2)
- Phylum Magnoliophyta: AngiospermsDocumento7 páginasPhylum Magnoliophyta: Angiospermskell73kAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Handbook Class 12Documento235 páginasBiology Handbook Class 12Michael John100% (3)
- Choice BoardDocumento5 páginasChoice BoardHAIZA HANIM BINTI ABD AZIZ MoeAún no hay calificaciones
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-1Documento8 páginasSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-1Manas Ranjan Jena100% (1)
- Sum Academy Larkana MCQ Test Chapter 4Documento20 páginasSum Academy Larkana MCQ Test Chapter 4Ali raza khero80% (5)
- Embryology of Flowering Plants - Terminology and ConceptsDocumento811 páginasEmbryology of Flowering Plants - Terminology and ConceptsMaiky Lopes PauloAún no hay calificaciones
- Plant Taxonomy NotesDocumento13 páginasPlant Taxonomy NotesMikaela MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Material of Class Xii Biology PDFDocumento181 páginasMaterial of Class Xii Biology PDFMURUGANAún no hay calificaciones
- Kingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowDocumento13 páginasKingdom Plantae: Plant Cell - Parts To KnowAthena Huynh100% (1)
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento13 páginasReproduction in Flowering PlantsMaogageoffreyAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 26 Instructor NotesDocumento15 páginasCH 26 Instructor NotesKeith ValmontAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Biology BitsDocumento34 páginas10 Biology BitsSuresh Raghava100% (1)
- Marks Wise Questions CH-1Documento27 páginasMarks Wise Questions CH-1lakshshah5116Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mega CAPE Unit 1 Bio P1 CollectionDocumento238 páginasMega CAPE Unit 1 Bio P1 CollectionJanille PowellAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 FertilizationDocumento30 páginas6 FertilizationPuran BistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio270 Tutorial Week 10Documento2 páginasBio270 Tutorial Week 10Mirza KarmilaAún no hay calificaciones
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFDocumento12 páginasHow Do Organisms Reproduce Important Questions PDFSomik JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio Notes PDFDocumento40 páginasBio Notes PDFYes NoAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 10 Study Guide KeyDocumento7 páginasUnit 10 Study Guide KeyyawahabAún no hay calificaciones
- Plant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Documento25 páginasPlant and Animal Organ Systems and Their Functions: General Biology 2Ica A TorioAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio IDocumento234 páginasBio ISimiYadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Reproduction of Plants and AnimalsDocumento37 páginasReproduction of Plants and AnimalsMark Dejarme DublinAún no hay calificaciones
- RPT Biology Form 5Documento18 páginasRPT Biology Form 5Mohamad Khairie Rano IbrahimAún no hay calificaciones
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Documento21 páginasLife Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Shyamal AryalAún no hay calificaciones
- In Vitro Pollination and in Vitro Fertilization": An Assignment OnDocumento13 páginasIn Vitro Pollination and in Vitro Fertilization": An Assignment OnJagrit KhanalAún no hay calificaciones
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-Mcq-Neet Class-Xii BiologyDocumento6 páginasSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants-Mcq-Neet Class-Xii BiologyAnjaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Support MaterialDocumento179 páginasBiology Support MaterialVarshAún no hay calificaciones
- Reproduction in Plants (Bol Question Bank)Documento2 páginasReproduction in Plants (Bol Question Bank)Sattu SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Class12 Bio QB Part 1Documento83 páginasClass12 Bio QB Part 1Rohit KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Kerala Plus Two Botany Focus Area Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento4 páginasKerala Plus Two Botany Focus Area Notes - Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsReshmaAún no hay calificaciones