Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
3
Cargado por
triloksinghmeena0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
6 vistas5 páginasupsc
Título original
Doc3
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoupsc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
6 vistas5 páginas3
Cargado por
triloksinghmeenaupsc
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 5
1) Though Green Energy is crucial to Indias energy security efforts,
there is a dearth of investment in the sector. Examine what efforts have
been made by the Union government to increase investments in green
energy in India.
Business Standard
2) As envisioned in the Treaty of Rome, the integration of European
countries, is still a work in progress. Examine.
Business Standard
3) Indias crop protection chemicals sector needs to invest more in R&D
to face many upcoming challenges. Analyse these challenges.
Business Standard
4) While the post-9/11 rhetoric suggested a common perceptual image,
both India and US have actually always had different frameworks for
confronting terrorism and extremism. Critically comment.
Business Standard
5) The Komagata Maru incident was an act of gross violation of human
rights and a landmark event during Indias freedom struggle. Critically
comment.
The Komagata Maru incident in 1914 was an incident in which the Canadian government denied their
entrance to enter Vancouver. The Komagata Maru incident was a long journey, that stayed at the docks
for two months with nowhere else to go and when they were sent back to India a terrible surprise was
waiting for them that violated at least three human rights in the end.
The Komagata Maru incident violated at least three human rights, even though the Universal
Declaration of Human Rights wasnt put into effect until December 1948. I think articles three, nine, and
thirteen of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights were violated during this incident. Article 3 states,
Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person. This was violated when 19 people were
killed during the gunfire. Article 9e states, No one shall be subjected to arbitrary arrest, detention or
exile. This was violated when the British gun ship tried arresting the 20 men they saw as leaders. Article
13 section 2 states, Everyone has the right to leave any country, including his own, and to return to his
country. This was violated when the British gun boat didnt let them go back to their home country.
6) Critically comment on the major causes behind instability in the Mid-
East region. Do you think the involvement of Western forces will help
resolve crises in the region? Explain why.
27092014
Q1) There is a growing concern over Atmospheric Brown Cloud and its impact on South Asia. What are
the causes and consequences of Atmospheric Brown Cloud?
Source-1
Source 2
Atmospheric brown cloud is a layer of air pollution containing aerosols such as soot or dust that
absorb as well as scatter incoming solar radiation. This leads to regional and global climatic effects and
poses risks to human health and food security. This layer extends from Earths surface to an altitude of
roughly 3 km.
Causes-
The ABC is created by a range of airborne particles and pollutants from combustion (e.g., wood-
fires, cars, and factories), biomass burning and industrial processes with incomplete burning. The cloud
is associated with the winter monsoon during which there is no rain to wash pollutants from the air.
Impacts-
1. Dimming- ABCs can reduce sunlight hitting the Earths surface. Particles such as Sulphates reflect
and scatter rays back into space. Black carbon in soot absorbs sunlight before it reaches the
ground.
2. Climate change- Particles and aerosols in the ABCs may act to inhibit the formation of rain drops
and rainfall. The net effect will be an extension of cloud life-times.
3. Weather change- the large heating and cooling effects of ABCs respectively in the atmosphere
and at the surface, combined with the impacts of greenhouse gases, may be also triggering
sharp shifts in weather patterns.
4. Glaciers retreating- Glaciers in India such as the Siachen, Gangotri and Chhota Shigiri glaciers are
retreating at rates of between 10 and 25 metres a year. It will be accelerated by the ABCs.
5. Food security threats- damage to crops will be as a result of increased ground level ozone. Other
effects may include damage linked with the various acidic and toxic particles from brown clouds
depositing on plants from the atmosphere. Reduced levels of photosynthesis and thus crop
production due to dimming.
6. Health impacts- Brown clouds contain a variety of toxic aerosols, carcinogens and particles
including particulate matter (PM). These have been linked with a variety of health effects from
respiratory disease and cardio-vascular problems.
Further, simply tackling the pollution linked with brown cloud formation without
simultaneously delivering big cuts in greenhouse gases could have a potentially disastrous effect
in increasing the Global warming.
Q2) What do you understand by Nuclear Umbrella? How relevant it is in contemporary world
geopolitics? Substantiate.
Source 1
Source 2
Nuclear Umbrella, is a guarantee given by a nuclear weapon state to non-nuclear weapon state citing
that military protection will be provided, if required nuclear weapons too, if any threat from third party.
This gives dominance to nuclear state by having an edge of holding nuclear arms whereas protected
state gets an additional security in case of war outbreak. There are essentially two nuclear umbrella, The
USA & Russia.
This umbrella has become tools of politics in several ways like:-
China who has often been refrain from entering umbrella deal is assumed to have extended hands to
Ukraine after Crimea annexation. There seems strategic interest in terms of military technology & design
offered by Ukraine. Same benefit is seen by Russia too.
Chinas continuous co-operation to Pakistan in terms of building nuclear weapons & missiles is always
a cause of concern to India.
NATO expressed its displeasure over Scotlands demand of independence by threatening to withdraw
the guarantee leaving the country open for aggressive peril from others.
Although such idea of guarantee is criticised saying that it violates the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
as nuclear umbrella are usual but never explicitly declared.
Q3) Write short notes on
1. OLED display
a. OLED are Organic Light Emitting Diode, it is basically a made of thin films of organic
material which produces light when electricity is passed through. It has the potential to
make the dream of having transparent and flexible phone and other electronic devices
possible. The technology have certain advantages over the current LCD and Plasma
displays, apart from being lighter, clear display, easy to fabricate, higher efficiency the
devices would also cost less in future. However, it would need more innovation and
time to make it cheaper by producing at large scale and making it water proof.
2. Spintronics
a. spinelectronics or fluxtronic, is an emerging technology exploiting both the intrinsic spin
of the electron and its associated magnetic moment, in addition to its fundamental
electronic charge, in solid-state devices.
b. Spintronics differs from the older magnetoelectronics, in that the spins are not only
manipulated by magnetic fields, but also by electrical fields.
3. Wireless Energy Transfer
a. Wireless energy transmission is the transmission of electrical energy from a power
source to an electrical load without man-made conductors. Wireless transmission is
useful in cases where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or impossible.
The problem of wireless power transmission differs from that of wireless
telecommunications, such as radio. In the latter, the proportion of energy received
becomes critical only if it is too low for the signal to be distinguished from the
background noise. With wireless power, efficiency is the more significant parameter. A
large part of the energy sent out by the generating plant must arrive at the receiver or
receivers to make the system economical.
b. The most common form of wireless power transmission is carried out using direct
induction followed by resonant magnetic induction. Other methods under consideration
are electromagnetic radiation in the form of microwaves or lasers[1] and electrical
conduction through natural media.
4. Vortex Engine
An atmospheric vortex engine (AVE) uses a controlled vortex to capture mechanical
energy produced when heat is carried upward by convection in the atmosphere. A tornado-like
vortex is produced by admitting warm or humid air tangentially into a circular arena. Tangential
entries cause the warm moist air to spin as it rises forming an anchored convective vortex. The
work of convection is captured with turbines located at ground level around the periphery of
the arena. The heat source can be solar energy, warm water or waste heat.
26092014
1.
También podría gustarte
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- EvaporationDocumento37 páginasEvaporationVimal KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Vision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 18 SDocumento34 páginasVision IAS Prelims 2020 Test 18 StriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Test 1 QuestionsDocumento18 páginasTest 1 QuestionstriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vajiram and Ravi Prelims 2020 Test 1 QuestionsDocumento27 páginasVajiram and Ravi Prelims 2020 Test 1 QuestionstriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lebs101 PDFDocumento30 páginasLebs101 PDFtriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- GuidelinesDocumento172 páginasGuidelinestriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 42&43Documento13 páginasLec 42&43triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Essay Test Series-4Documento19 páginasEssay Test Series-4triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 37&38Documento9 páginasLec 37&38triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 39,40,41Documento13 páginasLec 39,40,41triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identity PoliticsDocumento2 páginasIdentity PoliticstriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 31,32&33Documento12 páginasLec 31,32&33triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 34,35,36Documento12 páginasLec 34,35,36triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- (Insights Secure - 2017) UPSC Mains Questions On Current Affairs: 21 March 2017Documento2 páginas(Insights Secure - 2017) UPSC Mains Questions On Current Affairs: 21 March 2017triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
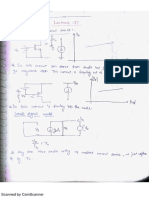
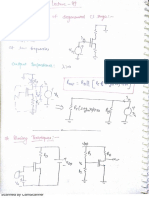
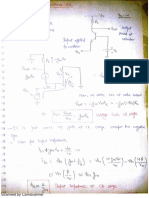
- Lec 24 25 Biasing TechniqueDocumento10 páginasLec 24 25 Biasing TechniquetriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 26,27,28Documento16 páginasLec 26,27,28triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 29&30Documento9 páginasLec 29&30triloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec-14-15 BJT Characteristics & BiasingDocumento7 páginasLec-14-15 BJT Characteristics & BiasingtriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Strike of The Bank Union Regarding These Issues:: Lok Sabha TV-Insight: Banking Reforms and ChallengesDocumento2 páginasStrike of The Bank Union Regarding These Issues:: Lok Sabha TV-Insight: Banking Reforms and ChallengestriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Rajasthan An OverviewDocumento1 páginaRajasthan An OverviewtriloksinghmeenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Experiment 2Documento8 páginasFluid Mechanics Lab Experiment 2SSShakeelAún no hay calificaciones
- En 2014 New Brochure WebDocumento20 páginasEn 2014 New Brochure WebSasa NackovicAún no hay calificaciones
- Polapak Condensing Unit: PPC Ver2.0Documento44 páginasPolapak Condensing Unit: PPC Ver2.0Lai WeikinAún no hay calificaciones
- Open and Closed Systems in ThermodynamicDocumento2 páginasOpen and Closed Systems in ThermodynamicArafath JazeebAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 5-Solar Thermal Energy Conversion SystemsDocumento25 páginasCH 5-Solar Thermal Energy Conversion SystemsVishnu PradeepAún no hay calificaciones
- Satellite Antenna TestingDocumento47 páginasSatellite Antenna Testingsailee_gharatAún no hay calificaciones
- Shallow Foundation - SettlementDocumento31 páginasShallow Foundation - SettlementDelina TedrosAún no hay calificaciones
- Almost Final Draft ProjectDocumento67 páginasAlmost Final Draft ProjectGanesh V IyerAún no hay calificaciones
- Quantum ComputingDocumento17 páginasQuantum ComputingAnkush100% (1)
- Mastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseDocumento6 páginasMastery Test MT1 and MT2 Solution: None of TheseU-line Anne Roque VillafloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Example 7: Reduced Diesel Fuel and Quake Variation: GRLWEAP Standard ExamplesDocumento2 páginasExample 7: Reduced Diesel Fuel and Quake Variation: GRLWEAP Standard ExamplesbozarromegustaAún no hay calificaciones
- Method Statement Fo Reinforcement Works BlogDocumento8 páginasMethod Statement Fo Reinforcement Works BlogMohasin Khan100% (1)
- The Physics of Superfluid Helium: W. F. VinenDocumento12 páginasThe Physics of Superfluid Helium: W. F. VinenPaulo CesarAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Plant Interview Book by Industrial GuideDocumento14 páginasChemical Plant Interview Book by Industrial GuideTom Jose KooduthottiyilAún no hay calificaciones
- P5 Q1 Experimental Design Updated To MJ22 ALL TOPICSDocumento6 páginasP5 Q1 Experimental Design Updated To MJ22 ALL TOPICSSaad NahraAún no hay calificaciones
- Products of CombustionDocumento27 páginasProducts of CombustionLorlie Bernales Blanca-TanjayAún no hay calificaciones
- The Mathematical Modelling of The Motion of A Horizontal Vibrating Screen Supported by Rosta Oscillating MountingsDocumento9 páginasThe Mathematical Modelling of The Motion of A Horizontal Vibrating Screen Supported by Rosta Oscillating MountingsVilayet AlekperovAún no hay calificaciones
- De Saint VenantDocumento13 páginasDe Saint VenantSinthya Nlend djikeAún no hay calificaciones
- CSE - 27 A3 Application of sf6 Alternatives For Retro Filling Existing EquipmentDocumento13 páginasCSE - 27 A3 Application of sf6 Alternatives For Retro Filling Existing EquipmentTXEMAAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch5 - Cooling of Power Semiconductor Devices PDFDocumento56 páginasCh5 - Cooling of Power Semiconductor Devices PDFmagicalmarshmallowAún no hay calificaciones
- Phase Behavior of Discotic Liquid Crystalline Polymers and Related Model CompoundsDocumento5 páginasPhase Behavior of Discotic Liquid Crystalline Polymers and Related Model CompoundsLeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Does Cloud Seeding Really Work? An Experiment Above Idaho Suggests Humans Can Turbocharge SnowfallDocumento3 páginasDoes Cloud Seeding Really Work? An Experiment Above Idaho Suggests Humans Can Turbocharge SnowfallAncaBotocAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Chemistry - Chapter 15 Benzene & Aromatic CompoundsDocumento9 páginasOrganic Chemistry - Chapter 15 Benzene & Aromatic CompoundsSairille ManejaAún no hay calificaciones
- ABC - TYPHOON ReportDocumento28 páginasABC - TYPHOON ReportRonica Reena T. BautoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ceramica EspumadaDocumento22 páginasCeramica EspumadaWILLIAN HPAún no hay calificaciones
- C&zpurlin ProfileDocumento8 páginasC&zpurlin ProfileRyan BeciosAún no hay calificaciones
- New Frontiers For The Pipeline Integrity ManagementDocumento16 páginasNew Frontiers For The Pipeline Integrity ManagementMubeenAún no hay calificaciones
- Welding Complete PPT With QuestionDocumento50 páginasWelding Complete PPT With QuestionKBSMANITAún no hay calificaciones
- Atmospheric Impacts of The Space Industry Require Oversight: CommentDocumento3 páginasAtmospheric Impacts of The Space Industry Require Oversight: CommentDylan HAún no hay calificaciones