Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Mid Term Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - Revisi
Cargado por
JoshuaUntung0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
283 vistas10 páginasigcse physics grade X
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoigcse physics grade X
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
283 vistas10 páginasMid Term Igcse Physics Grade 10 Sem 1 2014 Soal - Revisi
Cargado por
JoshuaUntungigcse physics grade X
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 10
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 1
Part one: Multiple Choise Questions [2 marks each]
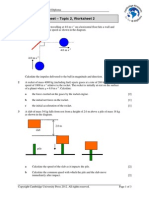
1. A student warms her hands near a fire.
Which waves carry most heat to her hands and are these waves electromagnetic?
waves electromagnetic
A. infra-red no
B. infra-red yes
C. visible light no
D. visible light yes
2. A beaker contains water at room temperature. How could a convection current be set up in the
water?
A. cool the water at X
B. cool the water at Y
C. stir the water at X
D. stir the water at Y
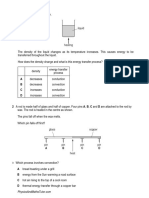
3. The table gives the melting points and boiling points of glycerine and benzene.
melting point boiling point
glycerine 18 C 290 C
benzene 5.4 C 80 C
At which temperature will both glycerine and benzene be liquid?
A 0 C B 50 C C 100 C D 150 C
4. A swimmer feels cold after leaving warm water on a warm, windy day.
Why does she feel cold even though the air is warm?
A. The less energetic water molecules on her skin escape quickly.
B. The more energetic water molecules on her skin do not escape quickly.
C. The water on her skin does not evaporate quickly enough to keep her warm.
D. The water on her skin evaporates quickly and cools her skin.
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 2
5. A skier walks from the bottom of a ski slope to the top and gains 10 000 J of gravitational
potential energy.
She skis down the slope.
At the bottom of the slope, her kinetic energy is 2000 J.
How much energy was converted into thermal energy and sound energy as the skier moved
down the slope?
A 2000 J B 8000 J C 10 000 J D 12 000 J
6. Which physical property is used to measure temperature in a liquid-in-glass thermometer?
A. the length of the thermometer
B. the thickness of the glass bulb
C. the volume of the glass bulb
D. the volume of the liquid
7. The graph shows the temperature of a substance as it is heated steadily.
In which part of the graph is the substance boiling?
8. A person holds a glass beaker in one hand and fills it quickly with hot water. It takes several
seconds before his hand starts to feel the heat.
Why is there this delay?
A. Glass is a poor conductor of heat.
B. Glass is a good conductor of heat.
C. Water is a poor conductor of heat.
D. Water is a good conductor of heat.
temperature
time
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 3
9. Two metal boxes containing air are standing in a room. Box X is on top of a heater. Box Y is on a
bench. The boxes are left for a long time.
Which line in the table best describes the average speed of the molecules in the containers?
box X
box Y
A fast
Zero
B fast
Slow
C slow
Fast
D zero fast
10. A night storage heater contains a large block of material that is heated electrically during the
night. During the day the block cools down, releasing thermal energy into the room.
Which thermal capacity and which night-time temperature increase will cause the most energy to
be stored by the block?
thermal capacity
of block
night-time
temperature increase
A large Large
B large small
B small large
C small small
11. Viewed through a microscope, very small particles can be seen moving with Brownian motion.
Which line in the table is correct?
type of motion
of particles
particles are
suspended in
A vibration a liquid or a gas
B vibration vibration a solid, a liquid or a gas
C random a liquid or a gas
D random random a solid, a liquid or a gas
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 4
12. A boy sits near a campfire. He pokes the fire with an iron bar.
His hand becomes hot.
In which ways does thermal energy (heat) from the fire reach his hand?
A. conduction and convection only
B. conduction and radiation only
C. convection and radiation only
D. conduction, convection and radiation
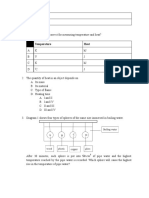
13. The same quantity of heat energy is applied to four different blocks.
The temperature rise produced is shown on each block.
Which block has the highest thermal capacity?
14. The diagram shows a heater used to heat a tank of cold water.
What is the main process by which heat moves through the water?
A. conduction
B. convection
C. evaporation
D. radiation
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 5
15. An engineer wants to fix a steel washer on to a steel rod. The rod is just too big to fit into the hole
of the washer.
How can the engineer fit the washer on to the rod?
A. Cool the washer and put it over the rod.
B. Cool the washer and rod to the same temperature and push them together.
C. Heat the rod and then place it in the hole.
D. Heat the washer and then place it over the rod.
16. Equal masses of two different liquids are heated using the same heater. The graph shows how the
temperature of each liquid changes with time.
What does the graph tell us about the liquids?
A. Liquid 1 has a higher melting point than liquid 2.
B. Liquid 1 has a higher boiling point than liquid 2.
C. Liquid 1 starts to melt sooner than liquid 2.
D. Liquid 1 starts to boil sooner than liquid 2.
17. A cup with a lid contains a hot drink.
When the lid is removed, the rate of heat loss from the drink increases.
What causes this?
A. convection only
B. evaporation only
C. both convection and evaporation
D. neither convection nor evaporation
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 6
18. A cupboard is placed in front of a heater. Air can move through a gap under the cupboard.
Which line in the table describes the temperature and the direction of the air that moves through
the gap?
air temperature air direction
A cool away from the heater
B cool towards the heater
C warm away from the heater
D warm towards the heater
19. The table lists the melting points and the boiling points of four different substances A, B, C and D.
Which substance is a gas at 25 C?
substance melting point / C boiling point / C
A 219 183
B 7 58
C 98 890
D 1083 2582
20. Which statement refers to convection?
A. It does not involve energy transfer.
B. It is the transfer of heat energy without the movement of particles.
C. It only occurs in liquids or gases.
D. It only occurs in solids.
21. A wooden wheel can be strengthened by putting a tight circle of iron around it.
Which action would make it easier to fit the circle over the wood?
A. cooling the iron circle
B. heating the iron circle
C. heating the wooden wheel
D. heating the wooden wheel and cooling the iron circle
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 7
22. A person uses chemical energy to run up some stairs.
She stops at the top of the stairs.
What has the chemical energy been converted to when she is at the top of the stairs?
A. kinetic energy and gravitational energy
B. kinetic energy and strain energy
C. gravitational energy and heat energy
D. strain energy and heat energy
23. Which of the following describes particles in a solid at room temperature?
A. Close together and stationary.
B. Close together and vibrating.
C. Close together and moving around at random.
D. Far apart and moving at random.
24. Spoons made of different materials were placed in four cups of coffee poured from the same jug.
Which spoon will be hottest to touch at end X?
25. A block of ice is heated at a constant rate. Eventually the melted ice boils.
The graph shows how the temperature changes with time.
How many minutes did it take to melt all the ice?
A 4 B 7 C 11 D 13
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 8
Part Two: Structured Questions
1. The diagram below shows a hot water storage tank.
The water is heated by an electric immersion heater
at the bottom.
a. How could heat loss from the tank be reduced?
What materials would be suitable for the job? [2]
____________________________________________
____________________________________________
b. Why is the heater placed at the bottom of the tank
rather than the top? [2]
___________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
c. The heater has a power output of 3 kW.
i What does the k stand for in kW? [1]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
ii How much energy (in joules) does the heater deliver in one second? [1]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
iii How much energy (in joules) does the heater deliver in 7 minutes? [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
d. The tank holds 100 kg of water. The specific heat capacity of water is 4200 J/(kg
O
C).
i How much energy (in joules) is needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1
O
C? [1]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
ii How much energy (in joules) is needed to raise the average temperature of all the water in the
tank by 1
O
C? [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
iii If the heater is switched on for 7 minutes, what is the average rise in temperature of the water
in the tank (assuming that no heat is lost)? [2]
__________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 9
2. The graph below shows how the temperature of some liquid in a beaker changed as it was heated
until it was boiling.
a. What was the boiling point of the liquid? [1]
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
b. State and explain what difference, if any, there would be in the final temperature if the
liquid was heated more strongly. [2]
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
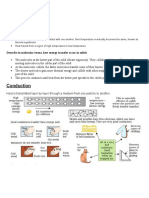
3. An electric soldering iron is used to melt solder, for joining wires in an electric circuit. A soldering
iron is shown in the figure.
Solder is a metal which melts easily. The heater coil inside the metal cylinder heats the
copper tip.
(a) (i) Suggest why the tip is made of copper.
________________________________________________________________________________________________[1]
(ii) Suggest why the handle is made of plastic.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________[1]
(b) The heater coil is switched on. When the tip is put in contact with the solder, some of the
heat is used to melt the solder.
(i) State the process by which the heat is transferred from the copper tip to the solder.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________[1]
Saint Peters Upper Secondary School
Physics for IGCSE GRADE 10
The Guru of Physics P a g e | 10
(ii) By which process or processes is the rest of the heat transferred to the surroundings?
Tick the boxes alongside any of the following (you may tick as many as you think are
correct).
conduction
convection
evaporation
radiation [2]
c. A short time after switching on the soldering iron, it reaches a steady temperature, even
though the heater coil is constantly generating heat. The soldering iron is rated at 40 W.
What is the rate at which heat is being lost from the soldering iron? Tick one box.
greater than 40 W
equal to 40 W
less than 40 W [1]
Love can make the strong become weak,
and the weak become strong
También podría gustarte
- Chapter 1 BJT AmplifierDocumento69 páginasChapter 1 BJT Amplifiernur_azhra90Aún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Physics - ElectricityDocumento3 páginasIGCSE Physics - ElectricityHyun Jung HongAún no hay calificaciones
- 10th Computer Science Exercises ProgramsDocumento18 páginas10th Computer Science Exercises ProgramsAditya Kumar100% (1)
- Uniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersDocumento17 páginasUniform Circular Motion Practice Qs With AnswersLawrence Lim Ah KowAún no hay calificaciones
- CHPTR 1 - Basic BJT Amplifier (I)Documento22 páginasCHPTR 1 - Basic BJT Amplifier (I)Edward FahmiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2016 Objmhcet Sample Chap Phy PDFDocumento50 páginas2016 Objmhcet Sample Chap Phy PDFAnusha D RejaAún no hay calificaciones
- 83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions SolutionsDocumento5 páginas83 Revision Questions For IGCSE Questions SolutionsDeepal PrasankaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 8 - Current MirrorDocumento18 páginasLab 8 - Current MirrorKram Nhoj TabatabAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2 Humidity SensorDocumento13 páginas1.2 Humidity SensorDarren NurseAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics AQADocumento55 páginasPhysics AQAMin JeongAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermodynamics ME10003: DR Kevin Robinson (4E 2.25)Documento235 páginasThermodynamics ME10003: DR Kevin Robinson (4E 2.25)shuaiyuan chenAún no hay calificaciones
- Electricity PracticeDocumento108 páginasElectricity PracticeVarshLokAún no hay calificaciones
- KS3 Science 2008 Paper 2 Level 5-7Documento28 páginasKS3 Science 2008 Paper 2 Level 5-7Saira HassanAún no hay calificaciones
- IB Physics 2 Assess WSE2Documento3 páginasIB Physics 2 Assess WSE2Abhijeet GawandeAún no hay calificaciones
- Feynman DiagramDocumento8 páginasFeynman DiagramSerrot OnaivlisAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Plate Tectonics KDDocumento16 páginas4 Plate Tectonics KDStephen Richard Kirkley100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics MCQs and Structured QuestionsDocumento22 páginasIGCSE Physics MCQs and Structured QuestionsJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Change in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500Documento7 páginasChange in Gravitational Potential Energy Final Kinetic Energy 1750 1750 17 500 17 500 450 1750 16 200 17 500Ziauddin TaposhAún no hay calificaciones
- Olp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Documento17 páginasOlp Igcse Heat & Electromagnetism CT 5 - Jan 2012Shabbir H. KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal physics worksheetDocumento15 páginasThermal physics worksheetilyasheee901100% (2)
- IGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Documento9 páginasIGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Brandeice BarrettAún no hay calificaciones
- Revision Worksheet Chapter Heat ANSWER KEYDocumento5 páginasRevision Worksheet Chapter Heat ANSWER KEYshamshadAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal MCDocumento5 páginasThermal MCDora AyeAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 11 First Six Weeks TestDocumento7 páginasGrade 11 First Six Weeks TestTanieka PowellAún no hay calificaciones
- Als Pass 34: Roficiency Ssessment Upplementary HeetDocumento1 páginaAls Pass 34: Roficiency Ssessment Upplementary HeetALS-MP CARAún no hay calificaciones
- UP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024Documento9 páginasUP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024erumriaz.1995Aún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Transfer Forms and ProcessesDocumento4 páginasHeat Transfer Forms and ProcessesLeah TomeAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseDocumento5 páginasPhysics Heat and Thermodynamics Study Guide: True/FalseRB100% (1)
- Summative G8Documento2 páginasSummative G8Claudene GellaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 8 Heat Transfer MCQ TitleDocumento7 páginasGrade 8 Heat Transfer MCQ TitleLissa Mae MacapobreAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Ciencias en Inglés QuintoDocumento10 páginasGuia Ciencias en Inglés QuintoJasmín GálvezAún no hay calificaciones
- F2 Chapter 9 - HeatDocumento6 páginasF2 Chapter 9 - HeatAnne Marian Anak JOSEPHAún no hay calificaciones
- SC F1 - Chapter 7Documento10 páginasSC F1 - Chapter 7Azrul EffindiAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal Processes (Multiple Choice) QPDocumento26 páginasThermal Processes (Multiple Choice) QPFernando SalimAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Documento20 páginasThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongAún no hay calificaciones
- Philippines Science High School Chemistry ExamDocumento3 páginasPhilippines Science High School Chemistry ExamHernan Acut ChavezAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Form 1 Chapter 7Documento10 páginasScience Form 1 Chapter 7Angie Kong Su MeiAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal Properties Physics Grade 9 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento3 páginasThermal Properties Physics Grade 9 Multiple Choice Questionsatik_kurniasihAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat and TemperatureDocumento7 páginasHeat and Temperatureanwar9602020Aún no hay calificaciones
- Questions On Temperature and HeatDocumento6 páginasQuestions On Temperature and Heatsample nameAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocumento12 páginasNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- L-1.2: Thermal Energy Section A: Choose The Best AnswerDocumento17 páginasL-1.2: Thermal Energy Section A: Choose The Best AnswerDani BaderAún no hay calificaciones
- Conduction: Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocumento10 páginasConduction: Transfer of Thermal Energyanwar9602020Aún no hay calificaciones
- Specific Heat Concepts ExplainedDocumento58 páginasSpecific Heat Concepts ExplainedSampath Kumar GuthalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1Documento6 páginasChemistry Ii Unit 1 Paper 1maxime namaAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento10 páginasThermal Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsSameer Abu MunsharAún no hay calificaciones
- Sci - Test Questions in SciG9Documento4 páginasSci - Test Questions in SciG9Ibe Mae Collera ViovicenteAún no hay calificaciones
- f1 Chapter 7Documento8 páginasf1 Chapter 7NurAnnyss AzizAún no hay calificaciones
- W37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityDocumento12 páginasW37 4.2 Understanding Specific Heat CapacityBiid HassanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Past PaperDocumento47 páginasChapter 3 Past PaperAria ElectrobellAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam in Science 120thermodynamicsDocumento6 páginasExam in Science 120thermodynamicsLara Concepcion CabigoAún no hay calificaciones
- Question Bank Calorimetry: 1. Define The Term HeatDocumento32 páginasQuestion Bank Calorimetry: 1. Define The Term HeatTajiriMollelAún no hay calificaciones
- SAT Subject Physics Key FormulasDocumento13 páginasSAT Subject Physics Key FormulasDheeraj KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Hasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFDocumento21 páginasHasil Ujian Putri Apriliani JAK2 FIS SMA TD Thermal Physics & Ideal Gas PDFIrnawati KarubiAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSAún no hay calificaciones
- Text 9Documento9 páginasText 9Debela mendaraAún no hay calificaciones
- First Written Test in Science 10 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in ADocumento5 páginasFirst Written Test in Science 10 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022 Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Correct Answer in Ajoan marie Pelias100% (1)
- Class 7 Chapter HeatDocumento10 páginasClass 7 Chapter HeatBranded HackerAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 4Documento16 páginasCH 4Iratechaos100% (1)
- SSC-PS Book-2023Documento55 páginasSSC-PS Book-2023Kgmghs Chirala100% (1)
- BAHAN MEMBUAT SOAL My First Day at SchoolDocumento26 páginasBAHAN MEMBUAT SOAL My First Day at SchoolJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Shape and SpaceDocumento32 páginasShape and SpaceJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- English 9: Name: - DateDocumento13 páginasEnglish 9: Name: - DateJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Physics MCQs and Structured QuestionsDocumento22 páginasIGCSE Physics MCQs and Structured QuestionsJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Moons of Our Solar System ASTRO P-CoDocumento3 páginasMoons of Our Solar System ASTRO P-CoJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Work and EnergyDocumento3 páginasWork and EnergyJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Latihan Ulangan Logaritma Kelas XDocumento1 páginaLatihan Ulangan Logaritma Kelas XJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- WAVE and SOUND IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 10 SEM 1 2014 Soal + JawabDocumento2 páginasWAVE and SOUND IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 10 SEM 1 2014 Soal + JawabJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Latihan Dinamika TambahanDocumento4 páginasLatihan Dinamika TambahanJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Bab1 Besaran Dan Satuan Work SheetDocumento13 páginasBab1 Besaran Dan Satuan Work SheetJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- WAVE and SOUND IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 10 SEM 1 2014 Soal + JawabDocumento2 páginasWAVE and SOUND IGCSE PHYSICS GRADE 10 SEM 1 2014 Soal + JawabJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- As Level Physics 2011 Smak Gs Kbi MeasurementDocumento13 páginasAs Level Physics 2011 Smak Gs Kbi MeasurementJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Latihan Dinamika TambahanDocumento4 páginasLatihan Dinamika TambahanJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Uji Kompetensi Kbi Force February 2012Documento3 páginasUji Kompetensi Kbi Force February 2012JoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Soal Latihan Fisika SBIDocumento4 páginasSoal Latihan Fisika SBIKim Ries KaAún no hay calificaciones
- Latihan Thermodinamika2Documento3 páginasLatihan Thermodinamika2JoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Uji Kompetensi Bab 1 Kbi Besaran Satuan EL CLASSICO D'PHYSICODocumento3 páginasUji Kompetensi Bab 1 Kbi Besaran Satuan EL CLASSICO D'PHYSICOJoshuaUntungAún no hay calificaciones
- Latihan Soal Dinamika Gesekan Kelas XI SMAK 1 2009Documento3 páginasLatihan Soal Dinamika Gesekan Kelas XI SMAK 1 2009Sondang PanjaitanAún no hay calificaciones
- Basics of UltrasonicsDocumento76 páginasBasics of UltrasonicsLokeshwar YadagiriAún no hay calificaciones
- Canned Goods Math Problem SolvedDocumento6 páginasCanned Goods Math Problem SolvedbreimanangAún no hay calificaciones
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Documento3 páginasMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency Spectrum Method-Based Stress Analysis For Oil Pipelines in Earthquake Disaster AreasDocumento24 páginasFrequency Spectrum Method-Based Stress Analysis For Oil Pipelines in Earthquake Disaster AreasNTRAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Conductivity ComparisonDocumento16 páginasHeat Conductivity ComparisonFatimah Mohd JamilAún no hay calificaciones
- Atoms WorksheetDocumento4 páginasAtoms WorksheetarifAún no hay calificaciones
- Vapour Pressure of Water at High TemperatureDocumento3 páginasVapour Pressure of Water at High TemperatureJose GalvanAún no hay calificaciones
- CE 370-Lecture-24 (Design of Eccentrically Loaded Short Columns) (Read-Only) PDFDocumento35 páginasCE 370-Lecture-24 (Design of Eccentrically Loaded Short Columns) (Read-Only) PDFJamal RkhAún no hay calificaciones
- Governors: Speed of A Prime Mover ConstantDocumento24 páginasGovernors: Speed of A Prime Mover ConstantKushalAún no hay calificaciones
- Neotecpipesys V2.5.77.0: - Dh2-Design Case - 1-3 - Rev-Da - HSC 6inch Line (40Mm PP) - 2 ConnectionsDocumento28 páginasNeotecpipesys V2.5.77.0: - Dh2-Design Case - 1-3 - Rev-Da - HSC 6inch Line (40Mm PP) - 2 ConnectionsManh Tien HoangAún no hay calificaciones
- Buckling: Stability of StructuresDocumento17 páginasBuckling: Stability of StructuresDieter RahmadiawanAún no hay calificaciones
- HEAT TRANSFER COURSE COVERS KEY TOPICSDocumento34 páginasHEAT TRANSFER COURSE COVERS KEY TOPICSSiskal DdAún no hay calificaciones
- MTM CYCLE Test 1 Question BankDocumento3 páginasMTM CYCLE Test 1 Question BankRanilprabhu MAún no hay calificaciones
- A4af A4bfDocumento23 páginasA4af A4bfjuan valderramaAún no hay calificaciones
- GEAS Oct2013 Ref 3 With AnswersDocumento6 páginasGEAS Oct2013 Ref 3 With AnswersRichard Regidor100% (2)
- Beam Deflections - Moment Area MethodDocumento12 páginasBeam Deflections - Moment Area Methodangelika MartinAún no hay calificaciones
- Modeling and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft Using Fem Package AnsysDocumento7 páginasModeling and Stress Analysis of Crankshaft Using Fem Package AnsysShreyas PaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetic Fields and Electric CurrentDocumento11 páginasMagnetic Fields and Electric CurrentRaghav MehtaAún no hay calificaciones
- Settlement of Pile Group Prof. Samirsinh P ParmarDocumento16 páginasSettlement of Pile Group Prof. Samirsinh P ParmarSamirsinh ParmarAún no hay calificaciones
- AERO 4630: Structural Dynamics Homework 5: 1 Problem 1: Viscously Damped PendulumDocumento5 páginasAERO 4630: Structural Dynamics Homework 5: 1 Problem 1: Viscously Damped PendulumMD GOLAM SARWARAún no hay calificaciones
- Measuring Strain With Strain Gages - National InstrumentsDocumento5 páginasMeasuring Strain With Strain Gages - National InstrumentsgrafpapAún no hay calificaciones
- Maximum Deflection of Beams Using Moment Area MethodDocumento5 páginasMaximum Deflection of Beams Using Moment Area Methodpmali2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Properties of Fluids PDFDocumento14 páginasProperties of Fluids PDFmaestro100% (3)
- Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Strengthened With Externally Bonded Steel Plate Using ANSYSDocumento10 páginasNonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Reinforced Concrete Beams Strengthened With Externally Bonded Steel Plate Using ANSYSDaiane BrisottoAún no hay calificaciones
- Density, units, dimensional analysis, and physics formulasDocumento2 páginasDensity, units, dimensional analysis, and physics formulasharmankalsi95Aún no hay calificaciones
- Free Electron Theory 2015-16 (VTU) PDFDocumento14 páginasFree Electron Theory 2015-16 (VTU) PDFU and me SAún no hay calificaciones
- Michelsen InterferometerDocumento22 páginasMichelsen InterferometerSelvaraju ChellappanAún no hay calificaciones
- The Hall Effect Discovery and ApplicationsDocumento17 páginasThe Hall Effect Discovery and Applicationsdiehardferret100% (1)
- Mike WeaverDocumento35 páginasMike WeavervilukAún no hay calificaciones
- Beam Deflection Determination MethodsDocumento27 páginasBeam Deflection Determination MethodsOtto Silva100% (1)