Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
MF0011 Slides Unit 06
Cargado por
rohitmahnot1989Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
MF0011 Slides Unit 06
Cargado por
rohitmahnot1989Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
1
Program : MBA
Semester : III
Subject Code : MF 0011
Subject Name : Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit number : 6
Unit Title : Demergers
Lecture Number :
Lecture Title : Demergers
HOME NEXT
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
2
Objectives:
After studying this unit, you should be able to:
Explain the meaning of demerger
Identify the characteristics of demerger
Describe the structure of demerger
Explain the tax implications of demerger
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Demergers
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
3
Introduction
Demerger: Meaning
Demerger: Characteristics
Demerger: Structure
Forms of Demerger
Spin-Off
Split-Off
Split-Up
Demerger: Income Tax Act
Demerger: Tax Implications
Summary
Glossary
Check Your Learning
Answers
Case Study
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Lecture Outline
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
4
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Problems with large business entities:
Hinders entrepreneurial initiatives
Side-lines core activities
Reduces accountability, and
Promotes investment in non-core activities.
Introduction
Possible reasons for demerger:
Demerger may allow them to strengthen their core competence and
realise the true value of their business.
Demerger is often used to divide or separate some undertakings of a
business, functioning till then under a common umbrella.
Is a way to get rid of underperforming or non-core business divisions
that can drag down profits.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
5
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
The term Demerger has not been defined in the Companies Act, 1956.
However, according to Sub-section (19AA) of Section 2 of the Income Tax Act:
Demerger in relation to companies means transfer, pursuant to a scheme of
arrangement under Sections 391 to 394 of the Companies Act, 1956, by a
demerged company of its one or more undertakings to any resulting
company in such a manner that all the property and liabilities of the
undertaking being transferred by the demerged company, immediately
before the demerger, become the property and liabilities of the resulting
company by virtue of the demerger.
Example: Possible Reasons for Demerger: Conglomerate
Rationalisation or embarking on specialisation in the manufacturing
process
Less successful part of the undertaking could be transferred to a newly
formed company
Demerger: Meaning
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
6
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Demerger is basically a scheme of arrangement under Sections 391 to 394
of the Companies Act which requires:
Approval by majority of shareholders holding shares that represent
three-fourths value in a meeting convened for the purpose
Sanction of the High Court.
Demerger results in transfer of one or more undertakings.
The transfer of undertakings is done by the demerged company, otherwise
known as transferor company. The company to which the undertaking is
being transferred is known as resulting company, otherwise known as
transferee company.
Demerger: Characteristics
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
7
asdad
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
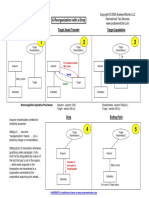
Demerger: Structure
Distribution of the shares of a firms subsidiary to the
shareholders of the firm on a pro rata basis
Neither the dilution of equity nor the transfer of ownership from
the current shareholders is involved
After the distribution, the operations and management of the
subsidiary are separated from those of the parent.
No cash transactions are involved in a demerger, it is a unique
mode of divesting assets. Hence, it cannot be motivated by a
desire to generate cash to pay off debt, as is often the case with
other modes of divestitures
Demerger
Click here to see an example of
the structure before and after
demerger for Bajaj Auto.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
S
p
i
n
-
O
f
f
An individual or an
organizational unit
leaving an existing
firm to start as a
new firm on the
basis of his/her
knowledge and
competences.
S
p
l
i
t
-
O
f
f
Restructuring of a
company where
the parent
company will offer
investors shares of
a subsidiary in
return for shares
of the parent
company.
S
p
l
i
t
-
U
p
A company splits
up into two or
more independent
companies
8
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Forms of Demerger
Some Examples:
1. Larsen and Toubro was considered more of a cement business than a construction
company. The company spun off its cement division. Due to this, the stock went up
tenfold. (Spin-Off)
2. In 2003 United Breweries de-merged itself into two companies United Breweries (the
beer company) and UB Holdings (the property and investment play). In about 3 years,
the collective value of investment went up 8 times. (Spin-Off)
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
9
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Company
takes
decision to
spin-off a
division
Parent
company
does the
paper work
with SEBI
Unit
Registered
and filed
with SEBI
Shares of
new
company
distributed to
shareholders
of previous
company
Company
goes public
1
2 3 4 5
PROCESS OF SPIN-OFF
Forms of Demerger: Spin-Off
No cash exchange (money is not received by the original parent).
Subsidiarys assets are not re-valued.
The transactions are basically a stock dividend and a tax-free
exchange.
Spin-Off
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
10
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Forms of Demerger: Spin-Off (Contd.)
Reason why spin-off entitys shares are distributed among the parent company
shareholders:
Parent company shareholders who are not interested in holding shares of the
spun off unit are free to sell the shares once the new company goes public.
Large institutional stock holders in the parent company are not allowed to keep
shares in spin-offs due to smaller market capitalisation and increased risk and
they look to sell their shares soon.
Proportion of Ownership
The existing stockholders have the same proportion of ownership in the new
entity as in the original firm.
There is separation of control.
The new entity exists as a separate decision-making unit.
It may develop policies and strategies different from those of the parent.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
11
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Transaction in which some, but not all, shareholders of the
parent company receive shares in a subsidiary, in return for
relinquishing their parent companys shares.
Some shareholders of the parent company get the subsidiarys
shares in return for which they must give up their parent
company shares.
Split-Off
Forms of Demerger: Split-Off
Example:
Viacom announced a split off of its interest in Blockbuster in 2004 whereby
Viacom offered its shareholders stock in Blockbuster in exchange for an
appropriate amount of Viacom stock. (Split-Off)
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
12
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Restructuring where the firm strategically breaks up the entire
corporate body.
Firm is broken up into a number of spin-offs, after which the parent
company does not exist any longer, and only the newly formed
companies exist.
The stockholders in the companies may not be the same, as the
stockholders trade their shares in the parent company with shares in
one or more of the units that are spun-off.
Split-
Up
Forms of Demerger: Split-Up
Features:
The entire firm is split up into a series of spin-offs.
The parent company no longer exists.
Only the new companies survive.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
13
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Demerger: Income Tax Act
I
n
c
o
m
e
T
a
x
A
c
t
All the assets and the liabilities of the undertaking are transferred
from the demerged company to the resulting company.
The transfer is on a going concern basis and at book value.
Shareholders holding not less than 75 per cent in value of the shares
in the demerged company become shareholders of the resulting
company or companies by virtue of the demerger.
In consideration of the demerger, the resulting company issues its
shares to the shareholders of the demerged company on a
proportionate basis.
The Income Tax Act stipulates the following conditions for a transaction to be
recognised as a demerger:
Click here to know the tax
benefits and concessions
available for demerger under IT
Act
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
14
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
Demerger: Tax Implications
Amendments to Income Tax Act were introduced by the Finance Act, 1999
(effective from 01-04-2000) to enable corporate enterprises to be assured
that:
Click here to read about the
controls to misuse of tax
implications and benefits
extended to authorities for
demergers
A
m
e
n
d
m
e
n
t
s
t
o
I
T
A
c
t
Demergers will be tax-neutral and not attract any additional liability to
tax.
Tax benefits and concessions available to the demerged undertaking
will be available to the resulting company after demerger.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
Summary
15
Demerger is often used to separate different undertakings of a business
functioning under a common umbrella.
A demerger is distribution of the shares of a firms subsidiary to the
shareholders of the firm on a pro rata basis. Neither the dilution of equity nor
the transfer of ownership from the current shareholders is involved.
Demerger can be by spin-off, split-off and split-up.
Spin-off is often used to get rid of unprofitable business divisions. In a split-
up, a company is split up into two or more independent companies.
Split-off provides shares in the subsidiary company to certain shareholders.
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
Glossary
16
Spin-off: When a division of a company or organisation becomes an
independent business and the resulting company takes assets,
property, technology, and/or products from the parent organisation.
Split-off: When the stock of a subsidiary is exchanged for shares in a
parent company.
Split-up: When a single company splits into two or more companies
and loses its original identity.
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
Check Your Learning
17
1. A ____________ results in the transfer by a company of one or more of its
undertakings to another company.
2. Demerger is often used to describe ________ of different undertakings of a
business, functioning till then under a common umbrella.
3. ____________ is not defined under the Companies Act.
4. The company whose undertaking is transferred is called the resulting
company. (True/False)
5. A demerger is distribution of the shares of a firms subsidiary to the
shareholders of the firm on a pro rata basis. (True/False)
6. There is no cash exchange in a spin-off. (True/False)
7. In split-off all the shareholders of the parent company get shares in the
subsidiary. (True/False)
8. In a split-up, a company is split up into two or more dependent companies.
(True/False)
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
18
Check Your Learning
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
9. Demerger constitutes a unique mode of divesting assets since they do not
involve any cash transaction. (True/False)
10.The resulting company in demerger can get the tax relief if the resulting
company is an ________________.
11.Demergers should be ________________ and should not attract any
additional liability to tax.
12.Accumulated losses and ________________ can be carried forward from the
demerged company to the resulting company.
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
Answers
19
1. Demerger.
2. Division or separation.
3. Demerger.
4. False.
5. True.
6. True.
7. False.
8. False.
9. True.
10. Indian company.
11. Tax neutral.
12. Unabsorbed depreciation.
HOME NEXT PREVIOUS
MF 0011Mergers & Acquisitions
Unit 6 - Demergers
Case Study
20
HOME PREVIOUS
Answer the following questions, based on the
given case:
Question
Discuss the impact of demerger decision on the
company value.
Hint answer:
Decisions like merger and demerger create big impact on
the share value of the firm. Kalyani Steels share value
increased by 20% before the demerger of its investment
arm.
Click on the icon besides, to
analyse the case on Demerger
También podría gustarte
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- 4.6 Project Management Internal Assessment 100 Marks (15 Sessions of 3 Hours Each)Documento1 página4.6 Project Management Internal Assessment 100 Marks (15 Sessions of 3 Hours Each)rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mb0049 Unit 01-SlmDocumento26 páginasMb0049 Unit 01-Slmrohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- MF0011 Slides Unit 04Documento24 páginasMF0011 Slides Unit 04rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- MF0011 Slides Unit 01Documento26 páginasMF0011 Slides Unit 01rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- MF0011 Slides Unit 05Documento25 páginasMF0011 Slides Unit 05rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing Management Assignment AnalysisDocumento3 páginasMarketing Management Assignment AnalysisMahfooz AlamAún no hay calificaciones
- MF0011 Slides Unit 03Documento36 páginasMF0011 Slides Unit 03rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- MF0011 Slides Unit 02Documento21 páginasMF0011 Slides Unit 02rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Measuring Consumer Satisfaction ParametersDocumento1 páginaMeasuring Consumer Satisfaction Parametersrohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- HR01 Human Resource Management: Assignment No.IDocumento6 páginasHR01 Human Resource Management: Assignment No.Irohitmahnot198950% (2)
- IPL CA (1) .Tinkesh R. PunjabiDocumento41 páginasIPL CA (1) .Tinkesh R. PunjabiTinkesh Punjabi100% (1)
- NJM Quiz Brand BachaoDocumento26 páginasNJM Quiz Brand Bachaorohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- US, China Headed For Cold War'Documento2 páginasUS, China Headed For Cold War'rohitmahnot1989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Eli Lilly & CoDocumento14 páginasEli Lilly & Corohitmahnot1989100% (3)
- Business Environment in IndiaDocumento4 páginasBusiness Environment in Indiarohitmahnot1989100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- 368 A 1 Reorganization With A DropDocumento1 página368 A 1 Reorganization With A DropEric MooreAún no hay calificaciones
- Stockholders' Equity: Paid-In Capital: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocumento46 páginasStockholders' Equity: Paid-In Capital: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinazee inmixAún no hay calificaciones
- Ilec Unit 2 Company Law: Company Formation and ManagementDocumento4 páginasIlec Unit 2 Company Law: Company Formation and Managementხათუნა გოგიაშვილიAún no hay calificaciones
- Companies Act 1994Documento34 páginasCompanies Act 1994msuddin7688% (26)
- Lifting of Corporate VeilDocumento20 páginasLifting of Corporate Veilgeetika singhAún no hay calificaciones
- 1partnership Basic ConceptsDocumento18 páginas1partnership Basic ConceptsAthelano B. Guieb IIIAún no hay calificaciones
- Forms of Business OrganizationDocumento1 páginaForms of Business OrganizationElla Simone100% (3)
- Applicability Doctrine Ultra ViresDocumento3 páginasApplicability Doctrine Ultra ViresdrdineshbhmsAún no hay calificaciones
- CORPORATION LAW II - CLASSIFICATION OF CORPORATIONSDocumento3 páginasCORPORATION LAW II - CLASSIFICATION OF CORPORATIONSJamey SimpsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Companies ActDocumento21 páginasCompanies ActamitkrhpcicAún no hay calificaciones
- Company Formation BasicsDocumento6 páginasCompany Formation Basicsgiuseppe isoliAún no hay calificaciones
- CorporationDocumento10 páginasCorporationchowchow123Aún no hay calificaciones
- MEMBERSHIP AND PARTNERSHIP GUIDEDocumento5 páginasMEMBERSHIP AND PARTNERSHIP GUIDErhea agnesAún no hay calificaciones
- TX312000 Newsletterpubs ConsolidatedGroupMay2016Documento37 páginasTX312000 Newsletterpubs ConsolidatedGroupMay2016Court RobertsAún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz# 2. Write Word Correct AnswerDocumento4 páginasQuiz# 2. Write Word Correct AnswerEron Roi Centina-gacutanAún no hay calificaciones
- Legal Personality AssignmentDocumento26 páginasLegal Personality AssignmentKAYNATALIAún no hay calificaciones
- Company Law Difference BetweenDocumento13 páginasCompany Law Difference Betweenshivani panjwani100% (1)
- Types of BusinessDocumento3 páginasTypes of BusinessAnonymous zHsbRY9Aún no hay calificaciones
- What Are The Common Forms of BusinessesDocumento28 páginasWhat Are The Common Forms of BusinessesMC AvergonzadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Stockholders' Equity Calculations for Multiple ProblemsDocumento5 páginasStockholders' Equity Calculations for Multiple ProblemsMariah MacasAún no hay calificaciones
- SuffixDocumento5 páginasSuffixErin StephensAún no hay calificaciones
- Limited Partnership CodalDocumento5 páginasLimited Partnership Codaljeanvaljean999Aún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate LawDocumento88 páginasCorporate Lawglenda e. calilaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Law in PakistanDocumento9 páginasCorporate Law in PakistanArshad IslamAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Veil Piercing and Alter Ego DoctrineDocumento20 páginasCorporate Veil Piercing and Alter Ego DoctrineJustin YañezAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Company & Seperate Legal EntityDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To Company & Seperate Legal EntitySamron DoraiAún no hay calificaciones
- Statement 1569252334387Documento12 páginasStatement 1569252334387Mritunjai SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporations A Comparative PerspectiveDocumento326 páginasCorporations A Comparative PerspectiveNino Frassica67% (3)
- SGFFFDocumento21 páginasSGFFFabdulla ateeqAún no hay calificaciones
- New York Placement ListDocumento4 páginasNew York Placement ListDan Primack100% (1)