Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Ionic Compound
Cargado por
Llenzycris SalazarDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ionic Compound
Cargado por
Llenzycris SalazarCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ionic Compound
Top
Sub Topics
1. Ionic Compound Definition
2. Ionic Compound Formula
3. Ionic Compound Examples
4. Ionic and Molecular
Compounds
5. Ionic and Covalent
Compounds
6. Binary Ionic Compound
7. Rules for Naming Ionic
Compounds
8. Ionic Compounds List
9. Ionic Compound Properties
10. Ionic Compound
Characteristics
11. Ionic Compound
Nomenclature
12. Ionic Compound Practice
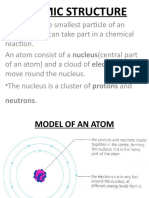
Substances resulting from the chemical combination of two or more elements in fixed
proportions are called compounds. Most elements do not exist in their free native state but are in
the combinations of two or more elements as chemical compounds. In ionic compounds the
constituent elements exist as ions. Ions are atoms or groups of atoms that carry a charge by
virtue of losing or gaining one or more electrons.
Ionic compounds result from the combination of a positive ion known as a cation and a negative
ion called an anion. Atoms in a compound are held together by covalent bonds. Bonds dictate
how atoms are held together in a compound or molecule, but ionic compounds are
composed of ions.
Ionic Compound Definition
Back to Top
Definition of ionic compound
An ionic compound is composed of cations and anions joined together. Such compounds are held together by
electrostatic forces, and adopt structures that maximize the attraction of oppositely charged species and minimize the
repulsion between charged species with the same sign.
To define ionic compound in simple words "its a combination of metals with nonmetals."
Ionic Compound Formula
Back to Top
Every ionic compound contains discrete ionic units with specific charges. In addition ionic compounds must always
contain equal amounts of positive and negative charge. These requirements dictate the ratio of cations to anions in
an ionic substance. The chemical formula of an ionic compound identifies its ionic units and the cation-to-anion ratio.
The following guidelines ensure uniformity in writing formulas for ionic compounds. The formula unit of an ionic
compound shows the
1. The cation is always listed before the anion.
2. The formula of any polyatomic ion is written as a unit.
3. Polyatomic ions are placed in parentheses with subscripts to indicate ratios different from 1:1.
Ionic Compound Examples
Back to Top
A chemical compound must have a net charge of zero. If it contains ions, the charges of the ions must add up to zero
in the formula for the compound. An ionic compound exists as a group of charged atoms. The chemical formula for an
ionic compound represents the positive charge of the cation equals the negative charge of the anion. Consequently
the overall charge is zero, and the ionic compound is neutral.
Give two examples of an ionic compound
Example of an ionic compound is given by considering the two common ionic compounds.
1. Sodium chloride (NaCl)
2. Magnesium oxide (MgO)
Some example of ionic compound are listed below.
S.No Ionic compound Formula
1 Sodium bromide NaBr
2 Potassium sulfide K
2
S
3 Zinc sulfate ZnSO
4
4 Ammonium phosphate (NH
4
)
3
PO
4
5 Aluminum chromate Al
2
(CrO
4
)
3
Ionic and Molecular Compounds
Back to Top
Compounds can be divided into two classes ionic or molecular compound. They are described in the following table.
The chemical formulas of the compounds show the elements that compose them.
Ionic vs molecular compounds table is given below.
S.No Ionic compounds Molecular compounds
1
Compounds are formed by combination of
reactive metals with reactive non metals.
Compounds are formed by the combination of
nonmetals with other non metals or with less
reactive metals.
2 Crystalline solids. Solids, liquids and gases.
3 Hard and brittle. Solids are brittle and weak or soft and waxy.
4 High melting points. Low melting points.
5 High boiling points. Low boiling points.
6
Good conductors of electricity when
molten, poor conductors of electricity and
heat when solid.
Poor conductors of heat and electricity.
7 Many are soluble in water.
Many are insoluble in water but soluble in
organic solvents.
Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Back to Top
The ionic vs covalent compounds table is given below.
S.No Ionic compounds Covalent compounds
1 Crystalline solids (made of ions) Solids, liquids and gases (made of molecules)
2 High melting and boiling points. Low melting and boiling points.
3 Conduct electricity when melted. Poor electrical conductor in all phases.
4
Many soluble in water but net is non polar
liquids.
many soluble in non polar liquids but not soluble
in water.
Binary Ionic Compound
Back to Top
Binary Ionic Compound Definition
A binary compounds contains only two elements. In a binary ionic compound, both of the elements are present ions.
The name of the compound consists of the name of the metal from which the cation was formed, by the name of
anion.
Potassium and Sulfur Ionic Compound
Consider an ionic compound formed when potassium reacts with sulfur. Potassium is a Group 1A metal, so a
potassium atom loses one electron to become a K
+
ion. Sulfur is a Group 6A nonmetal, so a sulfur atom gains two
electrons to become an S
2-
ion. To make the compound electrically neutral two K
+
ions are needed for each S
2-
ion.
Consequently the compound has the formula K2S.
Rules for Naming Ionic Compounds
Back to Top
The following rules apply for naming ionic compounds.
1. A simple cation has the same name as its parent element.
2. The cation is always named first and the anion second.
3. A simple cation takes its name from the name of the element. For example, Na
+
is called sodium in the names
of compounds containing this ion.
4. A simple anion is named by taking the first part of the element name and adding -ide. Thus the Cl
-
ion is called
chloride.
5. In some cases the cation can assume more than one charge, the charge is specified by a Roman numeral in
parentheses.
Ionic Compounds List
Back to Top
Ionic compounds are composed of cations and anions. The attraction between these oppositely charged ions is
called an ionic bond. The common ionic compound is given below as ionic compound table.
S.No Ionic compound Formula
1 Zinc oxide ZnO
2 Magnesium chloride MgCl
2
3 Copper sulfide CuS
4 Potassium bromide KBr
5 Calcium iodide CaI
2
6 Aluminum oxide Al
2
O
3
Ionic Compound Properties
Back to Top
Properties of an Ionic Compound
The positive and negative ions formed during ionic bonding are held together by enormously strong forces of
attraction between the oppositely charged ions. These ionic bonds between the charged particles result in a giant
structure of ions.
Because the ions are held together tightly in these giant structures it takes a lot of energy to break all the bonds. As a
result ionic compound melting point and boiling points are high.
Ionic Compound Characteristics
Back to Top
There are many important characteristics of compounds having ionic bonds.
1. An ionic compound is a collection of an equal number of positive and negative ions arranged in a three-
dimensional lattice.
2. Ionic compounds can be dissociated into their constituent ions with little effort.
3. Further they can be electrolyzed to produce elements or covalent molecules of the constituent atoms.
4. Water also weakens the attraction between the ions in an ionic compound.
5. This is why ionic compounds dissolve well in water.
6. Moreover ionic compounds can conduct electricity.
7. Most ionic compounds are made of metals.
Is Water an Ionic Compound?
Water is a polar solvent and polar and ionic compounds tend to dissolve in water. So water is ionic solvent.
Is SO
2
an Ionic Compound?
SO2 is not ionic but molecular compound, no electrons are actually transferred in the formation of this compound.
Is Salt an Ionic Compound?
Table salt is a familiar ionic compound formed from sodium and chlorine. Sodium forms an ion with a single positive
charge Na
+
and chlorine an ion with a single negative charge Cl
-
. The formula of salt is NaCl.
Is Sugar an Ionic Compound?
Sugar easily dissolve in water when we stir but its not an ionic compound. Sugar has many OH groups which forms
hydrogen bonds to water and hence its very soluble in water.
Ionic Compound Nomenclature
Back to Top
An ionic compound contains a metal and a nonmetal. Ionic compounds are also known as salts. An ionic
compound is designated by giving the name of the cation first and then the name of the anion.
The nomenclature of ionic compounds involves three kinds of compounds
1. Binary compounds (only two elements)
2. Compounds of polyatomic ions (two or more elements that stay together and act as though they are one ion).
3. Compounds of multivalent ions (contains more than one charge)
Ionic Compound Practice
Back to Top
Example problems are given based on ionic compound.
Solved Examples
Question 1: Write the formula for these binary ionic compounds.
1. Barium hydride
2. Sodium fluoride
3. Calcium oxide
Solution:
Write the formula of the positive ion and then the formula of the negative ion. Remember that the number of positive
and negative charges must be equal. Show the ratio of each ion in the formula of the compound by subscripts. Where
only one of either ion is present, do not show a subscript.
1. BaH2
2. NaF
3. CaO
Question 2: Name these ionic compounds each of which contains a polyatomic ion.
1. NaNO3
2. CaCO3
3. (NH4)2SO3
4. NaH2PO4
Solution:
To name ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions, name the positive ion first and then the negative ion, each as
a separate word.
1. Sodium nitrate
2. Calcium carbonate
3. Ammonium sulfite
4. Sodium dihydrogen phosphate
Salt and baking powder (sodium bicarbonate) are both ionic
compounds. Anything that is a metal and nonmetal bonded together is
an ionic compound.
NaCl - sodium chloride - table salt
KCl - potassium chloride - present in "light" salt (mixed with NaCl)
CaCl2 - calcium chloride - driveway salt
NaOH - sodium hydroxide - found in some surface cleaners as well as oven and drain cleaners
CaCO3 - calcium carbonate - found in calcium supplements
NH4NO3 - ammonium nitrate - found in some fertilizers
Ionic compound
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
It has been suggested that Ionic crystal be merged into this article. (Discuss)Proposed
since June 2014.
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this
article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged
and removed. (June 2011)
The crystal structure of sodium chloride, NaCl, a typical ionic compound. The purple spheres
represent sodium cations, Na
+
, and the green spheres represent chlorideanions, Cl
.
In chemistry, an ionic compound is a chemical compound in which ions are held together in a
lattice structure by ionic bonds. The positively charged ions are calledcations and the negatively
charged ions are called anions. These can be simple ionswhere a single atom has a charge
imbalance, or polyatomic ions made of multiple atoms. Ions in ionic compounds are held together by
the electrostatic forcesbetween oppositely charged bodies. Individual ions can have multiple nearest
neighbours, so are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous network.
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points, and they are hard and very brittle. As solids
they are almost always electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become
highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized.
Contents
[hide]
1 Nomenclature
2 Characteristics
3 Structure
4 Solubility
5 Electrical conductivity
6 See also
7 References
o 7.1 Bibliography
Nomenclature[edit]
According to the nomenclature defined by IUPAC, in the most simple case of a binary ionic
compound with no possible ambiguity about the stoichiometry, the common name is written using
two words.
[1]
The name of the cation comes first, followed by the name of the anion.
[2]
For example,
MgCl2 is named magnesium chloride, and Na2SO4 is named sodium sulfate (SO4
2
, sulfate, is an
example of a polyatomic ion). To obtain the empirical formula from these names, the stoichiometry
can be deduced from the charges on the ions, and the requirement of overall charge neutrality.
If the oxidation state of the cation is ambiguous, Stock nomenclature requires the oxidation
number to be written in Roman numerals in parentheses directly after the name of the anion (without
a space separating them). For example, FeSO4 is named iron(II) sulfate (with the 2+ charge on
the Fe
2+
ions balancing the 2 charge on the sulfate ion), whereas Fe2(SO4)3is named iron(III)
sulfate (because the two iron ions in each formula unit have a charge of 3+, to balance the 2 on
each of the three sulfate ions). If the Classical naming system is being used, some ionic compounds
have special "old" names, such as ferrous and ferric, for iron(II) and iron(III) respectively, and
cuprous and cupric, for copper(I) and copper(II) respectively, so under that system Fe2(SO4)3 is
named ferric sulfate.
Characteristics[edit]
Ions can be single atoms, as the sodium and chlorine in common table salt sodium chloride, or more
complex groups such as the carbonate in calcium carbonate. But to be considered an ion, they must
carry a positive or negative charge. Thus, in an ionic bond, one 'bonder' must have a positive charge
and the other a negative one. By sticking to each other, they resolve, or partially resolve, their
separate charge imbalances. Positive to positive and negative to negative ionic bonds do not occur.
Chemical compounds are never strictly ionic. Even the most electronegative/electropositive pairs
such as caesium fluorideexhibit a degree of covalency. Similarly, covalent compounds often exhibit
charge separations. See also HSAB theory.
Ionic compounds have very strong electrostatic bonds between particles. As a result, they generally
have very high melting and boiling points and a low vapour pressure.
[3]
They also have good
electrical conductivity when molten or in an aqueous solution.
[4]
Ionic inorganic compounds typically
have high melting points so are solids at room temperature and usually form crystals. Unlike organic
compounds they do not char nor ignite. On the other hand organic compounds have low melting
points, most of them are insoluble in water, and characteristically they ignite quite easily.
[5]
The ions produced by electron transfer attract each other by electrostatic attraction and this creates
an ionic bond.
Structure[edit]
Ions typically pack into extremely regular crystalline structures, in an arrangement that minimizes
the Coulomb energy(maximizing attractions and minimizing repulsions). For spherical ions (including
all simple ions), the arrangement of anions in these systems are often related to close-
packed arrangements of spheres, with the cations occupying interstices. Depending on
the stoichiometry of the ionic compound, and the coordination (principally determined by
the size ratio) of cations and anions, a variety of structures are commonly observed.
[6]
Common ionic compound structures with close-packed anions
[6]
Stoichiometry
Cation:anion
coordination
Interstitial sites
occupied
Cubic close
packing
Hexagonal close
packing
MX 6:6 all octahedral sodium chloride nickel arsenide
4:4 alternate tetrahedral zinc blende wurtzite
MX2 8:4 all tetrahedral fluorite
Common ionic compound structures with close-packed anions
[6]
Stoichiometry
Cation:anion
coordination
Interstitial sites
occupied
Cubic close
packing
Hexagonal close
packing
6:3
half octahedral (alternate
layers fully occupied)
cadmium chloride cadmium iodide
MX3 6:2 one-third octahedral
chromium(III)
chloride
[7]
bismuth iodide
M2X3 6:4 two-thirds octahedral
corundum
ABO3
two-thirds octahedral
ilmenite
AB2O4
one-eighth tetrahedral and
one-half octahedral
spinel, inverse
spinel
olivine
In some cases the anions take on a simple cubic packing, and the resulting common structures
observed are:
Common ionic compound structures with simple cubic packed anions
[7]
Stoichiometry Cation:anion coordination Interstitial sites occupied Example structure
MX 8:8 all filled cesium chloride
MX2 8:4 half filled calcium fluoride
M2X 4:8 half filled lithium oxide
Solubility[edit]
Following the aphorism, "like dissolves like", ionic compounds dissolve most readily in polar
solvents (such as water) or ionic liquids. Ionic compounds tend not to dissolve in nonpolar
solvents (such as diethyl ether or petrol/gasoline).
When the oppositely charged ions in the solid ionic lattice are surrounded by the opposite pole of a
polar molecule, the solid ions are pulled out of the lattice and into the liquid. When this force is more
than the electrostatic attraction of the lattice, the ions become dissolved in the liquid.
Electrical conductivity[edit]
Although ionic compounds contain charged atoms or clusters, they do not typically conduct
electricity when they are in thesolid state. In order to conduct, the charged particles must
be mobile rather than stationary in a crystal lattice. When the ionic compounds are dissolved in a
liquid or are themselves melted into a liquid, they can conduct electricity because the ions become
mobile.
[8]
In some unusual materials, fast ion conductors, one or more of the ionic components in the solid
phase has a significant mobility, allowing conductivity.
What are Some
Examples of Covalent
Compounds?
Covalent Compounds
By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D.
Chemistry Expert
Share this
Ads
Ionic
Bond Bonding
Chemistry Science
Compound
Chemistry Online
CHEMISTRY CATEGORIES
Chemistry 101
Chemistry Tests and Quizzes
Demonstrations - Experiments
Periodic Table and the Elements
Chemistry Disciplines - Branches of Chemistry
Chemistry Homework Help
Molecules and Compounds
Grow Crystals
Science Fair Projects
Chemistry for Kids
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Toxic Chemicals and Safety
Chemistry Laboratory
Careers and Education
Chemistry Facts and Pictures
Chemistry Basics
Science Demonstrations, Experiments, and Projects
Science Fair Ideas and Help
Updated Articles and Resources
VIEW MORE
FREE EMAIL NEWSLETTER
Let About.com send you
the latest from our
Chemistry Expert.
SIGN UP
You can opt-out at any time.
Please refer to our privacy policy for contact information.
Ethyl alcohol or ethanol is an example of a molecular compound containing
atoms joined by covalent bonds. Ben Mills
These are examples of covalent bonds and covalent compounds. Covalent
compounds also are known as molecular compounds. Organic compounds, such
as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids, are all examples of
molecular compounds. You can recognize these compounds because they
consist of nonmetals bonded to each other.
PCl
3
CH
3
CH
2
OH
O
3
- ozone
H
2
- hydrogen
H
2
O - water
HCl - hydrogen chloride
CH
4
- methane
NH
3
- ammonia
CO
2
- carbon dioxide
Ionic compounds include many everyday's substances that we are familiar with table salt (NaCl),
baking soda (NaHCO
3
), milk of magnesia (Mg(OH)
2
) and calcium carbonate (CaCO
3
) used as antacids.
Ionic compounds also include ionic crystals such as those found in naturally occurring gems, including
ruby (Al
2
O
3
) and sapphires.
- ionic compounds are generically called salts.
Covalent Compounds
Covalent compounds are more predominant than ionic compounds and are made of elements that are
non-metals. They include substances that we already know such as water (H
2
O), table sugar (sucrose =
C
12
H
22
O
11
), propane gas (C
3
H
8
), and drugs such as the antibiotic amoxicillin (C
16
H
19
N
3
O
5
S) and the
antidepressant Prozac (C
17
H
18
F
3
NO).
- covalent compounds are referred to as molecules.
PCl
3
CH
3
CH
2
OH
O
3
- ozone
H
2
- hydrogen
H
2
O - water
HCl - hydrogen chloride
CH
4
- methane
NH
3
- ammonia
CO
2
- carbon dioxide
More Bonding Examples
Examples of Ionic Bonds - Ionic Compounds
Examples of Compounds with Mixed Bonds
Learn About Chemical Bonding
Types of Chemical Bonds
Difference Between Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Types of Bonds Formed by Carbon
Video - Ionic Versus Covalent Bond
Online Chemistry Text - Chemical Bonds
Sodium bromide is used in conjunction with chlorine as a disinfectant for swimming pools.
Potassium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula K
2
S. The colourless solid is rarely
encountered, because it reacts readily with water, a reaction that affords potassium hydrosulfide (KSH)
and potassium hydroxide (KOH). Most commonly, the term potassium sulfide refers loosely to this
mixture, not the anhydrous solid.
Use in fireworks[edit]
Potassium sulfides are formed when black powder is burned and are important intermediates in many
pyrotechnic effects, such as senko hanabi and some glitter formulations.
[3]
Uses
This medication is a mineral used to treat or prevent low levels of zinc.
OTHER USES: This section contains uses of this drug that are not listed in the approved professional
labeling for the drug but that may be prescribed by your health care professional. Use this drug for a
condition that is listed in this section only if it has been so prescribed by your health care professional.
This medication may also be used to promote wound healing.
Ammonium phosphates are inorganic salts derived from the reaction between ammonia and phosphoric
acid. They are produced as solids and fluids and they may contain phosphate values in ortho- (usually
solid) and/or polyphosphate (usually fluid) form. The vast bulk of ammonium phosphate products are
produced and consumed as solid materials. This report concentrates on the use of ammonium
phosphates as fertilizers, which accounts for nearly 98% of total use, but brief mention is made of
animal feed and industrial uses in the United States.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of all solid ammonium phosphates:
Apparent world consumption of solid ammonium phosphate grew at an average annual rate of 2.6%
during 19932013, but grew at 3.4% during 19992013. Growth is forecast at 3.5% annually during
20132018. Ammonium phosphates will continue to grow at a faster rate than other complex
phosphate materials.
Ammonium phosphates are consumed primarily in fertilizer applications, although minor amounts are
used in animal feeds and industrial applications. The leading industrial applications include fire control
and flame-retardant applications. Animal feed and industrial applications combined consume less than
3% of total world apparent consumption.
Chromate conversion coating is a type of conversion coating used
topassivate aluminum, zinc, cadmium, copper, silver, magnesium, and tin alloys.
[1]
It is primarily used as
a corrosion inhibitor, primer, decorative finish, or to retainelectrical conductivity. The process is named
after the chromate found in chromic acid, also known as hexavalent chromium,
[2]
the chemical most
widely used in the immersion bath process whereby the coating is applied. However, hexavalent
chromium is toxic, thus, highly regulated,
[3]
so new, non-hexavalent chromium-based processes are
becoming more readily available at a commercial level.
[4]
One alternative contains trivalent chromium.
The RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) Directive is commonly referred to regarding elimination
of hexavalent chromium.
Chromate conversion coatings are commonly applied to everyday items such as hardware and tools, and
can usually be recognized by their distinctively iridescent, greenish-yellow color.
Ozone can be used for combustion reactions and combusting gases; ozone provides higher
temperatures than combusting in dioxygen (O2).
Hydrogen is the lightest and most common element in the cosmos. Its atomic number is 1. In its
elemental state, hydrogen is rare. But it is one of the components of water and vital to life.
Common Uses of Hydrogen
It is primarily used to create water. Hydrogen gas can be used for metallic ore reduction. Chemical
industries also use it for hydrochloric acid production. The same hydrogen gas is required for atomic
hydrogen welding (AHW).
También podría gustarte
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesAún no hay calificaciones
- Atomic Structure Power PointDocumento144 páginasAtomic Structure Power PointKasman Kasonde MumbaAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Atomic ConceptsCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2)
- 3 Fajan's RuleDocumento13 páginas3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersAún no hay calificaciones
- Christian Lara Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasChristian Lara Lab ReportLeslieAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical Bonding with AnswersCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Chemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006Documento12 páginasChemical Bonding: Presented By: Mohammad Fayiz Akhtar SP05-AA-0017 Presented To: Afsheen Khalil Presented On: 04-OCT-2006helperforeuAún no hay calificaciones
- Everything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksDe EverandEverything You Must Know about Radioactivity 6th Grade Chemistry | Children's Chemistry BooksAún no hay calificaciones
- CHPT 11.2 PowerpointDocumento59 páginasCHPT 11.2 PowerpointA A100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic Table with AnswersCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Balancing Chemical Equations - Clicker Questions - AnnotatedDocumento12 páginasBalancing Chemical Equations - Clicker Questions - AnnotatedBožana TomićAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (3)
- MF008 Fhs LNT 002 May11Documento32 páginasMF008 Fhs LNT 002 May11Lim Shu YingAún no hay calificaciones
- Why Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksDe EverandWhy Are Chemicals Not Named John? Naming Chemical Compounds 6th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksAún no hay calificaciones
- Saif Sir - How Elements Get NamesDocumento2 páginasSaif Sir - How Elements Get NamesSaif SentuAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic TableDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Periodic TableAún no hay calificaciones
- Acid Base WorksheetDocumento5 páginasAcid Base WorksheetOmar IjazAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsAún no hay calificaciones
- Shapes of Molecules and Ions PDFDocumento9 páginasShapes of Molecules and Ions PDFMagenta SparklegemAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2De EverandChemistry of Cell Review: Quick Review Notes Chapter 2Aún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDocumento5 páginasIGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsTanmay Karur100% (1)
- Some Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1De EverandSome Problems of Chemical Kinetics and Reactivity: Volume 1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocumento9 páginasChemical Bonding NotesLouisiana SollestreAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (2)
- 03 Enzymes Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Documento16 páginas03 Enzymes Biology Notes IGCSE 2014taryll_01Aún no hay calificaciones
- PeriodicityDocumento6 páginasPeriodicityHadi AlnaherAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Formulae and Equations - Part 1Documento22 páginasChemical Formulae and Equations - Part 1zkn 86Aún no hay calificaciones
- Empirical and Molecular FormulaeDocumento26 páginasEmpirical and Molecular FormulaeAin'sha NawiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical BondingDocumento51 páginasChemical BondingDaniel MaglalangAún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Unit 10 ExtractionDocumento17 páginasIGCSE Unit 10 ExtractionIsuriy AdasuriyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%Documento74 páginasFinal Exam 40% Exams 45% Report 5% Homework 10%kaleijaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Polymer - SlimeDocumento4 páginasLab Polymer - SlimeThats Gone WrongAún no hay calificaciones
- U3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT WatermarkDocumento45 páginasU3 Oxidation and Reduction PPT Watermarkapi-125934329Aún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocumento6 páginasOrganic Chemistry NotesAzib ZararAún no hay calificaciones
- 9halogens Group PresentationDocumento31 páginas9halogens Group PresentationQueen GeminiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDocumento17 páginasChemistry Solutes Solvents Solubility Solutions VCBCCTDIONYSUS100% (1)
- Lewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityDocumento6 páginasLewis Dot Structures of Atoms and Ions: Valence Electrons Noble Gas StabilityAndrew CabreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Molecular PolarityDocumento4 páginasMolecular PolarityTea RadicAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Documento4 páginasChemical Bonding WS Packet Margie Core 2013Lama DebanaAún no hay calificaciones
- BondingDocumento15 páginasBondingFrancis EssilfieAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 Chem Bond - Modul - ChemistryDocumento11 páginas05 Chem Bond - Modul - Chemistryrudi_z100% (1)
- Exothermic and Endothermic ReactionsDocumento5 páginasExothermic and Endothermic ReactionsSehyun OhAún no hay calificaciones
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocumento1 páginaCovalent Bonding Noteschongkee56100% (1)
- Rock Candy ExperimentDocumento4 páginasRock Candy ExperimentsamAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFDocumento4 páginasTypes of Chemical Reactions Close Reading PDFStefanie CorcoranAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Names and Formulas: 9.1 Naming IonsDocumento53 páginasChemical Names and Formulas: 9.1 Naming IonsLovieAlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- In-Class Worksheet AnswersDocumento6 páginasIn-Class Worksheet AnswersalgonzAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry PDFDocumento13 páginasChemistry PDFDanielAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry ReviewerDocumento4 páginasChemistry ReviewerCyreel ManaloAún no hay calificaciones
- REVISION NOTES Ionic & Covalent BondingDocumento8 páginasREVISION NOTES Ionic & Covalent BondingVictor KwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Arithmetic and Reactions: ObjectivesDocumento24 páginasChemical Arithmetic and Reactions: Objectivesgoputs6386Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 20 - Naming Chemical CompoundsDocumento60 páginasChapter 20 - Naming Chemical CompoundsAlwielland BelloAún no hay calificaciones
- CH2 BondingDocumento17 páginasCH2 BondingDoc CrocAún no hay calificaciones
- Flame TestDocumento9 páginasFlame TestChristopher YepmoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter No 1-Matter STD 8Documento17 páginasChapter No 1-Matter STD 8Harshita MunotAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocumento12 páginasNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electrolysis of Lead Bromide and BrineDocumento13 páginasElectrolysis of Lead Bromide and Brinesondos tawfiqAún no hay calificaciones
- Inorganic NomenclatureDocumento28 páginasInorganic NomenclatureAbhishek SadaphulAún no hay calificaciones
- Empirical Versus Molecular FormulasDocumento5 páginasEmpirical Versus Molecular FormulasJaz SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Calculate Breaker Size, Wire Size and Wattages: AnotherDocumento9 páginasHow To Calculate Breaker Size, Wire Size and Wattages: AnotherLlenzycris SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- New Prince of Tennis OVA Series That Will Be Airing October 29Documento4 páginasNew Prince of Tennis OVA Series That Will Be Airing October 29Llenzycris SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Baby Don'T Cry Lyrics: Read & Write Lyrics ExplanationsDocumento4 páginasBaby Don'T Cry Lyrics: Read & Write Lyrics ExplanationsLlenzycris SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ass in FeasibilityDocumento141 páginasAss in FeasibilityLlenzycris SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Food Science Report - GroupDocumento23 páginasFood Science Report - GroupMuhammad Salihin JaafarAún no hay calificaciones
- Phytochemical Andanti-Inflammatory Studies On Thehexane Extract of The Stem Bark Ofsteganotaenia AraliaceahoschtsDocumento93 páginasPhytochemical Andanti-Inflammatory Studies On Thehexane Extract of The Stem Bark Ofsteganotaenia AraliaceahoschtsPrily R PadjaAún no hay calificaciones
- Alchemy The Treasure of Alchemists by Jaques SadoulDocumento5 páginasAlchemy The Treasure of Alchemists by Jaques SadoulVladimir VergunAún no hay calificaciones
- Project Work On Water Tank Cleaning MachineDocumento2 páginasProject Work On Water Tank Cleaning MachinePrakash Pokhrel100% (1)
- Octahedral Molecular GeometryDocumento24 páginasOctahedral Molecular GeometryAnonymous gUjimJKAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 Types of Bearing DefectsDocumento5 páginas12 Types of Bearing Defectsjameel babooramAún no hay calificaciones
- Technical Discussion - Cutless BearingsDocumento7 páginasTechnical Discussion - Cutless BearingsSoodyod Yodyod0% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S2215098622001562 MainDocumento9 páginas1 s2.0 S2215098622001562 MainJUAN DAVID PRADO CORTESAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2.0 Drilling Ref. PFMEADocumento12 páginas1.2.0 Drilling Ref. PFMEAMani Rathinam RajamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Unimolecular ReactionDocumento16 páginasUnimolecular ReactionoxyzenAún no hay calificaciones
- Ceramic Engineering: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento6 páginasCeramic Engineering: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaFaiz AbdullahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocumento35 páginasChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- Comparative Investigation of Traditional and Modern Passive Design Strategies To Reduce The Energy Use in Residential Building of West-Maharashtra RegionDocumento17 páginasComparative Investigation of Traditional and Modern Passive Design Strategies To Reduce The Energy Use in Residential Building of West-Maharashtra RegionAnonymous CwJeBCAXp100% (1)
- Pearson's Classification of Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases Into Hard and Soft - Acids and BasesDocumento5 páginasPearson's Classification of Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases Into Hard and Soft - Acids and BasesThantea ChhakchhuakAún no hay calificaciones
- Metrology NOTEDocumento90 páginasMetrology NOTERyan Goh Chuang HongAún no hay calificaciones
- HFM Vatell SpecsDocumento3 páginasHFM Vatell SpecsPro_td_Vivimos_9063Aún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering Piping Design Guide Fiberglass Reinforced Piping SystemsDocumento36 páginasEngineering Piping Design Guide Fiberglass Reinforced Piping Systemsoscarhdef100% (1)
- Module - 1 Lecture Notes - 5: Remote Sensing: Introduction and Basic Concepts Spectral Reflectance CurvesDocumento13 páginasModule - 1 Lecture Notes - 5: Remote Sensing: Introduction and Basic Concepts Spectral Reflectance CurvesYogesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Indion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetDocumento6 páginasIndion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetsoumitrabanAún no hay calificaciones
- Notesch # 18Documento11 páginasNotesch # 18ZeeshanMahdiAún no hay calificaciones
- Petroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFDocumento28 páginasPetroleum Systems of Indonesia PDFWahyu Probo Ananto HadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratory ManualDocumento13 páginasLaboratory ManualPaul UyAún no hay calificaciones
- A Review On Techniques To Enhance Electrochemical Remediation of Contaminated SoilsDocumento19 páginasA Review On Techniques To Enhance Electrochemical Remediation of Contaminated SoilsAdelina96Aún no hay calificaciones
- Effects of Poultry Manure Supplemented by NPK 15-15-15 Fertilizer On Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.) Production in Port Harcourt (Nigeria)Documento7 páginasEffects of Poultry Manure Supplemented by NPK 15-15-15 Fertilizer On Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.) Production in Port Harcourt (Nigeria)tino3528Aún no hay calificaciones
- Becogur enDocumento2 páginasBecogur enRui Felizardo0% (1)
- Self Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLDocumento6 páginasSelf Etching Adhesive On Intact Enamel: Devarasa GM, Subba Reddy VV, Chaitra NLNiNis Khoirun NisaAún no hay calificaciones
- GEMSS-M-15 Rev 02 - Desalination Plant and Desalinated Water TanksDocumento20 páginasGEMSS-M-15 Rev 02 - Desalination Plant and Desalinated Water TanksKaramSobhyAún no hay calificaciones
- Salt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateDocumento3 páginasSalt Analysis-Vi Aluminum SulphateNANAún no hay calificaciones
- Concrete ExamDocumento26 páginasConcrete ExamKyra AlesonAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 - Chemical ReactionsDocumento9 páginasUnit 2 - Chemical ReactionsNobukhosi NdlovuAún no hay calificaciones
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarDe EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (19)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureDe EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (125)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldDe EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (58)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonDe EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (103)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellDe EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (82)
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachDe EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (6)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldDe EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (6)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceDe EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (5)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDe EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaDe EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyDe EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyAún no hay calificaciones
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootDe EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootAún no hay calificaciones
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestDe EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (28)
- Fire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterDe EverandFire on the Horizon: The Untold Story of the Gulf Oil DisasterAún no hay calificaciones
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreDe EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (33)
- Mini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreDe EverandMini Farming: Self-Sufficiency on 1/4 AcreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (76)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDe EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationDe EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (46)
- The Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchDe EverandThe Knowledge: How to Rebuild Our World from ScratchCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (133)
- Highest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersDe EverandHighest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersAún no hay calificaciones
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindDe EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAún no hay calificaciones
- The Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborDe EverandThe Book of the Moon: A Guide to Our Closest NeighborCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (11)
- The Assassination Complex: Inside the Government's Secret Drone Warfare ProgramDe EverandThe Assassination Complex: Inside the Government's Secret Drone Warfare ProgramCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (55)
- Project Management All-in-One For DummiesDe EverandProject Management All-in-One For DummiesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (6)
- How to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerDe EverandHow to Build a Car: The Autobiography of the World’s Greatest Formula 1 DesignerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (54)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyDe EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (24)