Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
DNS Protocol
Cargado por
Alaneus83%(6)83% encontró este documento útil (6 votos)
8K vistas2 páginasDNS Protocol
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoDNS Protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
83%(6)83% encontró este documento útil (6 votos)
8K vistas2 páginasDNS Protocol
Cargado por
AlaneusDNS Protocol
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 2
Determination of reducing sugars concentration by DNS method
M. Tech. I Sem (Biotechnology) Page 1
Aim: To determine the concentration of reducing sugars in unknown sample by DNS method.
Principle: Reducing sugars have an aldehyde group which can be oxidized through redox
reactions. This property of reducing sugar has been utilized in estimating their concentration in
many reactions such as Benedicts, Fehlings and DNS method.
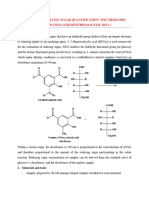
DNS (Dinitrosalicylic acid) is one of the reagents used to estimate reducing sugars in the
solution. Its a spectrophotometric method. 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid is reduced to 3 amino 5 nitro
salicylic acid while oxidizing the reducing sugars. The color change can be quantified
spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 540 nm.
Chemical reaction:
Reagents required:
DNS reagent composition (for 1000ml):
Sodium hydroxide: 10g
Sodium potassium tartarate: 192g
Dinitrosalicylic acid: 10g
Phenol: 2g
Sodium sulphite: 0.5g
Make up the volume to 1000ml with distilled water
Standard Glucose solution: 10 mg/ml glucose solution
Precaution: Add sodium potassium tartarate pinch by pinch and store the prepared DNS
solution in amber colored bottle.
Procedure:
1. Take 16 clean test tubes, label seven tubes as B, 1, 2 3, 4, 5, 6, U and other 8 tubes as
duplicates dB, d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6 and dU.
2. Add 0 ml, 0.1 ml, 0.2 ml, 0.4 ml, 0.6 ml, 0.8 ml, 1 ml of standard glucose solution to
tubes labeled B, 1, 2 3, 4, 5 and 6, respectively. Similarly make duplicates in duplicate
test tubes.
3. Add 1 ml of unknown sugar sample in U mark test tube. Similarly, make unknown
duplicate in duplicate test tube.
4. Add 1 ml of DNS to each test tube as mentioned in the table below.
5. Incubate the tubes in boiling water bath for 5 minutes.
Determination of reducing sugars concentration by DNS method
M. Tech. I Sem (Biotechnology) Page 2
6. Cool the tubes to room temperature and add 8 ml of distilled water and mix well.
7. Adjust the spectrophotometer with a blank.
8. Take 1ml of reaction mixture in a clean cuvette, and check the absorbance at 540nm.
9. Note down the absorbance values for each reaction mixture and their duplicates.
10. Calculate standard deviation for each pair of values.
11. Plot a graph between average optical density (O.D) at 540 nm against concentration of
glucose (S) and use linear regression analysis to draw the straight line with error bars
based on standard deviation.
12. Estimate the slope of line, line of equation to determine the concentration of reducing
sugar in an unknown sample.
Table: Experimental and observation Table
Serial
number
Standard
glucose
solution
(ml)
Distilled
water
(ml)
DNS
(ml)
Incubation Distilled
water
(ml)
Concentration
of glucose
(g/ml)
O.D.
(540 nm)
Avg
O.D
Standard
deviation
1 2
B 0 1 1
9
5
C
f
o
r
5
m
i
n
u
t
e
s
8 0
1 0.1 0.9 1 8 100
2 0.2 0.8 1 8 200
3 0.4 0.6 1 8 400
4 0.6 0.4 1 8 600
5 0.8 0.2 1 8 800
6 1.0 - 1 8 1000
Unkno
wn (U)
1.0 - 1 8 ??
Observation:
The intensity of the color observed will be proportional to the concentration of glucose present in
the solution.
Result:
The slope (O.D / S), equation of line (Y =mX +C) and goodness of fit (R
2
) from standard
curve drawn between O.D. vs. concentration of glucose are _________, _________
and_________, respectively.
The reducing sugar concentration in the unknown sample is _________ g/ml.
También podría gustarte
- Lab 4-Determination of Total Reducing Sugars - Hydrolyssi+DNS MethodDocumento4 páginasLab 4-Determination of Total Reducing Sugars - Hydrolyssi+DNS MethodDũng Nguyễn ViệtAún no hay calificaciones
- Glucose Dinitrosalicylic Acid MethodDocumento3 páginasGlucose Dinitrosalicylic Acid Methodarcheologists100% (1)
- Report Reducing SugarDocumento8 páginasReport Reducing SugarRedzuan Hussin83% (6)
- Determination of Glucose by Titration With Fehling's ReagentDocumento5 páginasDetermination of Glucose by Titration With Fehling's ReagentMohamed Abdelghni EmaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab ReportDocumento7 páginasLab ReportAlliedschool DefencecampusAún no hay calificaciones
- Industrial process for OXICONAZOLE Dr krishnasarma Pathy step-I 2,2’4’-tri-choloroacetophenone,Imidazole reacted in presence of acetonitrile to form 1-(2,4-dichlorophenacyl)-imidazole (I).Which is then reacted with hydroxylamine. hydrochloride to give (Z)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl) ethanone oxime (II). It is further reacted with 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl chloride in presence of sodium hydride to give (III) Oxiconazole and finally salt formation with nitric acidDocumento10 páginasIndustrial process for OXICONAZOLE Dr krishnasarma Pathy step-I 2,2’4’-tri-choloroacetophenone,Imidazole reacted in presence of acetonitrile to form 1-(2,4-dichlorophenacyl)-imidazole (I).Which is then reacted with hydroxylamine. hydrochloride to give (Z)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-imidazol-1-yl) ethanone oxime (II). It is further reacted with 2,4-Dichlorobenzyl chloride in presence of sodium hydride to give (III) Oxiconazole and finally salt formation with nitric acidDrkrishnasarma pathy100% (1)
- Experiment 5 Determination of Caffeine 2020Documento4 páginasExperiment 5 Determination of Caffeine 2020FYAún no hay calificaciones
- DNA Isolation ReportDocumento3 páginasDNA Isolation ReportJonathan DiabAún no hay calificaciones
- Glucose Assay by Dinitrosalicylic Colorimetric MethodDocumento7 páginasGlucose Assay by Dinitrosalicylic Colorimetric MethodAbdullah Noordin50% (2)
- GC Lab ManualDocumento5 páginasGC Lab ManualJC100% (1)
- Absorption Spectrum of A Conjugated DyeDocumento6 páginasAbsorption Spectrum of A Conjugated DyeKing Everest100% (1)
- Preparation and Recrystallization of AcetanilideDocumento6 páginasPreparation and Recrystallization of AcetanilideFluoruro De PotasioAún no hay calificaciones
- Onion Dna IsolationDocumento4 páginasOnion Dna IsolationSmriti SmreetiAún no hay calificaciones
- Antacid Analysisrty4Documento4 páginasAntacid Analysisrty4Melced BenasasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estimation of Protein by The Biuret MethodDocumento2 páginasEstimation of Protein by The Biuret MethodUsman Ghani100% (1)
- DNA Isolation, Restriction, Visualitation, and QuantificationDocumento20 páginasDNA Isolation, Restriction, Visualitation, and QuantificationSonianto kuddi100% (5)
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDocumento6 páginasThin Layer ChromatographyVictoria ReaganAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Documento5 páginasLab Report Sds-Page WB - PT 1 (1-5)Ezad juferiAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratory Plan 1:: Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) With Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP)Documento4 páginasLaboratory Plan 1:: Standardization of Sodium Hydroxide (Naoh) With Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP)Alliza Kaye CasullaAún no hay calificaciones
- ParacetamolDocumento2 páginasParacetamolDanielle PayneAún no hay calificaciones
- S Determination of Caffeine in BeveragesDocumento5 páginasS Determination of Caffeine in BeveragesVioleta Grigoras100% (1)
- Determine Iodine Number of Corn OilDocumento4 páginasDetermine Iodine Number of Corn OilVisarika Vaidya100% (1)
- Serial DilutionDocumento9 páginasSerial DilutionSaranya KannanAún no hay calificaciones
- Protein Assay Using The Bradford MethodDocumento3 páginasProtein Assay Using The Bradford MethodTimmy CoAún no hay calificaciones
- Quantitative Determination of Proteins Using Bradford MethodDocumento2 páginasQuantitative Determination of Proteins Using Bradford Methodann_michelle7Aún no hay calificaciones
- 000-Practice Set TSGPDocumento5 páginas000-Practice Set TSGPnids50% (2)
- CHEMISTRY 103 Exp. 12 Spectrophotometric Analysis Aspirin TabletDocumento6 páginasCHEMISTRY 103 Exp. 12 Spectrophotometric Analysis Aspirin TabletJamal Joseph100% (1)
- SDS-PAGE Separates Proteins by SizeDocumento11 páginasSDS-PAGE Separates Proteins by SizeBantita Treepong100% (1)
- Formal Report AspirinDocumento7 páginasFormal Report AspirinAlexandra Zambanini0% (1)
- The Bradford Method For Protein QuantitationDocumento7 páginasThe Bradford Method For Protein QuantitationChemiboyAún no hay calificaciones
- Effect of Temperature On Invertase ActivityDocumento3 páginasEffect of Temperature On Invertase ActivityElizar Nepomuceno Gonzales100% (2)
- AOAC Official Method 971.26 Color (Extractable) in Spices Spectrophotometric Method First Action 1971 Final Action 1980 - AOAC - 97126Documento1 páginaAOAC Official Method 971.26 Color (Extractable) in Spices Spectrophotometric Method First Action 1971 Final Action 1980 - AOAC - 97126Anju Doraisamy100% (1)
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Two-Component SystemDocumento5 páginasSpectrophotometric Analysis of A Two-Component Systemiabureid7460Aún no hay calificaciones
- Preparation of Plasmid DNA by Alkaline Lysis With SDS MinipreparationDocumento2 páginasPreparation of Plasmid DNA by Alkaline Lysis With SDS Minipreparationstevensb055100% (1)
- Activation Energy Lab Report GroupDocumento2 páginasActivation Energy Lab Report GroupSyazwani Abdullah100% (1)
- Lab 2. Plasmid DNA ExtractionDocumento5 páginasLab 2. Plasmid DNA Extractionanon_747148947100% (1)
- Formal LabDocumento4 páginasFormal Labljeanja2100% (1)
- Lab Manual FinalDocumento28 páginasLab Manual FinalErwin ManipolAún no hay calificaciones
- Determination of Calcium As OxalateDocumento17 páginasDetermination of Calcium As Oxalateasep wandi nugraha100% (1)
- DNA Isolation From Spleen ProtocolDocumento2 páginasDNA Isolation From Spleen ProtocolSherlock Wesley ConanAún no hay calificaciones
- Protein Purity and Molecular WeightDocumento6 páginasProtein Purity and Molecular WeightAbg Khairul Hannan Bin Abg AbdillahAún no hay calificaciones
- 11 How To Determine LOD in AAS PDFDocumento3 páginas11 How To Determine LOD in AAS PDFDaryusman Dt Rajo Intan67% (3)
- HPLC Analysis of Caffeine in BeveragesDocumento3 páginasHPLC Analysis of Caffeine in BeveragesIvelisse03120% (1)
- Unit 6-reducing sugarDocumento3 páginasUnit 6-reducing sugarMAI NGUYỄN TRẦN THANHAún no hay calificaciones
- Uv Vis SpectrophotometerDocumento8 páginasUv Vis SpectrophotometerFath Bond100% (1)
- Determining Reducing Sugar with the DNS MethodDocumento3 páginasDetermining Reducing Sugar with the DNS MethodMonisankar Mula83% (6)
- Biochem Lab ManualDocumento5 páginasBiochem Lab ManualshaneskiranrajaAún no hay calificaciones
- DNS-Experiment-3Documento3 páginasDNS-Experiment-317roopa2010Aún no hay calificaciones
- Nelson-Somogyi Assay for Glucose Using Copper and Molybdenum Blue ColorDocumento4 páginasNelson-Somogyi Assay for Glucose Using Copper and Molybdenum Blue ColorCAILA CACHEROAún no hay calificaciones
- ESTIMATION OF SERUM UreaDocumento4 páginasESTIMATION OF SERUM Ureasoroutaditya04Aún no hay calificaciones
- D Gluconic Acid D Glucano Delta LactoneDocumento3 páginasD Gluconic Acid D Glucano Delta LactoneI. Murali KrishnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calorimetric Determination of GlucoseDocumento5 páginasCalorimetric Determination of GlucoseNur Sakinah Abdul KaharAún no hay calificaciones
- G 3660 BulDocumento2 páginasG 3660 Bulsrinath_sreddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Spectrophotometric Carbohydrate Assays (DNSA and PhenolDocumento3 páginasSpectrophotometric Carbohydrate Assays (DNSA and Phenolnurul9535Aún no hay calificaciones
- Estimation of Total Amino AcidsDocumento21 páginasEstimation of Total Amino AcidsVijay BhaaskarlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Determination of Blood Glucose ConcentrationDocumento23 páginasDetermination of Blood Glucose ConcentrationdeasyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Albumin: Quantitative Determination of AlbuminDocumento2 páginasAlbumin: Quantitative Determination of AlbuminAhtziri MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Bioc 211 (Lab2)Documento4 páginasBioc 211 (Lab2)Camelia TincuAún no hay calificaciones
- Estimation of Total Reducing Sugar in The Given SampleDocumento12 páginasEstimation of Total Reducing Sugar in The Given SampleKHYATI BHINDEAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)Documento13 páginasLaboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)biokimia 2018Aún no hay calificaciones
- Archlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Documento16 páginasArchlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Goh Ka WeeAún no hay calificaciones
- August 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Documento6 páginasAugust 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Joanna Carel Lopez100% (3)
- CR Vs MarubeniDocumento15 páginasCR Vs MarubeniSudan TambiacAún no hay calificaciones
- Impact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianDocumento15 páginasImpact of IT On LIS & Changing Role of LibrarianshantashriAún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaDocumento35 páginasMarketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaMuamer ĆimićAún no hay calificaciones
- 15 - 5 - IoT Based Smart HomeDocumento6 páginas15 - 5 - IoT Based Smart HomeBhaskar Rao PAún no hay calificaciones
- Music 7: Music of Lowlands of LuzonDocumento14 páginasMusic 7: Music of Lowlands of LuzonGhia Cressida HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Planning A Real Estate ProjectDocumento81 páginasPlanning A Real Estate ProjectHaile SilasieAún no hay calificaciones
- April 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesDocumento16 páginasApril 26, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore Times100% (1)
- 2014 mlc703 AssignmentDocumento6 páginas2014 mlc703 AssignmentToral ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Portfolio Artifact Entry Form - Ostp Standard 3Documento1 páginaPortfolio Artifact Entry Form - Ostp Standard 3api-253007574Aún no hay calificaciones
- DLL - The Firm and Its EnvironmentDocumento5 páginasDLL - The Firm and Its Environmentfrances_peña_7100% (2)
- DELcraFT Works CleanEra ProjectDocumento31 páginasDELcraFT Works CleanEra Projectenrico_britaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Rtsa 2012Documento7 páginasRtsa 2012Justin RobinsonAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT FOUR: Fundamentals of Marketing Mix: - Learning ObjectivesDocumento49 páginasUNIT FOUR: Fundamentals of Marketing Mix: - Learning ObjectivesShaji ViswambharanAún no hay calificaciones
- Rishte ki baat SMS messages collectionDocumento108 páginasRishte ki baat SMS messages collectionTushar AggarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Cushman Wakefield - PDS India Capability Profile.Documento37 páginasCushman Wakefield - PDS India Capability Profile.nafis haiderAún no hay calificaciones
- FR Post-10Documento25 páginasFR Post-10kulich545Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ancient Greek Divination by Birthmarks and MolesDocumento8 páginasAncient Greek Divination by Birthmarks and MolessheaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Android software download guideDocumento60 páginasAndroid software download guideRizky PradaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Logic and Set Theory PropositionDocumento3 páginasLogic and Set Theory PropositionVince OjedaAún no hay calificaciones
- 50 Years of Teaching PianoDocumento122 páginas50 Years of Teaching PianoMyklan100% (35)
- 2023 Test Series-1Documento2 páginas2023 Test Series-1Touheed AhmadAún no hay calificaciones
- Instrumentation Positioner PresentationDocumento43 páginasInstrumentation Positioner PresentationSangram Patnaik100% (1)
- Sentinel 2 Products Specification DocumentDocumento510 páginasSentinel 2 Products Specification DocumentSherly BhengeAún no hay calificaciones
- Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)Documento6 páginasInterpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)afalfitraAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsDocumento157 páginasLecture Ready 01 With Keys and TapescriptsBảo Châu VươngAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice: CH142 Sample Exam 2 QuestionsDocumento12 páginasMultiple Choice: CH142 Sample Exam 2 QuestionsRiky GunawanAún no hay calificaciones
- Olympics Notes by Yousuf Jalal - PDF Version 1Documento13 páginasOlympics Notes by Yousuf Jalal - PDF Version 1saad jahangirAún no hay calificaciones
- Log File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsDocumento334 páginasLog File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsKossay BelkhammarAún no hay calificaciones