Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
DRUG STUDY Epinephrine
Cargado por
Mayet De Castro LejanoDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
DRUG STUDY Epinephrine
Cargado por
Mayet De Castro LejanoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Jessica Mercedes D.
Canto BN4N
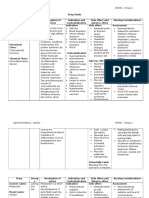
DRUG STUDY
Medication
Epinephrine
(Adrenaline)
Drug Classes:
Sympathomimeti
c
Alpha-adrenergic
agonist
Beta1 and beta2
adrenergic
agonist
Cardiac stimulant
Bronchodilator
Antasthmatic
drug
Nasal
decongestant
Mydriatic
Antiglaucoma
drug
Dosage:
Adults:
Injection: 0.5-
1mg IV
Intraspinal:
0.2-0.4mL of a
1:1,000
solution added
to anesthetic
spinal fluid
mixture
Children:
Injection:
0.01mg/kg q20
mins
Mechanism of Action:
Epinephrine acts by
binding to a variety of
adrenergic receptors.
Adrenaline is a
nonselective agonist of
all adrenergic receptors,
including , , ,
, and
receptors.[8]
Epinephrine's binding
to these receptors
triggers a number of
metabolic changes.
Binding to -adrenergic
receptors inhibits
insulin secretion by the
pancreas, stimulates
glycogenolysis in the
liver and muscle, and
stimulates glycolysis in
muscle.[9] -
Adrenergic receptor
binding triggers
glucagon secretion in
the pancreas, increased
adrenocorticotropic
Indication:
IV: treatment and
prohylaxis of cardiac
arrest and attacks of
transitory AV heart
block with syncopal
seizures; syncope
due to carotid sinus
syndrome, acute
hypersensitivity
reactions, serum
sickness, urticaria,
angioneurotic
edema, ina acute
asthmatic attacks to
relieve
bronchospasms not
controlled by
inhalation or SC
injection; relaxation
of uterine
musculature;
additive to local
anesthetic solutions
from injection to
prolong their
duration of action
Contraindications:
Contraindicate
d with allergy
or
hypersensitivit
y to
epinephrine or
components of
preparation;
narrow-angle
glaucoma;
shock other
than
anaphylactic
shock;
hypovolemia;
general
anesthesia with
halogenated
hydrocarbons;
organic brain
damage;
cerebral
arteriosclerosis
; cardiac
dilation and
coronary
Adverse Effects:
Systemic
Administration:
CNS: fear, anxiety,
tenseness,
restlessness, headache,
dizziness, drowsiness,
tremor, insomnia,
hallucinations,
seizures, CNS
depression, weakness,
blurred vision, tearing,
photophbia, CV:
Arrhythmias,
hypertension resulting
in intracranial
hemorrhage, CV
collapse with
hypotension,
palpitations,
tachycardia,
precordial pain, GI:
Nausea, vomiting,
anorexia, GU:
Constriction of blood
vessels and decreased
urine formation,
Nursing
Responsibilities:
Rotate SC
injection sites
to prevent
necrosis;
monitor sites
frequently
Use extreme
caution when
calculating and
preparing
doses;
epinephrine is
a very potent
drug.
Protect drug
solutions from
light, extreme
heat and
freezing.
Shake the
suspension for
injection well
before
withdrawing
the dose.
hormone (ACTH)
secretion by the
pituitary gland, and
increased lipolysis by
adipose tissue. Together
these effects lead to
increased blood glucose
and fatty acids,
providing substrates for
energy production
within cells throughout
the body.[9]
Reference: MIMS
Philippines.PIMS.111
th
edition.2007
and limit systemic
absorption
Injection: relief from
respiratory distress
of bronchial asthma,
chronic bronchitis,
emphysema, other
COPDs
Aerosols and
solutions for
nebulization:
Temporary relief
from acute attacks of
bronchial asthma,
COPD
Topical nasal
solution: Temporary
relief from nasal and
nasopharyngeal
mucosal congestion
due to a cold,
sinusitis, hay fever
or other upper
respiratory allergies
insufficiency;
tachyarrhythmi
a; ischemic
heart disease;
hypertension;
renal
dysfunction;
COPD patients
who have
developed
degenerative
heart disease;
diabetes
mellitus;
hyperthyroidis
m; lactation.
dysuria, urinary
retention in males
with prostatism,
OTHER: pallor,
respiratory difficulty,
orofactial dystonia,
sweating.
También podría gustarte
- Using Flowers For HealingDocumento28 páginasUsing Flowers For HealingKarina Castilhos100% (1)
- Healing With Herbs and SpicesDocumento23 páginasHealing With Herbs and Spicesnikanor1100% (2)
- Atkins Food List PDFDocumento15 páginasAtkins Food List PDFDaniélly Meira100% (3)
- Morphine SulfateDocumento5 páginasMorphine Sulfateapi-3797941100% (4)
- Theophylline Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasTheophylline Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (5)
- Benadryl Antihistamine Uses Side EffectsDocumento1 páginaBenadryl Antihistamine Uses Side Effectsgita24203965100% (1)
- VerapamilDocumento1 páginaVerapamilStephanie PeAún no hay calificaciones
- Emergency DrugsDocumento40 páginasEmergency Drugsmattheus101Aún no hay calificaciones
- NIcardipine Drug SummDocumento1 páginaNIcardipine Drug SummWarren50% (2)
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasEpinephrine Drug StudyAbigail De Leon80% (5)
- Dobutamine Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaDobutamine Drug Studyzyr2189100% (2)
- GPDocumento3 páginasGPYwagar YwagarAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study - Sodium BicarbonateDocumento3 páginasDrug Study - Sodium Bicarbonatejepong_paolo0283% (6)
- Drug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Documento6 páginasDrug Study (Epinephrine, Lidocaine, Diazepam)Abigaile Operiano100% (2)
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocumento3 páginasBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasNitroglycerin Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (6)
- Fentanyl Dosage and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento3 páginasFentanyl Dosage and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDavid Villanueva67% (3)
- DRUG STUDY EpinephrineDocumento2 páginasDRUG STUDY EpinephrineCarlo Francisco D. Canto78% (9)
- NCP in BurnsDocumento2 páginasNCP in BurnsMayet De Castro Lejano80% (5)
- Drug Study - Epinephrine (Adrenalin)Documento2 páginasDrug Study - Epinephrine (Adrenalin)mikErlh60% (5)
- Digitalis Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento2 páginasDigitalis Dose Nursing ResponsibilitiesMaureen Campos-Pinera67% (3)
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - DigoxinDanielle AglusolosAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan for Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan for Community Acquired PneumoniaEngely Mercader100% (1)
- Thyroid Disease in PregnancyDocumento36 páginasThyroid Disease in Pregnancypeni_dwiAún no hay calificaciones
- Atropine Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasAtropine Sulfate Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa67% (6)
- NCP For CHFDocumento2 páginasNCP For CHFMayet De Castro Lejano100% (1)
- Drug Study Atropine SulfateDocumento1 páginaDrug Study Atropine Sulfateirhizzp75% (8)
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Drug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricDocumento3 páginasDrug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricJhon Jade PalagtiwAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 DrugsDocumento2 páginas1 DrugsPatricia Lucero100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyIrveen Joy RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocumento1 páginaCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Dobutamine Nursing Responsibilities and Side EffectsDocumento2 páginasDobutamine Nursing Responsibilities and Side EffectsJaessa FelicianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- Vasopressin PDFDocumento4 páginasVasopressin PDFAnonymous hF5zAdvwCCAún no hay calificaciones
- Imdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsDocumento23 páginasImdur for Angina Relief in 60 SecondsJoyce Anne SupnetAún no hay calificaciones
- Norepinephrine Drug CardDocumento2 páginasNorepinephrine Drug CardYou know who100% (9)
- Pharmacologic: Cardiovascular: FlushingDocumento2 páginasPharmacologic: Cardiovascular: Flushingitsmeaya100% (5)
- AmiodaroneDocumento2 páginasAmiodaronePauling Frez100% (5)
- Benadryl Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasBenadryl Drug StudyCheezy BreadAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study ShenDocumento12 páginasDrug Study ShenLass KazeAún no hay calificaciones
- Cordarone for Arrhythmias: Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing CareDocumento1 páginaCordarone for Arrhythmias: Dosage, Side Effects and Nursing CarejaybamanAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento6 páginasDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongAún no hay calificaciones
- Doxazosin MesylateDocumento2 páginasDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Aún no hay calificaciones
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLDocumento5 páginasNoradrenaline (Norepinephrine) : 1mg/mLBrian RelsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento1 páginaGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonAún no hay calificaciones
- Dopamine HCLDocumento2 páginasDopamine HCLianecunarAún no hay calificaciones
- CaptoprilDocumento2 páginasCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasDrug StudyMäc LäntinAún no hay calificaciones
- DiphenhydramineDocumento10 páginasDiphenhydramineFebry Dian SinagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study ICUDocumento5 páginasDrug Study ICUEcko MoawiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocumento1 páginaDrug Study - Diazepammarengbib100% (1)
- Drug Study NewDocumento4 páginasDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniAún no hay calificaciones
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- DiazepamDocumento1 páginaDiazepamStephanie PeAún no hay calificaciones
- Terbutaline SulfateDocumento2 páginasTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study CaptoprilDocumento2 páginasDrug Study CaptoprilLyza Pamela T. Vinluan0% (1)
- GlipizideDocumento3 páginasGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento3 páginasClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEAún no hay calificaciones
- Morphine SulfateDocumento2 páginasMorphine SulfateArianne Nicole PinuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasEpinephrine Drug StudyJhoy Iris SarangayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Drugs ORDocumento17 páginasDrugs ORCatherine ZamoraAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 MG Iv BidDocumento17 páginas5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherAún no hay calificaciones
- HyrdrocortisoneDocumento7 páginasHyrdrocortisoneRoseben SomidoAún no hay calificaciones
- Rregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathDocumento4 páginasRregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathHannah BuquironAún no hay calificaciones
- Atropine - Atro-Pen ClassificationDocumento4 páginasAtropine - Atro-Pen ClassificationphatericAún no hay calificaciones
- Managing corticosteroids and their side effectsDocumento6 páginasManaging corticosteroids and their side effectsKrista Madranca CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- HaldolDocumento6 páginasHaldolJon ChuaAún no hay calificaciones
- LOVELYNDocumento1 páginaLOVELYNMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- C 2Documento9 páginasC 2Mayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Documento38 páginasUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)Trixie Anne GamotinAún no hay calificaciones
- The Progression From Acute Glomerulonephritis To Chronic Glomerulonephritis Is VariableDocumento2 páginasThe Progression From Acute Glomerulonephritis To Chronic Glomerulonephritis Is VariableMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- The Progression From Acute Glomerulonephritis To Chronic Glomerulonephritis Is VariableDocumento2 páginasThe Progression From Acute Glomerulonephritis To Chronic Glomerulonephritis Is VariableMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Glomerulonephritis Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentDocumento3 páginasGlomerulonephritis Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- NP SLCS X-8610-0112 Final WebDocumento0 páginasNP SLCS X-8610-0112 Final WebMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chronic Kidney Disease: The Philippine SituationDocumento28 páginasChronic Kidney Disease: The Philippine SituationMarffy LlamasAún no hay calificaciones
- Santos-Viola Carlos A.: Cubao, Quezon CityDocumento10 páginasSantos-Viola Carlos A.: Cubao, Quezon CityMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Education Is An Admirable Thing, But It Is Well To Remember From Time To Time That Nothing W Orth Knowing Can Be Taught.Documento1 páginaEducation Is An Admirable Thing, But It Is Well To Remember From Time To Time That Nothing W Orth Knowing Can Be Taught.Mayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Health Care ProviderDocumento3 páginasHealth Care ProviderMayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Copd Mayet (Ist Part)Documento3 páginasCopd Mayet (Ist Part)Mayet De Castro LejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Gouldian Finch Care and BreedingDocumento3 páginasGouldian Finch Care and BreedingJoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrional Status of The Dhaka University BodyDocumento35 páginasNutrional Status of The Dhaka University BodySharifMahmudAún no hay calificaciones
- Applied Social Psychology Module 2Documento5 páginasApplied Social Psychology Module 2swathy sudheerAún no hay calificaciones
- Welcome: N.K.LathaDocumento17 páginasWelcome: N.K.LathaJ Ta RaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physiology of LaborDocumento49 páginasPhysiology of LaborGunung MahameruAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding SmaDocumento40 páginasUnderstanding SmaThanos ZihnalisAún no hay calificaciones
- 1803ict Gary Monday4pm Scanlan Jordan s5054901 MajorassignmentDocumento8 páginas1803ict Gary Monday4pm Scanlan Jordan s5054901 Majorassignmentapi-319771684Aún no hay calificaciones
- Environmental Engineering Test PaperDocumento16 páginasEnvironmental Engineering Test PaperajaydevmalikAún no hay calificaciones
- DAFTAR OBAT PENGOBATAN MASSALDocumento6 páginasDAFTAR OBAT PENGOBATAN MASSALKayla NaylaAún no hay calificaciones
- AmoebiasisDocumento2 páginasAmoebiasisJay PeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection: Team 3: Cercado, Chiong, EsperidaDocumento28 páginasCentral Line Associated Blood Stream Infection: Team 3: Cercado, Chiong, EsperidaJuniferAún no hay calificaciones
- Mechanisms of Cough From AngiotensinDocumento1 páginaMechanisms of Cough From AngiotensinironAún no hay calificaciones
- Submitted By: TOOBA SAEED - 70074236: Natural Holistic Healing and Wellness CenterDocumento4 páginasSubmitted By: TOOBA SAEED - 70074236: Natural Holistic Healing and Wellness CenterTooba SaeedAún no hay calificaciones
- INTRAUTERINE DEATH WidyaDocumento11 páginasINTRAUTERINE DEATH WidyaNabilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Arginine Metabolism and its Role in Growth, Health and DiseaseDocumento26 páginasArginine Metabolism and its Role in Growth, Health and Diseaseאנריקה שטרמר דיאטן קליניAún no hay calificaciones
- SWDDocumento58 páginasSWDakheel ahammedAún no hay calificaciones
- Prescription vs OTC Drug RisksDocumento19 páginasPrescription vs OTC Drug Risks19-28 Manan PopatAún no hay calificaciones
- My Health, I Manage!: Paida (Patting, Slapping) TheoryDocumento1 páginaMy Health, I Manage!: Paida (Patting, Slapping) TheorydalbogondesAún no hay calificaciones
- First Aid Manual Rev 0Documento77 páginasFirst Aid Manual Rev 0Vinayak KaujalgiAún no hay calificaciones
- Approved Hospitals Attendants PDFDocumento59 páginasApproved Hospitals Attendants PDFsthnmAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiogenic ShockDocumento42 páginasCardiogenic ShockpashaAún no hay calificaciones
- Skin Graft Vs DC 8DRDocumento2 páginasSkin Graft Vs DC 8DRibraheemAún no hay calificaciones
- Gout Arthritis: Liyana Binti Mohd Arif C111 12 813 Ruth Dea Sarah Amalia Hutabarat C111 12 906Documento25 páginasGout Arthritis: Liyana Binti Mohd Arif C111 12 813 Ruth Dea Sarah Amalia Hutabarat C111 12 906azulqaidah95Aún no hay calificaciones
- Direct Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two CasesDocumento3 páginasDirect Pulp Capping in Primary Molars: Report of Two Casesemie sitorusAún no hay calificaciones