Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
29 - 5 IES Exam Syllabus SRIE
Cargado por
Suman Saha0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
14 vistas10 páginasIES exam syllabus SRIE
Título original
29_5 IES Exam Syllabus SRIE
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoIES exam syllabus SRIE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
14 vistas10 páginas29 - 5 IES Exam Syllabus SRIE
Cargado por
Suman SahaIES exam syllabus SRIE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 10
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 1
(As per UPSC Notification for 2011)
The standard of paper in General Ability Test will be such as may be expected of an Engineering/Science
Graduate. The standard of papers in other subjects will approximately be that of an Engineering Degree
Examination of an Indian University. There will be no practical examination in any of the subjects.
GENERAL ABILITY TEST:
Part A: General English. The question paper in General English will be designed to test the
candidates understanding of English and workmanlike use of words.
Part B: General Studies: The paper in General Studies will include knowledge of current events and
of such matters as of everyday observation and experience in their scientific aspects as may be
expected of an educated person. The paper will also include questions on History of India and
Geography of a nature which candidates should be able to answer without special study.
CIVIL ENGINEERING
(For both objective and conventional type papers)
PAPER-I
1. BUILDING MATERIALS
Timber : Different types and species of structural timber, density-moisture relationship, strength in
different directions, defects, influence of defects on permissible stress, preservation, dry and wet rots,
codal provisions for design, plywood.
Bricks : Types, Indian Standard classification, absorption, saturation factor, strength in masonry,
influence of morter strength on masonry strength.
Cement : Compounds of, different types, setting times, strength.
Cement Mortar : Ingredients, proportions, water demand, mortars for plastering and masony.
Concrete : Importance of W/C Ratio, Strength, ingredients including admixtures, worksability, testing
for strength, elasticity, non-destructive testing, mix design methods.
2. SOLID MECHANICS
Elastic constants, stress, plane stress, Mohrs circle of stress, strains, plane strain, Mohrs circle of strain,
combined stress; Elastic theories of failure; Simple bending, shear; Torsion of circular and rectangular
sections and simple members.
3. STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
Analysis of determinate structures different methods including graphical methods.
Analysis of indeterminate skeletal frames - moment distribution, slopedeflection, stiffness and force
methods, energy methods, Muller-Breslau principle and application.
Plastic analysis of indeterminate beams and simple frames - shape factors.
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 2
4. DESIGN OF STEEL STRUCTURES
Principles of working stress method. Design of connections, simple members, Built-up sections and
frames, Design of Industrial roofs. Principles of ultimate load design. Design of simple members and
frames.
5. DESIGN OF CONCRETE AND MASONRY STRUCTURES
Limit state design for bending, shear, axial compression and combined forces. Codal provisions for slabs,
beams, walls and footings. Working stress method of design of R.C. members. Principles of prestressed
concrete design, materials, methods of prestressing, losses. Design of simple members and determinate
structures. Introductions to prestressing of indeterminate structures. Design of brick masonry as per I.S.
Codes.
6. CONSTRUCTION PRACTICE, PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT
Concreting Equipment: Weight Batcher, Mixer, vibrator, batching plant, concrete pump. Cranes, hoists,
lifting equipment.
Earthwork Equipment: Power shovel, hoe, dozer, dumper, trailers and tractor, rollers, sheep foot rollers,
pumps.
Construction, Planning and Management : Bar chart, linked bar chart, work-break down structures,
Activity - on - arrow diagrams. Critical path, probabilistic activity durations; Event-based networks.
PERT network: Time-cost study, crashing; Resource allocation.
PAPER-II
1. (a) FLUID MECHANICS, OPEN CHANNEL FLOW, PIPE FLOW
Fluid Properties, Pressure, Thrust, Buoyancy; Flow Kinematics; Integration of flow equations; Flow
measurement; Relative motion; Moment of momentum; Viscosity, Boundary layer and Control, Drag,
Lift; dimensional Analysis, Modelling; Cavitation; Flow oscillations; Momentum and Energy principles in
Open channel flow, Flow controls, Hydraulic jump, Flow sections and properties; Normal flow, Gradually
varied flow; Surges; Flow development and losses in pipe flows, Measurements; Siphons; Surges and
Water hammer; Delivery of Power Pipe networks.
(b) HYDRAULIC MACHINES AND HYDROPOWER
Centrifugal pumps, types, performance parameters, scaling, pumps in parallel; Reciprocating pumps, air
vessels, performance parameters; Hydraulic ram; Hydraulic turbines, types, performance
parameters, controls, choice; Power house, classification and layout, storage, pondage, control of
supply.
2. (a) HYDROLOGY
Hydrological cycle, precipitation and related data analyses, PMP, unit and synthetic hydrographs;
Evaporation and transpiration; Floods and their management, PMF; Streams and their gauging; River
morphology; Routing of floods; Capacity of Reservoirs.
(b) WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
Water resources of the globe: Multipurpose uses of Water: Soil-Plant-Water relationships, irrigation
systems, water demand assessment; Storages and their yields, ground water yield and well hydraulics;
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 3
Waterlogging, drainage design; Irrigation revenue; Design of rigid boundary canals, Laceys and Tractive
force concepts in canal design, lining of canals; Sediment transport in canals; Non-Overflow and
overflow sections of gravity dams and their design, Energy dissipators and tailwater rating; Design of
headworks, distribution works, falls, cross-drainage works, outlets; River training.
3. ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING
(a) WATER SUPPLY ENGINEERING
Sources of supply, yields, design of intakes and conductors; Estimation of demand; Water quality
standards; Control of Water-borne diseases; Primary and secondary treatment, detailing and
maintenance of treatment units; Conveyance of treatment units; Conveyance and distribution systems
of treated water, leakages and control; Rural water supply; Institutional and industrial water supply.
(b) WASTE WATER ENGINEERING:
Urban rain water disposal; Systems of sewage collection and disposal; Design of sewers and sewerage
systems; pumping; Characteristics of sewage and its treatment, Disposal of products of sewage
treatment, streamflow rejuvenation Institutional and industrial sewage management; Plumbing Systems;
Rural and semi-urban sanitation.
(c) SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
Source, classification collection and disposal; Design and Management of landfills.
(d) AIR AND NOISE POLLUTION AND ECOLOGY
Sources and effects of air pollution, monitoring of air pollution; Noise pollution an standards; Ecological
chain and balance, Environmental assessment.
4. (a) SOIL MECHANICS
Properties of soil, classification and interrelationship; Compaction behaviour, methods of compaction
and their choice; Permeability and seepage, flow nets, Inverted filters; Compressibility and
consolidation; Shearing resistance, stresses and failure; soil testing in laboratory and in-situ; Stress path
and applications; Earth pressure theories, stress distribution in soil; soil exploration, samplers, load
tests, penetration tests.
(b) FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
Types of foundations, Selection criteria, bearing capacity, settlement, laboratory and field tests; Types
of piles and their design and layout, Foundations on expansive soils, swelling and its prevention,
foundation on swelling soils.
5. (a) SURVEYING
Classification of surveys, scales, accuracy; Measurement of distances direct and indirect methods;
optical and electronic devices; Measurement of directions, prismatic compass, local attraction;
Theodolites - types; Measurement of elevations - Spirit and trigonometric levelling; Relief
representation; Contours; Digital elevation modelling concept; Establishment of control by triangulations
and traversing - measurements and adjustment of observations, computation of coordinates; Field
astronomy, Concept of global positioning system; Map preparation by plane tabling and by
photogrammetry; Remote sensing concepts, map substitutes.
(b) TRANSPORTATION ENGINEERING
Planning of highway systems, alignment and geometric design, horizontal and vertical curves, grade
separation; Materials and construction methods for different surfaces and maintenance: Principles of
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 4
pavement design; Drainage. Traffic surveys, Intersections, signalling: Mass transit systems, accessibility,
networking. Tunnelling, alignment, methods of construction, disposal of muck, drainage, lighting and
ventilation, traffic control, emergency management. Planning of railway systems, terminology and
designs, relating to gauge, track, controls, transits, rolling stock, tractive power and track
modernisation; Maintenance; Appurtenant works; Containerisation.
Harbours - layouts, shipping lanes, anchoring, location identification; Littoral transport with erosion and
deposition; sounding methods; Dry and Wet docks, components and operational Tidal data and
analyses.
Airports - layout and orientation; Runway and taxiway design and drainage management; Zoning laws;
Visual aids and air traffic control; Helipads, hangers, service equipment.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
(For both objective and conventional type papers)
PAPER-I
1. Thermodynamics, Cycles and IC Engines:
Basic concepts, Open and Closed systems. Heat and work. Zeroth, First and Second Law, Application to
non-Flow and Flow processors. Entropy, Availability, Irreversibility and Tds relations. Claperyron and real
gas equations, Properties of ideal gases and vapours. Standard vapour, Gas power and Refrigeration
cycles. Two stage compressor. C-I and S.I. Engines. Pre-ignition, Detonation and Diesel-knock, Fuel
injection and Carburation, Supercharging. Turboprop and Rocket engines, Engine Cooling, Emission &
Control, Flue gas analysis, Measurement of Calorific values. Conventional and Nuclear fuels, Elements of
Nuclear power production.
2. Heat Transfer and Refrigeration and Airconditioning:
Modes of heat transfer. One dimensional steady and unsteady conduction. Composite slab and
Equivalent Resistance. Heat dissipation from extended surfaces, Heat exchangers, Overall heat transfer
coefficient, Empirical correlations for heat transfer in laminar and turbulent flows and for free and forced
Convection, Thermal boundary layer over a flat plate. Fundamentals of diffusive and connective mass
transfer, Black body and basic concepts in Radiation, Enclosure theory, Shape factor, Net work analysis.
Heat pump and Refrigeration cycles and systems, Refrigerants. Condensers, Evaporates and Expansion
devices, Psychrometry, Charts and application to air conditioning, Sensible heating and cooling, Effective
temperature, comfort indices, Load calculations, Solar refrigerations, controls, Duct design.
3. Fluid Mechanics.
Properties and classification of fluids, Manometry, forces on immersed surfaces, Center of pressure,
Buoyancy, Elements of stability of floating bodies. Kinematics and Dynamics. Irrotational and
incompressible. Inviscid flow. Velocity potential, Pressure field and Forces on immersed bodies.
Bernoullis equation, Fully developed flow through pipes, Pressure drop calculations, Measurement of
flow rate and Pressure drop. Elements of boundary layer theory, Integral approach, Laminar and
tubulent flows, Separations. Flow over weirs and notches. Open channel flow, Hydraulic jimp.
Dimensionless numbers, Dimensional analysis, Similitude and modelling. One-dimensional isentropic
flow, Normal shock wave, Flow through convergent - divergent ducts, Oblique shockwave, Rayleigh and
Fanno lines.
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 5
4. Fluid Machinery and Steam Generators.
Performance, Operation and control of hydraulic Pump and impulse an reaction Turbines, Specific speed,
Classification. Energy transfer, Coupling, Power transmission, Steam generators Fire-tube and water-
tube boilers. Flow of steam through Nozzles and Diffusers, Wetness and condensation. Various types of
steam and gas Turbines, Velocity diagrams. Partial admission. Reciprocating, Centrifugal and axial flow
Compressors, Multistage compression, role of Mach Number, Reheat, Regeneration, Efficiency,
Governance.
PAPER - II
5. THEORY OF MACHINES
Kinematic and dynamic analysis of planer mechanisms. Cams. Gears and gear trains. Flywheels.
Governors. Balancing of rigid rotors and field balancing. Balancing of single and multicylinder engines,
Linear vibration analysis of mechanical systems. Critical speeds and whirling of shafts Automatic
controls.
6. MACHINE DESIGN
Design of Joints : cotters, keys, splines, welded joints, threaded fasteners, joints formed by interference
fits. Design of friction drives : couplings and clutches, belt and chain drives, power screws. Design of
Power transmission systems : gears and gear drives shaft and axle, wire ropes. Design of bearings :
hydrodynamics bearings and rolling element bearings.
7. STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
Stress and strain in two dimensions, Principal stresses and strains, Mohrs construction, linear elastic
materials, isotropy and anisotropy, stress-strain relations, uniaxial loading, thermal stresses. Beams :
Bending moment and shear force diagram, bending stresses and deflection of beams. Shear stress
distribution. Torsion of shafts, helical springs. Combined stresses, thick-and think-walled pressure
vessels. Struts and columns. Strain energy concepts and theories of failure.
8. ENGINEERING MATERIALS
Basic concepts on structure of solids. Crystalline materials. Detects in crystalline materials. Alloys and
binary phase diagrams. Structure and properties of common engineering materials. Heat treatment of
steels. Plastics, Ceramics and composite materials. Common applications of various materials.
9. PRODUCTION ENGINEERING
Metal Forming : Basic Principles of forging, drawing and extrusion; High energy rate forming; Powder
metallurgy.
Metal Casting : Die casting, investment casting, Shall Moulding, Centrifugal Casting, Gating & Riser
design; melting furnaces.
Fabrication Processes : Principles of Gas, Arc, Shielded arc Welding; Advanced Welding Processes,
Weldability: Metallurgy of Welding.
Metal Cutting : Turning, Methods of Screw Production, Drilling, Boring, Milling, Gear Manufacturing,
Production of flat surfaces, Grinding & Finishing Processes. Computer Controlled Manufacturing
Systems-CNC, DNC, FMS, Automation and Robotics. Cutting Tools Materials, Tool Geometry, Mechanism
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 6
of Tool Wear, Tool Life & Machinability; Measurement of cutting forces. Economics of Machining.
Unconventional Machining Processes. Jigs and Fixtures. Fits and tolerances, Measurement of surface
texture, Comparators Alignment tests and reconditioning of Machine Tools.
10. INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
Production Planning and Control : Forecasting - Moving average, exponential smoothing, Operations,
scheduling; assembly line balancing, Product development, Break-even analysis, Capacity planning,
PERT and CPM. Control Operations : Inventory control ABC analysis, EOQ model, Materials requirement
planning. Job design, Job standards, Work measurement, Quality Management - Quality analysis and
control. Operations Research : Linear Programming Graphical and Simplex methods, Transportation
and assignment models. Single server queueing model. Value Engineering : Value analysis for
cost/value.
11. ELEMENTS OF COMPUTATION
Computer Organisation, Flow charting, Features of Common computer Languages - FORTRAN, d Base
III, Lotus 1-2-3, C and elementary Programming.
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
(For both objective and conventional types papers)
PAPER - I
1. EM Theory
Electric and magnetic fields. Gausss Law and Amperes Law. Fields in dielectrics, conductors and
magnetic materials. Maxwells equations. Time varying fields. Plane-Wave propagating in dielectric and
conducting media. Transmission lines.
2. Electrical Materials
Band Theory, Conductors, Semi-conductors and Insulators. Super-conductivity. Insulators for electrical
and electronic applications. Magnetic materials. Ferro and ferri magnetism. Ceramics, Properties and
applications. Hall effect and its applications. Special semi conductors.
3. Electrical Circuits
Circuits elements. Kirchoffs Laws. Mesh and nodal analysis. Network Theorems and applications.
Natural response and forced response. Transient response and steady state response for arbitrary
inputs. Properties of networks in terms of poles and zeros. Transfer function. Resonant circuits.
Threephase circuits. Two-port networks. Elements of two-element network synthesis.
4. Measurements and Instrumentation
Units and Standards. Error analysis, measurement of current, Voltage, power, Power-factor and energy.
Indicating instruments. Measurement of resistance, inductance, Capacitance and frequency. Bridge
measurements. Electronic measuring instruments. Digital Voltmeter and frequency counter. Transducers
and their applications to the measurement of nonelectrical quantities like temperature, pressure, flow-
rate displacement, acceleration, noise level etc. Data acquisition systems. A/D and D/A converters.
5. CONTROL SYSTEMS
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 7
Mathematical modelling of physical systems. Block diagrams and signal flow graphs and their reduction.
Time domain and frequency domain analysis of linear dynamical system. Errors for different type of
inputs and stability criteria for feedback systems. Stability analysis using Routh-Hurwitz array, Nyquist
plot and Bode plot. Root locus and Nicols chart and the estimation of gain and phase margin. Basic
concepts of compensator design. State variable matrix design. Sampled data system and performance of
such a system with the samples in the error channel. Stability of sampled data system. Elements of non-
linear control analysis. Control system components, electromechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic
components.
PAPER - II
1. Electrical Machines and Power Transformers
Magnetic Circuits - Analysis and Design of Power transformers. Construction and testing. Equivalent
circuits. Losses and efficiency. Regulation. Auto-transformer, 3-phase transformer. Parallel operation.
Basic concepts in rotating machines. EMF, torque, basic machine types. Construction and operation,
leakage losses and efficiency. D.C. Machines. Construction, Excitation methods. Circuit models.
Armature reaction and commutation. Characteristics and performance analysis. Generators and motors.
Starting and speed control. Testing, Losses and efficiency. Synchronous Machines. Construction. Circuit
model. Operating characteristics and performance analysis. Synchronous reactance. Efficiency. Voltage
regulation. Salient-pole machine, Parallel operation. Hunting. Short circuit transients. Induction
Machines. Construction. Principle of operation. Rotating fields. Characteristics and performance analysis.
Determination of circuit model. Circle diagram. Starting and speed control. Fractional KW motors. Single-
phase synchronous and induction motors.
2. Power systems
Types of Power Stations, Hydro, Thermal and Nuclear Stations. Pumped storage plants. Economics and
operating factors. Power transmission lines. Modeling and performance characteristics. Voltage control.
Load flow studies. Optimal power system operation. Load frequency control. Symmetrical short circuit
analysis. Z-Bus formulation. Symmetrical Components. Per Unit representation. Fault analysis. Transient
and steady-state stability of power systems. Equal area criterion. Power system Transients. Power
system Protection Circuit breakers. Relays. HVDC transmission.
3. ANALOG AND DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND CIRCUITS
Semiconductor device physics, PN junctions and transistors, circuit models and parameters, FET, Zener,
tunnel, Schottky, photo diodes and their applications, rectifier circuits, voltage regulators and multipliers,
switching behavior of diodes and transistors. Small signal amplifiers, biasing circuits, frequency response
and improvement, multistage amplifiers and feed-back amplifiers, D.C. amplifiers, coupling methods,
push pull amplifiers, operational amplifiers, wave shaping circuits. Multivibrators and flip-flops and their
applications. Digital logic gage families, universal gates-combinational circuits for arithmetic and logic
operational, sequential logic circuits. Counters, registers, RAM and ROMs.
4. MICROPROCESSORS
Microprocessor architecture-Instruction set and simple assembly language programming. Interfacing for
memory and I/O. Applications of Micro-processors in power system.
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 8
5. COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
Types of modulation; AM, FM and PM. Demodulators. Noise and bandwidth considerations. Digital
communication systems. Pulse code modulation and demodulation. Elements of sound and vision
broadcasting. Carrier communication. Frequency division and time division multiplexing, Telemetry
system in power engineering.
6. POWER ELECTRONICS
Power Semiconductor devices. Thyristor. Power transistor, GTOs and MOSFETs. Characteristics and
operation. AC to DC Converters; 1-phase and 3-phase DC to DC Converters. AC regulators. Thyristor
controlled reactors; switched capacitor networks. Inverters; single-phase and 3-phase. Pulse width
modulation. Sinusoidal modulation with uniform sampling. Switched mode power supplies.
ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
(For both objective and conventional type papers)
PAPER - I
1. Materials and Components
Structure and properties of Electrical Engineering materials; Conductors, Semiconductors and Insulators,
magnetic, Ferroelectric, Piezoelectric, Ceramic, Optical and Super-conducting materials. Passive
components and characteristics Resistors, Capacitors and Inductors; Ferrities, Quartz crystal Ceramic
resonators, Electromagnetic an Electromechanical components.
2. Physical Electronics, Electron Devices and ICs
Electrons and holes in semiconductors, Carrier Statistics, Mechanism of current flow in a semiconductor,
Hall effect; Junction theory; Different types of diodes and their characteristics; Bipolar Junction
transistor; Field effect transistors; Power switching devices like SCRs, CTOs, power MOSFETs; Basics of
ICs - bipolar, MOS and CMOS types; basic of Opto Electronics.
3. Signals and Systems
Classification of signals and systems: System modelling in terms of differential and difference equations;
State variable representation; Fourier series; Fourier representation; Fourier series; Fourier transforms
and their application to system analysis; Laplace transforms and their application to system analysis;
Convolution and superposition integrals and their applications; Ztransforms and their applications to the
analysis and characterisation of discrete time systems; Random signals and probability, Correlation
functions; Spectral density; Response of linear system to random inputs.
4. Network theory
Network analysis techniques; Network theorems, transient response, steady state sinusoidal response;
Network graphs and their applications in network analysis; Tellegens theorem. Two port networks; Z, Y,
h and transmission parameters. Combination of two ports, analysis of common two ports. Network
functions : parts of network functions, obtaining a network function from a given part. Transmission
criteria : delay and rise time, Elmores and other definitions effect of cascading. Elements of network
synthesis.
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 9
5. Electromagnetic Theory
Analysis of electrostatic and magnetostatic fields; Laplaces and Piossonss equations; Boundary value
problems and their solutions; Maxwells equations; application to wave propagation in bounded and
unbounded media; Transmission lines : basic theory, standing waves, matching applications,
misconstrue lines; Basics of wave guides and resonators; Elements of antenna theory.
6. Electronic Measurements and instrumentation
Basic concepts, standards and error analysis; Measurements of basic electrical quantities and
parameters; Electronic measuring instruments and their principles of working : analog and digital,
comparison, characteristics, application. Transducers; Electronic measurements of non electrical
quantities like temperature, pressure, humidity etc; basics of telemetry for industrial use.
PAPER - II
1. Analog Electronic Circuits
Transistor biasing and stabilization. Small signal analysis. Power amplifiers. Frequency response. Wide
banding techniques. Feedback amplifiers. Tuned amplifiers. Oscillators. Rectifiers and power supplies.
Op Amp PLL, other linear integrated circuits and applications. Pulse shaping circuits and waveform
generators.
2. Digital Electronic Circuits
Transistor as a switching element; Boolean algebra, simplification of Boolean functions, Karnaguh map
and applications; IC Logic gates and their characteristics; IC logic families : DTL, TTL, ECL, NMOS,
PMOS and CMOS gates and their comparison; Combinational logic Circuits; Half adder, Full adder; Digital
comparator; Multiplexer Demultiplexer; ROM and their applications. Flip flops. R-S, J.K, D and T
flipflops; Different types of counters and registers Waveform generators. A/D and D/A converters.
Semiconductor memories.
3. Control Systems
Transient and steady state response of control systems; Effect of feedback on stability and sensitivity;
Root locus techniques; Frequency response analysis. Concepts of gain and phase margins: Constant-M
and Constant-N Nichols Chart; Approximation of transient response from Constant-N Nichols Chart;
Approximation of transient response from closed loop frequency response; Design of Control Systems,
Compensators; Industrial controllers.
4. Communication Systems
Basic information theory; Modulation and detection in analogue and digital systems; Sampling and data
reconstructions; Quantization & coding; Time division and frequency division multiplexing; Equalization;
Optical Communication : in free space & fiber optic; Propagation of signals oat HF, VHF, UHF and
microwave frequency; Satellite Communication.
5. Microwave Engineering
Microwave Tubes and solid state devices, Microwave generation and amplifiers, Waveguides and other
Microwave Components and Circuits, Misconstrue circuits, Microwave Antennas, Microwave
IES Exam Syllabus
Visit Website: www.srieedu.org Page 10
Measurements, Masers, lasers; Microwave propagation. Microwave Communication Systems terrestrial
and Satellite based.
6. Computer Engineering
Number Systems. Data representation; Programming; Elements of a high level programming language
PASCAL/C; Use of basic data structures; Fundamentals of computer architecture; Processor design;
Control unit design; Memory organisation, I/o System Organisation. Microprocessors : Architecture and
instruction set of Microprocessors 8085 and 8086, Assembly language Programming. Microprocessor
Based system design : typical examples. Personal computers and their typical uses.
También podría gustarte
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Alchemical Psychology Uniform Edition o - HillmanDocumento207 páginasAlchemical Psychology Uniform Edition o - HillmanElsy Arana95% (22)
- HazopDocumento4 páginasHazopbaaziz2015Aún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Steel Structures TocDocumento6 páginasDesign of Steel Structures TocSuman Saha0% (1)
- Industrial Training (Tarun Kumar) - Final ReprtDocumento46 páginasIndustrial Training (Tarun Kumar) - Final ReprtSaumya GargAún no hay calificaciones
- IMPORT COMPOSITE SECTION FROM SECTION WIZARDDocumento15 páginasIMPORT COMPOSITE SECTION FROM SECTION WIZARDS Abbas Ahmed0% (1)
- Record of Appropriations and Obligations: TotalDocumento1 páginaRecord of Appropriations and Obligations: TotaljomarAún no hay calificaciones
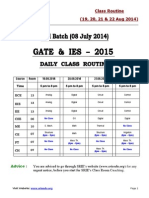
- Class Routine (30 & 31 August 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (30 & 31 August 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- GCNSDocumento10 páginasGCNSSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- PGCNXDocumento5 páginasPGCNXSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- ME Eng Sci Course List 2013Documento8 páginasME Eng Sci Course List 2013Suman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Conditions For Award of Specialisations - Aug13 PDFDocumento8 páginasConditions For Award of Specialisations - Aug13 PDFAshwin SheriefAún no hay calificaciones
- GCENDocumento10 páginasGCENSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- GCNSDocumento10 páginasGCNSSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Routine (12, 13, 14 & 15 Aug 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (12, 13, 14 & 15 Aug 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Faq Sts and SterDocumento7 páginasFaq Sts and SterSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2014-15 Postgraduate Tuition Fees for School of the Built EnvironmentDocumento6 páginas2014-15 Postgraduate Tuition Fees for School of the Built EnvironmentSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Qut EN50 27746 Dom Cms UnitDocumento3 páginasQut EN50 27746 Dom Cms UnitSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Revit Structure 2012 FundamentalsDocumento11 páginasRevit Structure 2012 FundamentalsSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Routine (16 & 17 August 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (16 & 17 August 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- SRIE Class Routine August 2014Documento1 páginaSRIE Class Routine August 2014Suman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Routine (02 & 03 August 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (02 & 03 August 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sefindia OrgDocumento47 páginasSefindia OrgSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
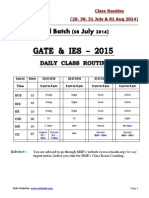
- Class Routine (02 & 03 August 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (02 & 03 August 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Publications Order Form TEMPLATEDocumento1 páginaPublications Order Form TEMPLATESuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Layout DrawingDocumento18 páginasLayout DrawingSandesh Kumar100% (1)
- T E D CAD: Eaching Ngineering Rawing ThroughDocumento5 páginasT E D CAD: Eaching Ngineering Rawing ThroughkamalaireshAún no hay calificaciones
- Entu140514 01Documento3 páginasEntu140514 01Suman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1499 Bridge NReqDocumento12 páginas1499 Bridge NReqSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Routine (29, 30, 31 July & 01 Aug 2014) : AdviceDocumento1 páginaClass Routine (29, 30, 31 July & 01 Aug 2014) : AdviceSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Order FormDocumento1 páginaOrder FormSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Application For A Student VisaDocumento27 páginasApplication For A Student VisaSuman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics of Structural Steel Work DetailingDocumento5 páginasEconomics of Structural Steel Work Detailingthomas kilian100% (2)
- LAB 1: Steps For Analysis & Design of Beam in SAP2000Documento16 páginasLAB 1: Steps For Analysis & Design of Beam in SAP2000Suman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Civ1501 Engineering Statics Semester 2, 2002: Solution To Assignment 2Documento2 páginasCiv1501 Engineering Statics Semester 2, 2002: Solution To Assignment 2Suman SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lali The Sun Also Rises Final PaperDocumento4 páginasLali The Sun Also Rises Final PaperDaniel AdamsAún no hay calificaciones
- Rebecca A. Endaya Beed-Iii Art Education: ExploreDocumento5 páginasRebecca A. Endaya Beed-Iii Art Education: ExploreBhecca Endaya0% (1)
- Understanding the Difference Between Positive and Normative EconomicsDocumento21 páginasUnderstanding the Difference Between Positive and Normative EconomicsKevin Fernandez MendioroAún no hay calificaciones
- Sidney W A Dekker From Threat and Error Management To ResilienceDocumento11 páginasSidney W A Dekker From Threat and Error Management To ResilienceDaniel fabian Sánchez henaoAún no hay calificaciones
- DP4XXX PricesDocumento78 páginasDP4XXX PricesWassim KaissouniAún no hay calificaciones
- Urea CycleDocumento2 páginasUrea CycleyoungdandareAún no hay calificaciones
- General Organic and Biological Chemistry 6th Edition Stoker Test BankDocumento12 páginasGeneral Organic and Biological Chemistry 6th Edition Stoker Test BankJenniferCookabdqk100% (14)
- Kiribati, Gilbertese BibleDocumento973 páginasKiribati, Gilbertese BibleAsia BiblesAún no hay calificaciones
- Main Unit (M8 Connector Type) : FS-N41CDocumento2 páginasMain Unit (M8 Connector Type) : FS-N41CJulian Gabriel PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Essay #01 (First Draft)Documento2 páginasEssay #01 (First Draft)thanhtam3819Aún no hay calificaciones
- IT Department - JdsDocumento2 páginasIT Department - JdsShahid NadeemAún no hay calificaciones
- Red Lion MP Sensor Product Manual PDFDocumento2 páginasRed Lion MP Sensor Product Manual PDFJigneshAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutritional Deficiency Disorder Edit OneDocumento23 páginasNutritional Deficiency Disorder Edit One01 HifzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Best Practice Guidelines For Cardiac Rehabilitation and Secondary Prevention: A SynopsisDocumento16 páginasBest Practice Guidelines For Cardiac Rehabilitation and Secondary Prevention: A SynopsisErdy VincentAún no hay calificaciones
- MR - Abhishek JiDocumento4 páginasMR - Abhishek Jimalikgaurav01Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 7Documento22 páginasChapter 7one loveAún no hay calificaciones
- Dada and Buddhist Thought - Sung-Won Ko PDFDocumento24 páginasDada and Buddhist Thought - Sung-Won Ko PDFJuan Manuel Gomez GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- HB Im70 QRDocumento1 páginaHB Im70 QROsamaAún no hay calificaciones
- (Homebrew) ShamanDocumento15 páginas(Homebrew) ShamanVictor Wanderley CorrêaAún no hay calificaciones
- Batangas State University - Testing and Admission OfficeDocumento2 páginasBatangas State University - Testing and Admission OfficeDolly Manalo100% (1)
- Vision CSP22 Abhyaas Test 3SDocumento44 páginasVision CSP22 Abhyaas Test 3SManasa DevarakondaAún no hay calificaciones
- Symbolic Calculus Sage ReferenceDocumento25 páginasSymbolic Calculus Sage ReferenceLn Amitav BiswasAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjectives For A Businessman 2023Documento2 páginasAdjectives For A Businessman 2023elyvuujavierAún no hay calificaciones
- Lect 5Documento8 páginasLect 5LuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Communication Thesis PDFDocumento2 páginasCommunication Thesis PDFBarbara0% (2)
- NRBC-Internship Report - ShafayetDocumento54 páginasNRBC-Internship Report - ShafayetShafayet JamilAún no hay calificaciones