Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
The Actuators For The Reentry of Soyuz
Cargado por
Junior Miranda0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
40 vistas7 páginasSoyuz is divided into three compartments, and only the compartment Descent (SA) is able to return to Earth. The propulsion system of the vessel is installed on the compartment Instruments Board (PAO) it consists of two redundant channels and can be divided into three functional units. The advantage of using a monopropellant is the gain in terms of weight and size.
Descripción original:
Título original
The Actuators for the Reentry of Soyuz
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoSoyuz is divided into three compartments, and only the compartment Descent (SA) is able to return to Earth. The propulsion system of the vessel is installed on the compartment Instruments Board (PAO) it consists of two redundant channels and can be divided into three functional units. The advantage of using a monopropellant is the gain in terms of weight and size.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
40 vistas7 páginasThe Actuators For The Reentry of Soyuz
Cargado por
Junior MirandaSoyuz is divided into three compartments, and only the compartment Descent (SA) is able to return to Earth. The propulsion system of the vessel is installed on the compartment Instruments Board (PAO) it consists of two redundant channels and can be divided into three functional units. The advantage of using a monopropellant is the gain in terms of weight and size.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 7
1
The actuators for the reentry of Soyuz
The Soyuz is divided into three compartments, and only the compartment Descent (SA) is able to return to
Earth. However, the heavy and bulky propulsion system of the vessel is installed on the compartment
Instruments Board (PAO).
When the SA is separated, it must nevertheless continue to move in space, in order to tackle the upper
layers of the atmosphere with an appropriate angle. It was therefore with a small propulsion system,
rudimentary, that just gives him enough maneuverability to achieve this goal.
1. General
Autonomous Guidance Fund Descent is provided by the System Actuators Descent, OBS (
). It consists of two redundant channels and can be divided into three
functional units:
- Under-pressurization system,
- The storage subsystem peroxide,
- Micromotors reaction URMD.
Eight micromotors URMD and four isolation valves (KO) are distributed throughout the compartment
Descent (SA). Otherwise, all elements of the OBS are grouped in the "all hydropneumatic" PGA
(), located behind a flap at the bottom of SA.
Fig. 1.1:
Scheme of
the
location of
the
hydropneu
matic
together.
OBS works
with a
monopropellant, ie a propellant which plays both the role of fuel and oxidizer. Here, it is the hydrogen
peroxide which has been selected.
The advantage of using a monopropellant is the gain in terms of weight and size, which are obviously very
limiting factor when you know the size of a SA. However, such a mode of propulsion provides a specific
impulse (Isp) relatively low.
2 technique. Description
The pressurization subsystem
On each of the two channels, it consists of a nitrogen tank (BA) at a pressure between 270 bars and 350
bars. BA are equipped with a pressure sensor (DBN) whose value is broadcast on the dashboard of the
vessel.
Fig. 2.1: Schematic of OBS.
Credit: Soyuz Crew Ops Manual.
Downstream of BA is installed a purge valve (KPA) and an expander (RA) that can pressurize the reservoir
2
of hydrogen peroxide does not exceed its operation limit. Level
regulators, both channels are set equal pressure through a valve
called KPA3.
Then, a check valve (KOA) gives access to the peroxide tank, the
pressure of which is measured by the pressure gauge DPR (sent on
the dashboard value).
If the tank pressure rises too high, valve protection KPRA allows to
relax. Its operating pressure is between 15 and 18 bars.
The storage subsystem peroxide
Each channel comprises a reservoir (BP) between 29.6 kg and
containing 31.4 kg of hydrogen peroxide at a pressure of between
1.5 bars and 4.5 bars. Downstream of reservoirs, two valves in
parallel (KPP) lead to the collector micromotors. Valves (KPRP)
allow to release the
pressure in the tanks
when required, and other
(KSP) allow purge tanks
end mission.
Downstream of the
collector, four valves (KO) isolate the four groups of micromotors.
Fig. 2.2: A PGA. The two yellow spheres are nitrogen tanks.
The two cylinders are black tanks peroxide.
Micromotors
The OBS comprises eight URMD micromotors ( ) used to
eject water and the oxygen formed by the disproportionation of peroxide.
The first version of the Soyuz (11F615), there were two engines for pitch (T1 and T2), two lace (R1 and
R2), with a thrust of 7.5 kgf, and two others to roll (K1 and K2), with a push of 15kgf. From the second
generation Soyuz, Soyuz T (11F732), two additional engines have been added to the roll redundancy (K1D
and K2D).
Fig. 2.3: A URMD micromotor exposed to the Historical Museum of the city of Korolev.
.
Each engine comprises an electrohydraulic valve control UEGK ( ),
a catalytic reactor and a nozzle. When UEGK valves open on command of the control system, the nitrogen
pressure causes the hydrogen peroxide in the catalytic reactor of the micromotor, and under the action of a
3
catalyst occurs the following redox reaction : 2 H
2
O
2
-> 2H
2
O + O
2
This reaction, called disproportionation, is exothermic. Water and oxygen are ejected by the nozzle, thus
creating a thrust generating a moment about the center of gravity of the vessel.
Fig. 2.4: Location of micromotors on the Fund Descent.
Credit: Soyuz Crew Ops Manual.
Even without the presence of the catalyst,
disproportionation takes place naturally in the hydrogen
peroxide, albeit much more slowly. It is estimated that after
195 days after filling the tanks BP1 and BP2, too much
peroxide is disproportionated order to ensure the return to
Earth safely. This is the criterion that determines the lifetime
of a Soyuz spacecraft.
3. Sequence of Operation
Throughout the duration of the mission of a Soyuz spacecraft, the OBS system is not used. Fourteen
seconds before the separation of the three compartments of the vessel, the pyrotechnic cartridges are
actuated, opening the various valves which put the two pressure channels (KPA1, 2.3, KPP, KO). The
pressurized nitrogen is released as well, pushing the peroxide into micromotors. UEGK valves thereof are
opened on demand of the control system to steer the vessel in the desired position. Since the beginning of
the reentry until the opening of the parachute, the SUS system is in control, then it passes the baton to the
KSP system.
Fig. 3.1: A nitrogen tank (BA) OBS.
Korolyov History Museum. .
At the time of release of the heat shield, it considers that it is necessary to steer the ship, and the OBS is no
longer useful. In contrast, hydrogen peroxide it contains is a danger to astronauts and for recovery teams .
The dump signal therefore constitutes a thermal shield order UEGK forced valve opening, which has the
effect of completely emptying the tanks peroxide.
4
4. History
The test release of November 3, 1966
While Soyuz had not yet made its first flight, a drop test ended in failure. The Fund Descent is indeed fell in
free fall after one of the lines of his parachute has been weakened by hydrogen peroxide in its venting. The
accident in December 1966 The December 14, 1966 , during the preparation of the second test flight of the
Soyuz, an incident occurs on the launcher leading to a postponement. Teams work directly on the launcher,
and turn eject (SAS) turns unexpectedly into service. It causes inflammation of hydrogen peroxide SIOS,
which triggers the full explosion of the launcher. Three people died in the accident.
Soyuz-1
When the first manned flight program, Soyuz-1 , which led to the death of cosmonaut Vladimir KOMAROV ,
the heat shield was not dropped and consequently the order of emptying BP1 and BP2 tanks did not been
sent. When the Fund Downhill impacted soil, hydrogen peroxide not only burned, but the release of oxygen
was being consumed all remnants of the vessel. Sergei Anokhin, team member of Korolev and former test
pilot, was among the first to visit the scene of the crash. He said afterwards: "I can not even tell you how
many aircraft in flames I saw during the war, but it was no comparison with what I saw here. Hydrogen
peroxide is much more horrible than kerosene. "
Soyuz T version
The first generation vessels (11F615), the OBS included only six micromotors URMD. From the Soyuz T
(11F732) version engines and rolling redundant K1D K2D were added, and the block housing the engine
pitch T1 and T2 has been changed.
Fig. 4.1: The K2 engine Soyuz-27 (left), and the pair K2/K2D Soyuz TM-14 (right).
/ DR.
Fig. 4.2: The pair micromotor T1/T2
Soyuz-27 (left) and Soyuz TM-14 (right).
5
/ DR.
Vessels for the International Space Station
Vessels bound for the new orbital station receive two changes, always with the aim of further reducing the
rate of disproportionation of peroxide. First, an additive is added to the hydrogen peroxide. Then, in tanks,
separators which separate the liquid phase from the gas phase are changed: the varnish is abandoned and
replaced by a Teflon derivative (Fluorplast-10). The Soyuz TM-31 is the first to benefit from these
improvements. The Soyuz TMA Version: ASEO the system
In the first half of 1999, section 27 of the RKK Energia launch studies on a thermoelectric cooling system
called ASEO ( ).
The purpose is again to increase the lifetime of the temperature profile in Soyuz peroxide around 3 C ( 3
C), limiting the dismutation of hydrogen peroxide. In addition, the tank insulation is improved through the
use of a new material, PET-011. The decision to locate the ASEO on Soyuz TMA is taken September 14,
2000. This project is complex because it is necessary to modify the structure of the Fund and the Descent
Control System vessel (SUBK) so that it feeds the new system.
Fig. 4.3: The PGA of Soyuz TMA-5.
Credit: RKK Energia.
In early 2002, studies have been completed and
the test phase ground in society Impoulss can
begin. When the tests are completed, the RKK
Energia up the ASEO in a vacuum chamber that
simulates the space environment. The test
begins June 4, 2002 and lasted 585 days, until
January 2004.
The ASEO made his first flight on Soyuz TMA-5 .
Ironically, an incident occurred with the PGA in the preparation of this vessel. The pressure gradient in the
test vacuum chamber has not been respected, which led to the perforation of the separator Teflon. All the
PGA had to be replaced by one that was scheduled for Soyuz TMA-6 . However, ASEO behaves nominally
throughout the mission.
Another incident is noteworthy: in early 2012, during a pressure test in vacuum chamber Soyuz TMA-04M ,
a procedural error causes an excessive increase in pressure in the compartment Descent. Therefore,
cracks appear at the four connectors in the location of the PGA (clearly visible in Figure 14). This is the
ship that must be replaced.
Photos 5.
Fig. 5.1: View of Soyuz TM-19 and summary elements
of OBS.
Credit: Speyer Technik Museum.
6
Fig. 5.2: The micromotor R1 Soyuz-27.
.
Fig. 5.3: The Soyuz TM-31 with its PGA.
Credit: RKK Energia.
Fig. 5.4: Technicians working on the PGA Energia Soyuz TMA-5.
Credit: RKK Energia.
Fig. 5.5: The location for the PGA of Soyuz TMA-11.
Credit: Buran.ru.
7
Fig. 5.6: A PGA subsidiary of Orevo MGTU Baoumann.
También podría gustarte
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- NASA Astronauts On Soyuz Experience and Lessons For The FutureDocumento42 páginasNASA Astronauts On Soyuz Experience and Lessons For The FutureBob AndrepontAún no hay calificaciones
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- SHENZHOU - Shroud ConfigurationDocumento1 páginaSHENZHOU - Shroud ConfigurationJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Shenzhou 2Documento1 páginaShenzhou 2Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Shenzhou 4Documento1 páginaShenzhou 4Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- Shenzhou 3Documento1 páginaShenzhou 3Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Vs-40 Sounding RocketDocumento5 páginasVs-40 Sounding RocketJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Spaceflight101 Com Spacerockets Long March 7Documento30 páginasSpaceflight101 Com Spacerockets Long March 7Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
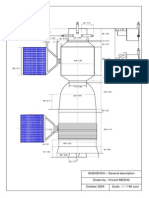
- SHENZHOU - General DescriptionDocumento1 páginaSHENZHOU - General DescriptionJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Ballistic Missiles and Missile Defense in AsiaDocumento84 páginasBallistic Missiles and Missile Defense in AsiaJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Turbo 2Documento1 páginaTurbo 2Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ambitious Goal of Sergei KorolevDocumento5 páginasAmbitious Goal of Sergei KorolevJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- A Better Focus On ShenzhouDocumento4 páginasA Better Focus On ShenzhouJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Expedition 14 Press KitDocumento118 páginasExpedition 14 Press KitUhrin ImreAún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- 2.8isometric ViewDocumento9 páginas2.8isometric ViewSiva KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Shenzhou - SinoDefenceDocumento10 páginasShenzhou - SinoDefenceJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- 9 Isometric DrawingsDocumento6 páginas9 Isometric DrawingsSiva KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- "Kurs" Radio Engineering SystemDocumento2 páginas"Kurs" Radio Engineering SystemJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Energia Blok YaDocumento5 páginasEnergia Blok YaJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- F-1 EngineDocumento11 páginasF-1 EnginentschkeAún no hay calificaciones
- ColunaDocumento1 páginaColunaJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Energia Blok YaDocumento5 páginasEnergia Blok YaJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Buran 2Documento4 páginasBuran 2Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- SaluytbakDocumento1 páginaSaluytbakJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cool Infographics Explain 8 Key Events On Orion's EFT-1 Test FlightDocumento6 páginasCool Infographics Explain 8 Key Events On Orion's EFT-1 Test FlightJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Angara A5Documento16 páginasAngara A5Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Solar ProbesDocumento27 páginasSolar ProbesJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cool Infographics Explain 8 Key Events On OrionDocumento6 páginasCool Infographics Explain 8 Key Events On OrionJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- All International Space Station Missions: Spacecraft Launch Landing/ Deorbit Mission Mission Crew 1998Documento10 páginasAll International Space Station Missions: Spacecraft Launch Landing/ Deorbit Mission Mission Crew 1998Junior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Delta IV Launch Services UserDocumento1 páginaDelta IV Launch Services UserJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Shenzhou - SinoDefenceDocumento10 páginasShenzhou - SinoDefenceJunior MirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Che 402: Analytical ChemistryDocumento12 páginasChe 402: Analytical ChemistryKrizzete HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- FIRST QUARTER-3rd Summative TestDocumento4 páginasFIRST QUARTER-3rd Summative TestLordy Picar100% (2)
- 2019 Second Semester Semi-Annual ReportDocumento48 páginas2019 Second Semester Semi-Annual ReportEdsel Alfred OtaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sports Aerodynamics - One Credit CourseDocumento12 páginasSports Aerodynamics - One Credit CourserajkalamaeroAún no hay calificaciones
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2102)
- Chap02 PDFDocumento32 páginasChap02 PDFAzalia Delgado VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- 新托福百日百句百篇(第一册)Documento274 páginas新托福百日百句百篇(第一册)张子楚Aún no hay calificaciones
- Estimations in Numbers and Measurement: Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocumento5 páginasEstimations in Numbers and Measurement: Multiple-Choice QuestionsJason Lam LamAún no hay calificaciones
- Mobile Phones and RadiationDocumento6 páginasMobile Phones and RadiationGehanShabanAún no hay calificaciones
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- 2.4 Electrical DrawingDocumento141 páginas2.4 Electrical DrawingFurqoni Bulan RizkiAún no hay calificaciones
- Cidam - Organization and ManagementDocumento7 páginasCidam - Organization and ManagementMarklester GrimaldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Attitudes and Job SatisfactionDocumento22 páginasAttitudes and Job Satisfactionchaudhary ahmadAún no hay calificaciones
- CPE 2 2 Time Scaled Event Network Exercises MacalinaoDocumento6 páginasCPE 2 2 Time Scaled Event Network Exercises MacalinaoJoshua Macalinao100% (1)
- Dynamics of Structures 4th Edition Chopra Solutions ManualDocumento38 páginasDynamics of Structures 4th Edition Chopra Solutions Manualseanmosstgdkf2100% (14)
- 2223 S3 Longman Edge U4 SuppWSDocumento9 páginas2223 S3 Longman Edge U4 SuppWShexu wangAún no hay calificaciones
- Industrial Accidents in Cement Industries of Nepal: Submitted ToDocumento58 páginasIndustrial Accidents in Cement Industries of Nepal: Submitted ToSushma Karn100% (1)
- Civil Engineering Laws and Ethics in The PhilippinesDocumento16 páginasCivil Engineering Laws and Ethics in The PhilippinesMonde Nuylan90% (48)
- NDT Question and AnswerDocumento11 páginasNDT Question and AnswerNina Aziz100% (1)
- Theories On Human DevelopmentDocumento42 páginasTheories On Human DevelopmentHANS CHRISTIAN DELOS REYESAún no hay calificaciones
- Nygård 2019Documento9 páginasNygård 2019Wágner B SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- RM PrelimDocumento14 páginasRM PrelimJazper InocAún no hay calificaciones
- Astm A247 06Documento1 páginaAstm A247 06juancarlosdominguezlopez49Aún no hay calificaciones
- I. Desired Learning Outcomes: Laboratory Activity 9 Test For ProteinsDocumento3 páginasI. Desired Learning Outcomes: Laboratory Activity 9 Test For ProteinsErika Joille PatayonAún no hay calificaciones
- Efficacy of Ayurvedic Interventions in Hypothyroidism: A Comprehensive ReviewDocumento7 páginasEfficacy of Ayurvedic Interventions in Hypothyroidism: A Comprehensive ReviewMikel MillerAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture ST1201Documento34 páginasLecture ST1201SheinzenAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento10 páginasUntitled조준영Aún no hay calificaciones
- Liquefaction Potential Based On Swedish Weight Sounding Test in Langaleso Village Sigy RegencyDocumento8 páginasLiquefaction Potential Based On Swedish Weight Sounding Test in Langaleso Village Sigy RegencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAún no hay calificaciones
- Megger MIT515 s.n101405643Documento3 páginasMegger MIT515 s.n101405643Magicneering PredictAún no hay calificaciones
- Thomann REACh GuideDocumento6 páginasThomann REACh GuidePuro BrassAún no hay calificaciones
- The Role of Underground Hydrogen Storage in Europe 1706118289Documento47 páginasThe Role of Underground Hydrogen Storage in Europe 1706118289guillermo peralesAún no hay calificaciones
- 0 BibliografíaDocumento3 páginas0 BibliografíaDaniel Espinosa RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Aerodynamics for Engineering StudentsDe EverandAerodynamics for Engineering StudentsCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (5)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideDe Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (7)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedDe EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionDe EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (10)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseDe EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (51)
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CDe EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CAún no hay calificaciones