Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Difference Between Dye & Pigment
Cargado por
Mehmood AhmedDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Difference Between Dye & Pigment
Cargado por
Mehmood AhmedCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
dyes-pigment s.st andardcon.com http://dyes-pigments.standardcon.com/difference-pigments-dyes.
html
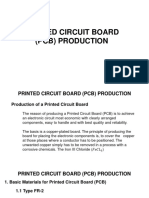
Difference Between Pigments and Dyes,Dyes and Pigments
Information,Dyes and Pigments Differences
What is Dye Dyes and Pigments Information
Both dyes and pigments are powerf ul colourants. The Basic dif f erence between them is that dyes get
dissolve in the substrate, while pigments tend to leave residues.
The major dif f erences between the Dyes and Pigments are highlighted below
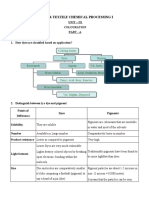
Points of
Difference
Dyes Pigments
Solubility They are soluble Pigments are colourants that
are insoluble in water and
most of the solvents
Number Available in Large number Comparatively lesser in
number
Product
resistance
Lower as compared to pigments Very high
Lightf astness Lower Dyes are very much vulnerable. Lights destroy
colored objects by breaking open electronic bonding
within the molecule
Traditionally pigments have
been f ound to be more
lightf ast than dyes
Size Dye molecules are comparatively smaller it's like
comparing a f ootball (pigment) to say a head of a
pin (dye)
Pigment particles are about
1-2 microns in size. (1 micron
=1/1000 meter). It means that
the particles can be seen
under a magnif ying glass
Bonding Taking the example of dyeing a wood surf ace, the
dye and the substrate (wood) that is dyed are
chemicals, that have certain f eatures called
f unctional groups. At the level of molecules these
groups serve as open pockets of electrostatic
charges (+ or -). The f unctional group in dyes, serve
as a method f or attaching the dye to the wood
For example taking the
example of a wood surf ace
Pigment requires the help of
a binder f or gluing. As it is an
inert substance which is
merely suspended in a
carrier/binder
Structure
during the
application
process
During application process there is a temporary
alteration in the structure of the dyes
During application, pigments
have the capacity to retain
particulate or crystalline
structure
Imparting of
Colours
Dyes can only impart colour by selective absorption
of the dyes
Pigments impart colours by
either scattering of light or by
selective absorption
Combustible
properties
Taking the example of a Candle making process, if
the candles are dyed it is easily combustible and can
be applied throughout the candle
In the example of a candle
making as pigments are
colored particles, they tend
to clog a wick when burned.
This makes them undesirable
f or a candle if it is colored
throughout and used f or
burning
Chemical
Composition
Usually the dyes are organic (i.e. carbon-based)
compounds
While pigments are normally
inorganic compounds, of ten
involving heavy toxic metals
Longevity
f actor
The dye based printing inks do not last as long as
the pigment inks
In case of ink based printing
prints made with pigments
lasts longer
Printing on
substrates
Compatible with almost all the substrates that
needs to be dyed
Owing to the physical makeup
of the pigment inks the range
f or suitable substrates are
limited
Colour gamut Taking the case of printing inks, dye based inks
of f ers a wide variety
As compared to dye-based
inks, pigment inksets
somewhat lags behind, on
the same paper stock
También podría gustarte
- Bullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsDe EverandBullies, Socialites and the Shy Ones: Exploring the Personalities of Watercolor PaintsAún no hay calificaciones
- Color MeasurementDocumento2 páginasColor Measurementmanox007Aún no hay calificaciones
- CORM 2011 Calculation of CCT and Duv and Practical Conversion FormulaeDocumento28 páginasCORM 2011 Calculation of CCT and Duv and Practical Conversion FormulaeAnonymous D0fu6XjKLAún no hay calificaciones
- Upload Mach Zehnder Interferometer and Its Temperature Based ApplicationsDocumento31 páginasUpload Mach Zehnder Interferometer and Its Temperature Based ApplicationsMridul ChakrabortyAún no hay calificaciones
- Feryforgues Are Fluorescence Quantum Yields So Tricky To Measure PDFDocumento5 páginasFeryforgues Are Fluorescence Quantum Yields So Tricky To Measure PDFNadia WilsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrostatic Equilibrium Centrifugal Field - Liquid HeightDocumento1 páginaHydrostatic Equilibrium Centrifugal Field - Liquid HeightLinda Fahlberg-Stojanovska100% (2)
- Designing For Board Level EMC AN2321Documento36 páginasDesigning For Board Level EMC AN2321Dodge WorthingtonAún no hay calificaciones
- Building ComputerDocumento24 páginasBuilding ComputerSaroswat RoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Sustainable Lighting Design With ZEMAX PDFDocumento22 páginasSustainable Lighting Design With ZEMAX PDFMujeeb Ur RahmanAún no hay calificaciones
- PCB Training PresentationDocumento31 páginasPCB Training Presentationkibrom atsbhaAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 Functional ProgrammingDocumento37 páginas04 Functional ProgrammingPaksmilerAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2Documento86 páginasChapter 2Habete ItfAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparison of Color Difference Methodes For Multi-Angle Application Konrad Lex BYK-GardnerDocumento24 páginasComparison of Color Difference Methodes For Multi-Angle Application Konrad Lex BYK-GardnerDinorahAún no hay calificaciones
- Clin. Chem. Assignment - SpectrophotometerDocumento3 páginasClin. Chem. Assignment - SpectrophotometerMartin ClydeAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Instructions: How To Create Professional PDF Files For Pre-PressDocumento21 páginasPDF Instructions: How To Create Professional PDF Files For Pre-Pressapple1374Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sprocess - Fps Fin LerDocumento12 páginasSprocess - Fps Fin LerArvindGovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mixture Designs: Simplex Lattice Simplex CentroidDocumento31 páginasMixture Designs: Simplex Lattice Simplex CentroidFakhri MuhammadAún no hay calificaciones
- Reverberation AlgorithmsDocumento123 páginasReverberation AlgorithmsFederico ScalasAún no hay calificaciones
- QLEDDocumento19 páginasQLEDrudrik joshiAún no hay calificaciones
- RnaiDocumento45 páginasRnaiRam Nivas Ahirwar100% (2)
- Color ChemistryDocumento15 páginasColor ChemistryZeeshan AhmadAún no hay calificaciones
- Difference Between SolventsDocumento3 páginasDifference Between SolventsBoonyarit LurdgrienggraiyingAún no hay calificaciones
- 07-073 Colorants FinalDocumento5 páginas07-073 Colorants Finalex_infinity0% (1)
- TPC - 1 TWO MARKS QUESTION WITH ANswer For Unit III DYEING NEWDocumento11 páginasTPC - 1 TWO MARKS QUESTION WITH ANswer For Unit III DYEING NEWJana MuthuAún no hay calificaciones
- Prussian Blue PigmentDocumento6 páginasPrussian Blue Pigmentsuleman205100% (1)
- Surface-Coating Industries (2022)Documento48 páginasSurface-Coating Industries (2022)sandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Dyes & Pigments: Van Der Waal's Forces Hydrogen Bonds Ionic BondsDocumento4 páginasDyes & Pigments: Van Der Waal's Forces Hydrogen Bonds Ionic BondsDr. Sadaf khanAún no hay calificaciones
- Aarav Vidhawan 12 S1 Chemistry ProjectDocumento31 páginasAarav Vidhawan 12 S1 Chemistry ProjectJaskaran SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Basics of Coloring Wood, TheDocumento4 páginasBasics of Coloring Wood, TheAdam BeaudoinAún no hay calificaciones
- PigmentsDocumento6 páginasPigmentsrashed141_tx100% (1)
- Difference Between Dyes and PigmentsDocumento5 páginasDifference Between Dyes and PigmentsHameedullah AnsariAún no hay calificaciones
- Color AffectsDocumento4 páginasColor Affectshyde2520015754Aún no hay calificaciones
- Is Carbon Black Pigment Organic or InorganicDocumento3 páginasIs Carbon Black Pigment Organic or Inorganicwiwat dussadinAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Organic Pigments RevisioDocumento97 páginasIntroduction To Organic Pigments RevisioDr. Sadaf khanAún no hay calificaciones
- Dyes and Its CharacteristicsDocumento12 páginasDyes and Its Characteristicsabhijeet080808Aún no hay calificaciones
- Project Report On Pigment Colour For PlasticsDocumento14 páginasProject Report On Pigment Colour For PlasticsEIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is A DyeDocumento2 páginasWhat Is A DyeRashid Ul HasanAún no hay calificaciones
- 1516193591FSC P8 M9 E-TextDocumento8 páginas1516193591FSC P8 M9 E-Textshafana_mduAún no hay calificaciones
- Dyes FinalDocumento17 páginasDyes FinalIshika BansalAún no hay calificaciones
- Gpt. Solve of Chemistry of Dyes and PigmentDocumento9 páginasGpt. Solve of Chemistry of Dyes and PigmentRaju HossainAún no hay calificaciones
- BTech Sem-III Unit-8-Colours and DyesDocumento40 páginasBTech Sem-III Unit-8-Colours and Dyesvirendra parmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Pigment and EkstenderDocumento11 páginasPigment and EkstenderRASentani Pati Sagala086Aún no hay calificaciones
- Week 1 Introduction of Dyeing MRDocumento4 páginasWeek 1 Introduction of Dyeing MRRR TAún no hay calificaciones
- DPF 10 PDFDocumento26 páginasDPF 10 PDFMd. Sabbir Sabbir HossainAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Introduction To DyeingDocumento4 páginas1 Introduction To DyeingSudipto DuttaAún no hay calificaciones
- Paint PigmentsDocumento11 páginasPaint PigmentsJuganta280100% (2)
- PigmentsDocumento18 páginasPigmentsClassic Adda100% (1)
- Textile PigmentsDocumento3 páginasTextile PigmentsTariqul IslamAún no hay calificaciones
- Cbse Chem ProjectDocumento26 páginasCbse Chem Projectann cherianAún no hay calificaciones
- To Prepare Pigments andDocumento7 páginasTo Prepare Pigments andSaji KuruvillaAún no hay calificaciones
- PigmentsDocumento7 páginasPigmentsAbdul MujeebAún no hay calificaciones
- Paints and Pigments PDFDocumento33 páginasPaints and Pigments PDFASWIN KUMAR100% (1)
- ColourDocumento21 páginasColourSreedevi KrishnakumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Synthetic Dye: SubstrateDocumento5 páginasSynthetic Dye: SubstrateRudra Prasad RoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Concept of ColorDocumento15 páginasBasic Concept of ColorMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Investigatory Project Class 12Documento35 páginasChemistry Investigatory Project Class 12SomAún no hay calificaciones
- Textile Dyeing LectureDocumento28 páginasTextile Dyeing LectureMuhammad Zohaib100% (1)
- DyesDocumento45 páginasDyesELSA ELDHOSEAún no hay calificaciones
- Current DYEINGDocumento38 páginasCurrent DYEINGTitilade AdewaleAún no hay calificaciones
- Pigment Vs DyeDocumento3 páginasPigment Vs DyeBoonyarit LurdgrienggraiyingAún no hay calificaciones
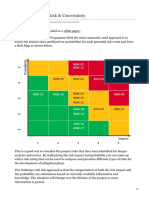
- Mapping Project Risk Amp UncertaintyDocumento5 páginasMapping Project Risk Amp UncertaintyMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec / PH Guide: Fruit Conduct MS/CM PH FactorDocumento2 páginasEc / PH Guide: Fruit Conduct MS/CM PH FactorMehmood Ahmed100% (1)
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocumento17 páginasWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Full Factorial DOE With MinitabDocumento11 páginasFull Factorial DOE With MinitabMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- .Au-Nominal EC and PH Values For Hydroponic CropsDocumento2 páginas.Au-Nominal EC and PH Values For Hydroponic CropsMehmood Ahmed100% (1)
- Data Catalogue Wheel Bolts / Nuts Fastener SpecificationsDocumento8 páginasData Catalogue Wheel Bolts / Nuts Fastener SpecificationsMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Peak Performance Buoyancy: PADI SayDocumento1 páginaPeak Performance Buoyancy: PADI SayMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Arduino Task ListDocumento3 páginasArduino Task ListMehmood Ahmed0% (1)
- The Hygge Manifesto: 5. Gratitude 6. HarmonyDocumento1 páginaThe Hygge Manifesto: 5. Gratitude 6. HarmonyMehmood Ahmed100% (2)
- The Prison of ResentmentDocumento2 páginasThe Prison of ResentmentMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Amazon - de - Online Return Center PDFDocumento2 páginasAmazon - de - Online Return Center PDFMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Our Pump CurveDocumento2 páginasOur Pump CurveMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- What Are Proteins?: VegetariansDocumento2 páginasWhat Are Proteins?: VegetariansMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Schedule Jan 2017Documento2 páginasSchedule Jan 2017Mehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Tensile Test: Materials Science and TestingDocumento9 páginasTensile Test: Materials Science and TestingMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Memtrex HFE-T: Pleated Filters With PTFE MembraneDocumento2 páginasMemtrex HFE-T: Pleated Filters With PTFE MembraneMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Ijert Ijert: University, Kherva, MehsanaDocumento11 páginasIjert Ijert: University, Kherva, MehsanaMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Destino SDocumento12 páginasDestino SMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Air DyeingDocumento3 páginasAir DyeingMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Direct High Intrinsic ViscosityDocumento8 páginasDirect High Intrinsic ViscosityMehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Halal Hysteria: and Fury, Signifying Nothing"Documento6 páginasHalal Hysteria: and Fury, Signifying Nothing"Mehmood AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Effects of Salt On Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Different Types of Reactive DyesDocumento6 páginasEffects of Salt On Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Different Types of Reactive Dyesahmed samirAún no hay calificaciones
- Agrocer BrochureDocumento24 páginasAgrocer BrochuresharemwAún no hay calificaciones
- ResearchDocumento3 páginasResearchDev Jovanovic33% (3)
- Washing Principle Denim DystarDocumento80 páginasWashing Principle Denim DystarLieven Verraest100% (4)
- Disperse DyesDocumento8 páginasDisperse Dyessyed asim najamAún no hay calificaciones
- Yarn Manufacturing McqsDocumento19 páginasYarn Manufacturing Mcqssandip kumar mishraAún no hay calificaciones
- Identification&Class DyesDocumento38 páginasIdentification&Class DyesAmit SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Selection and Types of Dyes: Dyeing An IntroductionDocumento8 páginasSelection and Types of Dyes: Dyeing An IntroductionrajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Histopathology Review BookletDocumento21 páginasHistopathology Review BookletMarie Llanes100% (1)
- Potentiostatic Studies On Indirect Electrochemical Reduction of Vat DyesDocumento8 páginasPotentiostatic Studies On Indirect Electrochemical Reduction of Vat DyesKarrar HaiderAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Introduction To BleachingDocumento13 páginas1 - Introduction To BleachingAnurag VermaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bacterial Decolorization and Degradation of Azo DyesDocumento12 páginasBacterial Decolorization and Degradation of Azo DyesFernanda Stuani PereiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Sub: Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II: Topic: Diagnostic AgentsDocumento20 páginasSub: Pharmaceutical Chemistry-II: Topic: Diagnostic AgentsRam PrajapatAún no hay calificaciones
- Importance of QualityDocumento14 páginasImportance of QualityKay ShailajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Textile Bro Text MatterDocumento16 páginasTextile Bro Text MatterVidiaMumtazAlamryAún no hay calificaciones
- Acid DyeDocumento3 páginasAcid DyeMD. Tofazzal HossainAún no hay calificaciones
- Synthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-Naphthol SudaDocumento4 páginasSynthesis of 1-Phenylazo-2-Naphthol SudaJohn ElegantAún no hay calificaciones
- Caesalpinia Sappan LDocumento4 páginasCaesalpinia Sappan LSriArthiAún no hay calificaciones
- Doktor 1938Documento8 páginasDoktor 1938AlexAún no hay calificaciones
- Dianix CCDocumento17 páginasDianix CCWaqas Ahmed100% (1)
- Paris REdDocumento9 páginasParis REdChristopher SchmidtAún no hay calificaciones
- Colonial Crafts - Natural Egg Dye CraftDocumento3 páginasColonial Crafts - Natural Egg Dye CraftKate R.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Copper Sulphate For Agriculture, Industry and Medicine PDFDocumento5 páginasCopper Sulphate For Agriculture, Industry and Medicine PDFabdulkidwai2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- US4976743Documento6 páginasUS4976743ozgurAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Safety in Textile IndustryDocumento4 páginasChemical Safety in Textile IndustryEditor IJTSRDAún no hay calificaciones
- Archroma News MarchDocumento13 páginasArchroma News Marchguven44Aún no hay calificaciones
- Denim Dry ProcessDocumento9 páginasDenim Dry ProcessZaman Parvez0% (1)
- Toaz - Info Chemistry Investigatory Project On Dyeing of Fabrics For Class 12 PRDocumento19 páginasToaz - Info Chemistry Investigatory Project On Dyeing of Fabrics For Class 12 PRmukesh kumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Direct Application On Polyester Using PROsperse Disperse DyesDocumento4 páginasDirect Application On Polyester Using PROsperse Disperse DyesYanmei BiAún no hay calificaciones
- Proposal PenelitianDocumento9 páginasProposal Penelitianfilda widaniatiAún no hay calificaciones