Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Design and Simulate Sample and Hold Circuit
Cargado por
Ren BurnettDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Design and Simulate Sample and Hold Circuit
Cargado por
Ren BurnettCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
UNIVERSITY OF GUYANA
FACULTY OF TECHNOLOGY
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Name: Frederick Cort
Reg.#: 11/0935/2437
Course: ELE 3204
Lecturer: Mr. Jomo Gill
2013/27
th
/Mar.
Aim : To Design and Simulate a Sample and Hold Circuit using a sinusoidal input to
observe the operation
Theory: The sample and hold circuit, as its name implies, samples an input signal
and holds on its last sampled value until the input is sampled again. For an analog
signal to be processed by a digital system, it must be converted to a digital signal
(discrete-time and discrete-amplitude). A sample and hold circuit makes it easier
for us to record the amplitude at each sample by holding the signal for a short
period of time at a given amplitude. Two important properties of a sample-and-
hold circuit are the highest possible sampling rate and how constant the sample
remains during the hold interval. Sample and hold circuits are commonly used in
analogue to digital converts, communication circuits, PWM circuits etc.
Components used:
Voltage Sources (Sinusoidal Input and Sample Signal)
2 100 Resistor
1 0.1F Capacitor
1 741 OpAmp
1 N-channel EMOSFET (BS170)
1 Oscilloscope
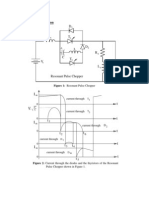
Sample and Hold Circuit
Diagram showing the sample and hold circuit with oscilloscopes connected
Simulation Results:
Diagram of Input Waveform
Diagram of Output Waveform
Diagram of the Input and Output Waveform
Sampler and Capacitor Waveform
Discussion :
In the above shown circuit the MOSFET(BS170) works as a switch while the
opamp 741 is wired as a voltage follower, the signal to be sampled (Vin) which
has a peak voltage of 1V is applied to the drain of MOSFET while the pulse voltage
(Vs) having a state of either 5V or 0V to turn on and off (respectively) the MOSFET
is applied to the gate of the MOSFET. The source pin of the MOSFET is connected
to the non inverting input of the opamp through the resistor R1. The capacitor
(C1) serves as the charge storing device and resistor (R2) serves as the load
resistor.
During the positive half cycle of the Vs, the MOSFET is ON which acts like a closed
switch and the capacitor C1 is charged by the Vin and the same voltage (Vin)
appears at the output of the opamp. When Vs is zero the MOSFET is switched off
and the only discharge path for C1 is through the inverting input of the opamp as
a result the voltage Vin is retained and it appears at the output of the opamp.
The time periods of the Vs during which the voltage across the capacitor (Vc) is
equal to Vin are called sample periods (Ts) and the time periods of Vs during
which the voltage across the capacitor C1 (Vc) is held constant are called hold
periods (Th).
Conclusion
To conclude this exercise the lab experiment done I better understood the
principle operation behind the sample and hold circuit as a result of designing the
circuit. Also learnt from this experiment it was experience that varying the
component values altered the output waveform to a great extent and as such
precise calculations are needed in the design or the trial and error method to
which I resorted to obtain the expected output. This experiment was very
beneficial in understanding how the circuit works in a practical basis.
References
http://www.circuitstoday.com/sample-and-hold-circuit
http://www.ece.vt.edu/ece3274/compare_sh.pdf
http://s.eeweb.com/members/floy_viola/answers/1355193178-SAMPLE-AND-
HOLD-CIRCUIT-USING-OP-AMP-741-_-MY-CIRCUITS-9.pdf
También podría gustarte
- Electrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsDe EverandElectrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsAún no hay calificaciones
- FM Balanced Slope DetectorDocumento5 páginasFM Balanced Slope DetectorPujjalPandeyAún no hay calificaciones
- Full Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesDocumento7 páginasFull Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesArun PratapAún no hay calificaciones
- 40 Ei 4p2-Lic Lab ManualDocumento94 páginas40 Ei 4p2-Lic Lab ManualsoundsisterAún no hay calificaciones
- LIC FLEXI Lab Manual Second Experiment Student Copy-3Documento5 páginasLIC FLEXI Lab Manual Second Experiment Student Copy-3Vignesh RamakrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- Eca Lab ManualDocumento78 páginasEca Lab ManualNageswariah.MAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrator and DifferentiatorDocumento7 páginasIntegrator and DifferentiatorManoj KavediaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 5: Design Single Stage and Telescopic Differential AmplifiersDocumento13 páginasLab 5: Design Single Stage and Telescopic Differential AmplifiersTamilinbaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 3.5.2 Challenge Frame Relay ConfigurationDocumento4 páginasLab 3.5.2 Challenge Frame Relay ConfigurationMark Zovighian0% (1)
- Differential and Multistage AmplifiersDocumento30 páginasDifferential and Multistage AmplifierskhsniperAún no hay calificaciones
- 08-Com101 AMDocumento11 páginas08-Com101 AMHồng HoanAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Documento13 páginasElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALAún no hay calificaciones
- Ee460 Lab Manual 2006Documento80 páginasEe460 Lab Manual 2006F0x123Aún no hay calificaciones
- ANALOG MULTIPLIERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND APPLICATIONSDocumento17 páginasANALOG MULTIPLIERS: KEY COMPONENTS AND APPLICATIONSMarykutty CyriacAún no hay calificaciones
- LIC Manual NewDocumento84 páginasLIC Manual NewVandhana PramodhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Eca Lab Manual PDFDocumento56 páginasEca Lab Manual PDFrppvch100% (5)
- FM Demodulation TechniquesDocumento15 páginasFM Demodulation TechniquesGeetanjali GoyalAún no hay calificaciones
- LAb 1Documento8 páginasLAb 1nazmyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveDocumento8 páginasLab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveRashid Rind Rashid Rind100% (1)
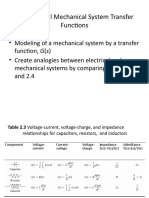
- Translational System Transfer FunctionsDocumento30 páginasTranslational System Transfer FunctionsRhizhailAún no hay calificaciones
- Simulate 3-Phase Inverter Using MATLABDocumento11 páginasSimulate 3-Phase Inverter Using MATLABseethahereAún no hay calificaciones
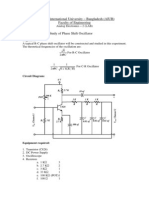
- Experiment Name-Study of Phase Shift OscillatorDocumento2 páginasExperiment Name-Study of Phase Shift Oscillatormrana_56100% (2)
- EC2257-Lab Manual For Circuits and Simulation Integrated LaboratoryDocumento38 páginasEC2257-Lab Manual For Circuits and Simulation Integrated Laboratorygokila_dr9897Aún no hay calificaciones
- Report - Phase ShifterDocumento8 páginasReport - Phase ShifterAmeer AliAún no hay calificaciones
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDocumento4 páginasEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Eee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyDocumento4 páginasEee2210 Analogue Elec II Omae Tie-PrintreadyMike ShakespeareAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocumento213 páginas02 Power Electronicsapi-19608934Aún no hay calificaciones
- Representing Power SystemsDocumento17 páginasRepresenting Power SystemsDr. Gollapalli Naresh100% (1)
- Electronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFDocumento41 páginasElectronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFtesterAún no hay calificaciones
- Inverting Amplifiers Lab ReportDocumento9 páginasInverting Amplifiers Lab ReportRaihan JannatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Labmanual Ecen474 PDFDocumento81 páginasLabmanual Ecen474 PDFSURAJ GUPTAAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Link CurrentDocumento8 páginasDC Link CurrentsubbannaAún no hay calificaciones
- Antenna Systems Demostrator ASD512pdfDocumento4 páginasAntenna Systems Demostrator ASD512pdfMiguel OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 1 ELECTRONICSDocumento38 páginasCHAPTER 1 ELECTRONICSRahul KumarAún no hay calificaciones
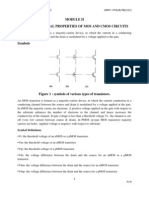
- Electrical Properties of Mos DeviceDocumento28 páginasElectrical Properties of Mos Devicemayamohan7250% (1)
- Wireless FM Microphone CircuitDocumento2 páginasWireless FM Microphone Circuitcuongspvl2713Aún no hay calificaciones
- 325 Lab 8 ReportDocumento10 páginas325 Lab 8 Reportapi-241454978Aún no hay calificaciones
- Applications of Balanced ModulatorDocumento5 páginasApplications of Balanced ModulatorSomeshwar GaddalaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Novel ZVS-ZCS Bi-Directional Flyback DC-DCDocumento6 páginasA Novel ZVS-ZCS Bi-Directional Flyback DC-DCArceu CamposAún no hay calificaciones
- Clipper and Clamper Circuits Lab GuideDocumento5 páginasClipper and Clamper Circuits Lab Guidepar1vej2Aún no hay calificaciones
- LIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsDocumento4 páginasLIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsMadhavan SamAún no hay calificaciones
- A Modified SEPIC Converter For High Power Factor Rectifier and Universal Input Voltage ApplicationsDocumento12 páginasA Modified SEPIC Converter For High Power Factor Rectifier and Universal Input Voltage ApplicationsBritto TigerAún no hay calificaciones
- Voltage Controlled Ring OscillatorDocumento4 páginasVoltage Controlled Ring OscillatorNurulMaisaraAwangAún no hay calificaciones
- Differential Voltage Current Conveyor (DVCC)Documento81 páginasDifferential Voltage Current Conveyor (DVCC)raam0006100% (1)
- Short Answer Type Questions: Signals & Transmission MediaDocumento4 páginasShort Answer Type Questions: Signals & Transmission MediaAndrew JonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Documento10 páginasLab 5 Diode As Rectifier BBN 10205 (Done)Zhamir ZhakwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Design Issues in CMOS OscillatorsDocumento4 páginasDesign Issues in CMOS OscillatorsdhrubAún no hay calificaciones
- EXPT - 02 - Study of Single Stage BJT AmplifierxDocumento5 páginasEXPT - 02 - Study of Single Stage BJT AmplifierxPrakash Narkhede100% (1)
- Considering: Rec. ITU-R P.530-8 1Documento34 páginasConsidering: Rec. ITU-R P.530-8 1Vladan BozicAún no hay calificaciones
- Mwoc Final Lab Manual 28-08-2010Documento77 páginasMwoc Final Lab Manual 28-08-2010downloadscribdpdfAún no hay calificaciones
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksDe EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksAún no hay calificaciones
- Real-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsDe EverandReal-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsAún no hay calificaciones
- Source:: Source: Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits, Ramakant A.GayakwadDocumento2 páginasSource:: Source: Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits, Ramakant A.GayakwadBatool HerzallahAún no hay calificaciones
- Source:: Source: Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits, Ramakant A.GayakwadDocumento2 páginasSource:: Source: Op-Amps and Linear Integrated Circuits, Ramakant A.GayakwadBatool HerzallahAún no hay calificaciones
- MSP HW1Documento2 páginasMSP HW1Batool HerzallahAún no hay calificaciones
- LM412 Sample and Hold: November 15, 2010 RendDocumento5 páginasLM412 Sample and Hold: November 15, 2010 RendSanthiya MurugesanAún no hay calificaciones
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocumento4 páginasNew Microsoft Word Documentalaa delewarAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Objective: 5.1 Center-Tapped TransformerDocumento3 páginas1 Objective: 5.1 Center-Tapped TransformerVicky GabrielaAún no hay calificaciones
- Multi-Location Dimming For Incandescent, CFL, LED and MLV LoadsDocumento4 páginasMulti-Location Dimming For Incandescent, CFL, LED and MLV LoadsRen BurnettAún no hay calificaciones
- Vavr-9ej262 R0 enDocumento19 páginasVavr-9ej262 R0 enKrishna ManandharAún no hay calificaciones
- Snake Repellent: Material Safety Data SheetDocumento2 páginasSnake Repellent: Material Safety Data SheetRen BurnettAún no hay calificaciones
- ADL 3 PH Induction MotorsDocumento6 páginasADL 3 PH Induction MotorsaswardiAún no hay calificaciones
- BasicMotorFormulasandCalculations6 14 13Documento4 páginasBasicMotorFormulasandCalculations6 14 13Ren BurnettAún no hay calificaciones
- Use and Care Guide - W10280544Documento32 páginasUse and Care Guide - W10280544Ren BurnettAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculating Motor Start TimeDocumento8 páginasCalculating Motor Start TimeRaj SekharAún no hay calificaciones
- Panasonic CordessDocumento56 páginasPanasonic CordessRen BurnettAún no hay calificaciones
- RC Circuit Voltage Decay ExponentiallyDocumento5 páginasRC Circuit Voltage Decay ExponentiallyCarl LightbourneAún no hay calificaciones
- VarPlus Can HDuty Capacitor 40/48kvar 525V 50/60HzDocumento2 páginasVarPlus Can HDuty Capacitor 40/48kvar 525V 50/60HzDewie HardiningrumAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocumento41 páginasIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanAún no hay calificaciones
- DatasheetDocumento4 páginasDatasheetLima LogictelAún no hay calificaciones
- 2B +RC+Triggering+CircuitDocumento3 páginas2B +RC+Triggering+CircuitklascoolAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture On Fundamentals of Signal and Power IntegrityDocumento40 páginasLecture On Fundamentals of Signal and Power IntegrityjaltitiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 5: Mathematical Models of Electrical Control System ComponentsDocumento15 páginasLesson 5: Mathematical Models of Electrical Control System ComponentsHasan AljabaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Workshop Manual Alternator enDocumento25 páginasWorkshop Manual Alternator enakaAún no hay calificaciones
- MSP430 Touch Pad ExperimentsDocumento39 páginasMSP430 Touch Pad ExperimentsNgotranduc ThangAún no hay calificaciones
- Laplace MatlabDocumento21 páginasLaplace MatlabIrwan WahyudiAún no hay calificaciones
- LM391 Audio Power Driver: General Description FeaturesDocumento12 páginasLM391 Audio Power Driver: General Description Featuresdhirajmore88Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hal Previous Exam Paper For ElectronicsDocumento18 páginasHal Previous Exam Paper For ElectronicsvenkateshmachineniAún no hay calificaciones
- Kia Service Training Basic ElectricityDocumento10 páginasKia Service Training Basic Electricityannie100% (41)
- 13.8kV Bus Duct Sizing For Arar Dated 23.03.2005Documento9 páginas13.8kV Bus Duct Sizing For Arar Dated 23.03.2005srigirisetty208Aún no hay calificaciones
- Grand Summary IGCSE Physics (Black & White)Documento56 páginasGrand Summary IGCSE Physics (Black & White)jun100% (1)
- ECE 5664 Spring 2021 Test #1Documento7 páginasECE 5664 Spring 2021 Test #1Muhammad FarooqAún no hay calificaciones
- Microprocessor Power Factor Controller CatalogueDocumento4 páginasMicroprocessor Power Factor Controller CatalogueYaser ShaikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminar Topic 3Documento5 páginasSeminar Topic 3Vijay Kumar ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- PHC Series PDFDocumento3 páginasPHC Series PDFguruh anindraAún no hay calificaciones
- Elspec BONUS 1350KVAr - User ManualDocumento126 páginasElspec BONUS 1350KVAr - User Manualkenji1134Aún no hay calificaciones
- Assign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Documento4 páginasAssign Single Phase Ac-2 (Unit-2)Sunil JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Soft-Switching Bidirectional DC-DC Converter Using A Lossless Active SnubberDocumento9 páginasSoft-Switching Bidirectional DC-DC Converter Using A Lossless Active SnubberHsekum RamukAún no hay calificaciones
- Metallized Polyester Film Capacitors Spec SheetDocumento1 páginaMetallized Polyester Film Capacitors Spec Sheetnanodocl5099Aún no hay calificaciones
- 5.3 Spark 2000 Ul EnglishDocumento77 páginas5.3 Spark 2000 Ul EnglishSmile Man100% (2)
- Forced CommutationDocumento2 páginasForced CommutationKireety MandavilliAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Electronic SurveillanceDocumento43 páginasBasic Electronic SurveillanceMike BaillieAún no hay calificaciones
- Tekna NFOGM MPFM Handbook v2 2005Documento115 páginasTekna NFOGM MPFM Handbook v2 2005ltrongluanvnAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-1 EDC Lab Manual Jntuk R20 - 201021Documento96 páginas2-1 EDC Lab Manual Jntuk R20 - 201021Durgasaiteja923 SunnyAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT-4 of HVEDocumento18 páginasUNIT-4 of HVEAayush PatidarAún no hay calificaciones
- AM Transmitter Circuit Project ReportDocumento8 páginasAM Transmitter Circuit Project ReportNguyễn Thanh TùngAún no hay calificaciones