Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Franki System
Cargado por
Ahmad Amanu SuryaDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Franki System
Cargado por
Ahmad Amanu SuryaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
A charge of zero-slump concrete is poured into the bottom of a steel driving pipe that is placed vertically
on the ground. A diesel-operated drop hammer is then driven on the concrete, forming a watertight
concrete plug.
[1][4][5][6]
1.
The concrete plug is driven into the ground by the drop hammer. The pipe is also dragged into the ground
due to friction developed between the steel and the concrete.
[1][4][5][6]
2.
When the desired depth is reached, the pipe is held in position by leadsstructures which guide and align
the pile and hammer.
[7]
The hammer is then applied to the concrete, driving it outwards through the
bottom of the pile and forming a mushroom-shaped base.
[1][4][5][6]
3.
At this point, a cylindrical rebar cage can be driven into the concrete if supplementary reinforcement is
desired.
[1][4][5][6]
4.
Additional charges of concrete are added and driven while the steel casing is simultaneously pulled up
until the shaft of the pile is formed.
[1][4][5][6]
5.
Small charges of concrete can be added while the base is being formed
[6]
to enlarge the base and improve
the piles settlement performance.
[3]
Franki piles can be installed raked (or sloped) with a tilt of up to 4:1.
[5]
Raked Franki piles are always
reinforced and are particularly suitable for structures subject to dynamic forces.
[1]
Driving methods such as open-ended coring, rock socketing, and composite shaft construction are
occasionally used to overcome unique site problems.
[3]
^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
Franki Pile (http://www.geoforum.com/info/pileinfo/view.asp?ID=15) GRV AB, Retrieved November
22, 2010
1.
^
a
b
c
d
e
History (http://www.franki-geotechnics.be/page.asp?q=history&id=501&title=History) Franki Foundations
Group Belgium, Retrieved December 7, 2010
2.
^
a
b
c
d
e
Franki Piles (http://esvc000701.wic052u.server-web.com/PDF/Frank_Piles.pdf) Frankipile Australia,
Retrieved December 8, 2010
3.
^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
Shamsher Prakash, Hari D. Sharma (1990). Pile foundations in Engineering Practice, p. 60. Wiley-
Interscience ISBN 0-471-61653-2.
4.
^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
FRANKIPILE (http://www.franki.de/pdf_en/FRANKI_pile.pdf) FRANKI Grundbau, Retrieved
December 7, 2010
5.
^
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
Dr. B.C. Punmia, Ashok Kumar J ain, B.C. Punmia, Arun Kr. J ain (2005). Soil Mechanics and
Foundations , p. 763. Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd. ISBN 81-7008-081-9.
6.
Franki Piling System - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Franki_Piling_System
2 dari 3 5/16/2014 11:07 PM
^ piledrivers.org PDF, Land Based Rigs (http://www.piledrivers.org/files/uploads/272D1300-0887-4849-
BDB0-4044B9FF8859.pdf)
7.
An animation of the installation process (http://esvc000701.wic052u.server-web.com/products
/all_products_pages/franki_flash.html).
Franki Pile, Pile Info, geoforum.com (http://www.geoforum.com/info/pileinfo/view.asp?ID=15)
piledrivers.org (http://www.piledrivers.org/), Pile Driving Contractors Association
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Franki_Piling_System&oldid=580361297"
Categories: Geotechnical engineering Civil engineering
This page was last modified on 5 November 2013 at 21:25.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may
apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipediais a registered
trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
Franki Piling System - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Franki_Piling_System
3 dari 3 5/16/2014 11:07 PM
También podría gustarte
- Drawing List Tanjung Balai 01Documento1 páginaDrawing List Tanjung Balai 01Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sheel No StifnesDocumento1 páginaSheel No StifnesAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
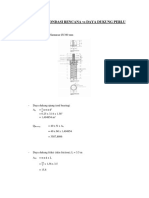
- Investigasi Pondasi Rencana Vs Daya Dukung PerluDocumento4 páginasInvestigasi Pondasi Rencana Vs Daya Dukung PerluAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Mark IndustriesDocumento1 páginaTest Mark IndustriesAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sheel No StifnesDocumento1 páginaSheel No StifnesAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMDocumento12 páginasFashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- CV Templates Curriculum VitaeDocumento5 páginasCV Templates Curriculum VitaeAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple PropertisDocumento5 páginasSimple PropertisAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- FdsDocumento4 páginasFdsAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMDocumento12 páginasFashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMDocumento12 páginasFashion Wanita: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- ReadmeDocumento3 páginasReadmekanaksanketAún no hay calificaciones
- Gynecologist CV TemplateDocumento6 páginasGynecologist CV TemplateSingh ViratAún no hay calificaciones
- Shopping Doc with 40+ CategoriesDocumento12 páginasShopping Doc with 40+ CategoriesAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Perawatan & Kecantikan: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMDocumento12 páginasPerawatan & Kecantikan: 1 Dari 12 8/31/2016 11:25 PMAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Long Sec Only Acad 2007 ModelDocumento1 páginaLong Sec Only Acad 2007 ModelAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- TABLE: Column Forces Story Column Unique Name Load Case/Combo Station PDocumento11 páginasTABLE: Column Forces Story Column Unique Name Load Case/Combo Station PAhmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lateral Loads ManualDocumento134 páginasLateral Loads ManualSam UhAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- 34 Ss 5Documento3 páginas34 Ss 5Ahmad Amanu SuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Hand Infection Guide: Felons to Flexor TenosynovitisDocumento68 páginasHand Infection Guide: Felons to Flexor TenosynovitisSuren VishvanathAún no hay calificaciones
- Brochure - Coming To Work in The Netherlands (2022)Documento16 páginasBrochure - Coming To Work in The Netherlands (2022)Tshifhiwa MathivhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Prep - VN: Where Did The Polo Family Come From?Documento1 páginaPrep - VN: Where Did The Polo Family Come From?Phương LanAún no hay calificaciones
- School of Architecture, Building and Design Foundation in Natural Build EnvironmentDocumento33 páginasSchool of Architecture, Building and Design Foundation in Natural Build Environmentapi-291031287Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gambaran Kebersihan Mulut Dan Karies Gigi Pada Vegetarian Lacto-Ovo Di Jurusan Keperawatan Universitas Klabat AirmadidiDocumento6 páginasGambaran Kebersihan Mulut Dan Karies Gigi Pada Vegetarian Lacto-Ovo Di Jurusan Keperawatan Universitas Klabat AirmadidiPRADNJA SURYA PARAMITHAAún no hay calificaciones
- Hidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University CollegeDocumento12 páginasHidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University Collegepy007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bo's Coffee AprmDocumento24 páginasBo's Coffee Aprmalliquemina100% (1)
- 12 Smart Micro-Habits To Increase Your Daily Productivity by Jari Roomer Better Advice Oct, 2021 MediumDocumento9 páginas12 Smart Micro-Habits To Increase Your Daily Productivity by Jari Roomer Better Advice Oct, 2021 MediumRaja KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Category Theory For Programmers by Bartosz MilewskiDocumento565 páginasCategory Theory For Programmers by Bartosz MilewskiJohn DowAún no hay calificaciones
- Adam Smith Abso Theory - PDF Swati AgarwalDocumento3 páginasAdam Smith Abso Theory - PDF Swati AgarwalSagarAún no hay calificaciones
- Merah Putih Restaurant MenuDocumento5 páginasMerah Putih Restaurant MenuGirie d'PrayogaAún no hay calificaciones
- Second Year Memo DownloadDocumento2 páginasSecond Year Memo DownloadMudiraj gari AbbaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Forouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionDocumento14 páginasForouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionFroyd WessAún no hay calificaciones
- Coursebook 1Documento84 páginasCoursebook 1houetofirmin2021Aún no hay calificaciones
- MAY-2006 International Business Paper - Mumbai UniversityDocumento2 páginasMAY-2006 International Business Paper - Mumbai UniversityMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKAún no hay calificaciones
- Helen Hodgson - Couple's Massage Handbook Deepen Your Relationship With The Healing Power of TouchDocumento268 páginasHelen Hodgson - Couple's Massage Handbook Deepen Your Relationship With The Healing Power of TouchLuca DatoAún no hay calificaciones
- Planificación Semanal Maestro de Inglés RAE 2022-2023Documento2 páginasPlanificación Semanal Maestro de Inglés RAE 2022-2023vanessabultron8804100% (1)
- Introduction To Competitor AnalysisDocumento18 páginasIntroduction To Competitor AnalysisSrinivas NandikantiAún no hay calificaciones
- Vol 013Documento470 páginasVol 013Ajay YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Social Responsibility and Ethics in Marketing: Anupreet Kaur MokhaDocumento7 páginasSocial Responsibility and Ethics in Marketing: Anupreet Kaur MokhaVlog With BongAún no hay calificaciones
- DSA Interview QuestionsDocumento1 páginaDSA Interview QuestionsPennAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos Regulares e IrregularesDocumento8 páginasVerbos Regulares e IrregularesJerson DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- SHS Track and Strand - FinalDocumento36 páginasSHS Track and Strand - FinalYuki BombitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Negotiating For SuccessDocumento11 páginasNegotiating For SuccessRoqaia AlwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chengyang Li Archive Cra 23Documento32 páginasChengyang Li Archive Cra 23Li ChengyangAún no hay calificaciones
- The Best Chess BooksDocumento3 páginasThe Best Chess BooksJames Warren100% (1)
- Research Methods LessonDocumento26 páginasResearch Methods LessonCarole Janne EndoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Myrrh PDFDocumento25 páginasMyrrh PDFukilabosAún no hay calificaciones
- Reduce Home Energy Use and Recycling TipsDocumento4 páginasReduce Home Energy Use and Recycling Tipsmin95Aún no hay calificaciones
- God Love Value CoreDocumento11 páginasGod Love Value CoreligayaAún no hay calificaciones