Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
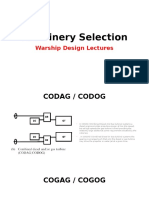
CODAG
Cargado por
aeromexpower2009Descripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
CODAG
Cargado por
aeromexpower2009Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Combined diesel and gas - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 1 of 2
Combined diesel and gas
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
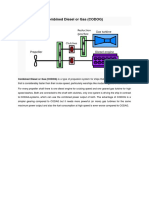
Combined diesel and gas (CODAG) is a type of propulsion system for ships which need Combined marine a maximum speed that is considerably faster than their cruise speed, particularly warships propulsion like modern frigates or corvettes. It consists of diesel engines for cruising and gas turbines CODAG that can be switched on for high-speed transits. In most CODLAG cases the difference of power output from diesel engines CODAD alone to diesel and turbine power combined is too large, COSAG that controllable pitch propellers can limit the rotations COGOG so that the diesels can continue to operate without COGAG changing the gear ratios of their transmissions. Because COGAS of that, special multi-speed gearboxes are needed. This CONAS contrasts to CODOG systems, which couple the diesels with a simple, fixed ratio gearboxes to the shaft and disengage them, when the turbine is switched on.
CODOG
Principle of a CODAG system, with two speed diesel gearboxes
E.g. for the new CODAG propulsed Fridtjof Nansen class frigate of the Royal Norwegian Navy, the gear ratio for the diesel engine is changed from about 1:7.7 (engine:propeller) for diesel-only to 1:5.3 when in diesel-and-turbine mode. Some ships even have three different gear ratios for the diesel engines: one each for single diesel and double diesel cruises and the third when the gas turbine is engaged. Such a propulsion system has a smaller footprint than a diesel-only power plant with the same maximal power output, since smaller engines can be used and the gas turbine and gearbox don't need that much additional space. Still it retains the high fuel efficiency of diesel engines when cruising, allowing greater range and lower fuel costs than with gas turbines alone. On the other hand, a more complex, heavy and troublesome gearing is needed. Typical cruising speed of CODAG warships on diesel-power is 20 kts and typical maximal speed with switched on turbine is 30 kts. CODAG has been pioneered by Germany with the Kln class frigate.
Contents
1 Turbines and diesels on separate shafts 2 CODAG WARP 3 CODAG-electric 4 External links
Turbines and diesels on separate shafts
Sometimes the engine arrangement of diesel engine and gas turbine with each system using its own shafts and propellers is also called CODAG. Such installations avoid the use of a complicated switching
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_diesel_and_gas
11/19/2007
Combined diesel and gas - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Page 2 of 2
gearbox but have some disadvantages compared to real CODAG systems: Since more propellers have to be used, they have to be smaller and thus less efficient. The propellers of the idling systems cause drag.
CODAG WARP
CODAG Water jet And Refined Propeller, a system developed by Blohm + Voss as option for their MEKO line of ships, also falls in this categegory but avoids the above mentioned problems. CODAG WARP uses two diesel engines to drive two propellers in a CODAD arrangement, i.e. both shafts can also be powered by any single engine, and a centerline water jet powered by a gas turbine. The idling water jet doesn't cause drag and since its nozzle can be placed further aft and higher it doesn't affect the size of the propellers.
CODAG-electric
Another solution to combining the two types of engines is to have engine connected to a generator, and then drive the propeller with an electric motor, much like a diesel-electric. The RMS Queen Mary 2 features such a design. Such a design also simplifies the use of propeller pods with the propulsion motors mounted inside the pods. A further CODAG innovation on the QM2 is that the turbines are mounted not in the engine room but directly under the funnel, thereby simplifying the supply of fresh air to the turbines.
External links
CODAG WARP @ naval-technology.com Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_diesel_and_gas" Category: Marine propulsion This page was last modified 17:32, 20 July 2007. All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. (See Copyrights for details.) Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a U.S. registered 501(c) (3) tax-deductible nonprofit charity.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Combined_diesel_and_gas
11/19/2007
También podría gustarte
- Retirement SpeechDocumento11 páginasRetirement SpeechRayan Castro100% (1)
- TD490HCDocumento4 páginasTD490HCaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Marine Propulsion For Small CraftsDocumento71 páginasMarine Propulsion For Small CraftsGermán Aguirrezabala100% (1)
- Marine Power CatalogueDocumento98 páginasMarine Power Cataloguesafaa salamAún no hay calificaciones
- (Catamaran) Effect of Hull Form and Its Associated Parameters On The Resistance - MaxsurfDocumento63 páginas(Catamaran) Effect of Hull Form and Its Associated Parameters On The Resistance - MaxsurfWm Erick Cr100% (1)
- Abrigo Vs Flores DigestDocumento4 páginasAbrigo Vs Flores DigestKatrina GraceAún no hay calificaciones
- Ackerman? Anti-Ackerman? or Parallel Steering?Documento10 páginasAckerman? Anti-Ackerman? or Parallel Steering?Alija SirotanovićAún no hay calificaciones
- 70m 120T Bollard Pull 10,800HPDocumento1 página70m 120T Bollard Pull 10,800HPMohd ZaidAún no hay calificaciones
- Garrido Vs TuasonDocumento1 páginaGarrido Vs Tuasoncmv mendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Review of All-Electric and Hybrid-Electric Propulsion Technology For Small VesselsDocumento34 páginasReview of All-Electric and Hybrid-Electric Propulsion Technology For Small VesselsFoe AungAún no hay calificaciones
- International Introduction To Securities and Investment Ed6 PDFDocumento204 páginasInternational Introduction To Securities and Investment Ed6 PDFdds50% (2)
- Stapersma - Matching Propulsion Engine With PropulsorDocumento8 páginasStapersma - Matching Propulsion Engine With PropulsorTuan Truong MinhAún no hay calificaciones
- Diesel Engines & Gas TurbinesDocumento13 páginasDiesel Engines & Gas TurbinesPriscila KImAún no hay calificaciones
- Marine EnginesDocumento12 páginasMarine EnginesSyukry MaulidyAún no hay calificaciones
- Tuning A Twin-Screw Rudder InstallationDocumento6 páginasTuning A Twin-Screw Rudder Installationaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- ENGLISH - 170059 PR Corporate Brochure - FinalDocumento60 páginasENGLISH - 170059 PR Corporate Brochure - FinalUjang KasepAún no hay calificaciones
- (Bloom's Modern Critical Views) (2000)Documento267 páginas(Bloom's Modern Critical Views) (2000)andreea1613232100% (1)
- BMTNG Patrol BoatDocumento2 páginasBMTNG Patrol BoatNico BossiAún no hay calificaciones
- Greatship Leaflets - Ahtsv - 80 T (Asmi)Documento2 páginasGreatship Leaflets - Ahtsv - 80 T (Asmi)bdasdasdAún no hay calificaciones
- GE Global Offshore & Marine Solutions Guide - 2014 EditionDocumento220 páginasGE Global Offshore & Marine Solutions Guide - 2014 Editionsurabhi0706100% (1)
- L 19 - Machinery Selection For Modern WarshipDocumento31 páginasL 19 - Machinery Selection For Modern Warshipknowme73Aún no hay calificaciones
- SDM Case Analysis Stihl IncorporatedDocumento17 páginasSDM Case Analysis Stihl Incorporatedmahtaabk100% (5)
- Diesel Electric Propulsion Plant - MANDocumento26 páginasDiesel Electric Propulsion Plant - MANThomas St100% (1)
- Energy Saving Basics - EsdsDocumento40 páginasEnergy Saving Basics - Esdsapi-238581599Aún no hay calificaciones
- 201ymm01 Mag TugandOSV 032Documento118 páginas201ymm01 Mag TugandOSV 032JaadAún no hay calificaciones
- Compact LNG C Design Brochure - 110609Documento4 páginasCompact LNG C Design Brochure - 110609pal_malayAún no hay calificaciones
- Weight Watchers Business Plan 2019Documento71 páginasWeight Watchers Business Plan 2019mhetfield100% (1)
- Combined Marine Propulsion Systems PDFDocumento20 páginasCombined Marine Propulsion Systems PDFMerrelAún no hay calificaciones
- Orca Energy SpecDocumento2 páginasOrca Energy SpecHanWee LowAún no hay calificaciones
- Power System Architecture NextwindDocumento4 páginasPower System Architecture NextwindRain ByarsAún no hay calificaciones
- Marine Products Systems CatalogueDocumento97 páginasMarine Products Systems CatalogueJhonnatan Quispe Franco100% (1)
- Ahts 0610Documento12 páginasAhts 0610seckin80100% (1)
- Design of Propulsion Systems For High-Speed CraftDocumento17 páginasDesign of Propulsion Systems For High-Speed Craftaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Motor in Ship PropulsionDocumento13 páginasElectric Motor in Ship PropulsionConcept of ReasoningAún no hay calificaciones
- Engine PresentationDocumento34 páginasEngine Presentationlink2u_007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Kombinasi Mesin Penggerak KapalDocumento7 páginasKombinasi Mesin Penggerak Kapalara sidy100% (1)
- GateRudder JMST 2015 PDFDocumento13 páginasGateRudder JMST 2015 PDFθανασης ΓκιοκαςAún no hay calificaciones
- Combined Marine Propulsion PDFDocumento10 páginasCombined Marine Propulsion PDFSea Man Mkt100% (1)
- All Electric Ship Integrated Power Systems PDFDocumento6 páginasAll Electric Ship Integrated Power Systems PDFMario BogdanovicAún no hay calificaciones
- A Review On The Faults of Electric MachiDocumento8 páginasA Review On The Faults of Electric Machifares noureddineAún no hay calificaciones
- Marine Products and Systems Catalogue PDFDocumento202 páginasMarine Products and Systems Catalogue PDFJojoHanAún no hay calificaciones
- Himsen H46 60VDocumento4 páginasHimsen H46 60VairtupasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ship AutomationDocumento6 páginasShip AutomationMathias HotmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Marine Propulsion SystemsDocumento5 páginasMarine Propulsion SystemsIbrahim SameirAún no hay calificaciones
- Marine Engines Running On LNG For Submission Ioannis BakasDocumento28 páginasMarine Engines Running On LNG For Submission Ioannis Bakaswaleed yehiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mtu 12v&16v2000m94Documento2 páginasMtu 12v&16v2000m94ozakyus50% (2)
- Hybrid Electric Propulsion For Military VehiclesDocumento84 páginasHybrid Electric Propulsion For Military VehiclesObject477Aún no hay calificaciones
- Multi-Engine Submarine Power SuppliesDocumento14 páginasMulti-Engine Submarine Power Suppliesdavid2404100% (2)
- Pac12 JB SM Paper 25-Nov-11Documento11 páginasPac12 JB SM Paper 25-Nov-11BuckinghamsterAún no hay calificaciones
- Hyundai Green ShipDocumento17 páginasHyundai Green ShipbovingAún no hay calificaciones
- ModernNaval Solutions - 2final - Ohmayer.nov 2012cDocumento39 páginasModernNaval Solutions - 2final - Ohmayer.nov 2012cPriscila KImAún no hay calificaciones
- Tug - BUYUKDEREDocumento6 páginasTug - BUYUKDEREudelmarkAún no hay calificaciones
- Propulsion of 46 000 50 000 DWT MR Tankers PDFDocumento33 páginasPropulsion of 46 000 50 000 DWT MR Tankers PDFKyaw ZinAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Report On HovercraftDocumento70 páginasFinal Report On HovercraftSingh KD100% (1)
- Diesel Engines and Gas Turbines in Cruise Vessel PropulsionDocumento13 páginasDiesel Engines and Gas Turbines in Cruise Vessel PropulsionFuchsbauAún no hay calificaciones
- ExercisesDocumento22 páginasExercisessiakeehoAún no hay calificaciones
- Propeller / Hull Status Report 2009Documento17 páginasPropeller / Hull Status Report 2009torbjorn25Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ang 1 Marine-Power-Plants PDFDocumento75 páginasAng 1 Marine-Power-Plants PDFVincent KohAún no hay calificaciones
- Alternative Fuels Low Speed Diesel EnginesDocumento16 páginasAlternative Fuels Low Speed Diesel EnginesŞansal DikmenerAún no hay calificaciones
- Expressor CompressorDocumento81 páginasExpressor Compressormep.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Diesel Engines For Alamarin-Jet 245 Rev.3.3Documento5 páginasDiesel Engines For Alamarin-Jet 245 Rev.3.3Flavio MedranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Slide Bearing For Electricar Machines BrochureDocumento6 páginasSlide Bearing For Electricar Machines BrochureGabriel BolívarAún no hay calificaciones
- Propulsion Solutions For Large High Speed VesselsDocumento29 páginasPropulsion Solutions For Large High Speed VesselshaujesAún no hay calificaciones
- Camarc - Jets or PropellersDocumento1 páginaCamarc - Jets or PropellersFausto SelettiAún no hay calificaciones
- Griffiths Diesel EngineDocumento30 páginasGriffiths Diesel Enginesunahsuggs50% (2)
- Bow and Stern Thrusters: For Commercial VesselsDocumento4 páginasBow and Stern Thrusters: For Commercial VesselsCatalin CataAún no hay calificaciones
- PIM130B1 - Daihatsu DT Series Archived JUN PDFDocumento5 páginasPIM130B1 - Daihatsu DT Series Archived JUN PDFAnonymous XGsiY6rAún no hay calificaciones
- Brochure Diesel Engines 2014 ENGDocumento8 páginasBrochure Diesel Engines 2014 ENGmsk5inAún no hay calificaciones
- M.sc. Thesis EEDI (Final Copy)Documento164 páginasM.sc. Thesis EEDI (Final Copy)manon16050% (2)
- Combined Power PlantDocumento10 páginasCombined Power PlantManoj SunchauriAún no hay calificaciones
- Propulsion Systems For Future LNG CarriersDocumento4 páginasPropulsion Systems For Future LNG CarriersbernardinodinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Waterjets Vs PropellersDocumento1 páginaWaterjets Vs Propellersaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Product CatalogDocumento20 páginasProduct Catalogaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Small Craft Power PredictionDocumento32 páginasSmall Craft Power Predictionaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Technical Specifications 2007 Audi A6 4.2 FSI Quattro Sedan: EngineDocumento2 páginasTechnical Specifications 2007 Audi A6 4.2 FSI Quattro Sedan: Engineaeromexpower2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- General Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersDocumento34 páginasGeneral Terms Conditions For Sales Purchases LPG and Chemical TankersSally AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Correctional Case StudyDocumento36 páginasCorrectional Case StudyRaachel Anne CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Business LettersDocumento11 páginasTypes of Business LettersernewstAún no hay calificaciones
- Case 3 - Ecuadorean Rose IndustryDocumento6 páginasCase 3 - Ecuadorean Rose IndustryMauricio BedonAún no hay calificaciones
- Au L 53229 Introduction To Persuasive Text Powerpoint - Ver - 1Documento13 páginasAu L 53229 Introduction To Persuasive Text Powerpoint - Ver - 1Gacha Path:3Aún no hay calificaciones
- Core Values Behavioral Statements Quarter 1 2 3 4Documento1 páginaCore Values Behavioral Statements Quarter 1 2 3 4Michael Fernandez ArevaloAún no hay calificaciones
- Department of Mba Ba5031 - International Trade Finance Part ADocumento5 páginasDepartment of Mba Ba5031 - International Trade Finance Part AHarihara PuthiranAún no hay calificaciones
- Shop Decjuba White DressDocumento1 páginaShop Decjuba White DresslovelyAún no hay calificaciones
- "If It Ain't Cheap, It Ain't Punk": Walter Benjamin's Progressive Cultural Production and DIY Punk Record LabelsDocumento21 páginas"If It Ain't Cheap, It Ain't Punk": Walter Benjamin's Progressive Cultural Production and DIY Punk Record LabelsIsadora Mandarino OteroAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 11: Re-Situating ConstructionismDocumento2 páginasChapter 11: Re-Situating ConstructionismEmilio GuerreroAún no hay calificaciones
- Philippine Literature During Spanish ColonizationDocumento4 páginasPhilippine Literature During Spanish ColonizationCharisel Jeanne CasalaAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 09Documento31 páginasCH 09Ammar YasserAún no hay calificaciones
- ISE II Sample Paper 1 (With Answers)Documento13 páginasISE II Sample Paper 1 (With Answers)Sara Pérez Muñoz100% (1)
- EIB Pan-European Guarantee Fund - Methodological NoteDocumento6 páginasEIB Pan-European Guarantee Fund - Methodological NoteJimmy SisaAún no hay calificaciones
- Who Is He? Where Is He? What Does He Do?Documento3 páginasWho Is He? Where Is He? What Does He Do?David Alexander Pacheco Morales100% (1)
- Ch.6 TariffsDocumento59 páginasCh.6 TariffsDina SamirAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes Chap 1 Introduction Central Problems of An EconomyDocumento2 páginasNotes Chap 1 Introduction Central Problems of An Economyapi-252136290100% (2)
- A Brief Journey Through Arabic GrammarDocumento28 páginasA Brief Journey Through Arabic GrammarMourad Diouri100% (5)
- E-Conclave Spon BrochureDocumento17 páginasE-Conclave Spon BrochureNimish KadamAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Write A Driving School Business Plan: Executive SummaryDocumento3 páginasHow To Write A Driving School Business Plan: Executive SummaryLucas Reigner KallyAún no hay calificaciones
- RwservletDocumento2 páginasRwservletsallyAún no hay calificaciones
- Juegos 360 RGHDocumento20 páginasJuegos 360 RGHAndres ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Contemporary World Reflection PaperDocumento8 páginasContemporary World Reflection PaperNyna Claire GangeAún no hay calificaciones