Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Mathematics
Cargado por
Benjamin HiTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Mathematics
Cargado por
Benjamin HiCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
WEEKLY LESSON PLAN
WEEK:6(4/2-8/2/2013)
MATHEMATICS
CLASS: 4S3,4S5,4A
LEARNING
SUB TOPIC
AREA
3.0 Sets
3.2
Understand
and use the
concept of
Subset,
universal set
and the
complement
of a set
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
Students will
be taught to:
3.2 Understand
and use the
concept of
Subset,
universal set
and the
complement of
a set
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Students will be able to:
i.
determine whether a given
set is a subset of a specific set and
use the symbol or .
ii.
represent subset by using
Venn diagram
iii.
list the subsets for a specific
set
iv.
illustrate the relationship
between set and universal set using
Venn diagram
v.
determine the complement
of a given set
vi.
determine the relationship
between set, subset,
universal set and the complement of
a set
NOTES
Pedagogy:
Contextual
Contrustivism
Mastery
Enquiry discovery
Noble values:
Accurate
Conscientious
Hard working
To obey instructions
Resources:
Text book
Work book
CHEMISTRY
CLASS: 4S1
LEARNING
AREA
3.0
CHEMICAL
FORMULAE
AND
EQUATIONS
SUB TOPIC
3.1
Understanding
and applying
the concepts of
relative atomic
mass and
relative
molecular mass
3.2 Analysing
the relationship
between the
number of
moles with the
number of
particles
3.3 Analysing
the relationship
between the
number of
moles with its
mass
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
Students will be
taught to:
3.1 Understanding
and applying the
concepts of
relative atomic
mass and relative
molecular mass
3.2 Analysing the
relationship
between the
number of moles
with the number of
particles
3.3 Analysing the
relationship
between the
number of moles
with its mass
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Students will be able to:
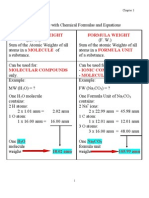
i. State the meaning of relative
atomic mass based on carbon12 scale
ii. State the meaning of relative
molecular mass based on carbon12 scale
iii. State why carbon-12 is used as
a standard for determining relative
atomic mass and relative
molecular mass
iv. Calculate the relative molecular
mass of substances
v. Define a mole as the amount of
matter that contains as many
particles as the number of atoms in
12 g of carbon-12
vi. State the meaning of Avogadro
constant
vii. Relate the number of particles
in one mole of a substance with the
Avogadro constant
vii. Solve the numerical problems
to convert the number of moles to
the number of particles of a given
substance and vice versa
NOTES
Thinking skill and
scientific skill:
Relating
Comparing and
Contrasting
Generating ideas
Conceptualizing
Scientific attitudes
and noble values:
Having critical and
analytical thinking
Thinking rationally
Resources:
Text book
Module chemistry
viii. State the meaning of molar
mass
ix. Relate molar mass to the
Avogadro constant
x. Relate molar mass of a
substance to its relative atomic
mass or its relative molecular mass
xi. Solve numerical problems to
convert the number of moles to its
mass and vice versa
CLASS: 5S4
LEARNING
AREA
4.0
Thermochemistr
y
SUB TOPIC
4.4.
Understanding
heat of
neutralisation
4.5
Understanding
heat of
combustion
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE
Students will
taught to:
4.4.
Understanding
heat of
neutralisation
4.5
Understanding
heat of
combustion
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Students will be able to:
4.4.1 state what heat of
neutralization is,
4.4.2 determine the heat of
neutralisation, construct energy
level diagrams for various types of
neutralisation reactions,
4.4.3 compare the heat of
neutralisation for the reaction
between a strong acid and a strong
alkali with the heat of
neutralisation for a reaction
between a weak acid and or a weak
alkali,
4.4.4 explain the difference of the
heat of neutralisation for a strong
acid and a strong alkali with the
heat of neutralization for a reaction
involving a weak acid and/or a
weak alkali,
4.4.5 solve numerical problems
related to heat of neutralisation.
4.5.1.state what heat of
combustion is,
determine heat of combustion for a
reaction,
4.5.2 construct an energy level
diagram for a combustion reaction,
compare the heat of combustion of
various alcohols,
4.5.3 state what fuel value is,
describe the difference between
heats of combustion of various
alcohols,
4.5.4 describe the applications of
fuel value,
compare and contrast fuel values
for various fuels,
4.5.5 solve numerical problems
related to heat of combustion
NOTES
Thinking skill and
scientific skill:
Interpreting data
Classifying
Communicating
Analysing
Making inference
Scientific attitudes
and noble values:
Being cooperative
Being objective
Thinking rationally
También podría gustarte
- Lesson Plan 380Documento13 páginasLesson Plan 380api-583311172Aún no hay calificaciones
- CHM 1025 Intro Chemistry PrepDocumento6 páginasCHM 1025 Intro Chemistry PrepJustin Lloyd MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- PascoSTEM8mod2 Chemical Reactions and TemperatureDocumento5 páginasPascoSTEM8mod2 Chemical Reactions and Temperatureرؤوف الجبيريAún no hay calificaciones
- Yearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4Documento30 páginasYearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4fakiah binti abdul khalid100% (2)
- RESEARCH FRAMEWORK THEORIESDocumento3 páginasRESEARCH FRAMEWORK THEORIESRachel Lorenzo SaldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics: 7.0 Acids and BasesDocumento3 páginasMathematics: 7.0 Acids and BasesRenSaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Ma 6003Documento2 páginasMa 6003bt20103080 Rijul SinglaAún no hay calificaciones
- CHM-1025 Syllabus Summer 2019 (2) (1) (1) - 2Documento11 páginasCHM-1025 Syllabus Summer 2019 (2) (1) (1) - 2459872305datAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 3 Chemistry Unit PlanDocumento26 páginasForm 3 Chemistry Unit PlanTifanie100% (2)
- Phy5001 - Mathematical-Physics - TH - 1.1 - 47 - Phy5001 - 59 AcpDocumento2 páginasPhy5001 - Mathematical-Physics - TH - 1.1 - 47 - Phy5001 - 59 AcpHaze Subin CAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Plan - HeatDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan - Heatapi-264952678Aún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics and Probability:: 60 MinutesDocumento2 páginasStatistics and Probability:: 60 MinutesSharlyn BalgoaAún no hay calificaciones
- Adaptive Teaching Guide: Private Education Assistance CommitteeDocumento6 páginasAdaptive Teaching Guide: Private Education Assistance CommitteeMarvin MoreteAún no hay calificaciones
- Form Four Yearly Plan 2014 Introducing ChemistryDocumento30 páginasForm Four Yearly Plan 2014 Introducing ChemistryRenSaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 4 Yearly Teaching Plan 2012Documento32 páginasForm 4 Yearly Teaching Plan 2012Aki ChanAún no hay calificaciones
- 120122Documento3 páginas120122Teuku Mohd HasbiAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 7 Midterm Exam Syllabus 2023Documento14 páginasGrade 7 Midterm Exam Syllabus 2023qirat.thanvi005066Aún no hay calificaciones
- RPH U6 2017Documento168 páginasRPH U6 2017Ngu LynAún no hay calificaciones
- calTPA #3Documento24 páginascalTPA #3Meagan Williams100% (2)
- 3V Physics - Lesson Plan - March - LopezDocumento12 páginas3V Physics - Lesson Plan - March - LopezMinorAún no hay calificaciones
- School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Date/Time: Quarter: Objectives A. Content StandardsDocumento3 páginasSchool: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Date/Time: Quarter: Objectives A. Content StandardsSharen DivinagraciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Course Syllabus in Mathematics IIDocumento9 páginasCourse Syllabus in Mathematics IIGena ClarishAún no hay calificaciones
- CHEM 1314 SyllabusDocumento10 páginasCHEM 1314 SyllabusMisuna L.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ep 10Documento9 páginasEp 10Marie PhillineAún no hay calificaciones
- Dup Fairy TaleDocumento3 páginasDup Fairy Taleapi-334370724Aún no hay calificaciones
- Miguel LorentzebookDocumento125 páginasMiguel LorentzebookJair CarneiroAún no hay calificaciones
- Molloy College Division of Education Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasMolloy College Division of Education Lesson Planapi-311117700Aún no hay calificaciones
- Atomic and Molecular Structure and SymmetryDocumento136 páginasAtomic and Molecular Structure and SymmetryAlmas FatimaAún no hay calificaciones
- Evolution in the Classroom: Teaching the Theory of Biochemical EvolutionDocumento8 páginasEvolution in the Classroom: Teaching the Theory of Biochemical EvolutionRichard OyogAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit PlanDocumento45 páginasUnit Plannjc72832100% (1)
- 1st Triangle CongruenceDocumento3 páginas1st Triangle CongruenceMary Ellen ManogAún no hay calificaciones
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE - Lesson Plan On Solubility and MiscibilityDocumento7 páginasPHYSICAL SCIENCE - Lesson Plan On Solubility and MiscibilityBarbeicaht Sallin100% (1)
- MTH 422 MTH 422 Partial Differential Equations Teacher - Co .KeDocumento82 páginasMTH 422 MTH 422 Partial Differential Equations Teacher - Co .KeVerla MfeerAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulating Hypotheses and Identifying Test-Statistic: Grade 11 4 Quarter, Week 2 (Second) 2 NCR Statistics & ProbabilityDocumento7 páginasFormulating Hypotheses and Identifying Test-Statistic: Grade 11 4 Quarter, Week 2 (Second) 2 NCR Statistics & ProbabilityGuiller Jobert Suarez100% (2)
- 2018 OdonovanwdphdrevisedDocumento127 páginas2018 OdonovanwdphdrevisedSweta AkhoriAún no hay calificaciones
- Matter and Energy Provider Guide - FINALDocumento1108 páginasMatter and Energy Provider Guide - FINALJames OsterhoutAún no hay calificaciones
- CS423: Data Warehousing and Data MiningDocumento3 páginasCS423: Data Warehousing and Data MiningDaud AliAún no hay calificaciones
- 9th Grade FinalDocumento13 páginas9th Grade FinalAref DahabrahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry PearsonDocumento4 páginasChemistry PearsonpriscillavvsicseAún no hay calificaciones
- 9th Chemistry Aug SeptDocumento5 páginas9th Chemistry Aug SeptRamAún no hay calificaciones
- Simplify Radical ExpressionsDocumento11 páginasSimplify Radical ExpressionsrobertAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry VaexperienceDocumento4 páginasChemistry VaexperiencepriscillavvsicseAún no hay calificaciones
- 1lesson ResearchDocumento1 página1lesson Researchapi-240186198Aún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 4: Module 2BDocumento813 páginasGrade 4: Module 2BRivka ShareAún no hay calificaciones
- PS HUMSS 12A Module 2 Lesson 5 Lesson 6Documento29 páginasPS HUMSS 12A Module 2 Lesson 5 Lesson 6Manuel keven MangadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Curriculum Timeline: Content Area: Math Grade: 10 Class: Secondary Math IIDocumento15 páginasCurriculum Timeline: Content Area: Math Grade: 10 Class: Secondary Math IIapi-466330668Aún no hay calificaciones
- MTH411Documento116 páginasMTH411Engdasew BirhaneAún no hay calificaciones
- Year 9 Science Yearly Exam Notification 2020 2Documento5 páginasYear 9 Science Yearly Exam Notification 2020 2api-436869436Aún no hay calificaciones
- I. Answer All The Questions Given in The Workbook (Pg1-3)Documento10 páginasI. Answer All The Questions Given in The Workbook (Pg1-3)KelvinYongAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.SCIENCE-8 heat and temp. Oct. 2-5,2023Documento3 páginas1.SCIENCE-8 heat and temp. Oct. 2-5,2023Lovelyn TamanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Charles Law Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasCharles Law Lesson PlanRea Delos ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Amity UniversityDocumento3 páginasAmity UniversityTushar VasudevAún no hay calificaciones
- Syllabus in Introduction To Logic (2011)Documento8 páginasSyllabus in Introduction To Logic (2011)jetzon2022Aún no hay calificaciones
- MYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit QuestionDocumento4 páginasMYP Unit Planner: Stage 1: Integrate Significant Concept, Area of Interaction and Unit Questionzarna nirmal rawal100% (1)
- A Textbook of Physical ChemistryDocumento720 páginasA Textbook of Physical ChemistryKARLA MARY SOLARTE ARAUJO100% (2)
- Deffirentiated InstructionDocumento29 páginasDeffirentiated InstructionchristaltabasaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 9 Physics SyllabusDocumento26 páginasGrade 9 Physics SyllabusMario ButlerAún no hay calificaciones
- Ring and Field Theory - Kaiming ZhaoDocumento198 páginasRing and Field Theory - Kaiming Zhaoalimimi035Aún no hay calificaciones
- CLASS: - Answer: Station 1: Step Answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Station 2Documento2 páginasCLASS: - Answer: Station 1: Step Answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Station 2Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Result: Class Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Station 5 Total PositionDocumento1 páginaResult: Class Station 1 Station 2 Station 3 Station 4 Station 5 Total PositionBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Test pH Scale with Common Household SubstancesDocumento1 páginaTest pH Scale with Common Household SubstancesBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Userdata Paziras Chem101 Chap 03ADocumento15 páginasUserdata Paziras Chem101 Chap 03AIra MunirahAún no hay calificaciones
- Userdata Paziras Chem101 Chap 03ADocumento15 páginasUserdata Paziras Chem101 Chap 03AIra MunirahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Elements Test Station 4Documento1 páginaChemical Elements Test Station 4Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocumento45 páginasChapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDaniel SinAún no hay calificaciones
- Test pH Scale with Common Household SubstancesDocumento1 páginaTest pH Scale with Common Household SubstancesBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusDocumento9 páginasForm 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Station 5: Test Your Memory Write The Element and Symbol According To The Proton Number Given. Each Group Member Must Write 4 AnswerDocumento1 páginaStation 5: Test Your Memory Write The Element and Symbol According To The Proton Number Given. Each Group Member Must Write 4 AnswerBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusDocumento9 páginasForm 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- F5 Maths YPDocumento19 páginasF5 Maths YPKelvinYongAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem Week 2013: Radon and XenonDocumento1 páginaChem Week 2013: Radon and XenonBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Elements Test Station 4Documento1 páginaChemical Elements Test Station 4Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Week Form 4: Stations Games: Chemical Elements Name Symbol Atomic NumberDocumento1 páginaChemistry Week Form 4: Stations Games: Chemical Elements Name Symbol Atomic NumberBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseDocumento7 páginasChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9 ExerciseAngie Kong Su MeiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem Week 2013: Radon and XenonDocumento1 páginaChem Week 2013: Radon and XenonBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusDocumento9 páginasForm 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2012 Chemistry (47494E36)Documento160 páginas(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Module SBP Perfect Score SPM 2012 Chemistry (47494E36)XiiaoAppleAún no hay calificaciones
- SMK Lutong: Bahagian ADocumento13 páginasSMK Lutong: Bahagian ABenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Marking Scheme Paper 3Documento23 páginasMarking Scheme Paper 3Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Skema Chemistry Paper 3Documento8 páginasSkema Chemistry Paper 3nurul atiqahAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Atomic Structure and States of MatterDocumento11 páginasUnderstanding Atomic Structure and States of MatterSemoi Mathew MatonAún no hay calificaciones
- Answer Q Paper 1Documento1 páginaAnswer Q Paper 1Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Addition ReactionsDocumento18 páginasAddition ReactionsBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Acids and AlkalisDocumento16 páginasAcids and Alkalispoorv1235570Aún no hay calificaciones
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4 Chemistry Paper 2 - QuestionsDocumento22 páginasPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun SBP 2011 Ting 4 Chemistry Paper 2 - Questionsnurul atiqah100% (1)
- HOTsSM MATEMATIKDocumento64 páginasHOTsSM MATEMATIKBenjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Kimia f4 Akhir Tahun SBP 2008Documento65 páginasKimia f4 Akhir Tahun SBP 2008Benjamin HiAún no hay calificaciones
- Pelaksanaan KBAT Dalam MatematikDocumento21 páginasPelaksanaan KBAT Dalam MatematikRoszelan Majid100% (1)
- PENGARUH CYBERBULLYING BODY SHAMING TERHADAP KEPERCAYAAN DIRIDocumento15 páginasPENGARUH CYBERBULLYING BODY SHAMING TERHADAP KEPERCAYAAN DIRIRizky Hizrah WumuAún no hay calificaciones
- 2004 Canon Bino BrochureDocumento6 páginas2004 Canon Bino BrochureCraig ThompsonAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is Gross Income - Definition, Formula, Calculation, and ExampleDocumento7 páginasWhat Is Gross Income - Definition, Formula, Calculation, and ExampleKapil SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- An IDEAL FLOW Has A Non-Zero Tangential Velocity at A Solid SurfaceDocumento46 páginasAn IDEAL FLOW Has A Non-Zero Tangential Velocity at A Solid SurfaceJayant SisodiaAún no hay calificaciones
- On-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsDocumento14 páginasOn-Chip ESD Protection Design For IcsMK BricksAún no hay calificaciones
- Huawei Switch S5700 How ToDocumento10 páginasHuawei Switch S5700 How ToJeanAún no hay calificaciones
- Phenolic Compounds in Rice May Reduce Health RisksDocumento7 páginasPhenolic Compounds in Rice May Reduce Health RisksMuhammad Usman AkramAún no hay calificaciones
- Investigation Report on Engine Room Fire on Ferry BerlinDocumento63 páginasInvestigation Report on Engine Room Fire on Ferry Berlin卓文翔Aún no hay calificaciones
- Communication in Application: WhatsappDocumento18 páginasCommunication in Application: WhatsappNurul SuhanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dice Resume CV Narendhar ReddyDocumento5 páginasDice Resume CV Narendhar ReddyjaniAún no hay calificaciones
- 2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolDocumento50 páginas2018 JC2 H2 Maths SA2 River Valley High SchoolZtolenstarAún no hay calificaciones
- User Manual - Rev3Documento31 páginasUser Manual - Rev3SyahdiAún no hay calificaciones
- Aluminium FOil SearchDocumento8 páginasAluminium FOil SearchAtul KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Weakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDDocumento38 páginasWeakness and Hypotonia: Prepared by DR Hodan Jama MDabdisalaan hassanAún no hay calificaciones
- MinistopDocumento23 páginasMinistopAlisa Gabriela Sioco OrdasAún no hay calificaciones
- FRP/HDPE septic tank specificationDocumento2 páginasFRP/HDPE septic tank specificationpeakfortuneAún no hay calificaciones
- REVISION OF INTEREST RATES ON DEPOSITS IN SANGAREDDYDocumento3 páginasREVISION OF INTEREST RATES ON DEPOSITS IN SANGAREDDYSRINIVASARAO JONNALAAún no hay calificaciones
- Epri ManualDocumento62 páginasEpri Manualdrjonesg19585102Aún no hay calificaciones
- Uhde Painting SpecificationDocumento34 páginasUhde Painting Specificationmohamed elmasryAún no hay calificaciones
- Case NoDocumento13 páginasCase NoLaurente JessicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Microscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeDocumento4 páginasMicroscopes Open Up An Entire World That You Can't See With The Naked EyeLouie Jane EleccionAún no hay calificaciones
- Remembering Manoj ShuklaDocumento2 páginasRemembering Manoj ShuklamadhukarshuklaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Machine Learning Top-Down Approach - Towards Data ScienceDocumento6 páginasIntroduction To Machine Learning Top-Down Approach - Towards Data ScienceKashaf BakaliAún no hay calificaciones
- PHCDocumento1 páginaPHCsinh24X7Aún no hay calificaciones
- Applying Graph Theory to Map ColoringDocumento25 páginasApplying Graph Theory to Map ColoringAnonymous BOreSFAún no hay calificaciones
- 6th GATEDocumento33 páginas6th GATESamejiel Aseviel LajesielAún no hay calificaciones
- Ajwin Handbuch enDocumento84 páginasAjwin Handbuch enEnzo AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- CEA-2010 by ManishDocumento10 páginasCEA-2010 by ManishShishpal Singh NegiAún no hay calificaciones
- Report On Indian Airlines Industry On Social Media, Mar 2015Documento9 páginasReport On Indian Airlines Industry On Social Media, Mar 2015Vang LianAún no hay calificaciones
- Abinitio Interview QuesDocumento30 páginasAbinitio Interview QuesVasu ManchikalapudiAún no hay calificaciones