Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Biology Final Exam Study Guide
Cargado por
api-236677776Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Biology Final Exam Study Guide
Cargado por
api-236677776Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Name:______________________
Biology: Final Exam Study Guide
15% of your Semester Grade
Study all labs, notes, and homework. You may make a hand-written, 3 x 5 notecard. 60% of test will cover Evolution -Be able to define natural selection and describe the steps of this biological process -Interpret types of natural selection (disruptive, directional, stabilizing) from graphs and word problems -Explain the terms: reproductive fitness, adaptation, selection pressure, evolution, and natural selection Understand reproductive isolating barriers, both pre-zygotic and post-zygotic -Explain the process of incipient speciation that Darwin described -Discuss key events and themes from the Darwin text, On the Origin of Species Gene flow natural selection fitness population individuals Sexual reproduction sexual selection mutation adaptations Fill in the blank: 1. Mutations happen to ____________. 2. Evolution happens to _______________. 3. ____________,such as large beak size, arise from random mutations that increase an individuals fitness. 4. _____________is the number of offspring an organism has during its lifetime, measures its evolutionary success 5. ________ is a piece of DNA that codes for a particular trait, such as beetle shell color. 6. ________ ___________ can best be defined as survival of the best adapted individuals to their environment. 7. The three sources of genetic variation are: ______________, _____________, and _______________. 8. Animals do not mate randomly, instead a trait like colorful feathers or a mating display represents a type of ________ ____________ to attract a mate. 9. A group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area are a __________. 10. If allele frequencies change from 20% Bb to 55% Bb in a rabbit population, the population is __________. 11. What is the relationship between evolution and genetics? populations gene evolving
Type of Natural Selection
Definition, graph, and specific animal example
Directional
Stabilizing
Disruptive
12. What are reproductive barriers and how they keep species separate?
13. Explain the difference among vestigial, homologous and analogous traits and give a specific example of each. VESTIGIAL TRAITS:
HOMOLOGOUS TRAITS:
ANALOGOUS TRAITS:
Darwin Text, On the Origin of Species, Short Answer Questions 14. Explain an example of a specialized animal adaptation mentioned in the Darwin text using the words adaptation, fitness, natural selection, and selection pressure.
15. Explain the evidence for evolution that has been discovered since the time of Darwin (Afterward). How has our understanding of the evolutionary process changed?
16. Describe the social and cultural climate during Darwins lifetime. How did people respond to his work in 1860? What events led to his eventual publication of On the Origin of Species in 1858?
30% of test will cover Genetics -Explain DNA structure, and why DNA replication must occur before cell division -Outline the processes of making a protein (transcription and translation) -Describe the work of Mendel and solve monohybrid and dihybrid Punnett squares -Be able to solve non-Mendelian inheritance Punnett square problems (Sex-linked, multiple alleles- ABO, incomplete dominance, and co-dominance) 1. What is the difference between dominant and recessive alleles?
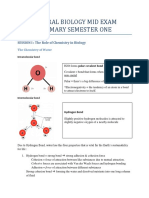
2. Draw a picture of DNA and label the following: nucleotide, sugar, base, phosphate, complimentary strand, double helix, and hydrogen bonds.
3. Explain why DNA needs to be replicated in cells.
4. Outline the process of transcription and translation. Include the terms mRNA, messenger, nucleus, amino acids, cytoplasm, and tRNA in your response.
5. What are 3 differences between mitosis and meiosis?
6. What are the four bases in DNA? ___________________ in RNA? __________________ 7. Transcribe and translate this DNA sequence. GGC CAG GCT TAT GAC CCG TAC CAT GAC CGA AAA GCC
8. Describe 3 differences between DNA and RNA.
9. Vocabulary: Word allele chromosome gene dominant recessive phenotype genotype heterozygous homozygous autosome sex chromosome Definition Any form of a particular gene for a trait. Example T or t
10. Describe the difference between incomplete dominance and co-dominance. Draw a Punnett square example for each.
11. Dihybrid Cross: a. What are the gametes for an individual who has the genotype of TTRr (FOIL): _________ b. What are the gametes for an individual who has the genotype of TtRr? ______________ c. What are the gametes for an individual who has the genotype ttRr? ________________ Multiple Alleles: Blood Type 12. A man with the genotype of AO marries a woman with a genotype/phenotype of AB. Will any of their children have type B blood?
13. A woman with type A blood marries a man with type B blood. They have a child with type O blood. How is this possible?
14. Assume that three claws (T) is dominant to two claws (t) in sloths, and that slowmovement (M) are dominant over fast movements (m). Cross a homozygous three clawed, fast moving sloth with a two-clawed, heterozygous slow-mover.
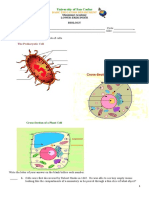
20% of the test will cover cells & cellular processes: - Understand key differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and between animal and plant cells - Explain types of cell transport (active vs. passive) - Identify specific types of cell transport and particle/water movement in diagrams (hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic solutions) 1. What are 3 key differences between prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (plants, animals, fungi, and protists)?
2. How are plant cells different from animal cells?
3. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory?
4. Draw a red blood cell in a hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solution. What will happen to each cell (burst, shrivel, same size)? Explain why with arrows showing the movement of WATER.
5. What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis? Is it passive or active transport? Why?
10% of the test will cover Introduction to Science: - Identify the parts of an experiment - Formulate a hypothesis, stating the independent and dependent variables - Know how to graph (line, bar, pie) and label data - Identify an observation as either qualitative or quantitative 1. List the steps of the scientific method in order.
2. What are dependent and independent variables? Give a specific example of each.
3. Why is a control group so important to an experiment?
4. Categorize each statement as observation (O) or inference (I). If its an observation, identify quantitative (QN) or qualitative (QL). The sky is gray. __________ The dog is chasing the cat. ___________ The cat looks really scared. __________ The scent of delicious chocolate is in the air. ________ There are 21 chairs in the science lab.___________ I dont like the song currently playing on the radio. It is awful! ___________ 8
También podría gustarte
- Worksheet 1: Biochemistry: NameDocumento24 páginasWorksheet 1: Biochemistry: Nameinfinite_kosmos100% (4)
- Doulci Activator For IOS 9Documento2 páginasDoulci Activator For IOS 9Syafiq Aiman100% (2)
- Cell QuizDocumento9 páginasCell QuizAhdzorizm PlcnAún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis WorksheetDocumento2 páginasMitosis Worksheetkatherine corvera100% (2)
- Grimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionDocumento18 páginasGrimoire of Baphomet A-Z EditionTheK1nGp1N100% (1)
- SCIENCE 10 Genetics Worksheets With Answers 1Documento4 páginasSCIENCE 10 Genetics Worksheets With Answers 1Anngela Arevalo Barcenas100% (1)
- MEIOSIS WorksheetDocumento8 páginasMEIOSIS WorksheetEliseo PamandananAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12De EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12Aún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet in BloodDocumento12 páginasWorksheet in BloodBryan Mae H. DegorioAún no hay calificaciones
- Dyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry PaperworkDocumento7 páginasDyi Dichotomous Key Guided Inquiry Paperworkapi-250608665Aún no hay calificaciones
- PCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideDe EverandPCAT Test Prep Biology Review--Exambusters Flash Cards--Workbook 3 of 4: PCAT Exam Study GuideCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (2)
- General Biology 2Documento35 páginasGeneral Biology 2Claries Cuenca100% (1)
- Grade 11 12 Science CurrDocumento264 páginasGrade 11 12 Science Currapi-301141568Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cell DivisionDocumento70 páginasCell Divisioncandice swanepoel100% (1)
- Cell and Cell TheoryDocumento13 páginasCell and Cell TheoryAnaJeanJumawidMarananAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocumento27 páginasCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsMARY ANN PANGANAún no hay calificaciones
- DNA Model (Cut-Out Sheet)Documento9 páginasDNA Model (Cut-Out Sheet)RA MemijeAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structure and Function: A Historical OverviewDocumento9 páginasCell Structure and Function: A Historical OverviewJesse ChateAún no hay calificaciones
- Classical (Mendelian) GeneticsDocumento32 páginasClassical (Mendelian) GeneticsKOMAL FATIMAAún no hay calificaciones
- The Basic Unit of Life - Cell TheoryDocumento21 páginasThe Basic Unit of Life - Cell TheoryMARY ANN PANGANAún no hay calificaciones
- Dichotomous Key Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasDichotomous Key Lesson Planapi-293760775Aún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1Documento4 páginasWorksheet As Level Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis 1AreebAún no hay calificaciones
- How Should Management Be Structured British English StudentDocumento7 páginasHow Should Management Be Structured British English Studentr i s uAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOLOGY (E/M): Passbooks Study GuideDe EverandBIOLOGY (E/M): Passbooks Study GuideAún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis WorksheetDocumento1 páginaMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- Edexcel iGCSE Biology Section E16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNADocumento2 páginasEdexcel iGCSE Biology Section E16 Chromosomes, Genes and DNACorry Sepvia100% (1)
- DNA Transcription Practice Test PDFDocumento5 páginasDNA Transcription Practice Test PDFWidjaya HS TeacherAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Cycle PowerPointDocumento23 páginasCell Cycle PowerPointroziel A.mabitasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Struct and FunctionDocumento4 páginasCell Struct and Functionamitdeo99Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocumento2 páginasCell Transport WorksheetVictoria Niño D100% (1)
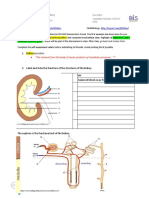
- Essential Biology Kidney WorksheetDocumento9 páginasEssential Biology Kidney WorksheetKarishmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Division Pipe Cleaner ActivityDocumento3 páginasCell Division Pipe Cleaner Activityanon_374314835Aún no hay calificaciones
- Life Science Lesson Plan-CellsDocumento2 páginasLife Science Lesson Plan-Cellsapi-372385087Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structures and Their Functions SLADocumento19 páginasCell Structures and Their Functions SLAMaricar Baria100% (1)
- Activities About HydrosphereDocumento4 páginasActivities About HydrosphereMaruja Ruiz100% (1)
- Cell and TransportDocumento77 páginasCell and TransportEugenie Francisco100% (1)
- Karnataka Email Id DataDocumento5173 páginasKarnataka Email Id DataSumalatha Venkataswamy100% (6)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To ScienceDocumento43 páginasChapter 1 - Introduction To Sciencenicky1213aAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitDocumento5 páginasScience Equipments Mathematics Equipment: Item Description Qty. UnitJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch. 3 Molecules of Life Review-2008Documento3 páginasCh. 3 Molecules of Life Review-2008Nopporn SaSaAún no hay calificaciones
- Meiosis WorksheetDocumento4 páginasMeiosis WorksheetCarl ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- 01 ElectricalDocumento15 páginas01 ElectricalKrishna KrishAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Test: Cell ReproductionDocumento3 páginasChapter Test: Cell Reproductionapi-25965241Aún no hay calificaciones
- DP 2 Biology Unit Science ResourcesDocumento4 páginasDP 2 Biology Unit Science Resourcesapi-246544437100% (1)
- Biology Unit Science 9Documento9 páginasBiology Unit Science 9api-373530490Aún no hay calificaciones
- General BiologyDocumento189 páginasGeneral BiologySamantha AgustinAún no hay calificaciones
- General Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDocumento26 páginasGeneral Biology Mid Exam Summary Semester OneDeborah ShirleenAún no hay calificaciones
- My COTDocumento3 páginasMy COTShellane Blanco SarduaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To BiologyDocumento6 páginasIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology 9 Grade and 10 GradeDocumento55 páginasBiology 9 Grade and 10 GradeA Muneeb QAún no hay calificaciones
- Asset QuestionsDocumento4 páginasAsset QuestionsReshma SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ds72-Review Summative Mitosis AssessmentDocumento4 páginasDs72-Review Summative Mitosis Assessmentapi-110789702Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Outline: ELL Tructure and UnctionDocumento5 páginasChapter Outline: ELL Tructure and Unctionrommel benamir100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento41 páginasCell Structure and FunctionAhkyluzLaniazAún no hay calificaciones
- Genbio2 12-Q3-SLM15Documento15 páginasGenbio2 12-Q3-SLM15Jordan Dingayan100% (1)
- (Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)Documento369 páginas(Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)NestiAún no hay calificaciones
- Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDocumento14 páginasCharacteristics and Classification of Living Organisms: IGCSE Biology (O610) WorkbookDr-Qussai ZuriegatAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Cycle StagesDocumento16 páginasCell Cycle StagesSean0% (1)
- Cell Parts FoldablesDocumento3 páginasCell Parts Foldablesapi-270241956Aún no hay calificaciones
- How Living Things ReproduceDocumento29 páginasHow Living Things ReproduceMargaux Cruz100% (1)
- Cell Biology and Disease UbD Unit PlanDocumento9 páginasCell Biology and Disease UbD Unit PlanAl MateoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsDocumento3 páginasMitosis and Meiosis WorksheetsVinson Eric0% (1)
- Lesson Plan - MitosisDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan - MitosisMolly Dugdale100% (1)
- 00-Intro Sci MetDocumento3 páginas00-Intro Sci Metapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Who Wants To Be A Great Scientist - Osmosis DiffusionDocumento34 páginasWho Wants To Be A Great Scientist - Osmosis Diffusionapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- 02-Contraceptives Grid ActivityDocumento5 páginas02-Contraceptives Grid Activityapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Respiratory System Study GuideDocumento2 páginasRespiratory System Study Guideapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sti SlidesDocumento18 páginasSti Slidesapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Muscle TypesDocumento19 páginasMuscle Typesapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Health Study Guide KeyDocumento6 páginasHealth Study Guide Keyapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gene To Protein Slides SultanyDocumento16 páginasGene To Protein Slides Sultanyapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- 02-Types of Contraception Research SheetDocumento1 página02-Types of Contraception Research Sheetapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- 01-Dear Abby AssignmentDocumento2 páginas01-Dear Abby Assignmentapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Muscle FatigueDocumento7 páginasMuscle Fatigueapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fetal Pig Drawing AssignmentDocumento1 páginaFetal Pig Drawing Assignmentapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bio Study Guide KeyDocumento8 páginasBio Study Guide Keyapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- 03 Skeleton SketchDocumento2 páginas03 Skeleton Sketchapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Natural Selection and SpeciationDocumento18 páginasNatural Selection and Speciationapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Population GeneticsDocumento12 páginasPopulation Geneticsapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 5 EcDocumento2 páginasAssignment 5 Ecapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- CladisticsDocumento9 páginasCladisticsapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 4Documento2 páginasAssignment 4api-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Darwin 3Documento2 páginasDarwin 3api-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocumento10 páginasNon Mendelian Geneticsapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Darwin 2Documento1 páginaDarwin 2api-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis Flipbook ProjectDocumento1 páginaMitosis Flipbook Projectapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Darwin AssignmentsDocumento1 páginaDarwin Assignmentsapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis ReadingDocumento4 páginasMitosis Readingapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mitosis SlidesDocumento14 páginasMitosis Slidesapi-236677776Aún no hay calificaciones
- JKFBDDocumento2 páginasJKFBDGustinarsari Dewi WAún no hay calificaciones
- OutliningDocumento17 páginasOutliningJohn Mark TabbadAún no hay calificaciones
- KPMG The Indian Services Sector Poised For Global AscendancyDocumento282 páginasKPMG The Indian Services Sector Poised For Global Ascendancyrahulp9999Aún no hay calificaciones
- MCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Documento11 páginasMCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Hiya ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Class 7 Summer Vacation PDFDocumento4 páginasClass 7 Summer Vacation PDFPrince RajAún no hay calificaciones
- All EscortsDocumento8 páginasAll Escortsvicky19937Aún no hay calificaciones
- Young Man Seeks Book to Contact Girl He MetDocumento1 páginaYoung Man Seeks Book to Contact Girl He MetJessie WattsAún no hay calificaciones
- TOTAL Income: POSSTORE JERTEH - Account For 2021 Start Date 8/1/2021 End Date 8/31/2021Documento9 páginasTOTAL Income: POSSTORE JERTEH - Account For 2021 Start Date 8/1/2021 End Date 8/31/2021Alice NguAún no hay calificaciones
- Fitting A Logistic Curve To DataDocumento12 páginasFitting A Logistic Curve To DataXiaoyan ZouAún no hay calificaciones
- Salzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Documento40 páginasSalzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Chandra SekaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Aerospace & Aviation Job RolesDocumento74 páginasAerospace & Aviation Job RolesBharat JainAún no hay calificaciones
- IkannnDocumento7 páginasIkannnarya saAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting Notes - 1Documento55 páginasAccounting Notes - 1Rahim MashaalAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 - JTC Template On Project ProposalDocumento10 páginas04 - JTC Template On Project Proposalbakelm alqamisAún no hay calificaciones
- The Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryDocumento2 páginasThe Apostolic Church, Ghana English Assembly - Koforidua District Topic: Equipping The Saints For The MinistryOfosu AnimAún no hay calificaciones
- How to use fireworks displays at Indian weddings to create magical memoriesDocumento3 páginasHow to use fireworks displays at Indian weddings to create magical memoriesChitra NarayananAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To ResearchDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To Researchapi-385504653Aún no hay calificaciones
- Krittika Takiar PDFDocumento2 páginasKrittika Takiar PDFSudhakar TomarAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Portfolio Cover LetterDocumento2 páginasFinal Portfolio Cover Letterapi-321017157Aún no hay calificaciones
- Insecticide Mode of Action Classification GuideDocumento6 páginasInsecticide Mode of Action Classification GuideJose Natividad Flores MayoriAún no hay calificaciones
- Pashmina vs Cashmere: Which Luxury Fiber Is SofterDocumento15 páginasPashmina vs Cashmere: Which Luxury Fiber Is SofterSJVN CIVIL DESIGN100% (1)
- Synthesis of The ArtDocumento2 páginasSynthesis of The ArtPiolo Vincent Fernandez100% (1)
- Ferret Fiasco: Archie Carr IIIDocumento8 páginasFerret Fiasco: Archie Carr IIIArchie Carr III100% (1)
- Class Homework Chapter 1Documento9 páginasClass Homework Chapter 1Ela BallıoğluAún no hay calificaciones
- Midterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFDocumento7 páginasMidterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFHan ZhongAún no hay calificaciones