Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Pump Pump Piping Presentation PDF
Cargado por
Poonam AshwinTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Pump Pump Piping Presentation PDF
Cargado por
Poonam AshwinCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
PUMPS
&
PUMP PIPING
By,
Sandeep More
Associate Engineer
Piping Department
Date 4
th
Dec 2006
Contents Contents
Pump Pump
-- Introduction to Pumps Introduction to Pumps
-- Classiication o Pump Classiication o Pump
-- Industry Codes & Standards Industry Codes & Standards
-- Selection Criteria or Pumps Selection Criteria or Pumps
-- NPSl & Caitation NPSl & Caitation
-- Deinitions Deinitions
Pump Piping Pump Piping
Suction piping or horizontal pumps Suction piping or horizontal pumps
Discharge piping or horizontal pumps Discharge piping or horizontal pumps
Arrangements o piping or pump handling hot suctions. Arrangements o piping or pump handling hot suctions.
Side suction & side discharge pump Side suction & side discharge pump
Vertical In line pumps Vertical In line pumps
Vertical pump ,\et \ell pump, Vertical pump ,\et \ell pump,
Vertical Barrel type or Cane pump Vertical Barrel type or Cane pump
Multi Serice pump Multi Serice pump
Reciprocating pump Piping Reciprocating pump Piping
Metering Pump Metering Pump
Pumps in the 1ankage Area Pumps in the 1ankage Area
Auxiliary pump piping arrangement Auxiliary pump piping arrangement
Pipe ent & drain System Pipe ent & drain System
Pump Location & Arrangement Pump Location & Arrangement
Pump Surrounding Support Pump Surrounding Support
ntoduction 1o Pump : ntoduction 1o Pump :
Pump is a mechanical deice used to add kinetic and potential energy to a
liquid or the purpose o moing it rom one point to another. 1his energy will
cause the liquid to do work such as low through a pipe or rise to a higher leel and
Pump gies pressure to luid passing through it and discharges the luid to the
outside.
Deinition :
Pumps are classiied on the basis o :-
1he applications they sere,
1he liquids they handle,
Orientation & Construction
No. o stages, No. o casings, 1ype o couplings ,Rigid , llexible,
1) D,vavic
2) Di.tacevevt
Classification Of Pump :
namic Pumps :
In which energy is continuously added to
increase the luid elocities within the machine
to alues greater than those occurring at the
discharge such that subsequent elocity
reduction within or beyond the pump produces
a pressure increase
isplacement Pump :
In which energy is periodically added by application o
orce to one or more moable boundaries o any desired
number o enclosed, luid-containing olumes, resulting
in a direct increase in pressure up to the alue required
to moe the luid through ales or ports into the
discharge line
1, Classiication by suction type :
- Single suction type
- Double suction type ,or big olume pump,
2, Classiication by the pump installation method :
- Vertical pump type
- lorizontal pump type
Other Classification :
Classification b structure and operation method :
Type
Classification
by structure
Classification
by operation metbod
$pecifics
lositi\e
displacement
pump
leciprocating
pump
- liston pump
- llunger pump
- Diapbragm pump
Tbis type of pump sucks in fluid tbrougb
reciprocating mo\ement of piston or plunger,
and discbarges fluid by pressing witb required
amount of pressure. lt is used wben bigb
pressure is required e\en tbougb tbe amount of
discbarge is small.
lotary
pump
- Gear pump
- $crew pump
- \ane pump
Tbis type of pump sucks in fluid tbrougb tbe
rotation mo\ement of rotor, and bas tbe
ad\antage of little pulsation due to tbe special
cbaracteristics in operation.
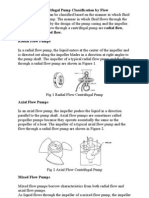
inetic pump
Centrifugal pump
- ladial flow
- \olute pump
- Mixed flow
pump
- Axial flow
pump
Tbis type of pump transfers energy to fluid
tbrougb centrifugal force by impeller rotation or
tbrougb tbe cbanges of size and direction of
section area of passage, and
con\erts \elocity energy pressure energy in \olute
cbamber or diffuser.
$pecial pump
- `et pump
- Gas lift pump
- Vesco pump
Tbis type of pump bas a efficiency and is not
used except for a special purpose.
evtrifvgat Pvv
A centriIugal pump transIorms mechanical energy Irom a rotating impeller into a
kinetic and potential energy required by the system.
Centriugal Pump
lorizontal Centriugal Pump
Reciprocating pumps :
W %hese are commonly used to move viscous liquids, inject chemicals or additives
into a system.
W #eciprocating pumps are used where a precise amount oI liquid is required to be
a delivered, also where the delivery pressure required is higher than can be
achieved with other types.
Reciprocating Piston 1ype Pump
orizontal & Vertical #eciprocating pump
#4tar, Pvv :
#otary pumps are used to move heavy or very viscous Iluids such as
grease, asphalt, heavy Iuel oil and sometimes heavy crude oils.
Gear Pump
Screw Pump
merican Petroleum nstitute (P
. 6, Centriugal Pumps or Petroleum, leay Duty Chemical, and Gas Industry Serices`.
2. 64, Positie Displacement Pumps - Reciprocating`.
3. 65, Positie Displacement Pumps - Controlled Volume`.
4. 66,Positie Displacement Pumps ,Rotary,
5. 6. General Purpose Gear Units or Reinery Serice`.
6. 68, Liquid Ring Vacuum Pumps`
. 682, Shat Sealing Systems or Centriugal and Rotary Pumps`.
merican Societ of Mechanical Lngineers (SML
. B3.M, lorizontal Lnd Suction Centriugal Pumps or Chemical Process`.
2. B3.2M, Vertical In-Line Centriugal Pumps or Chemical Process`
Process ndustr Practices (PP
. RLSP3l-9, Speciication or lorizontal Lnd Suction Centriugal Pumps`.
2. RLSP3V-9, Speciication or Vertical Centriugal Pumps`.
ndustr Codes and Standards : Ref : GLMS P-G-2
Selection Criteria Ior Centrifugal, Reciprocating, nd Rotar Pumps
efinitions
. Casing, Axially Split - Pump case split parallel to pump shat.
2. Casing, Radially Split - Pump case split transerse to pump shat axis.
3. Diuser -
Pump design in which the impeller is surrounded by diuser anes where the gradually enlarging passages change
liquid elocity head into pressure head.
4. Double Acting - Liquid is discharged during both orward and return strokes o the piston.
5. Duplex - Pump with two plungers or pistons.
6. lead, Acceleration - Pressure change due to changes in elocity in the piping system.
8. Impeller - Bladed member o rotating assembly o a centriugal pump which imparts orce to liquid.
9. Net Positie Suction lead ,NPSl, -
1otal suction head in meters ,eet, o liquid absolute determined at suction nozzle and reerred to datum
eleation, minus the apor pressure o liquid in meters ,eet, absolute. 1he datum eleation is the shat
centerline or horizontal pumps, the suction nozzle centerline or ertical in-line pumps, and the top o the
oundation or other ertical pumps.
. Net Positie Suction lead Aailable ,NPSlA, -
NPSl in meters ,eet, o liquid determined by Purchaser or the pumping system with the liquid at rated low
and
normal pumping temperature.
. Net Positie Suction lead Required ,NPSlR, -
NPSl in meters ,eet, determined by Supplier testing, usually with water. NPSlR is measured at the
suction lange and corrected to the datum eleation. NPSlR is the minimum NPSl at rated capacity required
to preent a head drop o more than 3 ,irst stage head in multistage pumps, due to caitation within pump.
2. Recirculation -
Controlling the quantity o low through a pump by bypassing discharge liquid back to suction.
4. Simplex - Pump with one plunger or piston.
5. Single Acting - Liquid is discharged only during orward stroke o the piston.
6. 1hrottling - Controlling low rate by reducing cross-sectional low area, usually by partially closing a ale in the
discharge piping.
. 1otal Dierential lead ,1Dl, - Pressure required in meters ,eet, o head that the pump must produce. 1he
head at the discharge pump lange minus the head at suction lange.
8. 1riplex - Pump with three plungers or pistons.
L1 POS1'L SUC1O HL (PSH
1he net positie suction head ,NPSl, is the absolute pressure iv ece.. 4f tbe tiqvia ra4r
re..vre that is aailable at the pump suction nozzle to moe the liquid into the eye
o the impeller.
1he dierence between NPSla and NPSlr is less than .3 .m at the time o
checking endor data sheet | that is, NPSla- NPSlr ,.3 m,|,
decision on NPSl test shall be made according to Lngineering Speciication SLS-
GA-2L and API 6.
Pumps where dierence between NPSlA and NPSlR is less than .6 meter are
not acceptable.
1he diameter o the pump suction port is usually bigger than the discharge or exit
diameter in order to minimize the kinetic energy head entering the pump, because
this kinetic energy decreases the maximum suction lit and enhances caitation.
NPSl Required d
NPSlr okl
\here, l : Pump dierential head
o : Caitation coeicient o 1homa
NPSl Aailable d
NPSla ,P - P2, k --- - zP l
Sp.Gr
\here, P : Pressure at suction liquid leel ,,,
P2 : Vapor pressure at suction temperature ,,,
zP : Pressure drop in suction line ,,,
l : leight between the normal liquid leel and pump centerline ,m,
Pump Dierential lead d
l ,Po- Ps, k----
Sp.Gr
\here, l : lead ,m,
Ps : Pump suction pressure ,,,
Po : Pump discharge pressure ,,,
Sp.Gr : Speciic graity at pumping temperature
C'11O
Deinition: Knocking due to ormation and subsequent collapse o apor bubbles.
,Indication: Noise,
Caitation is caused by the ormation o apor bubbles in a high-elocity, low-pressure
region and by the subsequent collapse when the bubbles moe to a higher pressure region.
Caitation can cause excessie erosion and ibration.
\ith moderate caitation in a centriugal pump, the pump will sound as though it is
pumping grael or a slurry o sand and grael.
Seere caitation will cause the discharge pressure to all and become highly erratic and
produce both low and pressure pulsation.
Cavitation occures due to :
Pump caitation can result rom insuicient aailable NPSl
ligh pump-suction elocities and long piping increase pressure luctuations in the
pump.
Vacuum systems seem more prone to unpredictable caitation than pressure systems.
Methods to avoid Cavitaion:
NPSla ,P,suction, - P,saturation, ~ NPSlr
Increase NPSla by
- Increase pressure at suction o pump
- Decrease liquid temperature
- Reduce head losses
- Reduce NPSlr ,Depends on Impeller inlet, Impeller design,
Pump low rate, impeller speed, type o liquid,
PUMP PIPING PUMP PIPING
Suction Piping for Horizontal Pumps :-
Line Size :
Suction piping is one or two line sizes larger than the pump suction nozzle size.
Flexibility of Suction Lines Flexibility of Suction Lines
Piping lexibility aects pump location.
Pump suction lines should be as short as possible, but with enough lexibility. Pump suction lines should be as short as possible, but with enough lexibility.
I possible , do not oerlap the pump and pipe support oundations, as it causes I possible , do not oerlap the pump and pipe support oundations, as it causes
structural design problems in combining oundations. structural design problems in combining oundations.
Suction Line Iittings Suction Line Iittings ::
Reducers should be as close as possible to the pump suction nozzle so that Reducers should be as close as possible to the pump suction nozzle so that
pump suction will not stared. pump suction will not stared.
Use Lccentric reducer with llat Surace up. ,lSU, Use Lccentric reducer with llat Surace up. ,lSU,
Always use long radius elbow. Always use long radius elbow.
Air pocket ormed along upper side o pipe by concentric
reducer.
Strainers : Strainers :- -
Strainers will be located between pump suction block ale and pump. Strainers will be located between pump suction block ale and pump.
1ype o strainer 1ype o strainer
, 1emporary strainer , 1emporary strainer
2, Permanent strainer 2, Permanent strainer
onical strainers onical strainers are longer than the basket type. are longer than the basket type.
1hese are used on suction lines 2` and larger. 1hese are used on suction lines 2` and larger.
lor lor basket and conical tpes basket and conical tpes a remoable a remoable
spool piece must be proided downstream o spool piece must be proided downstream o
suction block ale suction block ale
Flat strainers Flat strainers use with ery use with ery
short suction lines where no short suction lines where no
debris is expected debris is expected
athtub or tee type strainers athtub or tee type strainers as most as most
expensive , it does not require unbolting and expensive , it does not require unbolting and
removing spool piece to remove the strainer. removing spool piece to remove the strainer.
- tpe strainer to permit sericing o the
strainer. Also, a blow-o connection may be
proided in the end cap to lush the strainer.
Block Vale :-
Suction line should hae positie shut o ale, use gate ale at the Up stream
o strainer.
Pump ales are operating ales, thus keep them as low as possible
Consideration of Cavitation
Caitation occurs when NPSlr is larger than NPSla. Caitation occurs when NPSlr is larger than NPSla. Caitation reduces the Caitation reduces the
perormance o pump, causes ibration or noise and corrodes the materials. perormance o pump, causes ibration or noise and corrodes the materials.
1hereore, minimize pressure loss on pump piping and, care shall be taken to 1hereore, minimize pressure loss on pump piping and, care shall be taken to
aoid driting on the nozzle. aoid driting on the nozzle.
Minimum required straight pipe on suction nozzle to preent driting Minimum required straight pipe on suction nozzle to preent driting
$uction type
lequired straigbt
pipe on suction
lemarks
End suction 2D `D $ee figure 1.
$ide
suction
$ingle suction 2D and o\er
$ee figure
2-1 and 2-2.
Double suction
1JD and o\er or insertion of
rectifying plate
Top
suction
$ingle suction 2D and o\er
$ee figure `.
Double suction 1JD and o\er
D- Suction Nozzle Size
igure 1. End suction piping igure 2-1. Side suction piping
Or inserts rectiying plate
,eccentric suction : 2D and oer,
ligure 2-2. Side suction piping
Consideration o
straight pipe at
suction side is not
necessary or
straight-up or
straight down.
Single
Single suction
: 2D and oer
Double suction
: D and oer
igure 3. %op suction piping
Consideration o air pocket on suction line
, Allow approximately ,2,5 o slope on suction line toward suction resource
i suction resource is lower than pump suction nozzle.
2, Allow ,2 and oer o slope on suction line toward pump at acuum tower.
,2 and oer
3 , I gate ale is to be installed on the line whose suction resource is located lower than the pump
suction nozzle, ale stem shall be horizontal.
Suction piping on tower or essel :
Vortex breaker is installed on tower or essel nozzle connected to pump nozzle.
1pical rrangement rawing
1. PUMP SUC% LE
orizontal
Vertical
A, lorizontal ell directly into pump suction results in an unbalanced
thrust on pump bearings.
,B, Use spool piece 3 pipe diameters long or long radius ell with center
ertical ane.
,C, May be installed with or without spool piece but 2 pipe diameters
spool is preerred.
- Ilexibilit of pipe for pump alignment after piping
Iollowing diagrams indicate correct and incorrect methods of attaching suction
piping
Shows proper method o connecting pump suction to a suction
header in order to aoid air pockets.
Represents a common error made suction piping to a centriugal
pump by placing piping oer an embankment o a reseroir, or
other obstruction.
ischarge Piping for Horizontal Pumps :-
Line Size :
Discharge nozzle size is normally smaller than the suction nozzle size.
ischarge Line Iittings :
Normally we use concentric reducers in the discharge.
But i a clearance problem comes up between the suction and discharge piping ,
then we use o eccentric reducer
A pressure gauge is located in the discharge line, and should be upstream o the check
and gate ales
Check 'alve is used in a pump discharge line to preent backlow in to the pump
causing the impeller to turn backwards and possible ruining the bearings.
Block valve Isolate the pump rom piping to proide maximum access or both in
place or maintenance or remoal.
Pump ischarge Line
1) 1 1/2 and Under
2) 2 and Larger
Use Swing / all %ype Check valve Use inged Ilapper Check valve
3) 4)
lor ligher line size 8` and aboe
5)
Handling Hot suctions :
I essel suction nozzle is higher
\hen header going to the two pump
is at same eleation as suction nozzle.
1hese are used or ery hot larger piping
Side Suction nd Side ischarge Pump Side Suction nd Side ischarge Pump (Ior utilit Water Lines
1hese are used or large duty dierential pressure and large bore lines, the pressure 1hese are used or large duty dierential pressure and large bore lines, the pressure
dierence between the pump suction and discharge , and are usually multi dierence between the pump suction and discharge , and are usually multi--stage pumps, stage pumps,
the liquid going through seeral stages o increasing the pressure beore reaching the side the liquid going through seeral stages o increasing the pressure beore reaching the side
discharge nozzle. No o ells should be optimize allowable nozzle loading. discharge nozzle. No o ells should be optimize allowable nozzle loading.
1he two 1he two--diameter pup can be eliminated i the elbow rom the suction nozzle is diameter pup can be eliminated i the elbow rom the suction nozzle is
horizontal. horizontal.
1his pump is horizontal split case .
1he top case can be remoed or maintenance on
this type o pump .
keep the top o the pump clear.
'ertical n-Line Pumps : ( Hdrocarbon Services
1he main adantage o this type o pump is to
Lliminate many stress problems
Location when there is no oundation required
1his type o pump is mounted directly into the pipe line. lor smaller sizes, the piping
system supports the pump and motor.
lor heay or Larger size in-line pumps oundation will be required
'ertical Barrel 1pe or Can pump Dry well Pump ) : D Tank )
1his type o pump is installed in cooling tower water circulating serice, retention
ponds and suction is taken rom a sump below grade.
In most cases, there is no suction piping to be considered, but the discharge line must be
routed to ensure good access or pump maintenance
Pumps can be used or more than one serice, such as pulling suction rom one
source and discharging to three dierent locations or multi-serice suction, which
using a pump or more than one serice.
Multi Service Pumps
Multi - Service Pumps :-
Reciprocating Pump Piping :
W 1hese lines should run close to the ground so that hold-downs can be used.
Suction and discharge piping to positie displacement reciprocating pumps shall
contain hold down restraints on piping to minimize the potential o pulsation
loading on pump nozzles should pulsation dampeners become inoperatie.
1o minimize the damaging eects o water hammer and other impulse type loading
on pump nozzles, Use swing type check ales in discharge lines in the
ertical position aboe rigidly supported elbows so that hammer loads may
be distributed to grade or steel.
Reciprocating Pump Piping
1hese pumps measured accurate flow rates that can be adjusted in operation to 1he
me provide a wide range oI varying Ilow rates.
Metering system is to control liquid discharge under a variet of back pressure
conditions according to precise olumetric requirements.
Since metering pumps permit little or no backlow, they are especially useul or
injecting liquids into containers or Ilow lines against high pressures.
Metering Pump :
Reciprocating Metering Pump
Installation o Dampers and Back Pressure Vale
Pulsation amper :
1he damper contains a diaphragm or bellows isolating the metered liquid rom an
air or gas padded chamber. its use eliminates hydraulic hammer, established more aorable
NPSl conditions on the inlet side o the pump, and allows use o smaller pipe size by
reducing peak liquid elocity and acceleration.
lor location o pumps in the tank arm area:
. Group together i economical
2. Make accessible or maintenance and operation
3. Locate outside o dyke area
In the routing o the suction lines, the preerred method would be to drop rom
the tank to the pumps. Aoid a direct run rom the tank into the suction nozzle. 1his can
cause problems in oerstress o the pump connection.
Pumps in the 1ankage rea :
Support o Piping In the tankage area, the supporting o piping is normally by:
Pipe sleepers
lield supports
Many pumps hae auxiliary piping that is supplied by the endor or the engineering Many pumps hae auxiliary piping that is supplied by the endor or the engineering
contractor . contractor .
\hen pump luid is used a line is attached to the ent connection on the pump case. \hen pump luid is used a line is attached to the ent connection on the pump case.
1he circulated luid must be sent back to the pump stream and return to the seal to 1he circulated luid must be sent back to the pump stream and return to the seal to
pump internal clearances. pump internal clearances.
In iscous or high temperature hydrocarbon liquids the seal luid medium circulates In iscous or high temperature hydrocarbon liquids the seal luid medium circulates
rom an external source through connections on the pump seal . 1his medium may be rom an external source through connections on the pump seal . 1his medium may be
clean gas or oil . clean gas or oil .
In ig the cooling water in and out o this particular pump is rom aboe grade , In ig the cooling water in and out o this particular pump is rom aboe grade ,
howeer many cooling water systems are below grade so the piping layout designer must howeer many cooling water systems are below grade so the piping layout designer must
ind suitable location or this connection. ind suitable location or this connection.
uxiliar Pump Piping rrangement :
uxiliary Pump Piping
Pipe 'ent nd rain Sstem :
W Are provide to escape air or vapour trapped in the casing.
Seal Ilushing
PPL 'L1 R SS1LM IOR PUMP:
Install on the place where access is easy during the operation. Install on the place where access is easy during the operation.
Suicient space shall be proided at and around pumps to enable maintenance and
remoal o all internal and external parts.
1he minimum walkway clearance around pumps will be 2'-6`.
1he pump should be located as close as possible to the source o suction. 1he main
reason or this is to minimize pressure drop. 1his keeps line sizes and equipment
eleations to a minimum.
Minimum clearance o 3'- is required between pumps, adjacent equipment,
oundation or other obstructions.
Pumps should be located inboard o oerhead pipe rack as much as possible in order Pumps should be located inboard o oerhead pipe rack as much as possible in order
to sae the required plant area. to sae the required plant area.
Pump Location rrangement : Pump Location rrangement :
lor maintenance o the pumps located under the pipe racks or steel structures, lor maintenance o the pumps located under the pipe racks or steel structures,
maintenance beam or hook shall be planned upward o the pump unless, maintenance beam or hook shall be planned upward o the pump unless,
,, Access way o maintenance ehicle is proided under the pipe rack. ,, Access way o maintenance ehicle is proided under the pipe rack.
,2, Access o automobile crane is possible. ,2, Access o automobile crane is possible.
Maintenance space mm required around pump and without major disassembly. Maintenance space mm required around pump and without major disassembly.
Pumps shall generally be lined up in parallel with the pipe rack to maintain a Pumps shall generally be lined up in parallel with the pipe rack to maintain a
uniormity o location. uniormity o location.
Pump discharge points to be ixed in a line below pipe rack and to be about 5 mm Pump discharge points to be ixed in a line below pipe rack and to be about 5 mm
away rom pipe rack bay. away rom pipe rack bay.
In hydrocarbon or other lammable luid serice, threaded construction shall not be
used or piping connected to pump, including branch piping within 6 eet o pump
suction or discharge langes or through suction or discharge block ales, which eer
is greater. Socket weld unions are acceptable.
Pump Spacing Height of Pump foundation Pump Spacing Height of Pump foundation
Pump Spacing : Pump Spacing :--
Suction pipe size ,B, Suction pipe size ,B,
Pump spacing ,mm, Pump spacing ,mm,
leight o pump oundation : leight o pump oundation :--
leight o pump oundation shall be leight o pump oundation shall be 3mm rom ground leel or loor 3mm rom ground leel or loor
leel i it is on the paing or inside o building. But it shall be 3 leel i it is on the paing or inside o building. But it shall be 3 5mm or the 5mm or the
area where lood is expected. area where lood is expected.
Up to 2
1500 2000 2500 3000 4000
2 - 5 6 - 10 12 - 14 16 - 18
Others Others ::
, By , By--pass line which is installed on pump discharge line shall be routed without pass line which is installed on pump discharge line shall be routed without
pocket. pocket.
2, Aoid installation o chemical or water supply line near the suction nozzle o 2, Aoid installation o chemical or water supply line near the suction nozzle o
reseroir so that air shall not be sucked in. reseroir so that air shall not be sucked in.
Support regarding o eccentricity o pump : Support regarding o eccentricity o pump :
,, Support shall be installed so that pipe and ale may not load on the pump nozzle. ,, Support shall be installed so that pipe and ale may not load on the pump nozzle.
,, Support nozzle surroundings. ,But, do not exceed m.,
,2, Suction line and discharge line shall be supported respectiely.
Pump Surroundings Support :-
,3, I support is installed right close to suction or discharge nozzle, it shall be ,3, I support is installed right close to suction or discharge nozzle, it shall be minutely minutely
adjustable type so that centering can be conenient. adjustable type so that centering can be conenient.
,4, A support installed around suction or discharge nozzle shall be such a type that piping
can be remoed and pump can be dismantled easily.
Un-necessary support with respect to the load on pump nozzle :-
Although support would not seem to be necessary with respect to the load on pump
nozzle, indicate it on the drawing considering the temporary support o piping during
the time o pump maintenance.
%W3 WA
También podría gustarte
- Pumps, Fans and Blowers and CompressorsDocumento80 páginasPumps, Fans and Blowers and CompressorsRomart Barosa100% (2)
- Pump document title under 40 charactersDocumento32 páginasPump document title under 40 charactersKehinde Adebayo100% (1)
- Centrifugal PumpsDocumento30 páginasCentrifugal PumpsNitish NairAún no hay calificaciones
- The Affinity Laws of Centrifugal PumpsDocumento8 páginasThe Affinity Laws of Centrifugal PumpsArunkumar SubramanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Booster PumpDocumento28 páginasBooster PumpCollin PhelpsAún no hay calificaciones
- T II P Training Program On Basic Process Engineering PracticesDocumento26 páginasT II P Training Program On Basic Process Engineering PracticesAsmita AndaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump Matching and Performance CurvesDocumento25 páginasPump Matching and Performance CurvesAnsarAún no hay calificaciones
- Flygt Vertical Column FAS VersionDocumento8 páginasFlygt Vertical Column FAS VersioncomedyboAún no hay calificaciones
- Course2a-Energy Efficiency PDFDocumento59 páginasCourse2a-Energy Efficiency PDFNazaruddin SinagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Eccentric Reducers and Straight Runs of Pipe at Pump SuctionEccentric Reducers and Straight Runs of Pipe at Pump SuctionDocumento4 páginasEccentric Reducers and Straight Runs of Pipe at Pump SuctionEccentric Reducers and Straight Runs of Pipe at Pump SuctionSudha SamantAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydraulic Resevoir Design Criteria PDFDocumento10 páginasHydraulic Resevoir Design Criteria PDF2345421Aún no hay calificaciones
- Flowcheck Guide To PumpsDocumento3 páginasFlowcheck Guide To PumpsFA AyAún no hay calificaciones
- Strainer YoshitakeDocumento25 páginasStrainer YoshitakeMuhammad ImranAún no hay calificaciones
- Selection of PumpsDocumento8 páginasSelection of Pumpssmohsinshah9492100% (9)
- Mep All QuestionsDocumento79 páginasMep All QuestionsbabaAún no hay calificaciones
- Study of The Centrifugal Pump Efficiency at Throttling and Speed ControlDocumento4 páginasStudy of The Centrifugal Pump Efficiency at Throttling and Speed ControlHassan SouleymanAún no hay calificaciones
- Compressors: Me7313 Industrial Automation and ControlDocumento13 páginasCompressors: Me7313 Industrial Automation and ControlNuwan DinushaAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Centrifugal Pumps All Classification Working PrinciplesDocumento14 páginasTypes of Centrifugal Pumps All Classification Working PrinciplesajiAún no hay calificaciones
- Boiler Feed Pump New 1Documento39 páginasBoiler Feed Pump New 1789krishnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Write Up On PumpsDocumento74 páginasWrite Up On PumpsGopal Reddy100% (1)
- Hydraulic Pumps Lec NotesDocumento30 páginasHydraulic Pumps Lec NotesDarsh MenonAún no hay calificaciones
- Applying-NPSH-to-metering-pumps - WORLD PUMPS PDFDocumento3 páginasApplying-NPSH-to-metering-pumps - WORLD PUMPS PDFMuhammad ImranAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Final Control ElementDocumento77 páginasChapter 3 Final Control Elementmuhammad izzulAún no hay calificaciones
- Bell and Gossett Sump DesignDocumento8 páginasBell and Gossett Sump DesignVelpandian ManiAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump PresentationDocumento66 páginasPump PresentationAnonymous K3FaYFlAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Read Pump CurveDocumento4 páginasHow To Read Pump CurvenghiemvhAún no hay calificaciones
- Numerical Simulation of A Centrifugal PumpDocumento22 páginasNumerical Simulation of A Centrifugal PumpShaik Nizam UddinAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Pumps and Their UsesDocumento10 páginasTypes of Pumps and Their UsesArjohn De Los Santos100% (1)
- DAB Pump BookDocumento41 páginasDAB Pump BooksuosvannakAún no hay calificaciones
- Centrifugal Pumps: Training Program at Petronet LNGDocumento30 páginasCentrifugal Pumps: Training Program at Petronet LNGAditya Mahajan100% (1)
- Pump FAQ's by Hydraulic Institute (UK)Documento61 páginasPump FAQ's by Hydraulic Institute (UK)Sajjad Ahmed100% (2)
- Screw Pumps 2013Documento8 páginasScrew Pumps 2013Samad A BakarAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump & Pump Piping PresentationDocumento55 páginasPump & Pump Piping PresentationEduard Gonzalo Rojas Cervantes100% (1)
- Jacques Chaurette - Pump System Analysis and Sizing (2002) PDFDocumento158 páginasJacques Chaurette - Pump System Analysis and Sizing (2002) PDFShubhankar KunduAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump PipingDocumento58 páginasPump PipingSoumitra Gupta100% (3)
- Pump BrochureDocumento10 páginasPump Brochuresen_subhasis_58Aún no hay calificaciones
- NTPC Project ReportDocumento31 páginasNTPC Project ReportDeepak Ranjan ParidaAún no hay calificaciones
- PumpsDocumento54 páginasPumpsMark SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Reciprocating Pump PratishthaDocumento13 páginasReciprocating Pump Pratishthamike rosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Using Variable Speed Drives VSDs in Pump Applications 1700774456Documento36 páginasUsing Variable Speed Drives VSDs in Pump Applications 1700774456hamedAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation of PumpDocumento46 páginasPresentation of PumpArindam SamantaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Centrifugal Pumps ROTODYNAMIC TwoDocumento70 páginas2 Centrifugal Pumps ROTODYNAMIC TwoAbdallah Mansour100% (1)
- Knockout DrumsDocumento1 páginaKnockout DrumsCheng Kai CongAún no hay calificaciones
- Impellers Fadol NaamaniDocumento22 páginasImpellers Fadol NaamaniMohammad AmmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Tech Brief 2013 - Reading Centrifugal Pump Curves PDFDocumento5 páginasTech Brief 2013 - Reading Centrifugal Pump Curves PDFFawaaz KhurwolahAún no hay calificaciones
- API 610 - Why BEP Should Be Between Normal Point and Rated PointDocumento7 páginasAPI 610 - Why BEP Should Be Between Normal Point and Rated PointMuhammad ImranAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump PrimingDocumento1 páginaPump PrimingronakuchAún no hay calificaciones
- Compressor Turbo-Air API a4-IRDocumento12 páginasCompressor Turbo-Air API a4-IRMachineryengAún no hay calificaciones
- Installation Engineering Data and Design Handbook for Liquefied Gas PumpsDocumento8 páginasInstallation Engineering Data and Design Handbook for Liquefied Gas Pumpsaugur886Aún no hay calificaciones
- A1 Management & Technical Consultant Pune: Training Program On Reciprocating CompressorDocumento14 páginasA1 Management & Technical Consultant Pune: Training Program On Reciprocating CompressorSandeep KocharAún no hay calificaciones
- Centrifugal Pump Classification by FlowDocumento2 páginasCentrifugal Pump Classification by FlowrajashruthyAún no hay calificaciones
- ASME B73 Pump Standards OverviewDocumento16 páginasASME B73 Pump Standards Overviewdang2172014Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cavitation Analysis CFDDocumento4 páginasCavitation Analysis CFDshdjjfAún no hay calificaciones
- Pump & Pump PipingDocumento55 páginasPump & Pump PipingManan100% (1)
- PumpDocumento196 páginasPumprahul kumar67% (3)
- Function of A PumpDocumento178 páginasFunction of A Pumpmostafa nabilAún no hay calificaciones
- Pumps: Team:-1-Hoda Nady 2-Amira Abdelhafez 3-Aeisha Omar 4-Salma Hegazy Prof - Yahia Hassan Magdy 2/28/2022Documento22 páginasPumps: Team:-1-Hoda Nady 2-Amira Abdelhafez 3-Aeisha Omar 4-Salma Hegazy Prof - Yahia Hassan Magdy 2/28/2022Abdelhameed NadyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 7Documento28 páginasChapter 7lockas222Aún no hay calificaciones
- Industrial Plant EngineeringDocumento71 páginasIndustrial Plant EngineeringIan Llapitan0% (2)
- Centrifugal Pump CalcDocumento55 páginasCentrifugal Pump CalcSeptian FirdausAún no hay calificaciones
- Short CutsDocumento1 páginaShort CutsKrishna MechAún no hay calificaciones
- Piping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSDocumento278 páginasPiping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSmahmoud38140% (1)
- 89..MLOP - Policy WordingsDocumento19 páginas89..MLOP - Policy WordingsPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Motor InsuranceDocumento5 páginasMotor InsurancePoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping Workshop GuideDocumento385 páginasASME B31.3 Process Piping Workshop Guideriswandi50% (4)
- Vedic MathsDocumento220 páginasVedic Mathstargettutorials5740100% (7)
- 03 PipspecsDocumento24 páginas03 PipspecsPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- 500 DS MEC 024 - Rev.a Mech Data SheetDocumento6 páginas500 DS MEC 024 - Rev.a Mech Data SheetPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- 03 PipspecsDocumento24 páginas03 PipspecsPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Ashwin Udhe 1 Introduction To Piping Engineering PDFDocumento6 páginasAshwin Udhe 1 Introduction To Piping Engineering PDFPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Vedic MathsDocumento220 páginasVedic Mathstargettutorials5740100% (7)
- PipingDocumento15 páginasPipingPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Vedic 123Documento1 páginaVedic 123Poonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Vedic MathsDocumento220 páginasVedic Mathstargettutorials5740100% (7)
- Tank PipingDocumento29 páginasTank PipingDRJULIUSJORDAN100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump PipingDocumento22 páginasCentrifugal Pump PipingBhupender Sharma100% (3)
- Ashwin1 PDFDocumento5 páginasAshwin1 PDFPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- PipingDocumento15 páginasPipingPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Intro PipingDocumento64 páginasIntro PipingAjay Kumar92% (12)
- c1011 Symm DMX Architecture Prod Desc GD PDFDocumento0 páginasc1011 Symm DMX Architecture Prod Desc GD PDFPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- PdmsDocumento150 páginasPdmsPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- PIPING SYSTEM CODES AND DESIGNDocumento73 páginasPIPING SYSTEM CODES AND DESIGNSebin MathewsAún no hay calificaciones
- Piping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSDocumento278 páginasPiping and Instrumentation Drawings in Aspen HYSYSmahmoud38140% (1)
- IsometricDots-quarter Inch PDFDocumento0 páginasIsometricDots-quarter Inch PDFPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- CompressorDocumento35 páginasCompressoravinash13100% (1)
- 33C Piping SpecDocumento4 páginas33C Piping SpecPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- New SpecDocumento2 páginasNew SpecPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- 11ADocumento7 páginas11APoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Ball Valves, Flanges, Caps & More Steel ComponentsDocumento13 páginasBall Valves, Flanges, Caps & More Steel ComponentsPoonam AshwinAún no hay calificaciones
- College Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Solutions ManualDocumento36 páginasCollege Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Solutions Manualshippo.mackerels072100% (22)
- Booklet English 2016Documento17 páginasBooklet English 2016Noranita ZakariaAún no hay calificaciones
- Volume 4-6Documento757 páginasVolume 4-6AKAún no hay calificaciones
- Repair Max II Pump 310894lDocumento20 páginasRepair Max II Pump 310894lAndreina FajardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Description of Classroom Management PlanDocumento10 páginasDescription of Classroom Management Planapi-575843180Aún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study On Global Branding - DuluxDocumento18 páginasCase Study On Global Branding - DuluxAakriti NegiAún no hay calificaciones
- Materials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneDocumento10 páginasMaterials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneVikrant Saumitra mm20d401Aún no hay calificaciones
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Development Associates, IncDocumento3 páginasMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Development Associates, IncDedi MulyadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Delhi Police ResultDocumento26 páginasDelhi Police ResultExam Aspirant100% (1)
- Lambika YogaDocumento2 páginasLambika Yogavsyamkumar100% (3)
- Genigraphics Poster Template 36x48aDocumento1 páginaGenigraphics Poster Template 36x48aMenrie Elle ArabosAún no hay calificaciones
- MechanismDocumento17 páginasMechanismm_er100Aún no hay calificaciones
- IELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayDocumento2 páginasIELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayOlya HerasiyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lect 1.2 Principles of Food Process DesignDocumento43 páginasLect 1.2 Principles of Food Process Designmahmoud hassanAún no hay calificaciones
- English 2.2 FPT PolytechnicDocumento10 páginasEnglish 2.2 FPT PolytechnicKieu Mai Trang (FPL HCM)0% (1)
- Rustia V Cfi BatangasDocumento2 páginasRustia V Cfi BatangasAllen GrajoAún no hay calificaciones
- Aligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic CapabilitiesDocumento16 páginasAligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic Capabilitiesyasit10Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mechanics of Materials: Combined StressesDocumento3 páginasMechanics of Materials: Combined StressesUmut Enes SürücüAún no hay calificaciones
- Tiger Tales: From Colonial MalayaDocumento16 páginasTiger Tales: From Colonial MalayamatarsAún no hay calificaciones
- Armitage Tutorial for Cyber Attack ManagementDocumento54 páginasArmitage Tutorial for Cyber Attack Managementworkmumbai3870Aún no hay calificaciones
- ExportDocumento18 páginasExportDolon MukherjeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Advantages of Computerizing and Networking ComputersDocumento5 páginasAdvantages of Computerizing and Networking ComputersIn BioAún no hay calificaciones
- Internal Disease AnsDocumento52 páginasInternal Disease AnsKumar AdityaAún no hay calificaciones
- Day 2 TaskDocumento4 páginasDay 2 TaskYaathriganAún no hay calificaciones
- Salt Analysis-Ferric ChlorideDocumento3 páginasSalt Analysis-Ferric ChlorideVandana0% (1)
- Benokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)Documento617 páginasBenokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)colleen100% (1)
- Eca Important QuestionsDocumento3 páginasEca Important QuestionsSri KrishnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog To Digital Conversion (ADC)Documento62 páginasAnalog To Digital Conversion (ADC)Asin PillaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hall Design For SpeechDocumento1 páginaHall Design For SpeechSarovar SaroAún no hay calificaciones