Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Heat Exchanger Tube Bundle Inspection
Cargado por
Venkatesh Natla100%(4)100% encontró este documento útil (4 votos)
408 vistas3 páginastube bundle
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentotube bundle
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
100%(4)100% encontró este documento útil (4 votos)
408 vistas3 páginasHeat Exchanger Tube Bundle Inspection
Cargado por
Venkatesh Natlatube bundle
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 3
IndianOiI
6.0 INSPECTION PROCEDURES
6.1 INSPECTION OF SHELL, CHANNELS AND SHELL COVERS
General visual inspection of inside/ outside surfaces and welds
shall be done for signs of pitting, grooving, scaling, crack, erosion
of impingement attack etc.
Depth of pits can be measured by pit depth gauge.
Thickness survey of shell, nozzles and components etc. shall be
carried out using ultrasonic instruments.
Shell portions adjoining tube bundles, baffles and inlet impingement
plates shall be checked for erosion corrosion.
Carbon Steel shells need to be checked internally for localized
grooving in the vicinity of non ferrous baffles due to galvanic
corrosion.
Bottom section of shell as well as areas around outlet nozzles
should be critically examined in overhead condensers.
The gasket seats of all the nozzles, shell, channel and shell cover
flanges shall be visually examined for corrosion or damage.
Straight edge where possible may be used for checking flatness
and uniformity of gasket seats.
n Condensers/ Coolers where water is normally on tube side,
channel section and floating head shall be critically examined for
pitting and corrosion.
Thinning of partition plate edges, which may take place due to
galvanic corrosion, should also be examined.
Use of aluminum alloy sacrificed anodes in channel and floating
head side is to be practiced.
Painting of channel section, floating head with chlorinated
rubber/coaltar paint after thorough cleaning is to be carried out to
mitigate corrosion for cooler & condensers.
The condition of sacrificial anodes to be checked for reuse or
replacement. The procedure for installation of anodes in
condensers & coolers is enclosed as annexure -V
Drain nozzles and other small dia. connections are to be critically
examined for thinning.
Weld areas is to be critically examined if the service is caustic,
Amine, particularly if shell is not stress relieved.
Exchangers under Hydrogen service are to be checked for
hydrogen blistering.
Exchangers in Naphphenic acid environment are to be critically
checked at weld joint locations for naphphenic acid attack.
6.2 INSPECTION OF TUBE BUNDLES
Tube bundles should be inspected visually immediately after pulling
out and before cleaning. The colour, type, amount and locations of
deposits often help to pinpoint corrosion problems.
Page 30 of 84
IndianOiI
Corrosion product should be got analyzed.
Tubes near baffles shall be critically examined for any grooving and
baffles shall be checked for hole enlargement.
Tube ends should be examined for tube end corrosion and thinning.
Brass tubes shall be checked externally for signs of dezincification
or pitting or circumferential cracks.
nternal condition of all tubes can be checked with the help of
boroscope/ fiberscope, by cutting one tube as a representative
tube.
nternal condition of the tube in the peripheral or adjacent rows
could be examined by radiography when the tube bundle is out of
the shell.
n case a number of tubes are found leaking during hydraulic testing
it is advisable to remove one leaky tube at random for carrying out
through investigation for establishing reasons of failure and
deciding the residual service life of tube bundle.
Baffles, tie rods, tube sheets and floating head covers shall be
visually inspected for corrosion and distortion.
Gasket surfaces of tube sheets shall be checked for any damage.
Tube sheets and covers shall be checked for distortion by placing a
straight edge against them.
Tube wall thickness can be measured by measuring inside and
outside tube diameter with the help of calipers.
n case of stainless steel tube bundles, tubes should be critically
examined for pitting and stress corrosion cracking.
The tube bundle shall be retuned/ replaced after sufficient tubes
have been plugged to interfere with the performance of the
exchanger. As a general rule plugging in each pass is limited to
20%.
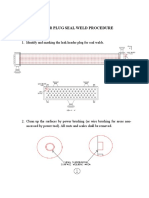
The metallurgy of taper plug is to be preferably same to that of tube
metallurgy to avoid galvanic corrosion.
The taper plugs should have an included angle of 5-1/2 degree or
less. The plug dimension depends on tube size and thickness. As a
guideline a typical plug dimension and fitment arrangement is
enclosed in Annexure-X.
6.3 INSPECTION OF GASKETS
The new gasket should be thoroughly checked for scratches and
damage surface.
Gasket should be properly positioned before tightening of bolt.
The use of particular type of gasket as specified by manufacturer is
to be ensured.
6.4 INSPECTION OF BREECH LOCK EXCHANGERS
The following components shall be cleaned thoroughly using chloride
free solvents and mechanical tools. After cleaning, these shall be
Page 31 of 84
IndianOiI
checked by liquid dye penetrant/ magnetic particle testing and offered
to inspection for witnessing.
(a) Following gasket seating surfaces;
Tube sheet to shell
Tube sheet to channel box
Channel box to channel cover
Diaphragm to shell barrel
(b) Lock ring and barrel acme threads
(c) Diaphragm (if replaced new one shall also be offered)
(d) Split ring, split ring grooves
(e) nner and outer compression rings
(f) nternal flange
(g) nner sleeve
(h) Special partition plate to channel box welded joints
(i) Shell
(j) Channel
(k) Partition plate welds
Page 32 of 84
También podría gustarte
- Heat Exchanger InspectionDocumento7 páginasHeat Exchanger InspectionHamid Albashir100% (1)
- Boiler Tube FailureDocumento7 páginasBoiler Tube FailureBhupendra GobadeAún no hay calificaciones
- Inspection of Heat ExchangerDocumento83 páginasInspection of Heat ExchangerRaghavanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tube To Tube SheetDocumento9 páginasTube To Tube Sheetcmpatel_00100% (2)
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Inspection GuideDocumento10 páginasShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Inspection GuideVarun MalhotraAún no hay calificaciones
- Header Plug Seal Weld ProcedureDocumento2 páginasHeader Plug Seal Weld ProcedureMohd Shafuaaz KassimAún no hay calificaciones
- Jutasama Tube Expansion ProcedureDocumento3 páginasJutasama Tube Expansion Procedurefizanlamin100% (1)
- Retubing Plan On Heat Exchanger in Methanol PlantDocumento22 páginasRetubing Plan On Heat Exchanger in Methanol PlantBayu FrilyanAún no hay calificaciones
- High-Pressure Shell & Tube Heat ExchangersDocumento19 páginasHigh-Pressure Shell & Tube Heat ExchangersNila Gama100% (1)
- Tube To Tube SheetDocumento59 páginasTube To Tube Sheet0101100175% (12)
- PWHT For Shell Nozzle of Steel Storage Tanks-21Documento27 páginasPWHT For Shell Nozzle of Steel Storage Tanks-21الGINIRAL FREE FIRE100% (1)
- Maintaining and Repairing Heat Exchanger TubesDocumento14 páginasMaintaining and Repairing Heat Exchanger TubesMicheal Brooks100% (1)
- Inspection, Maintenance and Testing of Fired HeatersDocumento27 páginasInspection, Maintenance and Testing of Fired HeatersVicente Regulez FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Inspection of Heat ExchangersDocumento20 páginasInspection of Heat Exchangersadel100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger InspectionDocumento27 páginasHeat Exchanger Inspectionglazetm100% (23)
- Rev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureDocumento24 páginasRev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureHansel FrancisAún no hay calificaciones
- 3LPE Repair ProcedureDocumento3 páginas3LPE Repair Procedurelhanx2Aún no hay calificaciones
- CHEVRON Maintenance Heat ExchangerDocumento23 páginasCHEVRON Maintenance Heat Exchangerbabak mir50% (2)
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design ConsiderationsDocumento55 páginasShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Design ConsiderationsCc12 22tAún no hay calificaciones
- Plug Process Repair Heat Exchangers PDFDocumento6 páginasPlug Process Repair Heat Exchangers PDFJOÃO CARLOS SILVAAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Exchanger InspectionDocumento11 páginasHeat Exchanger InspectionVivek Bhangale100% (1)
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocumento138 páginasShell and Tube Heat ExchangersMinh Hiếu CaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Collar Bolts: in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocumento2 páginasCollar Bolts: in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersMahdi HocineAún no hay calificaciones
- Tube To Tube-Sheet Welding For Special Process Heat ExchangersDocumento16 páginasTube To Tube-Sheet Welding For Special Process Heat Exchangers4nagAún no hay calificaciones
- LEAK PRESSURE TEST TITLEDocumento68 páginasLEAK PRESSURE TEST TITLEJayaraman KamarajAún no hay calificaciones
- CHEVRON Inspection and Testing Heat ExchangerDocumento21 páginasCHEVRON Inspection and Testing Heat ExchangerVivek Bhangale100% (3)
- Expansion ProcedureDocumento13 páginasExpansion ProcedureMani Tamil100% (1)
- Investigation and Repair of H (1) - E.R Flange LeakDocumento19 páginasInvestigation and Repair of H (1) - E.R Flange LeakriysallAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Exchanger Tube Material SpecificationsDocumento2 páginasHeat Exchanger Tube Material SpecificationssdrtfgAún no hay calificaciones
- CHE Retubing ReportDocumento29 páginasCHE Retubing ReportRajesh KtrAún no hay calificaciones
- Garlock Metal - Gaskets TorqueDocumento48 páginasGarlock Metal - Gaskets TorqueakenathorAún no hay calificaciones
- HEAT EXCHANGERS MDocumento143 páginasHEAT EXCHANGERS MHeet Patel100% (1)
- 09-00 - Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers For Routine ServiceDocumento17 páginas09-00 - Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers For Routine ServiceFolayemiAún no hay calificaciones
- Storage Tank FailureDocumento6 páginasStorage Tank Failureramyatan SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- KochDocumento181 páginasKochRichard FelipAún no hay calificaciones
- Post Weld Treatment Procedure For Piping Spools (Abj) KN Rev-2Documento15 páginasPost Weld Treatment Procedure For Piping Spools (Abj) KN Rev-2williamsenAún no hay calificaciones
- Breech LockDocumento12 páginasBreech LockPramod Dixit100% (1)
- 10080-1-SS-PP-018 - PMI Procedure PDFDocumento23 páginas10080-1-SS-PP-018 - PMI Procedure PDFDrM Design2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sop-miqa-Attk-001 - Pressure Vessel Inspection For Migas Re-Certification (2007)Documento10 páginasSop-miqa-Attk-001 - Pressure Vessel Inspection For Migas Re-Certification (2007)Iksan Adityo MulyoAún no hay calificaciones
- Flange Weld Build UpDocumento2 páginasFlange Weld Build UpMohd Shafuaaz KassimAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrity Assessment of Pressure VesselDocumento6 páginasIntegrity Assessment of Pressure Vesselmrb193100% (1)
- Method Statement For RetubingDocumento4 páginasMethod Statement For RetubingJeffrey78% (9)
- Collar Bolts in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocumento3 páginasCollar Bolts in Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersBaher ElsheikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Tube To Tubesheet Joint TypeDocumento2 páginasTube To Tubesheet Joint TypeExsan Othman100% (1)
- STS Qac Sop 002 Heat Exchanger Retubing ProcedureDocumento4 páginasSTS Qac Sop 002 Heat Exchanger Retubing Proceduremohd as shahiddin jafri50% (2)
- CRAHF Weld OverlayDocumento2 páginasCRAHF Weld OverlayGogulu KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- GIS 36-107 Integral Cladding Weld Overlay and Limited LooseDocumento17 páginasGIS 36-107 Integral Cladding Weld Overlay and Limited LooseMarkoJovicin100% (5)
- Heat Exchanger Inspection PDFDocumento8 páginasHeat Exchanger Inspection PDFreezmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Principles of Tube Line FabricationDocumento69 páginasBasic Principles of Tube Line Fabricationshan4600Aún no hay calificaciones
- OGA 2017 Integrity Management Assessing Dealing With Pipeline RoadDocumento38 páginasOGA 2017 Integrity Management Assessing Dealing With Pipeline Roadalpha bettaAún no hay calificaciones
- INSPECT HEAT EXCHANGERDocumento82 páginasINSPECT HEAT EXCHANGERBalaji VenkatesanAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydromechanical - Technical SpecificationsDocumento16 páginasHydromechanical - Technical SpecificationsdishkuAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 2 Onstream and Shutdown InspectionDocumento135 páginasSection 2 Onstream and Shutdown Inspectionariyamanjula2914100% (1)
- Above Ground Storage Tanks PresentationDocumento28 páginasAbove Ground Storage Tanks PresentationRamesh sivanAún no hay calificaciones
- MARINE SURVEYS - D4 Sm. 6 - 2019Documento50 páginasMARINE SURVEYS - D4 Sm. 6 - 2019Niki Veranda Agil PermadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Operation & Maintenance Manual For Bolted Steel Tanks: Complete InstallationDocumento6 páginasOperation & Maintenance Manual For Bolted Steel Tanks: Complete InstallationIrvansyah RazadinAún no hay calificaciones
- External Visual Inspections of Pressure VesselsDocumento2 páginasExternal Visual Inspections of Pressure Vesselssamy singaporeAún no hay calificaciones
- Piping FundamentalsDocumento47 páginasPiping FundamentalsNguyễn Thanh TùngAún no hay calificaciones
- #5 Guide To Ship's Piping (Black & White)Documento25 páginas#5 Guide To Ship's Piping (Black & White)Dony Eko Cahyadi100% (2)
- Inspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsDocumento9 páginasInspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsClaudia Mms100% (1)
- GtawDocumento1 páginaGtawVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Inspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsDocumento9 páginasInspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsClaudia Mms100% (1)
- Inspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsDocumento9 páginasInspection and Welding Repairs of Pressure VesselsClaudia Mms100% (1)
- Pipe Expansion and Support - International Site For Spirax SarcoDocumento8 páginasPipe Expansion and Support - International Site For Spirax SarcoVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Special ConsiderationDocumento1 páginaSpecial ConsiderationVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Tungsten Arc WeldingDocumento2 páginasGas Tungsten Arc WeldingVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Special ConsiderationDocumento1 páginaSpecial ConsiderationVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Oisd RP 233 DraftDocumento66 páginasOisd RP 233 DraftVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrode Classification by Aws A 5.1 PDFDocumento1 páginaElectrode Classification by Aws A 5.1 PDFVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Rajasthan Block, Barmer - Offshore Technology PDFDocumento1 páginaRajasthan Block, Barmer - Offshore Technology PDFVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Inspection Manual For PipingDocumento183 páginasInspection Manual For PipingMartin Zaballa100% (3)
- Api 5 LDocumento1 páginaApi 5 LVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Troubleshooting WeldingDocumento1 páginaTroubleshooting WeldingVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fitting of PipeDocumento1 páginaFitting of PipeVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Welding The Root by GtawDocumento1 páginaWelding The Root by GtawVenkatesh NatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ahmedabad City Gas Distribution Project (Vatva)Documento1 páginaAhmedabad City Gas Distribution Project (Vatva)suman0% (1)
- Ur S1 4361Documento4 páginasUr S1 4361APIAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding and Mitigating Tin WhiskersDocumento6 páginasUnderstanding and Mitigating Tin WhiskersJon SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Terminator II TMCX PDFDocumento2 páginasTerminator II TMCX PDFAldi NasohaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Diffusers BrochureDocumento20 páginasGas Diffusers BrochureReddisekharaGurramAún no hay calificaciones
- Diop, Cheikh Anta - A Origem Africana Da Civilização - Mito Ou RealidadeDocumento230 páginasDiop, Cheikh Anta - A Origem Africana Da Civilização - Mito Ou RealidadeJosé Renato Teixeira100% (1)
- SR - No. Name of The Book SpecificationDocumento7 páginasSR - No. Name of The Book SpecificationKiukStaksAún no hay calificaciones
- Electroplating Process & VariablesDocumento7 páginasElectroplating Process & VariablesRoynika shaluAún no hay calificaciones
- Sheet MetalDocumento75 páginasSheet MetalMalik Shahid SultanAún no hay calificaciones
- Fire Piping Astm A795Documento3 páginasFire Piping Astm A795sinahimsAún no hay calificaciones
- Madina Trading WPS DetailsDocumento11 páginasMadina Trading WPS DetailsMAT-LIONAún no hay calificaciones
- Alloys: Stainless SteelsDocumento2 páginasAlloys: Stainless Steelspankaj_pawar89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Algoma SteelDocumento18 páginasAlgoma Steelsahzaidi544Aún no hay calificaciones
- BS en 1708-3-12Documento22 páginasBS en 1708-3-12gaso99Aún no hay calificaciones
- Astm E381 2020Documento5 páginasAstm E381 2020sree sudha100% (1)
- Handbook To BC1 2012Documento53 páginasHandbook To BC1 2012undf2567% (3)
- Indian Stainless Steel IndustryDocumento29 páginasIndian Stainless Steel IndustryImran ansariAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Unit 2 - Arc, Gas, Plastic Welding, LBW, EBW and Thermit WeldingDocumento96 páginas3 Unit 2 - Arc, Gas, Plastic Welding, LBW, EBW and Thermit WeldingAditya KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Hot-Rolled - Plate: Data SheetDocumento2 páginasHot-Rolled - Plate: Data SheetRichard Vica CalvoAún no hay calificaciones
- Fractography - An Important Tool For Analyzing Metal FailurewsDocumento5 páginasFractography - An Important Tool For Analyzing Metal FailurewsalexandroneisAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipe CalculationDocumento10 páginasPipe CalculationTrishul Nath PallayAún no hay calificaciones
- Workshop PracticeDocumento114 páginasWorkshop PracticeDiriba SufeAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Turbine Super Alloy CompositionsDocumento3 páginasGas Turbine Super Alloy CompositionsYatishKumarJainAún no hay calificaciones
- Welding TechnologyDocumento390 páginasWelding Technologygueess100% (2)
- SAF-FRO - Welding Consumables CatalogueDocumento194 páginasSAF-FRO - Welding Consumables CatalogueLLAún no hay calificaciones
- Technical Brochure - Ferritics - MolyDocumento5 páginasTechnical Brochure - Ferritics - MolyJoshua WalkerAún no hay calificaciones
- Material P Group Table 4 PDFDocumento1 páginaMaterial P Group Table 4 PDFshantilalAún no hay calificaciones
- MS For Welding Consumable ControlDocumento10 páginasMS For Welding Consumable Controlmansih457100% (1)
- Technical Data Sheet: Quakercool 7101 AFSDocumento2 páginasTechnical Data Sheet: Quakercool 7101 AFSSayed Erfan SajadiehAún no hay calificaciones
- Trellex Traclag Pulley LaggingDocumento16 páginasTrellex Traclag Pulley LaggingViet Nam M-TechAún no hay calificaciones