Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Experiment For Determining The Spring Constant K of A Material Is As Follows
Cargado por
Costas PaschalidesDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Experiment For Determining The Spring Constant K of A Material Is As Follows
Cargado por
Costas PaschalidesCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
1.
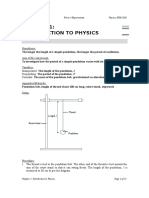
Experiment for determining the spring constant k of a material is as follows: F= kx Forces can be measured individually using a balance and an average for each mass can be found and used. L is found using a metre rule. And a set square to avoid parallax errors. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram above. Add 100g masses to the hanger and measure the extension by subtracting the original length from the reading on the metre rule. Continue to add masses until 20 N. Then remove masses and measure the extension (=compression) Repeat the experiment so that you get average values for the extension for each load. Plot a graph of Force against extension, of which the gradient will give you the spring constant k. F= kx Y=mx+c F=y x=extension c=0 and M (gradient) = k (spring constant)
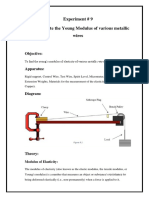
2. Experiment for determining the Young Modulus of a piece of wire: E= stress/ strain Stress is force per unit area Strain is extension per original length. Diameter of wire is calculated using a micrometer, measured at different points and axes along the wire The extension is calculated using a metre rule and by subtracting the original length from the readings. The wire to be used should have a length of about 2 metres, as larger length means larger extension for a given load, and therefore more easily readable extensions, reducing errors and uncertainties in the experiment. The wire should also be thin, because stress is force per unit area, so to get a larger stress you dont need such a large force if the area is small. Otherwise, a greater cross-sectional area means that a greater force has to be applied. Therefore, a thinner wire gives a greater extension. Strain is extension per original length, so there is a relationship between greater extension and longer length. Procedure: Thin copper wire is clamped between two wooden blocks at the end of the bench and passed over a pulley wheel at the other end. A weight hanger is attached to the wire close to the pulley and a metre rule is fixed to the bench. A stip of sticky tape is attatched to the wire so that the length of the wire from the end of the bench to the tape can
be measured and the extensions as well. The wire from the end of the bench to the strip of sticky tape is actually the part of the wire that is being investigated. Place masses (100g) and measure extension each time. Be careful! You should be wearing goggles protection when the wire breaks danger for eye damage. Experiment should be repeated to get Plot a graph of stress against strain. The gradient is the young modulus.
También podría gustarte
- PhysicsDocumento11 páginasPhysicszap_123Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2.8 Core Practical Investigating Force & ExtensioDocumento7 páginas1.2.8 Core Practical Investigating Force & Extensiokirisu kirisuAún no hay calificaciones
- Finding The Young Modulus of A Wire Student Worksheet: TheoryDocumento5 páginasFinding The Young Modulus of A Wire Student Worksheet: TheoryAleva KongAún no hay calificaciones
- Ses 211 Linear Distance MeasurementDocumento9 páginasSes 211 Linear Distance MeasurementFavour AbrahamAún no hay calificaciones
- Azim ExperimentDocumento3 páginasAzim Experimentfillyana01Aún no hay calificaciones
- Youngs ModulusDocumento4 páginasYoungs Modulusashishtelang2013100% (1)
- Experiment 9Documento4 páginasExperiment 9Muhammad ALI NoorAún no hay calificaciones
- TP: Tensile, Bending and Torsion Tests: 1. PrincipleDocumento2 páginasTP: Tensile, Bending and Torsion Tests: 1. PrincipleAlex SpechtAún no hay calificaciones
- D2 Measurement of Young Modulus of Iron: ObjectiveDocumento4 páginasD2 Measurement of Young Modulus of Iron: ObjectiveMartin JosephAún no hay calificaciones
- Youngs Modulus ExperimentDocumento1 páginaYoungs Modulus ExperimentArishaAún no hay calificaciones
- Deformation of SolidsDocumento13 páginasDeformation of SolidsKerry-Ann WilliamsAún no hay calificaciones
- Deformation of SolidDocumento37 páginasDeformation of SolidEllen Koh100% (1)
- Phy ProjectDocumento6 páginasPhy ProjectAryan KapoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Copper Wire Report For SubmissionDocumento11 páginasCopper Wire Report For SubmissionAdrien MccandlessAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab ReportDocumento5 páginasLab ReportMuhammad HaroonAún no hay calificaciones
- Standing Waves LabDocumento17 páginasStanding Waves LabOmarZinAbidineAún no hay calificaciones
- CP 3 - Young Modulus PDFDocumento3 páginasCP 3 - Young Modulus PDFcutie pieAún no hay calificaciones
- CP 3 - Young ModulusDocumento3 páginasCP 3 - Young ModulusPOPAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 7: Waves On A Vibrating String: Vincent Vuong March 4th, 2014 Tuesday 11am Roli Esha Ming-Hei TaiDocumento8 páginasExperiment 7: Waves On A Vibrating String: Vincent Vuong March 4th, 2014 Tuesday 11am Roli Esha Ming-Hei TaiVincent VuongAún no hay calificaciones
- An Approximation of The Acceleration of Gravity Using Experimental Methods With Period, Amplitude, and Length DependenciesDocumento5 páginasAn Approximation of The Acceleration of Gravity Using Experimental Methods With Period, Amplitude, and Length DependenciesMichael FangAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics RP1Documento3 páginasPhysics RP1Nicky.P - PianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Outline: Mechanical Properties of Textile FibersDocumento13 páginasOutline: Mechanical Properties of Textile FibersTamanna TasnimAún no hay calificaciones
- SurveysDocumento5 páginasSurveysVier Eli Dakiwag BusligAún no hay calificaciones
- Tape Corrections Bsce 2ya 1Documento12 páginasTape Corrections Bsce 2ya 1PHEBY MOOGAún no hay calificaciones
- Siddharth Physics IADocumento7 páginasSiddharth Physics IAElement Ender1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017Documento33 páginasAqa A Level Physics - Required Practicals: JUNE 2017LouisAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 6 SonometerDocumento2 páginasExperiment 6 Sonometerjigs2k2100% (1)
- SPM Physics Paper3 NotaDocumento52 páginasSPM Physics Paper3 Notanlweing100% (2)
- Determination of Young's Modulus of Metal WireDocumento5 páginasDetermination of Young's Modulus of Metal WireZaeem Ul IslamAún no hay calificaciones
- Tape Corrections Bsce 2ya 5Documento13 páginasTape Corrections Bsce 2ya 5PHEBY MOOG100% (1)
- Physics For EngineersDocumento5 páginasPhysics For EngineersKonstantinos FilippakosAún no hay calificaciones
- How Length Affects The Resistance of A Wire CourseworkDocumento5 páginasHow Length Affects The Resistance of A Wire Courseworkdkcvybifg100% (1)
- Topic 3 Tape CorrectionsDocumento38 páginasTopic 3 Tape CorrectionsShaine GaleraAún no hay calificaciones
- School Base Assessment-1Documento48 páginasSchool Base Assessment-1Marissa FreemanAún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering Council Certificate Level Engineering Materials C102 Tutorial 6 - Materials TestingDocumento11 páginasEngineering Council Certificate Level Engineering Materials C102 Tutorial 6 - Materials TestingcataiceAún no hay calificaciones
- Finding The Young Modulus of A Wire Student Worksheet: TheoryDocumento5 páginasFinding The Young Modulus of A Wire Student Worksheet: TheoryNgundi GedeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Young Modulus1Documento2 páginasYoung Modulus1Shahnaz AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiments Physics Form 4Documento52 páginasExperiments Physics Form 4cikgusya67% (3)
- A Level Physics Required Practical No 4Documento2 páginasA Level Physics Required Practical No 4Daniel FulstonAún no hay calificaciones
- Sonometer ExperimentDocumento4 páginasSonometer ExperimentRajeev Verma63% (8)
- Physics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsDocumento29 páginasPhysics 1 SPH 2170: Precision MeasurementsJuan SomoAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.tension Test FinalDocumento7 páginas5.tension Test FinalFausto Da GamaAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.stress StrainDocumento37 páginas6.stress StrainRose EizzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Project FinalDocumento20 páginasProject FinalRizwana 17Aún no hay calificaciones
- Recipiente Sub PresiuneDocumento10 páginasRecipiente Sub Presiunec_e_z_a_rAún no hay calificaciones
- T6 Deformation of SolidsDocumento4 páginasT6 Deformation of SolidsyanasakaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Electromagnetic Lab Write-UpDocumento5 páginasElectromagnetic Lab Write-Upapi-375748727Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chain Surveying 2Documento17 páginasChain Surveying 2Alamin SheikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Phy12l E303 2Q1516Documento4 páginasPhy12l E303 2Q1516Michelle Mae Gonzaga RaagasAún no hay calificaciones
- Young's ModulusDocumento12 páginasYoung's ModulusXi HaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Strain Gauges Are Used To Measure The Strain of A MaterialDocumento7 páginasStrain Gauges Are Used To Measure The Strain of A MaterialThinesh Rau KrishnamurtyAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement of Frequency of AC SupplyDocumento3 páginasMeasurement of Frequency of AC SupplyArmaghan Abidi100% (1)
- Calculation of Resistivity of Constantan Wire by Different MethodsDocumento5 páginasCalculation of Resistivity of Constantan Wire by Different Methodssallekmo100% (1)
- Practical No. 5 - SolvedDocumento3 páginasPractical No. 5 - SolvedMuhammad Nauman100% (1)
- Introduction To Physics: 1.1 PendulumDocumento68 páginasIntroduction To Physics: 1.1 Pendulumfahmi100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresDe EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Accounting A LEVEL Unit 1 TheoryDocumento1 páginaAccounting A LEVEL Unit 1 TheoryCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Group Bonus SchemesDocumento1 páginaGroup Bonus SchemesCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- OverheadsDocumento1 páginaOverheadsCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Unrealised Manufacturing Profit From Unsold StockDocumento2 páginasUnrealised Manufacturing Profit From Unsold StockCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Introductory SpeechDocumento1 páginaIntroductory SpeechCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Exponentials and LogarithmsDocumento2 páginasExponentials and LogarithmsCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- 132 Device IdentificationDocumento1 página132 Device IdentificationCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- 212 Latent Heat of Water BunsenDocumento1 página212 Latent Heat of Water BunsenCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- 135 Potential DividerDocumento1 página135 Potential DividerCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- 133D Instructions For 133DDocumento1 página133D Instructions For 133DCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- AS-Unit-1 Student Book (Question&Answer)Documento18 páginasAS-Unit-1 Student Book (Question&Answer)Mirza Galib0% (2)
- 210 Latent Heat of IceDocumento2 páginas210 Latent Heat of IceCostas PaschalidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Unit3B ExperimentsDocumento2 páginasPhysics Unit3B ExperimentsCostas Paschalides100% (1)
- As Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionDocumento15 páginasAs Unit-2 Student Book (QuestionCostas Paschalides100% (2)
- Linear Motion4Documento9 páginasLinear Motion4Jai GaizinAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Digital ForensicsDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 Digital ForensicsAbhinav GadekarAún no hay calificaciones
- Training On Optical Fiber NetworkDocumento96 páginasTraining On Optical Fiber Networkpriyasingh1682100% (1)
- Aveva Pdms v12.0 Sp6.25 Full Software 2014 DownloadDocumento1 páginaAveva Pdms v12.0 Sp6.25 Full Software 2014 DownloadMegatoreAún no hay calificaciones
- Binocular Vision Development, Depth Perception and DisordersDocumento275 páginasBinocular Vision Development, Depth Perception and DisordersJuliana ToméAún no hay calificaciones
- Fuzzy Hungarian Method For Solving Intuitionistic FuzzyDocumento7 páginasFuzzy Hungarian Method For Solving Intuitionistic Fuzzybima sentosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Practice Guideline On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia PDFDocumento12 páginasClinical Practice Guideline On Diagnosis and Treatment of Hyponatremia PDFLuis Mochas HClAún no hay calificaciones
- II. Optional Parts of Business LettersDocumento4 páginasII. Optional Parts of Business Lettersyelai gutangAún no hay calificaciones
- Effects of The Cone and Edge On The Acoustic Characteristics Ofa Cone LoudspeakerDocumento13 páginasEffects of The Cone and Edge On The Acoustic Characteristics Ofa Cone LoudspeakerJavierAún no hay calificaciones
- Spiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide ForDocumento6 páginasSpiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide Formohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- TYBTech Syllabus MechanicalDocumento49 páginasTYBTech Syllabus MechanicalswapnillkAún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz Questions TD 1Documento6 páginasQuiz Questions TD 1Susmita PandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dashboard Design Best PracticesDocumento43 páginasDashboard Design Best Practicesgabriel_babiano8003100% (4)
- User AgentDocumento2 páginasUser AgenthuongAún no hay calificaciones
- BaseballDocumento37 páginasBaseballBeeWinAún no hay calificaciones
- Strike RiskDocumento4 páginasStrike RiskAdilson Leite ProençaAún no hay calificaciones
- Petroleum Formation Evaluation Questions AnswersDocumento2 páginasPetroleum Formation Evaluation Questions AnswersdeusdedithaugustokiaAún no hay calificaciones
- 03 - Random Effect ModelDocumento10 páginas03 - Random Effect ModelAdji Pelangi SaputriAún no hay calificaciones
- The Zwolftonspiel of Josef Matthias Hauer: John RDocumento36 páginasThe Zwolftonspiel of Josef Matthias Hauer: John RMax Kühn100% (1)
- QP NTSE Stage 1 2016 17 AndhraPradeshDocumento27 páginasQP NTSE Stage 1 2016 17 AndhraPradeshsudhir_narang_3Aún no hay calificaciones
- ConceptBook NAUTITECH-40-OPEN 180703 EnglishDocumento104 páginasConceptBook NAUTITECH-40-OPEN 180703 EnglishDenis ClaracAún no hay calificaciones
- Metoda Securiti Pada DNP3 ProtokolDocumento16 páginasMetoda Securiti Pada DNP3 ProtokolDeny AriefAún no hay calificaciones
- Norma Astm d5731 PLTDocumento6 páginasNorma Astm d5731 PLTrodriahumAún no hay calificaciones
- Switchgear and Protection May 2022Documento1 páginaSwitchgear and Protection May 2022Sanapala RAJENDRA PRASADAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced MultisimDocumento146 páginasAdvanced MultisimHec Itou75% (4)
- FMF-01-10-911-302 - 100 GPM - 60 HZ Electric Motor DriveDocumento1 páginaFMF-01-10-911-302 - 100 GPM - 60 HZ Electric Motor DriveMarkAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics & Probability: Q4 - Learning Activity Sheet #1 Testing HypothesisDocumento2 páginasStatistics & Probability: Q4 - Learning Activity Sheet #1 Testing HypothesisEeNihc DPAún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Draft Ammendment To IRS T29 MAR13Documento11 páginasRevised Draft Ammendment To IRS T29 MAR13Shipra MishraAún no hay calificaciones
- Sag 38 2 12 0709 2Documento7 páginasSag 38 2 12 0709 2Yoselin GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Seam 2 LM FinalDocumento84 páginas1 Seam 2 LM FinalTrestan TenegraAún no hay calificaciones