Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
MU0018 SLM Unit 14
Cargado por
rakeshrakesh1Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
MU0018 SLM Unit 14
Cargado por
rakeshrakesh1Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Change Management
Unit 14
Unit 14
Change Management During Turbulent Times
Structure: 14.1 Introduction Objectives 14.2 Trends Affecting Organisation Design 14.3 Major Contextual Factors Affecting the Conduct of the Business 14.4 Implications for Organisation Design 14.5 Managing Change during Turbulent Times Setting clear expectations 14.6 Strengthen Relationship and Maintain Lines of Communication 14.7 Summary 14.8 Glossary 14.9 Terminal Questions 14.10 Answers 14.11 Case Study
14.1 Introduction
After studying the previous units, you are familiar with the concepts of role of change agents. We have also studied the role of internal consultant, the role of organisational management and the skills that are required for the role of change agent. It also makes us to understand the human resource development in managing change. Everyone live in turbulent times. The word turbulence began when applied to corporate change. Turbulence is defined as disorder, violent agitation, and irregular movement and not stable. According to 1Professors Paul Nautt and Don Schon turbulence is the absence of clear and stable path, no guideline to propose and achieve resolutions. In simple terms turbulence is not easy to understand. It results in disorder or uncertainty, which often results in lack of clear understanding about the organisation. Thus turbulence is not affected by any external factors in the environment. In fact, turbulence plans itself by imposing formal procedures and makes them to get exposed to unexpected changes.
www.emeraldinsight.com/journals.htm?articleid=1697169&show=pdf
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 296
Change Management
Unit 14
This unit mainly concentrates on the trends that affect organisation design, the major contextual factors that affect the conduct of the business, the implications for organisation design. It also describes how to mange change during turbulent times, to set clear expectations and to strengthen relationship and to maintain the lines of communication. Learning Objectives After studying this unit, you should be able to: explain the trends affecting organisation design. discuss the major contextual factors that affect the conduct of business. discuss the implications for organisation design. explain how to mange change during turbulent times and set clear expectations. explain how to strengthen a relationship and to maintain the lines of communication.
14.2 Trends Affecting Organisation Design
An organisational design is formal guided process for information and technology and integrating various resources such as tasks, and employees within the organisation. Organisation design is used to match and achieve the organisation form as expected. The probability of achieving success is more through the organisation process. Here managers and the members in the organisation work together to achieve the organisation needs. Organisation design supports the organisation's structure with its mission. This implies it should maintain the complex relationship between the tasks, workflow, duty and authority and to ensure that all support and achieve the objectives of the organisation. A good organisation design creates the environment to work effectively. It also assists the organisation in communication, productivity and innovation. In the absence of the organisation design or in case of poor organisation design, an organisation cannot give effective performance even if the organisation consists of best mission, people and leadership. Most of the productivity and performance related issues are traced back to poor organisation design. For example, in an organisation, the production and sales department work as different units, they need to communicate with each other to know about
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 297
Change Management
Unit 14
customers needs but they are not allowed to communicate as a result the organisations performance comes down. The work done, business processes, information sharing all these factors directly affects the performance of the organisation. All these factors are a part of organisation design and each factor is important for an organisation to be successful. It was noticed that a report entitled the changing business affects the industry, lifestyles and social structures that also affects organisations environment such as the strategies, structures, employment practices, and the way the organisation functions and are required to work with change. The major trends affecting organisation design are shown in the figure 14.1 and listed:
Figure 14.1: Major Trends Affecting Organisation Design Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 298
Change Management
Unit 14
Trends affecting organisation design: Decline in the traditional family forms. Increase in choice of home, work and leisure. Increase in the mobility of individuals regarding residence, working and personal relationships. Increase in variability in personal identities due to the increase in mobility and transient working arrangements, personal relations and leisure. Increase in freedom from traditional obligation leads to more self centeredness, dissipation, self-indulgence and hedonistic psychologies. Insecurity, lack of confidence due to anxiety and risk are the high threat faced by the organisation. Focus on individuality and self-interest leads to personal creativity giving rise to innovative organisation. Increase in the international division of labour with higher global separation between underdeveloped economies and the developed economies. Increase in the ability of information and communication technologies leads to the refusal of traditional form of organisation that includes public sector and organisations. Increase in genetic engineering to control the pattern of reproduction, technology to improve health both physically and psychologically. Increase in socio-economic inequality divergence in cultural, education and material living standards. These changes that are mentioned above have an impact in reaching the nature and design of the organisations across the globe. Thus, these trends provide the directions to organisations to move in order with the changing environment and to support the utilisation of information technological revolution across the globe. Self Assessment Questions 1. ______________ supports the organisation's structure with its mission. 2. Insecurity, lack of confidence due to anxiety and risk are the high threat faced by the organization. (True/False)? 3. A Socio-economic inequality decreases divergence in cultural, education and material living standards. (True/False)?
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 299
Change Management
Unit 14
Activity 1: Suppose you are hired as a consultant for a traditionally managed Textile and Apparel company. Make a list of trends that can affect the change in the organisation. (Hint: Figure 14.1 Major trends affecting Organisational design)
14.3 Major Contextual Factors Affecting the Conduct of the Business
Globalisation allows the forces to affect the performance of business and the nature of organisation involved in productive pursuit. These expansions have led to re-examination and redefinition of the organisation design principle. The major contextual factors are: Organisation deconstruction. Distributed Intelligence. Technological connectivity. Creative destruction. Disruptive innovation. Knowledge workers. Leveraging knowledge. Social responsibility of business. Social architecture. Clash of cultures. Organisation deconstruction The significance of the concept of traditional organisation more exists in the post-industrial world. The post-industrial social order is the process of transition from a mechanistic, stable and systematic viewpoint to initiate on the complexity, knowledge and change. There is a fundamental change in organising the organisation and an organisation. The organisation is not limited within a border that is separated from its constituents in its environment. To achieve the objectives of an organisation the suppliers, vendors, outsourced business processes and customers are increased and are made as partners. To attain maximum individual gain at the price of other partners as the whole cost of an
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 300
Change Management
Unit 14
organisation as lost its accuracy. To achieve a common goal all the partners in the organisation work effectively together. It is been noticed that the concept of organisation as undergone change. The geographical space is no longer a restrictive factor for the growth and expansion of the organisation. It is seen that the geographical space is assisted through instant coordination and control of information. The decision making and real time distributed action have become an order for the day, due to this the stable organisation have become unstable. The deconstructed organisation thus is less open to command and control mechanisms. Distributed intelligence The domain of operations increases as the organisational space gets distributed; the workers replace manpower with traditional skills and the base of the information is enlarged. To make knowledgeable decision that is essential for an organisation the required information gets extremely distributed among the members of domain in the organisation. By grouping together the views, ideas, opinions and perceptions of all the relevant members in the organisation the distributed intelligence are converted into collective intelligence. Due to this process of convergence the organisations learn to create knowledge and utilise it for rethinking strategies and systems and processes have also brought constant improvement. Technological connectivity All over the world, organisations and individuals make the best use of IT in designing processes, in generating and using knowledge. Latest technology and new developments are increasing rapidly beyond their area of products and services. The IT revolutions have changed the way we work. The work carried out is instantaneous and global. New forms of communities and interaction are emerging. Many people use cell phones, emails are sent in abundant and Google searches are done everyday. Geography is no longer restricted on limits of social and economic organisation. Creative destruction Global competitive pressures, emerging economies, saturated markets and demanding customers are crisis faced by all organisations. The concept of industrial era fails to give a solution to the emergent problems. The structure, system and processes that were functional to the environment have survived their utility. In the changed circumstances, organisations have
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 301
Change Management
Unit 14
choice instead of systematically destroying the process they had. It is hard to destroy the process that was created by the organisation and achieved success rate, since new process have to be created. Thus Creative destruction means to destroy the old structure or edifice and create a new structure. For the support of organic-non-hierarchical structures the mechanistic-hierarchical structure are destroyed and external customer focus are replaced instead of internally focused systems and processes. Disruptive innovation Through disruptive Innovation the organisations gain competitive advantage. The disruptive Innovation is a business model that aims significantly to transform the demands and requirements of a mainstream market and thus disrupting its former members. It introduces the product and services that are required for the emerging market or organisation. Some quality performances of the products are not acceptable by the mainstream market. The performance of the product is tested in the emerging or niche market and the organisation expands its customer base by creating new niche markets. Understanding a product increases as it influences the sensitivity of its value in the mainstream markets. The change in the mainstream markets view acts as a medium to enable the innovation to disrupt and replace existing services, mainstream products or business models. For example, the digital communications and transmissions are disrupting analogue communications and transmission. The mainframe markets are disrupted by desktop computers. Knowledge workers Knowledge workers are the individuals who are valued for their ability to act and communicate with knowledge within a specific subject area. They always advance the overall understanding of that subject through focused analysis, design and development. The subsequent pressure to raise the productivity of knowledge workers and the qualitative change in the nature of workforce requires a shift in the work structure. Production equipment is the primary skill of manual worker. To make the manual workers or the employees to be productive the production equipment are used as a task management and industrial engineering by an organisation. Manual workers are usually assigned a task and each knowledge worker possesses individual strengths and needs to have a total
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 302
Change Management
Unit 14
responsibility for the task, and should be able to manage themselves. The knowledge workers are viewed as capital asset and manual workers are viewed as costs to be controlled and reduced. This makes the organisations to develop new performance measures and new strategies. The industries highlight the need for retaining well-trained talent due to the shift the knowledge-intensive. This leads to the integration of global labour markets. For most of the organisations global labour and talent strategies have become important as global sourcing and manufacturing strategies. Leveraging knowledge The access to information anywhere and everywhere is changing the economies of knowledge. The Knowledge is more and available, at the same time it is focused. The manifestation of knowledge is the rise of search engines such as Goggle that has Infinite amount of information available immediately. To access the knowledge has become universal, but the transformation is much more reflective than the broad access to the knowledge. The economy is uncertain, and knowledge is the only lasting source of economical advantage. The shift in markets makes the technologies grow, products are outdated and competitors multiply, to be successful the organisations constantly create new knowledge, circulate it throughout the organisation and quickly represent it in new technologies and products. These activities define the knowledge-creating organisation, and their exclusive business is continuous innovation. The new models emerging are knowledge production, access, distribution, and ownership. Individuals are not responsible for innovations; there as been a rise of open-source approaches in knowledge development as communities responsible for innovations. Knowledge production is rising worldwide. The organisations need to leverage or control the new knowledge creation else there is a risk in drowning of too much information. Social responsibility of business As the businesses are global, this results in the mega-corporation that has a wide range of implications for the legitimacy in organisations that they operate. The mega-corporations are under inspection by societal and regulatory mechanisms. Certain people do not accept the present
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 303
Change Management
Unit 14
organisation concerns of shareholders value, free trade, intellectual property rights and profit repatriation. There is a threat to global operators by the scandal, environmental misfortune, value-conflict and clash of ethical standards. Thus the business leaders are forcefully required to argue and demonstrate the intellectual, social and economic case for business in an organisation and the contributions to social welfare. Social architecture Social architecture that is suitable for the organisations should be developed to connect and synthesise a wide range of unexpected organisational and contextual forces that are impacting on performance of organisation. In a comparatively stable environment, the social architecture of organisation is regarded as ordered arrangement of parts with fixed positions and roles. The social architecture has to be flexible and adaptive to emerging concerns as organisations are functioning within a disorganised environment with complex set of factors. The organisations with complex systems are governed by a set of principles that are qualitatively different from those of the simple system with inherent order. Organisation needs to constantly reposition and self-organise themselves with the chaining configuration of environmental forces. Through emergent structures, process and behaviour the complex systems get adjusted or adapted to the changes in an organisation. Clash of cultures The integration of diverse organisational cultures has emerged as a major concern part due to the increasing trend towards mergers and acquisition of corporations at the global scale. Outsourcing of business processes in different parts of the world brings cultures together with various norms, orientations and practices. The organisations achieve synergy if the inter-cultural issues are resolved and the relationships are managed. To attain the achievement towards a common purpose the strategic alliances and private-public joint ventures are required to integrate the district organisational cultures. Various cultural norms and practices have to be managed to understand the purpose for which organisations go into partnership arrangement. Culture
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 304
Change Management
Unit 14
provides the direction to responses of organisation members, it also influences the management processes such as monitoring and control performance appraisal, information sharing norms, the like and work standards. Cultural differences are essential as a significant factor in developing right designs of an organisation. It is very important for organisations to incorporate the above mentioned concerns in the design of structure, process and culture. There is no particularly best way to respond to the emerging realities suitable options are necessary to be generated by organisations to develop such designs as that enable them to gain and maintain economical benefit. Self Assessment Questions 4. Globalisation has freely allowed the forces to affect the performance of business and the nature of organisation involved in productive pursuit. (True/False) 5. The post-industrial social order is the process of transition from a mechanistic, stable and systematic viewpoint to initiate on the complexity, knowledge and change. (True/False)? 6. All over the world, organisations and individuals make the best use of IT in designing processes and in generating and using knowledge (True/False)? 7. ___________ means to destroy the old structure or edifice and create a new structure. 8. The ______________ is a business model that aims significantly to transform the demands and requirements of a mainstream market and thus disrupting its former members. 9. The integration of diverse organisational cultures as resulted in a minor concern part due to the increasing trend towards mergers and acquisition of corporations at the global scale. (True/False)? Activity 2 Visit any organisation and make a list of factors that affect the conduct of the business. (Hint: Contextual factors)
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 305
Change Management
Unit 14
14.4 Implications for Organisation Design
The focus of organisation design theory needs to continuously expand beyond the boundaries of the single firm and multi-firm networks to include the community based organisation design and is the main implication for organisation design. The identification and description of designs that develop combined behaviour among firms without restricting the ability of the individual firms and to continuously compete within their own marketplace should be the goal for organisational design. One definite framework that addresses inter-firm behaviour according to 2Dyer and Singh are four potential sources of inter organisational competitive advantage they are relation-specific assets, knowledge-sharing routines, complementary resources and capabilities and effective governance. The role of community facilitator is the second implication. The organisations core activity system is not activated by the facilitator but the facilitator creates and maintains the conditions under which the organisations survive and grow. The final implication is the anticipation of future organisational forms to identify the function and characteristics and plan for their arrival. By exploring the potential and limits of the current organisational forms, the anticipation of new organisational forms is approached and the newest form of organising the community-of-firms model requires to be scanned. For example, a collaborative community of firms is a powerful means of producing a wide range of innovative products and services based on a single technology. Many organisations are experimenting innovative approaches to structure, systems, strategy, resource allocation and human resource management but they have not found a way for the organisations to tackle the turbulence in the environment. Many forms are evolving as organisations explore to feasible options to withstand pressures of change. All these have resulted in the development of new perspectives on management necessitated by a typical shift in the world of business.
http://books.google.co.in/books?id=UkHHEXoDJmMC&pg=PA16&dq=implications+for+organisation+de sign&hl=en&ei=dU-cTMLA9GxcaqYpMgJ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CDcQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=f alse
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 306
Change Management
Unit 14
The various aspects of organisation that are affected by the emergent principles of design are shown in the table 14.1:
Table 14.1 Emergent Principles of the Organisation Design Aspects Vision Strategy Systems Structure Culture People Conventional Principles Stable for a longer period Top down/planned Control focused Pre-determined/fixed Strong/monolithic Organisation/full-oriented Emergent Principles Shifts over a shorter time span Bottom-up/evolving Responsiveness focused Emergent/flexible Weak/pluralistic Individual/part-oriented
Due to the uncertainties in the environment and the result of frequent shifts in technological breakthroughs and market condition the envisioning process and the articulation of mission requires a shorter time span. To continuously build the gap between strategies and their execution, the planned/top down approach is supplemented else it is replaced by bottomup approach with active involvement of employees. Thus strategies develop from the experiences and implicit knowledge of organisation members. The systems and processes are developed to improve responsiveness to the changing conditions rather than to regulate and control the behaviour tightly. The systems are based and guided on principles of self-direction and self-regulation. The structural forms apart from being fixed with positions and roles are also allowed to emerge in response to the changing work demands and stakeholders expectations. The structure has self organising properties, shared responsibilities and in-built flexibility with interchangeable roles. The organisations are made to function in multiple socio-cultural environments with different groups of technology, work practices, standards and values. Professional, cultural demographic and social ecological differences necessitate the development of pluralistic culture, essential for synergising creative potentials required for diversity. The conventional design was based on the condition that the needs of the people should be supportive to the needs of the organisation. The employees in the organisation should put effort for the welfare of the organisation. The organisation has a small and limited responsibility to the human resources. The emergent principle is based on the idea that the most
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 307
Change Management
Unit 14
valued asset of the organisation is human capital that enables the organisations to gain and maintain economical advantage. Thus the organisation should have a strong focus on the welfare of their human resources in the area of their work, employability, leisure, family and community on the whole. As a result the major areas of concern for organisations are that the development of personality and multi-faceted approach that should satisfy the employees. Self Assessment Questions 10. To continuously build the gap between strategies and their execution, the ____________ is supplemented else it is replaced by bottom-up approach with active involvement of employees. 11. The _____________ was based on the condition that the needs of the people should be supportive to the needs of the organisation. 12. The emergent principle is based on the idea that the most valued asset of the organisation is human capital that enables the organisations to gain and maintain economical advantage. (True/False)? Activity 3 Visit an organisation and collect information about principles and implications of the organisation. (Hint: emergent principles)
14.5 Managing Change during Turbulent Times
Due to an unhealthy economy, all of us are working in turbulent times and organisations are under deep pressure, and reacting with aggressive thriftiness measures such as reducing, restructuring, rescheduling, and merging with competitors or strategic alliances. They are also closing unprofitable facilities, moving managers to open work environment from private offices. Effective working is very important when few employees are present in an organisation, it is seen that in the current world only the strongest organisation survives for a longer period. During the turbulent times the leaders focus on managing a balance between cost cutting and supporting the employees to serve in a better way to the organisation.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 308
Change Management
Unit 14
The enterprises that emerge from considerable organisational changes are stronger and more competitive and are more focused on the effectiveness of the employee this is done by increasing productivity through teamwork and collaboration, rising organisational innovation, enforcing responsibility at all levels, making the workplace to attract, inspire and to retain talent and to accommodate the needs of multigenerational workforce. Economic and world events brought unexpected changes inflation, productivity challenges, technology shifts, and global competition all hit the business world at about the same time and made the classical planning methods suddenly outdated. During this time many organisations followed 3 Peter duckers suggestions that helped employees managing during turbulent times and managing the complex work. In the times of disorganised changes maintaining productivity is a fundamental necessity of managers, and it is done for four key resources they are capital, crucial physical assets, time, and knowledge. For example, 4 Siemens organisation has successfully beaten their competition by significantly increasing their productivity of capital or resources. Another effective method of managing in turbulent times is strategic assignment of critical resources. The managers need to be smart about selecting areas of potential results and allocating resources consequently. In chaotic times, there is a natural tendency to use resources to solve current problems, but the top priority should be given to the areas of potential opportunities. 5Drucker suggested managers to avoid working on problems that were important in the past and that was not expected to be beneficial in the future.
http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Managing+Change+during+Turbul ent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2ccSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0C FwQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%20Times&f=false 4 http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Managing+Change+during+Turbul ent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2ccSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0C FwQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%20Times&f=false 5 http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Managing+Change+during+Turbul ent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2ccSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0C FwQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%20Times&f=false
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 309
Change Management
Unit 14
An exit strategy is essential to be developed so that resources are allocated to areas with the highest probability of future achievements and success for the organisation. For example, the 6organisation GE followed a critical activity called work out program and was successful. This activity was designed to eliminate work that did not meet the strategic needs of the organisation. This activity was suggested by Drucker in the past. Stimulating innovation during managing change is a critical managerial competence essential in turbulent times. The most challenging task for managers is to respond effectively to the task that cannot be planned in advance to the time. This circumstance is more complicated, when its function is in global business environment. The leaders or the managers should be prepared to lead this environment of multidimensional changes and organise their organisations to function effectively during the transformations of their organisational culture. Setting clear expectations To manage the change in the organisation effectively setting clear expectation or goals are necessary with in the organisation. The organisation should provide clarity about the most critical elements of the change by explicitly bringing out the implications and expectations for the employees. Reducing uncertainty increases morale and decreases distracting emotions of the employees. To Select and postpone the nonessential projects, and to recognise the importance of making symbolic changes and to increase or decrease the unrestricted responsibilities in order to accomplish the heavy lifting associated with major change. It is important to focus on employees to do the work that is required and it is essential for the organisation to be clear about the employees needs and to ensure that the needs of the employees are satisfied. The managers set their expectations and follow them. The managers or the leaders should: Demonstrate strong ethics. Ensure confidentiality in the organisation.
6
http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Managing+Change+during+Turbul ent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2ccSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0C FwQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%20Times&f=false
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 310
Change Management
Unit 14
Show empathy for the emotional and personal effects of change and be available and listen to the employees concerns. Ensure the communication of key event and activities, that is to provide details on who, what, when, and where as known. Programme regular updates for all team members in the organisation. Communicate the decisions and justify and to recognise that individual have various communication needs. Manage the change and undertake the obstacles to bring effective change in the organisation. Focus on delivering value in running and changing the business. Stick to fated timelines and processes and act according to the agreements.
Self Assessment Questions 13. During the turbulent times the leaders focus on managing a balance between ___________ and supporting the employees to serve in a better way to the organisation. 14. Another effective method of managing in turbulent times is __________ of critical resources. 15. To manage the change in the organisation effectively setting clear expectation or goals are necessary with in the organisation (True/False)? Activity 4 Suppose you are a manager of an organisation, how do you mange the change during turbulent times and what steps do you follow to set the expectations right. (Hint: Effective working and set expectations)
14.6 Strengthen Communication
Relationship
and
Maintain
Lines
of
Many employees feel demoralised and disconnected at turbulent times, so it is essential to strengthen the bonds across the organisation and mostly within teams of the organisation. The organisation leader or manager should interact with the employees and must support them in a group and individually. All these actions are easy to neglect or optional, but they
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 311
Change Management
Unit 14
support and help employees and make the employees to be as cohesive and loyal to the organisation. Even if the organisation is facing difficulty or drowning, ensure to communicate with the employees the possibilities for growth and personal development this should be followed even if the days of the organisation are numbered. Involve the employees in discussions about building the future, balancing reality with confidence. To determine the confidence and commitment in the change effort, regular pulse checks of the team and the organisation is established. This is done formally through surveys or informally through casual conversations and meetings. These checks recognise concerns faster and are addressed rapidly and effectively. The feedbacks are often very useful in helping to shape both business and change-management activities and ensure that the surveys are not thrashed completely. Employees or people in the organisation look for information and leadership during uncertainty or turbulent times, and the need increases exponentially at the time of the change effort. Within a sequence of space misunderstanding within the organisation is possible, its important to reach the employees repeatedly through any and all means such as town hall events, meetings, lunches, e-mails, newsletters, web casts, and blogs. Effective leaders are highly visible in both formal and informal ways. It is noticed that managing change requires an ongoing focus has new events occur and due to the change progresses people who have initially accepted the new direction revert. When ensuring accountability for results, the managers or leaders recognise and address the emotional dimensions of change and truly transform their organisations and win assurance of their employees during the turbulent times. Self Assessment Questions 16. Many employees feel demoralised and disconnected at ________, so it is essential to strengthen the bonds across the organisation and mostly within teams of the organisation. 17. Do not involve the employees in discussions about building the future, balancing reality with confidence. (True/False) 18. The feedbacks are often very useful in helping to shape both business and change-management activities. (True/False)
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 312
Change Management
Unit 14
Activity 5 Visit an organisation and collect information how the managers manage to strengthen relationship within the organisation and how the communication can take place effectively. (Hint: Interact and meetings)
14.7 Summary
In this unit, we have learnt the major trends and the changes that are affecting industry, lifestyles and social cultures that in turn affect the design of the organisation. As we know that good organisational design helps to work effectively with production and innovation whereas in the absence of the organisation design, there will be issues related to production and performance. Globalisation has become a major factor affecting the conduct of the business. This is because globalisation brings about distributed intelligence, disruptive innovation, clash of cultures, social responsibility of business and many more. We have also learnt the implications for organisation design, where organisational design concept continuously expand to bring in the community based organisation design. An unhealthy economy creates turbulent times in the organisation, which results in reducing employees, rescheduling, and merging with competitors. Managing turbulent times in organisation basically involves managing a balance between cost cutting and supporting the employees to deliver good performance. It is noticed that by strengthening relationship and maintaining line of communication, we can get good outcomes even during turbulent times in the organisation.
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 313
Change Management
Unit 14
14.8 Glossary
Term Contextual factors Disruptive innovation Description The factors of the context. The terms used in the business and technology to describe innovations and to improve the service in the way the organisation wants. The individuals who are valued for their ability to act and communicate with knowledge within a specific subject area. A mechanically determined structure having date arranged in many levels like a tree structure form. The majority of customers in the technology market or product.
Knowledge workers
Mechanistichierarchical structure Mainstream market
14.9 Terminal Questions
1. Discuss the major trends affecting the organisation design. 2. Explain briefly any five contextual factors that are affecting the conduct of the Business. 3. Discuss the implications of organisation design. 4. Explain in brief about managing change during turbulent times and setting clear expectations. 5. Discuss in brief how to strengthen relationship and maintain lines of communication in an organisation during turbulent times.
14.10 Answers
Answers to Self Assessment Questions: 1. Organisation design 2. True 3. False 4. True 5. True 6. True 7. Creative destruction 8. Disruptive Innovation 9. False 10. Planned/top down approach
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 314
Change Management
Unit 14
11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18.
Conventional design True Cost cutting Strategic assignment True Turbulent times False True
Answers to Terminal Questions: 1. Refer section 14.2 Trends affecting Organisation Design. 2. Refer section 14.3 Major Contextual Factors Affecting the Conduct of the Business. 3. Refer section 14.4 Implications for Organisation Design. 4. Refer section 14.5 and 14.5.1 Managing Change during Turbulent Times and Setting clear Expectations. 5. Refer section 14.6 Strengthen Relationship and Maintain Lines of Communication.
14.11 Case Study
Managing change during turbulent times at XYZ: A XYZ financial services player with more then 20,000 advisors and 2.5 million clients across the world, requested Sys-Indy organisation to support in a program aimed at institutionalising service management capability based on ITIL. The main aim was to improve the availability and performance of its IT systems during turbulent times and to increase the overall client satisfaction. Sys-Indy conducted an assessment across the technology groups to identify the existing process maturity and improvement opportunities. As part of the program, detailed roadmaps and communication plans were developed, training were conducted and detailed cost benefit analyses was carried out for executing the initiatives. The initiatives have been prioritised were executed within each process area, Sys- Indy assisted the program management and execution. This
Sikkim Manipal University Page No. 315
Change Management
Unit 14
service management was very challenging but the transformation had begun and the client made significant progress, with savings of Rs 9,950,000 within the first eight months. Questions 1. During the turbulent times what was the main goal of XYZ Financial services? (Hint: performance) 2. What was the first step taken by the Sys-Indy to achieve progress and did it satisfy the client? (Hint: assessment and program management)
References Radha R Sharma (2007), Change management - Concepts and Applications. E-Reference http://www.businesslink.gov.uk/bdotg/action/detail?itemId=1074411173& type=RESOURCES http://www.allbusiness.com/management/689725-1.html http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Ma naging+Change+during+Turbulent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2c cSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CFwQ6AE wBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%2 0Times&f=false http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Ma naging+Change+during+Turbulent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2c cSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CFwQ6AE wBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%2 0Times&f=false http://books.google.co.in/books?id=vsCeCHxH7jQC&pg=PA148&dq=Ma naging+Change+during+Turbulent+Times&hl=en&ei=2GWcTNyYGcG2c cSC7f4J&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CFwQ6AE wBw#v=onepage&q=Managing%20Change%20during%20Turbulent%2 0Times&f=false
Sikkim Manipal University
Page No. 316
También podría gustarte
- Performance AppraDocumento51 páginasPerformance Apprarakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ma HS Iii SemDocumento23 páginasMa HS Iii Semrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Table of ContentsDocumento1 páginaTable of Contentsrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Zeme Church Delhi: Certificate of Child DedicationDocumento1 páginaZeme Church Delhi: Certificate of Child Dedicationrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Centre For Child Rights: Hildren'SDocumento4 páginasCentre For Child Rights: Hildren'Srakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Holiday Homework OF: EnglishDocumento4 páginasHoliday Homework OF: Englishrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- January: Monday Tuesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayDocumento13 páginasJanuary: Monday Tuesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sundayrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- "A Comparative Study of Two Wheeler Industry in India" With Special Reference To Hero MotocorpDocumento1 página"A Comparative Study of Two Wheeler Industry in India" With Special Reference To Hero Motocorprakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- View DetailsDocumento2 páginasView Detailsrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
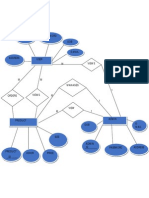
- Er-Diagram: User Id Password DOBDocumento1 páginaEr-Diagram: User Id Password DOBrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- A Synopsis ON "A Study On Measuring Customer Satisfaction On Honda City"Documento8 páginasA Synopsis ON "A Study On Measuring Customer Satisfaction On Honda City"rakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Analysis of Working Capital Management in Parle Biscuits Pvt. LTDDocumento1 páginaAnalysis of Working Capital Management in Parle Biscuits Pvt. LTDrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2.2 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) : Agent Reservati Cancella Customer Records Change PasswordDocumento2 páginas2.2 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) : Agent Reservati Cancella Customer Records Change Passwordrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Financial Analysis of L & T: Neev Education Pvt. LTDDocumento3 páginasFinancial Analysis of L & T: Neev Education Pvt. LTDrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Smu Neev EducationDocumento1 páginaSmu Neev Educationrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Part - A: Fresh Application FormDocumento3 páginasPart - A: Fresh Application Formrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Source File of Showroom: Project OnDocumento1 páginaSource File of Showroom: Project Onrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Export Procedure IN CM Logistics India Pvt. LTDDocumento1 páginaExport Procedure IN CM Logistics India Pvt. LTDrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Document 12Documento1 páginaDocument 12rakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Growth of Retail Marketing in India: Project Guide Submitted byDocumento5 páginasGrowth of Retail Marketing in India: Project Guide Submitted byrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Concurrent Course For Hon. Prog.: (Language Credit Course) English LanguageDocumento3 páginasConcurrent Course For Hon. Prog.: (Language Credit Course) English Languagerakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- EflDocumento14 páginasEflrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bhabendra Nath SaikiaDocumento1 páginaBhabendra Nath Saikiarakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 6 - Adobe Photoshop: Image ResolutionDocumento2 páginasChapter 6 - Adobe Photoshop: Image Resolutionrakeshrakesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Contractions 29.01Documento1 páginaContractions 29.01Katita la OriginalAún no hay calificaciones
- Ef3 Englisch 04 14 08052014Documento20 páginasEf3 Englisch 04 14 08052014PiPradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Finance Budget - Ankur WarikooDocumento28 páginasFinance Budget - Ankur WarikooVivek Gupta100% (1)
- Content Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)Documento6 páginasContent Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)AngelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Title Toolbox 1 ADocumento2 páginasTitle Toolbox 1 AGet LiveHelpAún no hay calificaciones
- Soil MechDocumento21 páginasSoil MechAhsan AbbasAún no hay calificaciones
- Sticker BookDocumento66 páginasSticker BookIvan SutlovicAún no hay calificaciones
- Branch Audit Guidelines 2018-19: Financial Management & Accounts DepartmentDocumento43 páginasBranch Audit Guidelines 2018-19: Financial Management & Accounts DepartmentBerkshire Hathway coldAún no hay calificaciones
- AutoPIPE Tutorial PDFDocumento156 páginasAutoPIPE Tutorial PDFdhaktodesatyajitAún no hay calificaciones
- Neon Wilderness MenuDocumento2 páginasNeon Wilderness MenuAlisa HAún no hay calificaciones
- Mutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFDocumento2 páginasMutants Genetic Gladiators Hack PDFFercho GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Internship Proposal FormDocumento3 páginasInternship Proposal FormMuhammad FidaAún no hay calificaciones
- People Vs SB - Paredes - Ex Post FactoDocumento2 páginasPeople Vs SB - Paredes - Ex Post FactoMara Aleah CaoileAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Make Papaya SoapDocumento10 páginasHow To Make Papaya SoapEmz GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Why Do Climates Change ?: Climate Changes Over The Last MillenniumDocumento44 páginasWhy Do Climates Change ?: Climate Changes Over The Last Millenniumshaira alliah de castroAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Manifestos Da ArteDocumento3 páginas5 Manifestos Da ArteCinthia MendonçaAún no hay calificaciones
- Once Upon A Timein AmericaDocumento335 páginasOnce Upon A Timein Americaqwerty-keysAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Paper For Professional Ethics in Accounting and FinanceDocumento6 páginasSample Paper For Professional Ethics in Accounting and FinanceWinnieOngAún no hay calificaciones
- Ealpha - Week 4 - Half A Day - ForeshadowingDocumento2 páginasEalpha - Week 4 - Half A Day - ForeshadowingaalshehabAún no hay calificaciones
- China Email ListDocumento3 páginasChina Email ListRosie Brown40% (5)
- 2020 LBG q1 Ims Pillar 3 DisclosuresDocumento8 páginas2020 LBG q1 Ims Pillar 3 DisclosuressaxobobAún no hay calificaciones
- West Bengal State University Department of EnglishDocumento33 páginasWest Bengal State University Department of Englishnandan yadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Effectives of e Wallets NewDocumento15 páginasEffectives of e Wallets NewRicardo SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Bearing Capacity of Closed and Open Ended Piles Installed in Loose Sand PDFDocumento22 páginasBearing Capacity of Closed and Open Ended Piles Installed in Loose Sand PDFAnonymous 8KOUFYqAún no hay calificaciones
- 100 Cases Ethics NotesDocumento16 páginas100 Cases Ethics Noteskoki74Aún no hay calificaciones
- RagragsakanDocumento6 páginasRagragsakanRazel Hijastro86% (7)
- Bus Bar Arrangement of SubstationDocumento17 páginasBus Bar Arrangement of SubstationBbimafidon_248613673Aún no hay calificaciones
- Din en 10346Documento45 páginasDin en 10346Lucero AlemanAún no hay calificaciones
- Apy1 Kinematics Review - 2015 - KeyDocumento13 páginasApy1 Kinematics Review - 2015 - KeyemadAún no hay calificaciones
- GnatusDocumento36 páginasGnatusNacer Mezghiche100% (1)