Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Open Relay Exchange
Cargado por
athusDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Open Relay Exchange
Cargado por
athusCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Blocking Open Relays
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Blocking_Open_Relays.aspx
Home
Buy
Download
Details
Support
Blocking Open Relays
Table of Contents
An increasing number of spammers are exploiting open e-mail relays to send spam and disguise the true source of their messages. Open relays are e-mail servers that are configured to accept and transfer e-mail on behalf of any user anywhere, including unrelated third parties. If your computer acts as an open relay, it allows any e-mail sender anywhere to send messages.
How spammers detect open relays
Spammers use automated software to scan the Internet trying to find open relays. If they find out that your server is open, they will probably send spam through it. The software they are using scans a range of Internet IP addresses by trying to establish a network connection on port 25. If the connection succeeds, an IP address is listed and used for sending. There are at least two advantages for the spammers: This technique lets spammers hide their identities because it appears that the spam actually comes from you. This makes extremely hard to track them down. It is virtually impossible to get caught by their ISP. All ISPs deny sending spam from their networks. If the spammers cannot be tracked down, they cannot be reported to their ISP which would broke down their account anyway, because of violating the Acceptable User Policy. Recipients of the spam sent from your computer could flood your server with complaints. The spam and resulting e-mail traffic could overwhelm your system. If you are maintaining an open relay, you are leaving your door open to the theft of your computer services.
How ISPs reject messages from open relays
When you send messages from an SMTP server running on your computer, some ISPs perform a relay check. They identify your computer's IP address and try to establish a connection to port number 25 which is the port used to send e-mail. If the server on your computer accepts the connection - your message is rejected.
Detection
PostCast Server has a feature that allows you to check if your computer runs as an open relay. Open the Setup Wizard from the Tools menu and press the "Open Relay" button in the Network Diagnostics step:
1 of 4
16/03/13 23:38
Blocking Open Relays
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Blocking_Open_Relays.aspx
Solutions
Accept only connections from local computer or LAN When you enter your Internet IP address in the Host Name text box in the Settings screen, everyone can connect to the server from the Internet. You can run the server using the Internet IP address, but you need to either change the port number or allow access only to certain IP addresses. If you do not need to accept connections from the Internet, select the LAN IP address or 127.0.0.1 in the Host Name drop down list in the Settings screen:
Change the port number Change the number of the port from 25 to some random number (1-65535). Instruct the users to change the settings in their e-mail programs. This will trick the IP scanner software because your port 25 will be closed and your computer will not respond to their queries. Make sure that no other SMTP server software is running on your system, including "Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP)" service if you are running Windows NT, 2000, XP, or 2003:
2 of 4
16/03/13 23:38
Blocking Open Relays
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Blocking_Open_Relays.aspx
Restrict access to a list of IP addresses The basic way to implement e-mail relay protection is to configure your e-mail server to allow only certain TCP/IP addresses and address ranges to relay through your server. With this technique, your e-mail server will reject any relay attempt from TCP/IP addresses outside of your network. If, for example, computers on your network have IP addresses that begin with 192.168.0, go to Tools>Settings>Security and enter that as a value in the "Allow access ONLY for users with these IP addresses" list:
Anti-Spam Methods:
Overview Port 25 Blocking Internet Black and White Lists Blocking Open Relays DNS Lookups
3 of 4
16/03/13 23:38
Port 25 Blocking
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Port_25_Blocking.aspx
Home
Buy
Download
Details
Support
Port 25 Blocking
Table of Contents
Many ISPs are blocking what is called "Port 25" which is the port used to send e-mail. They are doing this to cut down on the amount of spam that is sent from their networks. All e-mail sent via the Internet is routed through the port 25, the channel used for communication between an e-mail client and an e-mail server. Even though port 25 blocking will probably become an industry standard, however, the filter can create problems for e-mail servers and block legitimate e-mail as well as spam. Port 25 blocking allows ISPs to block spam sent out through their networks, but it tends to punish the innocent that have a need to send through e-mail servers other than those belonging to their ISP. The ISPs that block port 25 require their SMTP server to be used instead of the remote SMTP server or a SMTP server running on your computer.
How the port 25 is used
All e-mail sent via the Internet is routed through port 25. When an e-mail server that runs on your computer delivers messages, it always uses port 25 to transmit data to remote e-mail servers. Therefore, if your ISP is blocking the port, your messages will not get through. There are two different ways the port 25 is being used by PostCast Server: Incoming Connections PostCast Server uses port 25 to accept incoming connections from e-mail clients. You can freely change that value in both server and client program and everything will continue to work because all TCP/IP connections are directed to your computer. Unless you block connections to your computer, the program will accept messages using any port number you specify (1-65535). Outgoing Connections PostCast Server also uses the port 25 for sending. It connects to remote servers and delivers the messages from the Outbox folder. Exactly the same rules apply except that every remote server expects the connection ONLY on port #25. This is the standard port number and while you can change the port number in the program to allow clients to send the messages internally, the remote servers always use port 25. If your ISP blocks remote connections to port 25, you cannot send any messages. PostCast Server will not be able to connect to the remote servers.
ISPs that block Port 25
This list contains some of the major ISPs that block port 25 on their servers:
AT&T (can be
MindSpring
1 of 4
16/03/13 23:39
Port 25 Blocking
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Port_25_Blocking.aspx
unblocked at the request) BellSouth MSN CableOne NetZero Charter Comcast ATTBI Cox People PC Sprynet Sympatico.ca
EarthLink Verio Flashnet MediaOne Verizon
Related News Stories
Anti-spam tool brings MSN under fire: http://www.zdnet.com/zdnn/stories /news/0,4586,5080821,00.html Hotmail spam filters block outgoing e-mail: http://news.com.com /2009-1023-251171.html?legacy=cnet MSN filter sparks subscriber ire: http://news.com.com /2100-1023-255459.html?legacy=cnet&tag=bplst
Detection
You can detect whether your ISP blocks port 25 using the Setup Wizard in PostCast Server. In the Network Diagnostics step, press the "Port 25 blocking" button to run the test:
You can also see if the port is blocked by running a telnet command: Press Start/Run and enter: telnet://[emailserver]:25 Replace [emailserver] with the address of any external e-mail server. For example: mx1.hotmail.com mail.telenet.net.au Do not use your ISP's e-mail server address. If the port is not blocked, you should receive a
2 of 4
16/03/13 23:39
Port 25 Blocking
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Port_25_Blocking.aspx
response starting with the '220 ' string.
Solutions
To bypass the port 25 blocking you have these options: Use a different ISP You can use a different ISP to connect to the Internet. Smaller local ISPs usually do not block Port 25. Here are some web sites that can help you find thousands of ISPs: http://www.findanisp.com/ http://www.thelist.com/ http://www.isps.com/ Use socks proxy servers You can send e-mail using the socks proxy access to a computer on the Internet. This feature enables you to relay e-mail through other servers. When the message is sent using a third-party socks proxy, your IP address does not appear as the source of the message. The best solution is to connect to your ISP's socks proxy directly if it is provided by the ISP. Some ISPs offer access to their socks proxy server. See if your ISP provides socks proxy access in the support section on their web site. If they do, you can use their socks proxy server address to configure the program to send messages. Their server's (non-dynamic) IP address will be the source of your outgoing messages instead of your dynamic IP address assigned to your computer at the moment your Internet connection is established. Use backup SMTP servers You can specify one or more backup SMTP servers and instruct the program to forward all messages to them. This is not a complete solution because the program will still be unable to send messages from your computer. For more information, see SMTP Gateways. If you do not need to send messages If you only want to receive messages sent to the server you can use the "Mail Reflector" service offered by no-ip.com. This service enables them to be the primary e-mail exchanger for your domain. When e-mail destined for your domain arrives at their servers, they forward it on to your inbound e-mail server, which can be on a different (and unblocked) port of your choosing. Price is $39.95 per Year. See this web page for more information: http://www.noip.com/services/mail/reflector Anti-Spam Methods:
Overview Port 25 Blocking Internet Black and White Lists Blocking Open Relays
3 of 4
16/03/13 23:39
DNS Lookups
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/DNS_Lookups.aspx
Home
Buy
Download
Details
Support
DNS Lookups
Table of Contents
This method tries to eliminate spam sent by e-mail servers connected through Internet dial-up connections, as well as most ADSL and cable connections. IP addresses of those connections are usually not registered to any DNS as a qualified host meaning that they do not have their own static IP and a registered host name like mail.domain.com. A DNS lookup uses an Internet domain name to find an IP address, where a reverse DNS lookup is using an Internet IP address to find a domain name. Reverse DNS lookup technique is able to identify if the sending e-mail server is legitimate and has a valid host name. Many spammers use misconfigured hosts to disguise the source of the spam. A DNS query that does not recover a matching host name and IP address is a good indication that the message is spam. DNS lookup is not always a good solution. Many legitimate e-mail servers are incorrectly configured, or have intentionally not registered a name with DNS, so a reverse query does not return a matching host name. Also, this anti-spam method runs DNS queries on a large number or e-mails and consumes valuable network resources. A number of problems, including network delays and improperly configured networks or servers, can prevent legitimate messages from getting through the filter. In January 2003, AT&T WorldNet started using reverse DNS and was forced to remove the filter just 24 hours after it was deployed, after subscribers reported that messages were going undelivered.
Ways to do DNS lookups
Reverse DNS lookup This method is time-consuming and it is rarely used. The receiving server performs a reverse DNS lookup on the IP address of the incoming connection and checks if there is a valid domain name associated to it. HELO lookup The receiving server will get the host name of the sending e-mail server from the SMTP HELO command, perform a simple DNS query (forward DNS lookup) and verify that the IP address is indeed the IP address of the incoming connection. If the resulting IP address does not match the incoming connection IP address (sender's IP address), e-mail is rejected. Sender's address lookup When ISPs check whether an incoming e-mail is accepted, they can do a DNS check on the sender's e-mail address. For example, if your address is , then the ISP does an nslookup on domain.com. If no records are found - the message is rejected. A variation of this method is checking if there is an MX DNS record of the domain.com. MX
1 of 3
16/03/13 23:44
DNS Lookups
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/DNS_Lookups.aspx
record returns an address like mx1.domain.com used to connect to the server that accepts messages for domain.com. Even if the domain in the sender's e-mail address is valid, but there is no e-mail server for domain.com - the message is not accepted.
Solutions
The solution depends on which method is used to block spam. 1. Reverse DNS lookup
Get a domain name
To get a domain name for your dynamic IP address you can use the no-ip.com DNS service which enables you to host a server using a dynamically assigned IP address. When you send messages, if any of ISPs perform a reverse DNS lookup of your IP address, they will always get a valid domain name and accept messages sent from your computer. The basic service is free, but the names are sub domains of names already registered by No-IP like: "servequake.com" or "myvnc.com". For more information, visit this web page: http://www.no-ip.com/services/page/free/dynamic/dns No-IP Plus enables you to use your own, separately registered domain name. The price for one year is $24.95: http://www.no-ip.com/services.php/page/plus
Use backup SMTP servers
The Professional Edition of PostCast Server has a feature that allows you to specify one or more backup SMTP servers. If only certain domains are unable to receive messages from PostCast Server, you can use this option to forward those messages to your ISP's SMTP server. Open the Settings/Undelivered/Gateways window to configure this feature. For more information, see SMTP Gateways.
Use socks proxy servers
This feature enables you to relay e-mail through other servers. When the message is sent using a third-party socks proxy, your IP address does not appear as the source of the message. The best solution is to connect to your ISP's socks proxy directly if it is provided by the ISP. Their server's (non-dynamic) IP address will be the source of your outgoing messages. For more infromation, see Firewall and Proxy Support.
2. Sender's address lookup Make sure that e-mail address in the From field of your messages is always valid. 3. HELO lookup AOL, Hotmail, Yahoo, and some other ISPs perform a HELO lookup when receiving messages. If the lookup is not successful, they simply reject to deliver the message to the recipient without sending any error message. There are three possible ways to solve this problem.
2 of 3
16/03/13 23:44
DNS Lookups
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/DNS_Lookups.aspx
1. You can select the "Resolved Internet IP" option in the HELO handshaking settings in the Settings/Advanced screen. The program will perform a DNS query to find out which address points to your IP. This option sometimes does not return the correct values if you are behind a router. If that is the case, you can use the http://network-tools.com/ service to check your IP address and look for "Host name" which should then be copied into the "Use this Identification" box in HELO handshaking settings. 2. Try to change the server identity in the HELO handshaking settings in the Settings/Advanced screen to the "mail.domain.com" format. For example, if your ISP provides e-mail address such as joe@domain.com, set the HELO handshaking identification to mail.domain.com. Try also with only 'domain.com' format. 3. If you have a domain name that points to your computer's IP address, then enter that domain name in the HELO handshaking settings in PostCast Server. You can use the no-ip.com service to host a domain name on your computer.
Anti-Spam Methods:
Overview Port 25 Blocking Internet Black and White Lists Blocking Open Relays DNS Lookups
Home | Buy | Download | Details | Support 1997-2013 Oricode, Inc. All rights reserved. | Privacy Statement
3 of 3
16/03/13 23:44
Internet Black and White Lists
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Internet_Black_and_Whi...
Home
Buy
Download
Details
Support
Internet Black and White Lists
Table of Contents
Two of the least effective and most damaging methods for fighting spam are white lists and black lists. In many cases, these lists harm innocent people and prevent critical business e-mail from being delivered. One of the drawbacks is that if you block an entire domain, you may be blocking as much as 90 percent of wanted e-mail while blocking only 10 percent of unwanted spam. If you are sending e-mail from an e-mail server on your computer and your IP address is on one of the lists, that can affect you in two ways: Your messages cannot be delivered if a recipient's e-mail server checks IP addresses of incoming connections against black and white lists. If your messages are successfully delivered to recipients, they can run an anti-spam software that uses black lists to categorize your messages as spam. Your e-mail can end up in a folder for spam or be deleted and will probably never be read.
Black lists
A spam black list is a list of IP addresses and domains of known spam e-mail servers. Black lists are used to block all e-mail that comes from certain servers on the Internet that have been identified as being used to send spam. A well-known black list is hosted by SpamCop, located at www.spamcop.net. Another one is Open Relay Database, located at www.ordb.org. Many anti-spam products also maintain their own black lists and include optional subscriptions to third-party black list services.
White lists
White lists are the opposite of blacklists. They list trusted e-mail addresses and domains that are always allowed to send e-mail, no matter what the content is. White lists are used to require that senders authenticate their identity prior to e-mail being delivered to the recipient. White lists will definitely allow e-mail coming from a trusted site to come through, but do not provide a solution for blocking spam. White lists require constant maintenance to be very effective. If not properly maintained, the risk of losing e-mail from legitimate sources is high.
Dial-up Lists (DUL)
Some ISPs block access to their servers if the incoming connections originate from dynamic IP addresses. Their goal is to force users that are running e-mail servers on their dial-up connections to send all outgoing e-mail through their ISP's e-mail server. If you send messages from PostCast Server using a dial-up connection, you will probably experience this problem with AOL.
1 of 3
16/03/13 23:45
Internet Black and White Lists
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Internet_Black_and_Whi...
A well-known DUL list is MAPS Dial-up User List: http://mail-abuse.org/dul/
Detection
PostCast Server has a feature that allows you to check if your computer's IP address is blacklisted. The program uses a DNSbl service that lets you check whether a particular IP address is being blocked by any of more than 100 anti-spam services: http://www.dnsbl.info/ Open the Setup Wizard from the Tools menu and press the "Blacklisted IP" button in the Network Diagnostics step:
You can also see the status of the IP address you are using if you visit this location: http://dnsbl.info/lookup.asp?IP=[IPADDRESS] Replace [IPADDRESS] with your Internet IP address. You can get the correct value by pressing CTRL+I in PostCast Server or by visiting http://www.myip.com/ web site.
Solutions
If you are using a dial-up connection, usually a few anti-spam services have your IP in their lists. If you discover that a significant number of black lists have your IP address, you have these options: Establish a new connection Establish a new dial-up connection to your ISP. That usually results in assigning a different Internet IP address to your computer. Run the test again to see if the new address is also blacklisted. Use a different ISP You can use a different ISP to connect to the Internet. Each ISP has its own range of IP addresses they assign to dial-up users. There is a good chance that the IP addresses of a different ISP are not blacklisted. Here are some web sites that can help you find thousands of ISPs: http://www.findanisp.com/ http://www.thelist.com/ http://www.isps.com/
2 of 3
16/03/13 23:45
Internet Black and White Lists
http://www.postcastserver.com/help/Internet_Black_and_Whi...
Ask your ISP for a static IP address outside of the dial-up space Ask the list maintainers to exclude your host Use socks proxy servers You can send e-mail using the socks proxy access to a computer on the Internet. This feature enables you to relay e-mail through other servers. When the message is sent using a third-party socks proxy, your IP address does not appear as the source of the message. The best solution is to connect to your ISP's socks proxy directly if it is provided by the ISP. Their server's (non-dynamic) IP address will be the source of your outgoing messages. For more information, see Firewall and Proxy Support. Use backup SMTP servers The professional edition of PostCast Server has a feature that allows you to specify one or more backup SMTP servers. If only certain domains are unable to receive messages from PostCast Server, you can use this option to forward those messages to your ISP's SMTP server. Open the Settings/Undelivered/Gateways window to configure this feature. For more information, see SMTP Gateways. Anti-Spam Methods:
Overview Port 25 Blocking Internet Black and White Lists Blocking Open Relays DNS Lookups
Home | Buy | Download | Details | Support 1997-2013 Oricode, Inc. All rights reserved. | Privacy Statement
3 of 3
16/03/13 23:45
También podría gustarte
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2100)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Spatial Data Analysis Theory and PracticeDocumento9 páginasSpatial Data Analysis Theory and PracticeJuan Carlos Muñoz CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Proxy Bypassing With A SSL VPN: Adri An Puente Z. February 27, 2008Documento23 páginasProxy Bypassing With A SSL VPN: Adri An Puente Z. February 27, 2008walaba06Aún no hay calificaciones
- IT General Controls IcqDocumento19 páginasIT General Controls IcqYuyu YcAún no hay calificaciones
- 769D 771D 773D 775D PDFDocumento116 páginas769D 771D 773D 775D PDFDenis Huanca80% (5)
- Tape Library Error CodesDocumento5 páginasTape Library Error CodesathusAún no hay calificaciones
- Cyber Security: ICDL ModuleDocumento13 páginasCyber Security: ICDL ModuleLuisa NghidenguaAún no hay calificaciones
- Maritime Cyber Security - Threats and Opportunities PDFDocumento20 páginasMaritime Cyber Security - Threats and Opportunities PDFconfesiones100% (2)
- HP Compaq dc5750 SFF Specifications DownloadDocumento4 páginasHP Compaq dc5750 SFF Specifications DownloadathusAún no hay calificaciones
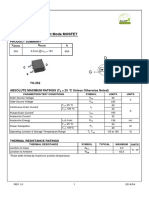
- MOS 2 Power-Transistor: Features Product SummaryDocumento10 páginasMOS 2 Power-Transistor: Features Product SummarydiegooliveiraEEAún no hay calificaciones
- P0603BDG N Chanel-MosfetDocumento5 páginasP0603BDG N Chanel-MosfetathusAún no hay calificaciones
- P0603BDL: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETDocumento5 páginasP0603BDL: N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFETLuisa GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Single N-Channel Trench MOSFET 30V, 24A, 10.1m : Features General DescriptionDocumento7 páginasSingle N-Channel Trench MOSFET 30V, 24A, 10.1m : Features General DescriptionabrkAún no hay calificaciones
- Tpca8057-H Mosfet Ps3 Placa Modelo PQX 001Documento9 páginasTpca8057-H Mosfet Ps3 Placa Modelo PQX 001Eisenhower Garcia LealAún no hay calificaciones
- Sc403 User ManualDocumento24 páginasSc403 User ManualathusAún no hay calificaciones
- DLO AdminGuide 8.0Documento260 páginasDLO AdminGuide 8.0juanmaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Development Manual For The TFT Series Offline Communication Development Kitú¿09-16ú® PDFDocumento106 páginasDevelopment Manual For The TFT Series Offline Communication Development Kitú¿09-16ú® PDFathusAún no hay calificaciones
- ERS CLI Commands RefDocumento488 páginasERS CLI Commands RefsujinsgeorgeAún no hay calificaciones
- Installing The Mac OS X Agent PDFDocumento1 páginaInstalling The Mac OS X Agent PDFathusAún no hay calificaciones
- Sheet UltraBac Solutions XuiS PDFDocumento2 páginasSheet UltraBac Solutions XuiS PDFathusAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Test A Bare Metal Restore (With Source Still Online)Documento13 páginasHow To Test A Bare Metal Restore (With Source Still Online)athusAún no hay calificaciones
- SymantecDLO 7.5 BestPracticesDocumento19 páginasSymantecDLO 7.5 BestPracticesathusAún no hay calificaciones
- DLO AdminGuide 8.0Documento260 páginasDLO AdminGuide 8.0juanmaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Deploying Forensics Science & Technology For Resolving National Cyber-Security ChallengesDocumento26 páginasDeploying Forensics Science & Technology For Resolving National Cyber-Security ChallengesHend AlmehairiAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam 2 Chapters 5 8 PDFDocumento37 páginasExam 2 Chapters 5 8 PDFStephen DavisAún no hay calificaciones
- Codeforces Problems DPDocumento17 páginasCodeforces Problems DPZulqarnayn0% (1)
- TutorialDocumento19 páginasTutorialRicardo XixaAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced Persistent ThreatsDocumento22 páginasAdvanced Persistent ThreatsjuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Senate Hearing, 106TH Congress - Cyber Attacks: Removing Roadblocks To Investigation and Information SharingDocumento86 páginasSenate Hearing, 106TH Congress - Cyber Attacks: Removing Roadblocks To Investigation and Information SharingScribd Government DocsAún no hay calificaciones
- Cyber Crime Awareness Among Pupil Teachers of PunjabDocumento8 páginasCyber Crime Awareness Among Pupil Teachers of PunjabManojAún no hay calificaciones
- Scilab Part IDocumento36 páginasScilab Part ISkye Jaba100% (1)
- Chapter 7 CEH v8 Gaining Access To A SystemDocumento16 páginasChapter 7 CEH v8 Gaining Access To A SystemLeroy SerepeAún no hay calificaciones
- Aurora Final-RewriteDocumento7 páginasAurora Final-Rewriteapi-231695908Aún no hay calificaciones
- ScriptDocumento3 páginasScriptAna Claudia AndradeAún no hay calificaciones
- ATS1192 ProspectDocumento2 páginasATS1192 Prospectsilviu_djAún no hay calificaciones
- 1IA08Documento4 páginas1IA08Henggar Tri WijayantoAún no hay calificaciones
- L1 Assessment Question For LinuxDocumento3 páginasL1 Assessment Question For LinuxMedha JhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Skew DesignDocumento29 páginasSkew DesignAshok KoyyalamudiAún no hay calificaciones
- TRUMP WILL WIN - HERE'S WHY - Howell WoltzDocumento9 páginasTRUMP WILL WIN - HERE'S WHY - Howell WoltzHang LEAún no hay calificaciones
- Metasploit Pro - The Attacker's Playbook: Test Your Defenses More Efficiently With Metasploit ProDocumento2 páginasMetasploit Pro - The Attacker's Playbook: Test Your Defenses More Efficiently With Metasploit Promadhan rajAún no hay calificaciones
- Linux Installation StepsDocumento43 páginasLinux Installation StepsSamit KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- GROUP 4 REPORT (Ethical Dilemmas Google Clip & Sentencing Software)Documento22 páginasGROUP 4 REPORT (Ethical Dilemmas Google Clip & Sentencing Software)Cathrena DequinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Admit CardDocumento2 páginasAdmit CardPankaj SanghaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Thesis Fulltext PDFDocumento134 páginasThesis Fulltext PDFed jireh nangcaAún no hay calificaciones
- BB OfficerDocumento1 páginaBB OfficerMooinul Islam AzadAún no hay calificaciones
- Chat LogsDocumento241 páginasChat LogsNancy EdwardsAún no hay calificaciones