Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Hidrogeologia Terminos Inlgles
Cargado por
hhu1985Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Hidrogeologia Terminos Inlgles
Cargado por
hhu1985Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
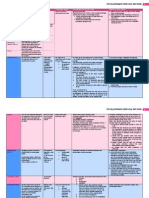
1 D Representation of detailed data Signs are printed in several colours grouped as shown below: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
violet: groundwater and springs orange: physical and chemical characteristics of groundwater quality and temperature blue: surface water and karst hydrography red: man-made features and alterations to the natural groundwater regime dark green: horizon contours (isopachytes) and limits of certain features, such as permafrost black: geological information
6.
Detailed examples of internationally used colour charts (ITC Colour Chad [1982], ITC Journal 1982-2, Enschede) are given in brackets to standardize the colours.
1 1.1 1.2 1.3
Groundwater and springs colour: violet (ITC No. 062) contours of the potentiometric surface (solid or broken lines with height relative to reference level) direction of groundwater flow connection between karstic loss and resurgence, a ) p ro ven , b ) inferred groundwater divide a) stationary, b) periodically changing limit of area with confined groundwater limit of area of artesian flow lens of fresh water surrounded by salt water
1.4
1.5 1.6 1.7
1.8
limit of area with insignificant natural replenishrnent from rainfall to groundwater (50 % screen colour)
1.9
spring, classified alter average discharge, e.g. a) less than 1001/s, b) 100 - 1000 l/s, c) more than 10001/s perennial karst spring submarne spring group of springs (relevant symbols are enclosed by circles) ternporary karst spring line of springs groundwater seepage area
1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15
Groundwater quality and temperature colour: orange (ITC No. 650)
2.1
boundary of salive groundwater in an aquifer (the definition of fresh, brackish and salive water may differ from one area to another, but should be defined on the basis of TDS or chloride content) isolines of equal groundwater salinity (isochlors) contours of the interface between fresh and salive groundwater, in m below reference leve] area of sea water intrusion area of mineralized groundwater inland area with mineralized water overlying fresh groundwater limit of mineralization of shallow groundwater inland
2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7
2.8 2.9 2.10
stream with mineralized water (blue stream with orange band) lagoon or lake with salive or brackish water (blue shoreline with orange band inside) periodical salt-water lake (broken blue shore line with orange band inside) shott (playa) with episodical water (dotted blue shore line with orange band inside) salt marsh limit of formations containing minerals with potential for affecting groundwater quality (grey line with orange band) spring of cold mineral or brackish water thermal spring thermomineral spring area of increased geothermal heat meltwater chamber beneath glacier glacier burst from meltwater chamber beneath glacier
2.11 2.12 2.13
2.14 2,15 2,16 2.17 2.18 2.19
Surface water and karst hydrography
(For mapping karst creas on large scale maps, more symbols are available in special literature, and the map maker is referred to special legends, e.g. Burger & Dubertret (1975); ISU (1978).) colour: blue (ITC No. 006) 3.1 stream with a) perennial, b) intetTnittent runoff hydraulic character of streams a) gaining (fed by groundwater)
3.2
3.3 3.4 3.5
b) losing (feeding the aquifer), including bank infiltration e) alternating (gaining or losing) d) independent (no communication with the aquifer) e) no information dry valley, possibly with episodical runoff (ephemeral stream) braided stream (sandur) stream ending in inland depression
cf.2.8 stream with mineralized water (blue stream with orange band) 3.6 karstic loss in river valley a) perennial flow downstream b) seasonal flow downstream c) no flow downstream
cf.1.3 connection between karstic loss and resurgence, a) proveo b) inferred 3.7 3.8 3.9 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 aven, karstic shaft or cave limit of karst area main surface water divide secondary surface water divide flow gauging station, mean annual runoff [m3/s] catchment anea [1000 km2] glacier glacier burst from ice dammed lake
3 .1 4 water fall 3.15 fresh water lake
cf.2.9 lagoon or lake with salive or brackish water (blue shore line with orange band inside) cf.2.10 periodical salt-water lake (broken blue shore line with orange band inside)
cf.2.11 shott (playa) with episodical water (dotted blue shore line with orange band inside) 3.16 3.17 3.18 periodical fresh water lake dry lake with only episodical water river marsh
3.19 bog
4 Man-made features and alterations to the natural groundwater regime
(More detailed graphical elements frequently used on vulnerability maps, depictions of human influence on groundwater systems and pollution are provided in the IAH guidebook on vulnerability mapping, see Section III of this Legend.) colour: red (ITC No. 660) 4.1 well, shaft or borehole, for monitoring or with little output, with phreatic or confined groundwater group of wells or boreholes, with phreatic or confined groundwater well or borehole, artesian flowing group of wells or boreholes, artesian flowing mineral water well thermomineral water well thermal water well injection well pumping station, pumped well field, average quantity of discharge or pumping (categories at the discretion of the author), e.g. a) 3 - 30 million m3/year b) 30 - 300 million m3/year c) more than 300 million m3/year
4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9
4.10 4.11 4.12 4,13
pumping station from spring (red square with violet dot inside) underground drainage gallery (e.g. Kanat) river intake pipeline
4.14 aqueduct 4.15 storage reservoir or pond, a) perennial, b) temporary dam or weir, with capacity of the reservoir in million m3 levee or coastal dyke flood-tide barrage or tidal power plant groundwater recharge site installation for desalination oasis limit of area of intensive groundwater exploitation
4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 4.20 4.21 4.22
4.23 area of underground mining affecting the natural groundwater regime 4.24 4.25 area of open cast mining affecting the natural groundwater regime irrigation area
5 5.1
Horizon contours (isopachytes) and limas of certain features, such as permafrost. colour: dark green (ITC No. 606) horizon contours or isopachytes (solid or broken unes with depth in m relative to reference level)
5.2 5.3 5.4
thickness of aquifer in m limit of permafrost anea (variation of broken lines for continuous, discontinous and isolated distribution) talik (unfrozen zone) under a river, lake or reservoir (river or lake in blue, green dots surrounding)
Geological information colocar: black
6. 1
geological or hydrogeological boundary (a more detailed classification of boundaries based on their hydrodynamic character is given in Section II of this Legend) fault, certain (solid line) or inferred (broken line) overthrust, certain or inferred hydraulic character of boundaries (combined with no. 6.1 to 6.3) a) acting as barrier b) acting as conduit without significance to groundwater flow d) no information fractured belt of hydrogeological importante
6.2 6.3 6.4
6.5
cf.2.13 limit of formations containing minerals with potential for affecting groundwater quality (grey line with orange band)
6.6
salt plug (Diapir) a) near surface b) at depth (dotted fine)
6.7 crea and edge of solution chambers formed in salirle formations (subrosion) 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 boundary of infilled erosional channel volcanic cone volcanic crater line of cross section
También podría gustarte
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Introduction To Coastal EngineeringDocumento27 páginasIntroduction To Coastal EngineeringVidya Pravesh CheekhooryAún no hay calificaciones
- Short Notes Rivers Drainage System of India - SSC RRB TNPSC Exams Free PDF Material For SSC Railway RRB TNPSC ExamsDocumento42 páginasShort Notes Rivers Drainage System of India - SSC RRB TNPSC Exams Free PDF Material For SSC Railway RRB TNPSC ExamsDhil SanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tropopause Definition and DescriptionDocumento4 páginasTropopause Definition and DescriptionĐoàn Hồng NgọcAún no hay calificaciones
- Floods and SocietyDocumento5 páginasFloods and SocietyaviralpareekAún no hay calificaciones
- Danube River Is The Second LongestDocumento12 páginasDanube River Is The Second LongestliviuAún no hay calificaciones
- 7589 1 OceanDocumento23 páginas7589 1 OceanchanchalAún no hay calificaciones
- Air Masses Fronts and Pressure System Presentation 2017Documento36 páginasAir Masses Fronts and Pressure System Presentation 2017api-271661638Aún no hay calificaciones
- Armorica Barents and Kara FormationDocumento11 páginasArmorica Barents and Kara Formationgigio marinoAún no hay calificaciones
- J Indian Geophys Union 4 185Documento6 páginasJ Indian Geophys Union 4 185georgesapuleteAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Indian GeographyDocumento81 páginas4 Indian Geographyamlan baruahAún no hay calificaciones
- T&P in ForceDocumento29 páginasT&P in Forcebandar abbAún no hay calificaciones
- M1 Watershed AnalysisDocumento26 páginasM1 Watershed AnalysisEunnice Panaligan100% (1)
- Chebotarev 1955 Metamorphism of Natural Waters 2Documento34 páginasChebotarev 1955 Metamorphism of Natural Waters 2Trevor FranklinAún no hay calificaciones
- B1 Ice Part 1 - 2021Documento45 páginasB1 Ice Part 1 - 2021giannyp0paAún no hay calificaciones
- West Philippine Sea Brief On DecisionDocumento7 páginasWest Philippine Sea Brief On DecisionJohn Fredrick BucuAún no hay calificaciones
- Sea Breeze - Causes, Diagram and Effects - JotscrollDocumento5 páginasSea Breeze - Causes, Diagram and Effects - JotscrollnadeemuzairAún no hay calificaciones
- IPCC Special Report On Oceans and CryosphereDocumento1170 páginasIPCC Special Report On Oceans and CryosphereTech2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ocean-Tides, Waves& CurrentsDocumento7 páginasOcean-Tides, Waves& Currentssushma100% (1)
- Oceanography of The Arabian SeaDocumento39 páginasOceanography of The Arabian SeaDeckHand YachtsAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 17 - WEATHER SYSTEM (Southwest Monsoon, Northeast Monsoon)Documento8 páginasModule 17 - WEATHER SYSTEM (Southwest Monsoon, Northeast Monsoon)jerwin remocalAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 1Documento26 páginasModule 1Afroz AhamedAún no hay calificaciones
- UNCLOS Summary TableDocumento3 páginasUNCLOS Summary Tablecmv mendoza100% (3)
- Guidelines Safety Zones Offshore InstallationsDocumento4 páginasGuidelines Safety Zones Offshore InstallationsJithin VaralilAún no hay calificaciones
- Himalayan RiversDocumento8 páginasHimalayan RiverskarthikAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 9 - Week 8: Assignment 8Documento3 páginasUnit 9 - Week 8: Assignment 8JohnAún no hay calificaciones
- HurricanesDocumento25 páginasHurricanesSwayamjit MohapatraAún no hay calificaciones
- ESCMC Catalogo Da BibliotecaDocumento141 páginasESCMC Catalogo Da Bibliotecaeusoqueroessapesquis0% (1)
- Fishing Template West Coast of India PDFDocumento2 páginasFishing Template West Coast of India PDFAlmandine Apl61% (18)
- Morphological Change in Lower Meghna River EstuarineDocumento28 páginasMorphological Change in Lower Meghna River EstuarineS M Ehasanul HaqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Reading Maps and Understanding Rainfall PatternsDocumento232 páginasReading Maps and Understanding Rainfall Patternsimteyaz alam100% (1)