Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Alkane
Cargado por
NaeemMushtaqDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Alkane
Cargado por
NaeemMushtaqCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
1. Dodec-1-ene has the structure shown.
CH3(CH2)9CH = CH2 (a) Draw the structures of the organic molecules produced when dodec-1-ene reacts with each of the following.
(b) (i) What type of isomerism is shown by the organic products in (i), (ii) and (iv)? (ii) Draw structures to represent these isomers, choosing any one of these products. [3] (c) Dodec-2-ene shows another type of isomerism. Draw and label diagrams which show these two isomers. [2] 2. Crude oil is the principal source of hydrocarbons. The following are examples of such hydrocarbons.
(a) Give the structural formulae of the organic products in the following reactions. (i) The reaction of ethane with bromine in the presence of u.v. light. (ii) The polymerisation of propene. (iii) The oxidation of propene with cold, acidified potassium manganate(VII). (iv) The reaction of cyclohexene with hydrogen bromide. (v) The reaction of cyclohexene with hot acidified potassium manganate(VII). [5] (b) Write equations for the following reactions. (i) The complete combustion of ethane. (ii) The action of steam on propene in the presence of a catalyst. (iii) The reaction of cyclohexene with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. [3] (c) The process of cracking produces useful substances from oil. (i) Explain why cracking is useful. (ii) Suggest an equation for the cracking of C16H34 into at least three fragments. [3] (d) Draw structures for each of the following polymers showing two repeat units. (i) poly(ethene) (ii) pvc [poly(chloroethene)] [2] [Total : 13] 4 Some perfumes and scents of flowers and fruit contain compounds which are structural isomers. Two such examples are citronellol and geraniol.
(a) Confirm that citronellol and geraniol are isomers by calculating their molecular formula and their relative molecular mass, Mr. (i) Molecular formula (ii) Mr [2] (b) Name two functional groups present in both molecules. [3] Citronellol and geraniol also show stereo isomerism. (c) On the diagram of the structure of citronellol above, draw a circle around a chiral carbon atom. [1] (d) (i) Draw the other cis-trans isomer of geraniol. [In parts (d) and (f) use R to represent a part of the molecule.] (ii) Explain why geraniol has no optical isomers. [2] (e) State what you would expect to see if citronellol was reacted with aqueous bromine. [1] (f) Draw structures of the organic products when geraniol reacts with each of the following reagents. [2] 2(i) an excess of H+/Cr2O7 under reflux (ii) hydrogen bromide, HBr [Total : 11]
También podría gustarte
- Alkanes and Alkenes QuestionsDocumento20 páginasAlkanes and Alkenes Questionscusgakunga100% (2)
- Structured QuestionsDocumento2 páginasStructured Questionsmalikimran28Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationDocumento15 páginasMini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationSahanNivanthaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Synoptic Practice PaperDocumento8 páginasChemistry Synoptic Practice PaperJeffry JunusAún no hay calificaciones
- Section B Answer ALL Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocumento6 páginasSection B Answer ALL Questions in The Spaces ProvidedSweetie AndersonAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkanes: Self-Attempt Questions 1 (I)Documento7 páginasAlkanes: Self-Attempt Questions 1 (I)EdcademiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Assignment - Organic ChemistryDocumento7 páginasChemistry Assignment - Organic ChemistryIsaac MapulangaAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Chemistry Structured Questions (Topical)Documento28 páginasOrganic Chemistry Structured Questions (Topical)Lee Jun Hui100% (1)
- Chemistry QuizDocumento23 páginasChemistry QuizJoshuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Alcohol QuestionDocumento5 páginasAlcohol Questionlucylovesbooks6770Aún no hay calificaciones
- Test 4 - Chemistry of ArenesDocumento3 páginasTest 4 - Chemistry of ArenesElizabeth ProtoctisAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic ChemDocumento4 páginasOrganic ChemKarren MakamureAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem and Phy RevisionDocumento89 páginasChem and Phy RevisionBwalya kelvinAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Olympiad 2010 PaperDocumento11 páginasChemistry Olympiad 2010 PaperAlokShuklaAún no hay calificaciones
- 01 Crude - Oil - Alkanes - & - Alkenes QPDocumento11 páginas01 Crude - Oil - Alkanes - & - Alkenes QPcharlesma123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Alkane Alkene QuestionsDocumento10 páginasAlkane Alkene QuestionsormattAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Symposium Questions 2023Documento17 páginasChemistry Symposium Questions 2023Doris KinyuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Form Six Chemistry 1Documento6 páginasForm Six Chemistry 1abubakarimuyanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Worksheet 1 Year 11Documento8 páginasChemistry Worksheet 1 Year 11fatma.darghouth2Aún no hay calificaciones
- NSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsDocumento47 páginasNSS Chemistry Part 11 Chemistry of Carbon CompoundsFelix YueAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem F342 1562 C 2017 1Documento8 páginasChem F342 1562 C 2017 1APOORVA OJHAAún no hay calificaciones
- Cbse Test Paper-05: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 4. Carbon and Its CompoundsDocumento1 páginaCbse Test Paper-05: Science & Technology (Class-10) Chapter 4. Carbon and Its CompoundsbannaduraiAún no hay calificaciones
- Haloalkanes QDocumento7 páginasHaloalkanes Qlucylovesbooks6770Aún no hay calificaciones
- JC2 Chemistry Practice Paper - GCE A Levels Chemistry 6092Documento7 páginasJC2 Chemistry Practice Paper - GCE A Levels Chemistry 6092Chong56Aún no hay calificaciones
- CA0002OCDocumento27 páginasCA0002OCYourChemistryTeacherAún no hay calificaciones
- CQ Petroleum ProductsDocumento15 páginasCQ Petroleum Productsapi-3826629Aún no hay calificaciones
- Section B Answer ALL Questions in The Spaces Provided.: "Nothing Limits Excellence"Documento5 páginasSection B Answer ALL Questions in The Spaces Provided.: "Nothing Limits Excellence"Sweetie AndersonAún no hay calificaciones
- TEST Hydrocarbon Kelas XI SMT 1Documento9 páginasTEST Hydrocarbon Kelas XI SMT 1Nafa Rida Aisy PutriAún no hay calificaciones
- KK Mid Semi 1Documento26 páginasKK Mid Semi 1chikondikosamu24Aún no hay calificaciones
- Class 12th Chemistry Solved Sample Paper 1Documento11 páginasClass 12th Chemistry Solved Sample Paper 1cbsestudymaterialsAún no hay calificaciones
- 01) Xii Theory Paper 24-01-24Documento3 páginas01) Xii Theory Paper 24-01-24bbfnpsy2cdAún no hay calificaciones
- TTTTDocumento1 páginaTTTTAnonymous BT988qyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry 12th Full Book Paper 2024Documento3 páginasChemistry 12th Full Book Paper 2024Muhammad AwaisAún no hay calificaciones
- Promo Time-Trial For O2Documento4 páginasPromo Time-Trial For O22022 BALAKRISHNAN ADHITHIAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Questions AlkenesDocumento9 páginasPractice Questions Alkenesibrahim ahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- DocumentDocumento89 páginasDocumentRajeev Sharma100% (1)
- Chemistry 2Documento4 páginasChemistry 2jasmina.mushy22Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cet (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Documento3 páginasCet (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids)Arnab Jana100% (1)
- Previous HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Documento10 páginasPrevious HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Adithya K SanjeevAún no hay calificaciones
- Isc 2010 Question Paper ChemistryDocumento6 páginasIsc 2010 Question Paper Chemistrypornika majumderAún no hay calificaciones
- RHN DCs MB 7 D Ar AZqf RQ DNDocumento4 páginasRHN DCs MB 7 D Ar AZqf RQ DNTr Mazhar PunjabiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry 5070 End of YearDocumento7 páginasChemistry 5070 End of Yearsamuelbandamiracle20Aún no hay calificaciones
- STC 221 20202021 Full TimeDocumento3 páginasSTC 221 20202021 Full Timewww.williamskimberly10100% (1)
- ISC Board Question Paper Class XII - 2009Documento5 páginasISC Board Question Paper Class XII - 2009Biswajit GhoshAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry STD 11 Finalterm QP2022-2023Documento7 páginasChemistry STD 11 Finalterm QP2022-2023abdul0000djAún no hay calificaciones
- TripleScenceOnly AlcoholsDocumento10 páginasTripleScenceOnly AlcoholsKhadijahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Revision 2Documento2 páginasChemistry Revision 2Dilan NyaririAún no hay calificaciones
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)Documento11 páginasSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Paper 2 (SMJK Sam Tet Ipoh)sherry_christyAún no hay calificaciones
- CHE 232 Test 1Documento11 páginasCHE 232 Test 1moatlhodiAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkenes TutorialDocumento8 páginasAlkenes TutorialVarshLokAún no hay calificaciones
- Hsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-11. Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocumento4 páginasHsslive-Xii-Chemistry-Qb-Anil-11. Alcohols, Phenols and EthersAryan R.MohanAún no hay calificaciones
- Acjc 08 Paper 3Documento8 páginasAcjc 08 Paper 3Zenaida AtinorAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry s4 Theory and Pract.Documento26 páginasChemistry s4 Theory and Pract.kubwimanajeandamour359Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chem Question Paper Jan 2000 Unit-6Documento10 páginasChem Question Paper Jan 2000 Unit-6Shahariar HassanAún no hay calificaciones
- AlkeneDocumento5 páginasAlkeneWeng Hong0% (1)
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesDe EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneAún no hay calificaciones
- Fuel Cells, Solar Panels, and Storage Devices: Materials and MethodsDe EverandFuel Cells, Solar Panels, and Storage Devices: Materials and MethodsAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkyl and Aryl Halides NEETDocumento10 páginasAlkyl and Aryl Halides NEETJagrav GargAún no hay calificaciones
- Stereo ChemistryDocumento45 páginasStereo ChemistryFafa AlunksAún no hay calificaciones
- BenzimidazolDocumento145 páginasBenzimidazolMartinez Fuentes PaulinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Why Are Isomers Important in Our LivesDocumento5 páginasWhy Are Isomers Important in Our Livesomair_leoAún no hay calificaciones
- AS 4.1.2 AlkanesDocumento14 páginasAS 4.1.2 AlkanesLexy Lawton-BoweringAún no hay calificaciones
- Stereoisomerism: Review of ConceptsDocumento25 páginasStereoisomerism: Review of Concepts丁文婷Aún no hay calificaciones
- C9e Answers Active Reading 04Documento4 páginasC9e Answers Active Reading 04Jordan Camina75% (8)
- Week 7: Chemistry Homework - SPM 2020: NotesDocumento2 páginasWeek 7: Chemistry Homework - SPM 2020: NotesRAJA ARISSA DALILIAún no hay calificaciones
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesDocumento7 páginasHsslive-Xi-Chem-Prvs-Qn-12. Organic Chemistry Some Basic PrinciplesLayanAún no hay calificaciones
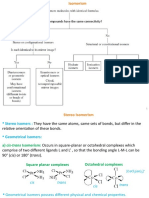
- Do The Compounds Have The Same Connectivity?Documento9 páginasDo The Compounds Have The Same Connectivity?Kushagra SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Isomers and IsomerismDocumento37 páginasIsomers and IsomerismAnwherSehdatAún no hay calificaciones
- UST Pharmacy Org Chem Lec MonthliesDocumento72 páginasUST Pharmacy Org Chem Lec MonthliesGab ParagasAún no hay calificaciones
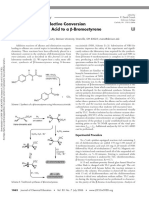
- Rapid and Stereoselective Conversion ofa trans-Cinnamic Acid to a βDocumento3 páginasRapid and Stereoselective Conversion ofa trans-Cinnamic Acid to a βAitor PastorAún no hay calificaciones
- CHM 122 Introductory Organic Chemistry 2 Units FDocumento65 páginasCHM 122 Introductory Organic Chemistry 2 Units Fstephenalfa7Aún no hay calificaciones
- Plan Ai TS 2022-2023Documento2 páginasPlan Ai TS 2022-2023ShouryavardhanAún no hay calificaciones
- 2015 ASOE PaperDocumento29 páginas2015 ASOE PaperFaisal AldiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Epimers, Anomers, Enantiomers and MutarotationDocumento7 páginasEpimers, Anomers, Enantiomers and MutarotationgayathriAún no hay calificaciones
- GeneralChemistry (Organic Compounds)Documento27 páginasGeneralChemistry (Organic Compounds)yen perioles100% (1)
- Reaction Mechanism PDFDocumento14 páginasReaction Mechanism PDFSreeragAún no hay calificaciones
- 9701 w16 QP 42Documento16 páginas9701 w16 QP 42Abdelmoneim Elmansy IgcseAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem1011 Exam Practice Test 2Documento27 páginasChem1011 Exam Practice Test 2Chirisuu PantsuAún no hay calificaciones
- Classification Nomenclature and IsomerismDocumento52 páginasClassification Nomenclature and IsomerismPawankumar Gupta89% (9)
- Hydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURUDocumento11 páginasHydrocarbons ChapterNotes-JEEMAIN - GURURaagAún no hay calificaciones
- 474 - CHM 222Documento68 páginas474 - CHM 222Tariq AbdullahiAún no hay calificaciones
- Coordination ChemistryDocumento10 páginasCoordination ChemistrycharleslukeAún no hay calificaciones
- Nomenclature and IsomerismDocumento3 páginasNomenclature and Isomerismapi-3710134100% (1)
- UOP I-210 CatDocumento3 páginasUOP I-210 Cathml2827Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry SyllabusDocumento86 páginasChemistry SyllabusveereshAún no hay calificaciones
- ) Anilin PDFDocumento1616 páginas) Anilin PDFAnisa RachmadaniAún no hay calificaciones
- 'A' Level Chemistry (Organic & Options)Documento220 páginas'A' Level Chemistry (Organic & Options)Wilbur Muzondo100% (1)