Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Institute of Health Sciences
Cargado por
Florygene Kris DisagonTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Institute of Health Sciences
Cargado por
Florygene Kris DisagonCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
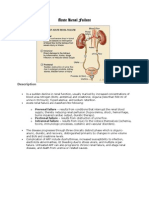
Saint Joseph College Institute of Health Sciences Cavite City NURSING Name: Mario Braga Impression: s/p colectomy
Cues/Evide nces Subjective: Objective: Fluid imbalance: Hypovolemi a PR=108 bpm BP=110/64 mmHg ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis Risk for electrolyte imbalance (specificall y hypernatre mia and hyperkale mia) Scientific Rationale Age: 50 y/o PLANNING Nursing Objective Within 3-4 hrs. of giving nursing intervention, the client will Be free of complications resulting from electrolyte imbalance as manifested by: Display vital signs and laboratory results within normal range for individual. Identify individual risks and engage in appropriate behaviors or lifestyle changes to prevent or reduce frequency of electrolyte imbalances. CARE PLAN Sex: M IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Scientific Order/Action Rationale Identify client with current or newly diagnosed condition commonly associated with electrolyte imbalances, such as inability to eat or drink febrile illness, active bleeding or other fluid loss, including vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal drainage, burns. Note clients age and developmental level, which may increase risk for electrolyte imbalance. to further assess the client and prevent more serious complications
EVALUATIO N
Elderly clients are more prone to electrolyte imbalances related to fluid imbalances, use of multiple medications including diuretics, heart and blood pressure medications, lack of appetite or interest in eating or drinking, lack of appropriate dietary and/or medication supervision at home,
and so on. It is the most common Assess mental problem of status, noting hypernatremia. client/caregiver report of change altered attention span, recall of recent events, other Cognitive functions. Tachycardia, bradycardia, and other Monitor heart rate dysrhythmias are and rhythm by associated with palpation and potassium, calcium, and auscultation. magnesium imbalances. Because the ECG reflects electrophysiological, anatomical, metabolic, and hemodynamic alterations, it is routinely used for the diagnosis of electrolyte and metabolic disturbances, as well as myocardial ischemia, cardiac dysrhythmias, structural changes of the myocardium, and drug effects.
Review electrocardiogram (ECG).
Assess fluid intake Many factors, such as and output. inability to drink, large diuresis or chronic kidney failure, trauma, and surgery, affect individuals fluid balance, disrupting electrolyte transport,
function, and excretion. Review laboratory results for abnormal findings Electrolytes include sodium, potassium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate (carbon dioxide) and magnesium. These chemicals are essential in many bodily functions including fluid balance, movement of fluid within and between body Na+ compartments, nerve Monitor for physical conduction, muscle or mental disorders contraction including impacting fluid the heart; blood clotting intake and pH balance. Impaired thirst Note presence of sensation, inability to medical conditions express thirst or obtain that may impact needed fluids may lead sodium level. to hypernatremia. Hypernatremia can result from simple conditions such as febrile illness causing fluid loss and/or restricted fluid intake, or complicated conditions such as kidney and endocrine diseases affecting sodium intake or excretion. Diuretics, laxatives,
Review regimen.
drug
K+ Note current medical conditions that may impact potassium level.
theophylline, and trimeterine can decrease sodium level. Metabolic acidosis, burn or crush injuries, Monitor ECG, as massive hemolysis, indicated diabetes, kidney disease/renal failure, cancer, and sickle cell trait are associated with Evaluate reports hyperkalemia of abdominal cramping, Abnormal potassium fatigue, levels, both low and hyperactive high, are associated bowel motility, with changes in the muscle twitching, ECG. and cramps, followed by Signs/ symptoms muscle suggesting weakness. Note hyperkalemia. presence of depressed reflexes, ascending flaccid paralysis of legs and arms. Review regimen. drug Medications such as albuterol, terbutaline, or some diuretics may decrease potassium level.
Cues/Evide nces Subjective: Objective: The client undergoes colectomy 2 days ago Presence of incision site Pus and redness is not indicted
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis Risk for infection related to a site for organism invasion secondary to colectomy 2 days ago as manifested by Presence of incision site and Pus and redness is not indicted
Scientific Rationale
PLANNING Nursing Objective Within 1-2 hrs of giving intervention, the client will be able to identify behaviors and practices to prevent and reduce the risk for infection as manifested by:
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Scientific Order/Action Rationale Independent: Monitor white blood count (WBC). Rising WBC indicates the bodys attempt to combat pathogens. Redness, swelling, increased pain, or purulent drainage is suspicious of infection and should be cultured. Hand washing reduces the risk of transmitting pathogens from one area of the body to another as well as from one patient to another. Prevents entry of bacteria, reducing risk of nosocomial infections.
EVALUATIO N
Demonstrate meticulous hand Stress and model washing proper handtechnique by the washing technique time of discharge to client and caregivers. Describe methods of transmission of infection Maintain aseptic technique with any Describe the procedures. Provide influence of routine site nutrition on care/wound care, as prevention of
Monitor incisions, injured sites and exit sites of tubes, drains and catheters for signs of infection.
infection. appropriate. Early detection of developing infection provides opportunity for timely intervention and prevention of more serious complications. Limits stasis of body fluids, promotes optimal functioning of organ systems and GI tract.
Inspect dressings and wound; note characteristics of drainage. Encourage frequent position changes and being out of bed or ambulation, as tolerated. Provide routine catheter care and promote meticulous perianal care. Keep urinary drainage system closed and remove indwelling catheter as soon as possible.
Reduces bacterial colonization and risk of ascending UTI.
Monitor vital signs.
Temperature elevation and tachycardia may reflect developing sepsis.
Collaborative: Encourage intake of protein and calorie rich foods.
Optimal nutritional status promotes wound
healing. Administer antibiotics, as indicated. All agents are either toxic to the pathogens or retard the pathogens growth. Ideally medications should be selected based on a culture from the infected area. A broad-spectrum agent may be started until culture reports are available.
Cues/Evide nces Subjective: Objective: Disruption of epidermal and dermal tissues: presence of surgical incision The client undergoes colectomy 2 days ago +2 edema Decreased blood pressure 110/64 mm Hg No other data about pus drainage and redness in the incision site
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis Impaired skin integrity related to post surgical wound and decreased blood and nutrients to tissues secondary to edema as manifested by: presence of surgical incision The client undergoes colectomy 2 days ago +2 edema Decreased blood pressure 110/64 mm Hg
Scientific Rationale
PLANNING Nursing Objective Within 1 hr of giving nursing intervention, the client will demonstrate progressive healing of tissue as manifested by: Participate in risk assessment Express willingness to participate in prevention of pressure ulcers. Describe etiology and preventive measures
IMPLEMENTATION Nursing Scientific Order/Action Rationale Observe wound, note characteristic of drainage. Change dressings, as needed using aseptict echnique Postoperative hemorrhage is most likely to occur during first48 hours whereas infection may develop at anytime. Large amount of serous drainage require that dressings, be change frequently to reduce skin irritation potential for infection May required treating preoperative inflammation or intra operative contamination To stimulate circulation
EVALUATIO N
Irrigate wound as indicated, using normal saline diluted with antibiotic solution Gently massage healthy skin around the affected site
Increase protein and To maintain nitrogen carbohydrate intake balance
Administer meds. as indicated.(antibiotic)
Antibiotic is the drug used to treat and prevent infection caused by bacteria.
nursingcareplan.blogspot.com prenhall.com
También podría gustarte
- 3 Drugs Study Updates Issues HemodialysisDocumento7 páginas3 Drugs Study Updates Issues HemodialysisKim GalamgamAún no hay calificaciones
- Sickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasSickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanArisa Vijungco100% (4)
- Ecf Case StudyDocumento54 páginasEcf Case Studyapi-290929891Aún no hay calificaciones
- Perioperative NursingDocumento271 páginasPerioperative NursingCodered Review100% (3)
- 3E Group 4 H Dysfunction.Documento6 páginas3E Group 4 H Dysfunction.Shane PangilinanAún no hay calificaciones
- Renal SystemDocumento80 páginasRenal SystemJerilee SoCute Watts100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocumento9 páginasNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasAún no hay calificaciones
- REVIEWER3Documento33 páginasREVIEWER3Maye ArugayAún no hay calificaciones
- Kidney TransplantDocumento1 páginaKidney Transplantsunilk09Aún no hay calificaciones
- Reducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresDocumento10 páginasReducing Hematoma Through Comfort MeasuresKier Jucar de GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento5 páginasAcute Renal FailureJean De Vera MelendezAún no hay calificaciones
- DengueDocumento14 páginasDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubreAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 Diabetes Nursing Care PlansDocumento14 páginas6 Diabetes Nursing Care PlansMerlyn Rivera PelecinAún no hay calificaciones
- Liver Cirrhosis Case PresDocumento77 páginasLiver Cirrhosis Case Presmarlx580% (5)
- NSBO22 General NotesDocumento72 páginasNSBO22 General Notesjunxicooper100% (1)
- Case ScenarioDocumento40 páginasCase ScenarioDave Michael GeliAún no hay calificaciones
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDocumento11 páginasDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis82% (33)
- Signs and Symptoms Vital SignsDocumento3 páginasSigns and Symptoms Vital SignsCris CandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Patho CardsDocumento195 páginasNursing Patho Cardsgiogmail100% (1)
- Drug Study 2Documento7 páginasDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerAún no hay calificaciones
- Polycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaDocumento6 páginasPolycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaEileen OoiAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocumento3 páginasExam 1 Study GuideNataraj LoganathanAún no hay calificaciones
- Impaired kidney function nursing careDocumento21 páginasImpaired kidney function nursing careKate ManalastasAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care for Gastroenteritis PatientDocumento10 páginasNursing Care for Gastroenteritis PatientJoia De LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Management of LeukemiaDocumento13 páginasNursing Management of LeukemiabeingfiredAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP LatestDocumento6 páginasNCP LatestThirdy AquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pre-Operative Nursing CareDocumento79 páginasPre-Operative Nursing CarePeter FrimpongAún no hay calificaciones
- MNT For Metabolic StressDocumento107 páginasMNT For Metabolic StressMeyar Y. Abu AsadAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study: Foley Catheter Sepsis Leads to Septic Shock and MODSTITLEMotor Vehicle Trauma Causes Hypovolemic Shock in Blunt Abdomen Injury PatientDocumento3 páginasCase Study: Foley Catheter Sepsis Leads to Septic Shock and MODSTITLEMotor Vehicle Trauma Causes Hypovolemic Shock in Blunt Abdomen Injury PatientJrBong SemaneroAún no hay calificaciones
- Liver Cirrhosis GuideDocumento8 páginasLiver Cirrhosis GuidegoyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Addison's DseDocumento9 páginasAddison's DseKath RubioAún no hay calificaciones
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento35 páginasAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- Assignment 2 - FuntechamDocumento5 páginasAssignment 2 - FuntechamJuan Miguel O. ApatAún no hay calificaciones
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento5 páginasRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- Risk for Infection Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasRisk for Infection Nursing Care PlanMariquita Buenafe57% (7)
- Preoperative Surgical NursngDocumento271 páginasPreoperative Surgical NursngPaw PawAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid Imbalance (NCP)Documento9 páginasFluid Imbalance (NCP)Putry RainismAún no hay calificaciones
- Intestinal ObstructionDocumento13 páginasIntestinal Obstructionsantosh kumarAún no hay calificaciones
- GroupA RenalDisordersDocumento13 páginasGroupA RenalDisordersPaulAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP For EclampsiaDocumento6 páginasNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- Perioperative NursingDocumento13 páginasPerioperative NursingTobiDaAún no hay calificaciones
- MNT For Metabolic StressDocumento107 páginasMNT For Metabolic StressBobby SwadharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- The UWI School of Nursing, Mona Practice Clinical WorksheetDocumento10 páginasThe UWI School of Nursing, Mona Practice Clinical WorksheetOdessia BenjaminAún no hay calificaciones
- NCPDocumento14 páginasNCPclaidelynAún no hay calificaciones
- Iii. Nursing Care PlansDocumento13 páginasIii. Nursing Care PlansLharra Cagulada-Postrano100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure (ACF)Documento12 páginasAcute Renal Failure (ACF)Aewooncardivilla21Aún no hay calificaciones
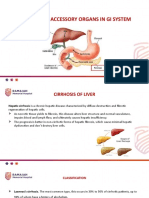
- Disorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemDocumento29 páginasDisorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemY. Beatrice AbigailAún no hay calificaciones
- Guide For Pre-Clinical Practice Research and PlanningDocumento5 páginasGuide For Pre-Clinical Practice Research and PlanningAnonymous ZSqTiYX7nAún no hay calificaciones
- Liver DiseaseDocumento8 páginasLiver Diseaseأبوأحمد الحكيمAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocumento16 páginasFluids and Electrolytesjc_sibal13Aún no hay calificaciones
- Appendectomy Possible NCPDocumento6 páginasAppendectomy Possible NCPIrish Nicole DC100% (1)
- Med Surg ReviewDocumento6 páginasMed Surg ReviewSabhi Sandhu75% (4)
- Acute Glomerulonephritis 1Documento19 páginasAcute Glomerulonephritis 1Jane Ann AlolodAún no hay calificaciones
- Gastritis Nursing InterventionsDocumento11 páginasGastritis Nursing InterventionsMike Faustino SolangonAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento7 páginasNursing Diagnosis Impaired Gas ExchangeZycon Rodney Ae'zecquel Gachallan50% (2)
- Assessment of the Politraumatized PatientDe EverandAssessment of the Politraumatized PatientAún no hay calificaciones
- Philhealth Accredited Animal Bite CenterDocumento5 páginasPhilhealth Accredited Animal Bite CenterFlorygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- Colorectal PATHOPHYSIODocumento3 páginasColorectal PATHOPHYSIOFlorygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- AudiDocumento3 páginasAudiFlorygene Kris Disagon0% (1)
- HypophosphatemiaDocumento11 páginasHypophosphatemiaFlorygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- Florygene Kris A. Disagon HypervolemiaDocumento4 páginasFlorygene Kris A. Disagon HypervolemiaFlorygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- St. Joseph College Institute of Health Sciences Cavite City An Output of Activity in NCM 104 (Immunology) by BSN Iii Makadiyos Batch 2014Documento5 páginasSt. Joseph College Institute of Health Sciences Cavite City An Output of Activity in NCM 104 (Immunology) by BSN Iii Makadiyos Batch 2014Florygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- BereavementDocumento15 páginasBereavementFlorygene Kris DisagonAún no hay calificaciones
- A Major Threat Now A Days .: Jitunu Sahoo Preetam Kajal Rout Swaroop Kishan JenaDocumento23 páginasA Major Threat Now A Days .: Jitunu Sahoo Preetam Kajal Rout Swaroop Kishan Jenaameet_maharanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dialysis Induced Hypoglycemia in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease PatientsDocumento3 páginasDialysis Induced Hypoglycemia in Non-Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease Patientsscience worldAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoulder Stiffness - Current Concepts and Concerns (2015Documento235 páginasShoulder Stiffness - Current Concepts and Concerns (2015Joaquin Villagra Jara100% (2)
- Writing Medicine Sample Test 1 2010 PDFDocumento4 páginasWriting Medicine Sample Test 1 2010 PDFpratim deyAún no hay calificaciones
- NMES Electrode Placement GuideDocumento2 páginasNMES Electrode Placement GuideSkye EllisAún no hay calificaciones
- Pneumonia NCPDocumento7 páginasPneumonia NCPitsmeaya100% (3)
- Cancer NursingDocumento42 páginasCancer NursingXaa YaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diabetic Gastropathy: Delayed Gastric Emptying and SymptomsDocumento7 páginasDiabetic Gastropathy: Delayed Gastric Emptying and SymptomsIlham Suryo Wibowo AntonoAún no hay calificaciones
- Stroke Due To HypertensionDocumento10 páginasStroke Due To HypertensionEnrique LuAún no hay calificaciones
- Research Paper - Celiac DiseaseDocumento5 páginasResearch Paper - Celiac Diseaseapi-316625517100% (1)
- DSM 5 OverviewDocumento78 páginasDSM 5 Overviewoyehello23Aún no hay calificaciones
- 011 Exam Focus Dec 22Documento25 páginas011 Exam Focus Dec 22Moyooree BiswasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ayurveda Articles PDFDocumento704 páginasAyurveda Articles PDFAnonymous TWzli5100% (2)
- 4 Qi Imbalances and 5 Elements: A New System For Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento5 páginas4 Qi Imbalances and 5 Elements: A New System For Diagnosis and Treatmentpixey55Aún no hay calificaciones
- Farmakologi Pada Kasus TraumaDocumento31 páginasFarmakologi Pada Kasus TraumajikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial of LabourDocumento2 páginasTrial of Labourgeorgeloto12Aún no hay calificaciones
- ENEMADocumento4 páginasENEMAangelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Detection and Reporting of ADRsDocumento2 páginasDetection and Reporting of ADRsIftikar hussainAún no hay calificaciones
- Dengue Lecture FinalDocumento21 páginasDengue Lecture FinalSheila YapAún no hay calificaciones
- Long Face SyndromeDocumento35 páginasLong Face SyndromeDisha Nighot100% (1)
- Aspergillosis by Gaurav KambojDocumento4 páginasAspergillosis by Gaurav KambojmehakAún no hay calificaciones
- Osce Bank PDFDocumento15 páginasOsce Bank PDFnassir197083% (6)
- Medical History FormatDocumento5 páginasMedical History Formatkrzia TehAún no hay calificaciones
- RinderpestDocumento5 páginasRinderpestKinara PutriAún no hay calificaciones
- Low Frequency Tens "Transcutaneos Electrical Nervestimulation"Documento72 páginasLow Frequency Tens "Transcutaneos Electrical Nervestimulation"Florian BeldimanAún no hay calificaciones
- Anemia NCPDocumento6 páginasAnemia NCPApril Jumawan ManzanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Slides HyperemesisGravidarum Obstetrics PDFDocumento6 páginasSlides HyperemesisGravidarum Obstetrics PDFRaulMorenoPerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Blood Module eDocumento6 páginasBlood Module eTAHAAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Case Logs ReportDocumento14 páginasClinical Case Logs ReportSeth Therizwhiz RockerfellaAún no hay calificaciones
- Classification and Causes of Age-related CataractDocumento16 páginasClassification and Causes of Age-related CataracttataAún no hay calificaciones