Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Anti TB Drugs
Cargado por
dhaineyDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Anti TB Drugs
Cargado por
dhaineyCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
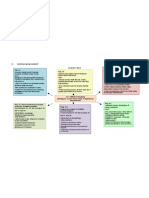
BACILLARY POPULATION (IN LUNG FIELDS) • History of gout or predisposition to gout (PZA)
• Patients taking steroids for more than 6 months –
• population A Immunosuppression
– bacilli lining the cavity wall
– rapid growth and multiplication due to abundant VITAL FACTORS IN THE CHEMOTHERAPY OF TB
supply of O2 • Correct dosage
– reside in neutral or slightly alkaline [pH] • Regularity of administration
environment • Adequate duration
– source of infectiousness, communicability, and • Proper drug combination
resistant mutants
• population B (Persisters) PRIMARY HEALTH CARE [PHILIPPINES]
– bacilli in caseous nodules and inner linings of • For 2 months daily Rx -intensive
cavitary lesions – Rifampicin 450mg
– slow or intermittent metabolism [persisters] – INH 300mg
– environment contains little O2 and pH is slightly – Pyrazinamide 1000mg to 15000mg
acidic
– source of relapse à difficult to eradicate • For 4 months -maintenance
• population C (Intracellular Bacilli) – Rifampicin 450mg
– bacilli inside macrophages [intracellular – INH 300mg
population]
– slow metabolizers [persisters] • Pyrazinamide 500mg/ tab (aka Para amino salicylic
– environment is poorly oxygenated and frankly acid)
acidic • Above 50 kilos – 3tabs (1,500 mg)
– source of relapse • 50 kilos and below – 2tabs (1,000 mg)
• Rifater, Pyrina – RNZ (Rifampicin, INH, PZA)
– For 2 months
Streptomycin • Rifinah – RN (Rifampicin, and INH)
S**M
(Oldest, 1944) – For 4 months
active
REASONS FOR RX FAILURE
1. Non-observance of vital factors of Rx by either
Pop. A physician or px
Second most active
Most active 2. Very extensive disease
3. Uncontrolled DM and alcoholism
Weakly active Most active
4. Primary resistance to drugs
INH Pop. B RFP 5. Inherent of cellular immunity in the px
Less active than RFP 2nd most active ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS [ADR] – 1ST MONTH
• Loss of appetite and tiredness without reason - INH
Pop. C • Unexplained nausea and vomiting, collapse - INH
• Rash and persistent itchiness - INH
• Yellowish discolorations of skin and eyeballs - Rifamp
Most active
2
• Flu-like syndrome- fever, chills, pain
PZA • When R is given intermittently in high dose - Rifamp
• Tingling and burning sensation of hands and feet
• Swelling and generalized edema
ETHAMBUTOL • Shortness of breath - INH
• Bacteriostatic to populations A and C • Petechiae and ecchymoses – Rifampicin
• Inhibits the growth of mutants resistant to INH and RFP
• Not hepatotoxic but causes optic neuritis, give to adults
only, not in children.
• Advice- stop medication for few days and do
desensitization
• Hepatotoxic:
– Isoniazid – Dose- 1/10, ¼, ½ à average dose
– Pyrazinamide ß Causes gout
DRUG DOSE ADJUSTMENT
– Rifampicin
• INH – 5-10mg/kg, up to 400mg/ day
SHORT COURSE THERAPY OR SHORT COURSE • Rifampicin – 10mg/kg, up to 600mg/day
CHEMOTHERAPY [AUGUST 19, 1986]
• Pyrazinamide – 25-35 mg/kg, not to exceed 2grams
Given for the first 2 months - Intesnsive daily
– INH [Isoniazid] 300 mg PO daily • irrespective of serum uric and level for as long as px is
– PZA [Pyrazinamide] 500 mg PO daily asymptomatic
– RFP [Rifampicin] 450 mg PO AC OD • Ethambutol – 25mg/ kg/ day for 1st 2 months
– 15mg/ kg for next 4 months
Given for the next 4 months – Maintenance • Streptomycin – 15-20mg/ kg up to 1 gram daily by IM
– INH
– RFP Same dose as mentioned above INH PROPHYLACTIC USE
– Infants and children up to 6 years who converts to [+]
• Total number of Rx= 6 months PPD [without previous BCG]
– PPD [–] medical personnel and students who are in
CONTRAINDICATIONS TO SCC close contact with active cases in wards
• History of liver disease (SGPT, SGOT, alcoholics)
• History of chronic and acute renal disease
– Recent tuberculin converters in close contact with open II. Relapse cases
cases of TB III. X-ray smear (+)
– Px on corticosteroid, anti-metabolite therapy with
previous TB history III. 2 HRZ (2 RIP) / 4 HR (4 RI)
• dose- 10mg/kg/ day I. New cases, smear (--) but with minimal
- 300-400mg daily pulmonary TB on x-ray confirmed by medical
officer
II. New extrapulmonary TB (Not serious)
Best recommended Rx regimen for pulmonary TB • H = Isoniazid H
[MDRTB ?] • R = Rifampicin
– RHZE or RHZS daily [2 months] • Z = Pyrazinamide
– RH [4 months] daily • E = Ethambutol
• Chemoprophylaxis of adult patient [13-35 years]
– INH + Ethambutol daily for 6 months; • INH & rifampicin- hepatotoxic
– Or INH + Rifampicin daily for 4 months • Streptomycin & ethambutol- parenteral route
• Rifampicin- nephrotoxic
• 4 drugs given initially [2 months] • Pyrazinamide- increase uric acid- gout
– Big bacillary population especially cavitary lesion • Ethambutol- cause optic neuritis in chidren
– Previous use of anti-TB drugs
– High primary resistance to H ?
– Close contact with resistant source case
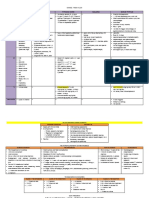
MDT FOR LEPROSY [WHO]
Disease Paucibacillary Multibacillary
Other Name Tuberculoid, Lepromatous, mid
Indeterminate type borderline (Serious,
fingerless)
Rx Rifampicin 600mg once -Same
a month, Dapsone 100
mg 1-2 mg/kg/d -Same
-Clofazimine
(Lamprene) 300mg
once a month AND 50
mg/d
Rx duration 6 months 2 years or until skin
smears are negative
Surveillance after Rx Annual exams for at Annual exams for at
14
completion least 2 years least 5 years
SIDE NOTES
• Give Vitamin B complex (Pyridoxine) to prevent INH
(Isoniazid H) toxicity
• DOT – Direct Observance Therapy
• Streptomycin – Only anti TB drug administered IM
• Increased dose in INH causes convulsions
• 2 months is INTENSIVE, 4 months is MAINTENANCE
• Myrin P – Combination of the following drugs, 2 months:
(INTENSIVE)
– R = Rifampicin
– I = Isoniazid
– P = Pyrazinamide
– E = Ethambutol
• Myrin (4 months), only R I E
• Rifampicin has PAE against leprosy, it is leprocidal
• PHILCAT – Philippine Coalition Against tuberculosis
Rx regimen
I. 2 HRZE (2 RIPE) / 4HR (4 RI)
I. New pulmonary smear (+) cases
II. New seriously ill pulmonary smear negative
cases with parenchymal involvement
III. New seriously ill extrapulmonary TB cases
II. 2 HRZES (2 RIPES) / 1 HREZ (1 RIPE) / 5 HRE (5 RIE)
I. Failure cases
También podría gustarte
- Fixcom 4Documento2 páginasFixcom 4Jenny Vi Codeniera100% (2)
- FHP - NCP - Kidney FailureDocumento9 páginasFHP - NCP - Kidney FailureFrancis AdrianAún no hay calificaciones
- AshmaDocumento51 páginasAshmaAliyi MuktarAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 5: Antimycobacerial Drugs by Dr. Frederick Loyola July 7, 2010Documento7 páginasLec 5: Antimycobacerial Drugs by Dr. Frederick Loyola July 7, 2010Rachel Leslie de LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- 01 - Bronchial AsthmaDocumento6 páginas01 - Bronchial AsthmaFrank VaronaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocumento1 páginaNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- Period of Communicability: ChloramphenicolDocumento10 páginasPeriod of Communicability: ChloramphenicolDona Mae TaberaAún no hay calificaciones
- Antiprotozoal Drugs ResistanceDocumento4 páginasAntiprotozoal Drugs Resistance111techie999Aún no hay calificaciones
- Agitated PatientDocumento2 páginasAgitated PatientCassandra GeldenhuysAún no hay calificaciones
- 08 OpioidsDocumento44 páginas08 OpioidsRamya RAún no hay calificaciones
- Book Herbal Medication Herb Charts - Priest and PriestDocumento27 páginasBook Herbal Medication Herb Charts - Priest and PriestAlejandra Guerrero100% (2)
- Characteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseDocumento4 páginasCharacteristics Indication Origin Market Name Absorption Peak Plasma Level Half-Life Excretion DoseShafiqah AbdullahAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseases of Public Health Part 1Documento3 páginasDiseases of Public Health Part 1Jas GandingcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Anti-Tb MedsDocumento32 páginasAnti-Tb MedsMiaMDAún no hay calificaciones
- Anti T.B DrugsDocumento120 páginasAnti T.B DrugsromalaramAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic PharmacologyDocumento8 páginasBasic PharmacologyLaureece Salm ApduhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Contora, Isah TblrenalDocumento7 páginasContora, Isah TblrenalisahAún no hay calificaciones
- Asthma: Chronic Inflammatory Airway DiseaseDocumento14 páginasAsthma: Chronic Inflammatory Airway DiseaseyyAún no hay calificaciones
- DiphenhydramineDocumento3 páginasDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisDocumento19 páginasNursing Care Plan: Congestive Heart Failure-Deep Vein ThrombosisRiza Angela BarazanAún no hay calificaciones
- Management of TB in Primary CareDocumento49 páginasManagement of TB in Primary CareMonysyha AtriAún no hay calificaciones
- Psychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerDocumento5 páginasPsychopharmacology-Mood StabilizerVon Hippo100% (1)
- HYPOKALEMIADocumento3 páginasHYPOKALEMIADienizs Labini TadenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hepatitis B Case StudyDocumento16 páginasHepatitis B Case StudyDan Dan ManaoisAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxygen, Nutri, ElimDocumento74 páginasOxygen, Nutri, ElimNina Anne ParacadAún no hay calificaciones
- Asthma and COPDDocumento79 páginasAsthma and COPDDawit g/kidanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pedia Reviewer 5 Dse For JIsDocumento27 páginasPedia Reviewer 5 Dse For JIssrzmx9psm7Aún no hay calificaciones
- Immunomodulators InfographicDocumento1 páginaImmunomodulators InfographicThais RomanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Bronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALDocumento1 páginaBronchitis N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalAún no hay calificaciones
- General Pharmacology (1-7)Documento7 páginasGeneral Pharmacology (1-7)LotfyAdel100% (1)
- Drug Study RifampicinDocumento2 páginasDrug Study RifampicinJamil Lorca100% (5)
- RNA VirusesDocumento11 páginasRNA VirusesKate Alyssa CatonAún no hay calificaciones
- Inhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDocumento7 páginasInhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDaniel LesmanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento11 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationYzel Vasquez AdavanAún no hay calificaciones
- Respiration Pulse SitesDocumento2 páginasRespiration Pulse SitesFatima Doran PandaogAún no hay calificaciones
- AcetaminophenDocumento1 páginaAcetaminophensalwakh266Aún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocumento5 páginasNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2018-2019 Cns DepressantsDocumento5 páginas2018-2019 Cns DepressantsMary AgorillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Valproic Acid Drug Data SheetDocumento4 páginasValproic Acid Drug Data SheetJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Impaired Electrolytes NCPDocumento2 páginasImpaired Electrolytes NCPNora BacolAún no hay calificaciones
- Pet 3Documento6 páginasPet 3api-608882001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Att by DR M Farooq Presented On 28-10-2008Documento105 páginasAtt by DR M Farooq Presented On 28-10-2008drfarooq_malik6331Aún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study of AppendicitisDocumento14 páginasCase Study of AppendicitisArvin Ian Penaflor89% (27)
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.05Documento3 páginasShanz - Pedia Ii 2.05Petrina XuAún no hay calificaciones
- Guideline For Management Protocol of Children With Fever and Respiratory SymptomsDocumento44 páginasGuideline For Management Protocol of Children With Fever and Respiratory SymptomsKushagr GautamAún no hay calificaciones
- CHN National Tuberculosis ProgramDocumento3 páginasCHN National Tuberculosis ProgramMutya XDAún no hay calificaciones
- Mood Range: Severe Moderate Mild Hypomanic EuphoricDocumento13 páginasMood Range: Severe Moderate Mild Hypomanic EuphoricSen SioAún no hay calificaciones
- Anti-Tubercular DrugsDocumento11 páginasAnti-Tubercular DrugsAudrey Beatrice ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study 5Documento4 páginasDrug Study 5Butts McgeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes, 1/e: Anti Epileptic DrugsDocumento7 páginasNotes, 1/e: Anti Epileptic DrugsvkAún no hay calificaciones
- Decrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous SystemDocumento1 páginaDecrease All Properties of Cardiac Muscle: - H.R - C.O.P Essential For Normal Development of Nervous Systemahmed K.Abd el SaterAún no hay calificaciones
- (Surg2) 5.1d Anesthesia PointersDocumento12 páginas(Surg2) 5.1d Anesthesia PointersAlloiBialbaAún no hay calificaciones
- AnalgesiaDocumento40 páginasAnalgesiacardiacanesthesiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Thorax To RectumDocumento35 páginasThorax To RectumdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Examination of The SkinDocumento3 páginasPhysical Examination of The Skindhainey100% (1)
- Cancer ChemotherapyDocumento4 páginasCancer Chemotherapydhainey100% (2)
- TrematodesDocumento5 páginasTrematodesdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Aliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocumento13 páginasAliphatic and Aromatic HydrocarbonsdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Intestinal NematodesDocumento9 páginasThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- HerniaDocumento8 páginasHerniadhainey100% (1)
- Chelating AgentsDocumento24 páginasChelating AgentsdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Abdominal PainDocumento12 páginasAbdominal Paindhainey100% (2)
- Anti Fungal and Anti ProtozoalDocumento17 páginasAnti Fungal and Anti Protozoaldhainey100% (2)
- Anti Helminthic DrugsDocumento3 páginasAnti Helminthic Drugsdhainey100% (2)
- Botanical Medications and SupplementsDocumento3 páginasBotanical Medications and Supplementsdhainey100% (1)
- Parasitology Pictures Part 2Documento22 páginasParasitology Pictures Part 2dhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- The FilariaeDocumento4 páginasThe FilariaedhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chest and Lungs ExaminationDocumento75 páginasChest and Lungs Examinationdhainey100% (10)
- Genus EchinococcusDocumento6 páginasGenus EchinococcusdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Parasitology PicturesDocumento4 páginasParasitology Picturesdhainey100% (1)
- Intestinal FlagellatesDocumento5 páginasIntestinal Flagellatesdhainey100% (3)
- CESTODES Intro-Pseudophyylideans-SparganosisDocumento37 páginasCESTODES Intro-Pseudophyylideans-Sparganosisdhainey100% (1)
- The FolateDocumento3 páginasThe FolatedhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Coagulants and Anti CoagulantsDocumento22 páginasCoagulants and Anti Coagulantsdhainey100% (2)
- AminoglycosidesDocumento4 páginasAminoglycosidesdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Toxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiaDocumento40 páginasToxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiadhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- QuinolonesDocumento2 páginasQuinolonesdhainey100% (1)
- Tumors of The Small and Large IntestineDocumento14 páginasTumors of The Small and Large Intestinedhainey100% (4)
- BT ReactionsDocumento14 páginasBT ReactionsdhaineyAún no hay calificaciones
- Female Sex HormonesDocumento29 páginasFemale Sex Hormonesdhainey100% (5)
- Intestinal Coccidia - SarcocystisDocumento29 páginasIntestinal Coccidia - Sarcocystisdhainey100% (3)
- Anti Microbial TherapyDocumento39 páginasAnti Microbial Therapydhainey100% (1)
- Chicken Meat BenifitsDocumento1 páginaChicken Meat BenifitsLok Raj JoshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hematocrit and Hemoglobin DeterminationDocumento32 páginasHematocrit and Hemoglobin DeterminationCeliz HilarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Ophthalmonics 1st EditionDocumento116 páginasOphthalmonics 1st Editiondhavalb2086% (7)
- Understanding Hiatal HerniaDocumento37 páginasUnderstanding Hiatal HerniaRaju Shrestha100% (2)
- Masters ThesisDocumento61 páginasMasters ThesissampathdtAún no hay calificaciones
- Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses: PathophysiologyDocumento5 páginasPigmented Purpuric Dermatoses: PathophysiologyrohitAún no hay calificaciones
- Pdhpe Assessment Task Term 1 Drug Use in AdolescentsDocumento10 páginasPdhpe Assessment Task Term 1 Drug Use in Adolescentsapi-463236687100% (2)
- Producing Insulin Through Genetic EngineeringDocumento32 páginasProducing Insulin Through Genetic EngineeringblessingaliuAún no hay calificaciones
- Adult T-Cell Leukemia Lymphoma (Atll) A Rare Case Associated With Human T-Cell Virus (Htlv-1)Documento19 páginasAdult T-Cell Leukemia Lymphoma (Atll) A Rare Case Associated With Human T-Cell Virus (Htlv-1)Priya ChandakAún no hay calificaciones
- Pre TestDocumento6 páginasPre TestPRINTDESK by DanAún no hay calificaciones
- An Unusual Location of Carcinoma: The Clitoris and The VulvaDocumento2 páginasAn Unusual Location of Carcinoma: The Clitoris and The VulvaIOSRjournalAún no hay calificaciones
- Significance of Family History in Homoeopathic PrescribingDocumento8 páginasSignificance of Family History in Homoeopathic PrescribingHomoeopathic Pulse50% (2)
- Genetic Attribution For Schizophrenia, Depression, and Skin Cancer: Impact On Social DistanceDocumento7 páginasGenetic Attribution For Schizophrenia, Depression, and Skin Cancer: Impact On Social DistancenigoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mov3. GENERAL - UMN (Pyramidal) & LMN DisordersDocumento9 páginasMov3. GENERAL - UMN (Pyramidal) & LMN DisordersherlambangkusumoAún no hay calificaciones
- Current Opinion Hematol RR AML 2019Documento8 páginasCurrent Opinion Hematol RR AML 2019Ernesto PiconAún no hay calificaciones
- Kuretase Case Report 2Documento3 páginasKuretase Case Report 2Lydia AmaliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocumento5 páginasPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Kjjhhgfdsasdf HJKLKJHGFDSSDFG HJKLDocumento4 páginasKjjhhgfdsasdf HJKLKJHGFDSSDFG HJKLbubble_inAún no hay calificaciones
- Strategic PlanDocumento84 páginasStrategic PlanAurutchat VichaiditAún no hay calificaciones
- Glycemic Index For 60+ Foods - Harvard HealthDocumento4 páginasGlycemic Index For 60+ Foods - Harvard HealthHoracio's PhotosAún no hay calificaciones
- Resume: Hema Latha KoyeladaDocumento3 páginasResume: Hema Latha KoyeladaSai CharanAún no hay calificaciones
- Emergency Surgery Section ECTES 2018 ValenciaDocumento5 páginasEmergency Surgery Section ECTES 2018 Valenciagarbass1905Aún no hay calificaciones
- Molecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaDocumento31 páginasMolecular Basis of Acute LeukemiaVivek SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Moderna Strategic Plan Presentation - 7assona GroupDocumento36 páginasModerna Strategic Plan Presentation - 7assona GroupBeshoy Zakaria100% (1)
- Uveal Coloboma: The Related SyndromesDocumento3 páginasUveal Coloboma: The Related Syndromeslavinia diaAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is Pancreas ????: By: Group 8Documento9 páginasWhat Is Pancreas ????: By: Group 8Putu RikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical guidelines for liver transplantationDocumento53 páginasClinical guidelines for liver transplantationMadalina StoicescuAún no hay calificaciones
- Review More Than BlueDocumento1 páginaReview More Than BlueB2 - Dimatulac, Jessieryl A.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Diagnostic Pediatric Hematopathology - 2011Documento588 páginasDiagnostic Pediatric Hematopathology - 2011Omar SarvelAún no hay calificaciones
- NO CANCER RISK EPA 2012 Chemicals - EvaluatedDocumento29 páginasNO CANCER RISK EPA 2012 Chemicals - EvaluateduncleadolphAún no hay calificaciones