Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Transactional and Analytical Database Systems
Cargado por
thelionphoenixTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Transactional and Analytical Database Systems
Cargado por
thelionphoenixCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
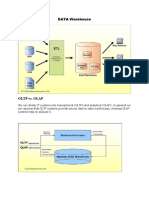
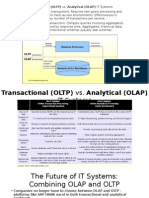
OLTP vs. OLAP We can divide IT systems into transactional (OLTP) and analytical (OLAP).
In general we can assume that OLTP systems provide source data to data warehouses, whereas OLAP systems help to analyze it.
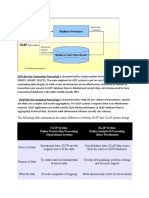
- OLTP (On-line Transaction Processing) is characterized by a large number of short on-line transactions (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). The main emphasis for OLTP systems is put on very fast query processing, maintaining data integrity in multi-access environments and an effectiveness measured by number of transactions per second. In OLTP database there is detailed and current data, and schema used to store transactional databases is the entity model (usually 3NF). - OLAP (On-line Analytical Processing) is characterized by relatively low volume of transactions. Queries are often very complex and involve aggregations. For OLAP systems a response time is an effectiveness measure. OLAP applications are widely used by Data Mining techniques. In OLAP database there is aggregated, historical data, stored in multi-dimensional schemas (usually star schema). The following table summarizes the major differences between OLTP and OLAP system design. OLTP System Online Transaction OLAP System Online Analytical
Processing Processing (Operational System) (Data Warehouse) Operational data; OLTPs are the Consolidation data; OLAP data comes Source of data original source of the data. from the various OLTP Databases To control and run fundamental To help with planning, problem Purpose of data business tasks solving, and decision support Reveals a snapshot of ongoing Multi-dimensional views of various What the data business processes kinds of business activities Inserts and Short and fast inserts and updates Periodic long-running batch jobs Updates initiated by end users refresh the data Relatively standardized and simple Often complex queries involving Queries queries Returning relatively few aggregations records Depends on the amount of data involved; batch data refreshes and Processing Typically very fast complex queries may take many Speed hours; query speed can be improved by creating indexes Larger due to the existence of Space Can be relatively small if historical aggregation structures and history Requirements data is archived data; requires more indexes than OLTP Typically de-normalized with fewer Database Highly normalized with many tables; use of star and/or snowflake Design tables schemas Backup religiously; operational Instead of regular backups, some data is critical to run the business, Backup and environments may consider simply data loss is likely to entail Recovery reloading the OLTP data as a recovery significant monetary loss and legal method liability
In Brief "OLTP Short database transactions Online update/insert/delete Normalization is promoted High volume transactions Transaction recovery is necessary OLAP Current and historical data
Long database transactions Batch update/insert/delete Denormalization is promoted Low volume transactions Transaction recovery is not necessary "
También podría gustarte
- Data Warehouse IntroductionDocumento5 páginasData Warehouse IntroductionVenkatesan RajAún no hay calificaciones
- DATABASE MGT. S-WPS OfficeDocumento47 páginasDATABASE MGT. S-WPS OfficeJoweeh Lyn Arcibal100% (1)
- DataModel Document GenerationDocumento26 páginasDataModel Document Generationanu_hearts@yahoo.comAún no hay calificaciones
- Designing Star Schema Databases in 40 CharactersDocumento15 páginasDesigning Star Schema Databases in 40 CharactersBalamurali KoneruAún no hay calificaciones
- Etl Testing MaterialDocumento17 páginasEtl Testing MaterialMallanna Rb100% (2)
- DocDocumento500 páginasDocMonica MarciucAún no hay calificaciones
- Authorizations SAP BIDocumento5 páginasAuthorizations SAP BISuryya Kanta AdhikaryAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Warehousing and OLAP FundamentalsDocumento57 páginasData Warehousing and OLAP FundamentalsTrần Hữu DuậtAún no hay calificaciones
- DB2 Backup ScriptDocumento4 páginasDB2 Backup ScriptmaxventoAún no hay calificaciones
- ETL TestingDocumento32 páginasETL TestingsudhavishuAún no hay calificaciones
- THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"De EverandTHE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"Calificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (1)
- DWH - Data Warehousing Concepts ExplainedDocumento50 páginasDWH - Data Warehousing Concepts ExplainedgeoinsysAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Architecture: A Primer for the Data Scientist: A Primer for the Data ScientistDe EverandData Architecture: A Primer for the Data Scientist: A Primer for the Data ScientistCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (3)
- Operating System Ii Memory Management Memory Management Is A Form of Resource Management AppliedDocumento23 páginasOperating System Ii Memory Management Memory Management Is A Form of Resource Management AppliedSALIHU ABDULGANIYU100% (1)
- Netezza Oracle Configuration in DatastageDocumento8 páginasNetezza Oracle Configuration in DatastagePraphulla RayalaAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP Vs OlapDocumento2 páginasOLTP Vs OlapAnirudh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Transactional and Analytical SystemsDocumento2 páginasOLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Transactional and Analytical SystemsSanjayAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP Vs OLAPDocumento3 páginasOLTP Vs OLAPSai LakshmiAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP Vs OLAPDocumento2 páginasOLTP Vs OLAPAnees Khan0% (1)
- OLTP Vs OLAPDocumento2 páginasOLTP Vs OLAPBodhiswatta SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bia Assignment GulshanDocumento4 páginasBia Assignment GulshanGulshan TomarAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences in Online Transaction and Analytical Processing SystemsDocumento1 páginaOLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences in Online Transaction and Analytical Processing SystemsalidxbpkAún no hay calificaciones
- Olap Vs Oltp: Online Analytical ProcessingDocumento2 páginasOlap Vs Oltp: Online Analytical ProcessingKarthik EgAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP (On-Line Transaction Processing) Is Characterized by A Large Number of Short On-Line TransactionsDocumento12 páginasOLTP (On-Line Transaction Processing) Is Characterized by A Large Number of Short On-Line TransactionseazyAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP vs OLAP Systems ComparisonDocumento10 páginasOLTP vs OLAP Systems ComparisoneazyAún no hay calificaciones
- OLAP Vs OLTPDocumento2 páginasOLAP Vs OLTPnandini swamiAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP Vs OLAP PDFDocumento9 páginasOLTP Vs OLAP PDFMansi Kaushik100% (1)
- OLTP vs. OLAPDocumento3 páginasOLTP vs. OLAPorion werrtyAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTPDocumento4 páginasOLTPsumit_bedi0143Aún no hay calificaciones
- Testing PDFDocumento17 páginasTesting PDFabreddy2003Aún no hay calificaciones
- Oltp Vs OlapDocumento14 páginasOltp Vs Olaprgarun90Aún no hay calificaciones
- Online Transaction ProcessingDocumento17 páginasOnline Transaction ProcessingJavzaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Imran Introduction To DWH-1Documento35 páginasImran Introduction To DWH-1imran saeedAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Online Transactional and Analytical Processing SystemsDocumento13 páginasOLTP vs OLAP: Key Differences Between Online Transactional and Analytical Processing SystemsNimi KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Online Analytical Processing, or OLAP (Documento34 páginasOnline Analytical Processing, or OLAP (sanaroohiAún no hay calificaciones
- OLTPDocumento12 páginasOLTPpoojamittal_26Aún no hay calificaciones
- Soham ChakrabortyDocumento16 páginasSoham ChakrabortySoham ChakrabortyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 12 - Data Warehousing and Online Analytical ProcessingDocumento20 páginasChapter 12 - Data Warehousing and Online Analytical Processingsushantsaurabh5479Aún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP Vs OLAPDocumento1 páginaOLTP Vs OLAPxolinAún no hay calificaciones
- Olap & Oltp: Presentation ONDocumento14 páginasOlap & Oltp: Presentation ONadihindAún no hay calificaciones
- 964 1587060215467 Lo3Documento16 páginas964 1587060215467 Lo3johann jayatillekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Master DatabaseDocumento6 páginasMaster DatabaseDivya GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Product Table Feature Table: SourcesDocumento23 páginasProduct Table Feature Table: SourcesTiago AlvesAún no hay calificaciones
- 11000120032-Soham ChakrabortyDocumento16 páginas11000120032-Soham ChakrabortySoham ChakrabortyAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Databases: Understanding OLTP and OLAP SystemsDocumento5 páginasTypes of Databases: Understanding OLTP and OLAP SystemsNiel Franco BalosAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Mining and Key Differences Between Database, Data Warehouse, OLTP and OLAPDocumento13 páginasData Mining and Key Differences Between Database, Data Warehouse, OLTP and OLAPfreelancer boyAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2Documento34 páginasUnit 2MananAún no hay calificaciones
- CH3 Database SystemsDocumento20 páginasCH3 Database Systemshxxx.games105Aún no hay calificaciones
- Enterprise Application Characteristics: 3.1 Diverse ApplicationsDocumento4 páginasEnterprise Application Characteristics: 3.1 Diverse ApplicationsAlexandru MoldovanAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Intelligence Chapter OverviewDocumento15 páginasBusiness Intelligence Chapter OverviewhzarrabiAún no hay calificaciones
- DW Unit-1 (1) XXXXXXXXDocumento70 páginasDW Unit-1 (1) XXXXXXXXDhananjay JahagirdarAún no hay calificaciones
- Pid 54211Documento6 páginasPid 54211Shubham MalpaniAún no hay calificaciones
- A QuestionsDocumento1 páginaA Questionsvijay.alloju20Aún no hay calificaciones
- OLTP: Numerous Short Transactions. Requires Fast Query Processing andDocumento3 páginasOLTP: Numerous Short Transactions. Requires Fast Query Processing andJasmina TachevaAún no hay calificaciones
- Informatica and Datawarehouse PDFDocumento156 páginasInformatica and Datawarehouse PDFsmruti_2012Aún no hay calificaciones
- Traditional Enterprise BIDocumento47 páginasTraditional Enterprise BIAyoubAún no hay calificaciones
- ETL Data Loading ChallengesDocumento3 páginasETL Data Loading Challengesराजस करंदीकरAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 3 DMDocumento5 páginasAssignment 3 DMAli AbuAún no hay calificaciones
- Simulation and Modeling OLAP Data WarehouseDocumento40 páginasSimulation and Modeling OLAP Data WarehouseWeb GuruAún no hay calificaciones
- Oracle BI - Topic - Data WarehousingDocumento4 páginasOracle BI - Topic - Data WarehousingAbebeAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Warehousing: Chapter # 3 Carlo VercellisDocumento17 páginasData Warehousing: Chapter # 3 Carlo Vercellisnothing muchAún no hay calificaciones
- Bi Lectures ChatgptDocumento48 páginasBi Lectures Chatgptjr.developer.78Aún no hay calificaciones
- Designingthe Star Schema DatabaseDocumento18 páginasDesigningthe Star Schema Databasesaprsa1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Online Analytical ProcessingDocumento17 páginasOnline Analytical ProcessingShudodhaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Report On OLTP and OLAP Systems For An Automobile Company: Project Team MembersDocumento6 páginasReport On OLTP and OLAP Systems For An Automobile Company: Project Team MembersALISHA BEHERAAún no hay calificaciones
- U1-U5 Consolidated PDFDocumento222 páginasU1-U5 Consolidated PDFRaghuAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversityDocumento19 páginasData Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversitythelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversityDocumento34 páginasData Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversitythelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- FALLSEM2012-13 CP0248 11-Jul-2012 RM01Documento39 páginasFALLSEM2012-13 CP0248 11-Jul-2012 RM01thelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversityDocumento19 páginasData Warehousing: L.Ramanathan Asst. Prof. Scse VIT UniversitythelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Winsem2012-13 Cp0535 Syb Cse301 SyllabusDocumento1 páginaWinsem2012-13 Cp0535 Syb Cse301 SyllabusthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Winsem2012-13 Cp0535 Modqst Model QPDocumento4 páginasWinsem2012-13 Cp0535 Modqst Model QPthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Winsem2012-13 Cp0535 Qz01ans DWDM Quiz Key FinalDocumento6 páginasWinsem2012-13 Cp0535 Qz01ans DWDM Quiz Key FinalthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Winsem2012-13 Cp0535 Qz01qst DWDM Quiz QP FinalDocumento4 páginasWinsem2012-13 Cp0535 Qz01qst DWDM Quiz QP FinalthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- WINSEM2012-13 CP0535 17-Jan-2013 RM01 Application of OLAPDocumento2 páginasWINSEM2012-13 CP0535 17-Jan-2013 RM01 Application of OLAPthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Winsem2012-13 Cp0535 30-Jan-2013 Rm01 DWDM Model Quiz PaperDocumento2 páginasWinsem2012-13 Cp0535 30-Jan-2013 Rm01 DWDM Model Quiz PaperthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- WINSEM2012 13 CP0535 24 Jan 2013 RM01 DataWare House SchemasDocumento4 páginasWINSEM2012 13 CP0535 24 Jan 2013 RM01 DataWare House SchemasthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- SyllabusDocumento2 páginasSyllabusthelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocumento593 páginasHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- How To PrayDocumento13 páginasHow To PraythelionphoenixAún no hay calificaciones
- Alphabet Chart Bahasa TamilDocumento1 páginaAlphabet Chart Bahasa TamilsanthiraselvarajAún no hay calificaciones
- ArtikelDocumento4 páginasArtikelYosua SimatupangAún no hay calificaciones
- DE Sample ResumeDocumento6 páginasDE Sample ResumeSri GuruAún no hay calificaciones
- SpiidyDocumento10 páginasSpiidyلوك بيرAún no hay calificaciones
- Patchset SHDocumento145 páginasPatchset SHInderjit SinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Oracle DemoDocumento370 páginasOracle DemoJames AndersonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter#7 - Jagged Arrays and ArrayListsDocumento29 páginasChapter#7 - Jagged Arrays and ArrayListsdohaAún no hay calificaciones
- Company RequirmentDocumento2 páginasCompany RequirmentJannatul Fardous LinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Multitenant Administrators GuideDocumento627 páginasMultitenant Administrators GuidePaohua ChuangAún no hay calificaciones
- Relational Keys, Indexes, and Keys ExplainedDocumento19 páginasRelational Keys, Indexes, and Keys Explainedtembo saidiAún no hay calificaciones
- CT042-3-1-IDB-Week 1 - IntroDocumento22 páginasCT042-3-1-IDB-Week 1 - IntroBasu ThapaAún no hay calificaciones
- My New SOPDocumento2 páginasMy New SOPmailvikas100% (2)
- DP-50&DP-50Vet - System Recovery Guide - ENDocumento11 páginasDP-50&DP-50Vet - System Recovery Guide - ENsamuel debebeAún no hay calificaciones
- Purpose: Assignment Items To Subinventory Using Custom APIDocumento30 páginasPurpose: Assignment Items To Subinventory Using Custom APISayed MahfouzAún no hay calificaciones
- Datastage Jobs Best Practices and Performance TuningDocumento4 páginasDatastage Jobs Best Practices and Performance Tuningvinu_kb89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Computer FundamentalsDocumento7 páginasComputer FundamentalsAdnan SohailAún no hay calificaciones
- Sravani Soma-ETL ResumeDocumento3 páginasSravani Soma-ETL ResumeABDULLA SHAIKAún no hay calificaciones
- Oracle: Primavera P6 Professional Administration GuideDocumento78 páginasOracle: Primavera P6 Professional Administration GuidePillarAún no hay calificaciones
- Pranita Sonavane: Email ContactDocumento4 páginasPranita Sonavane: Email ContactGuruRakshithAún no hay calificaciones
- MySQL Performance TuningDocumento11 páginasMySQL Performance TuningArunmoy BoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Structures and Algorithms for Hash TablesDocumento34 páginasData Structures and Algorithms for Hash TablesdukuhwaruAún no hay calificaciones
- Coding Aplikasi Pemesanan Tiket PesawatDocumento16 páginasCoding Aplikasi Pemesanan Tiket PesawatBagus NugrohoAún no hay calificaciones
- Republic of the Philippines Commission on Elections List of Regular Voters (Precinct LevelDocumento46 páginasRepublic of the Philippines Commission on Elections List of Regular Voters (Precinct LevelAngelika CalingasanAún no hay calificaciones