Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Engine Nomenclature
Cargado por
Alonso Trancon ArellanoDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Engine Nomenclature
Cargado por
Alonso Trancon ArellanoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Section 7
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
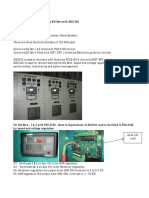
ENGINE DESIGNATION ENGINE DESIGNATION NAME PLATE ENGINE DESIGNATION STANDARDISATION ENGINE DESIGNATION NEW (1) ENGINE DESIGNATION NEW (2) NAME PLATE DC-BSC-7-1 EPA PLATE MSHA PLATE HORSE POWER SAE HP DIN PS KW ROTATION AND CYLINDER NUMBERING ROTATION AND CYLINDER NUMBERING
BSC-7-1
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 12 13 14 15 16 17
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 1
BSC-7-2
ENGINE DESIGNATION DOCUMENTATION DC-BSC-7-2
The example shows a combination of engine designation arrangements. This arrangement can be found on technical documentation or specification sheets. Example: B slash F indicates that the information in the document is either for a turbo charged (B) engine and / or for a naturally aspirated (F) engine. The information as shown in the above illustration will not appear on any name plate. Turbo charging is designated with the letter "B" as a prefix, the "B" is derived from the name of the inventor of the charger, A. R. Bchi. The method of engine cooling is defined by the letters M and L. M = MEDIUM a mixture of water and glycol or, as in the case of 1011/2011, engine lubricating OIL. L = LUFT (AIR) in case of the 1011/ 2011 the engines designated with the letter L , they have an integrated cooling system and the cylinder head is AIR cooled. By improving or optimizing an engine, it will be identified with the letter F. Any further optimization will change the engine family designation number. Example : 1011 to 2011 The letter E indicates that the engine is externally cooled. The engine has a remote mounted radiator or heat exchanger. The cooling fan can be engine, electrically or hydraulically driven. The engine cylinder head is OIL cooled.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 2
BSC-7-3
ENGINE DESIGNATION NAME PLATE DC-BSC-7-3
Model number as show in the illustration appears on engine name plate. As specified, the engine is: Turbo charged, high speed, four cycle, liquid cooled engine with 112mm (11.2cm) piston stroke. M indicates that the engine is equipped with an external cooling system and the cylinder head is oil cooled. With the increased power output, the external cooling system must be utilized to be able to handle the increased cooling demand.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 3
BSC-7-4
ENGINE DESIGNATION STANDARDISATION DC-BSC-7-4
1 2 3 4 Engine Design Code Engine Series Cylinder Arrangement Number of Cylinders 5 6 7 Special Engine Designation Piston Stroke in cm (approx) Basic Variants (Cooling)
A standardization of the Engine Designation for all Deutz engine has been introduced and will completed by the year 2007. 1 Engine Design Code (Letters) For all engine series the following letters are being used: T = Turbo charged C = Charge Air Cooling (Intercooling) D = Diesel G = Gas 2 Engine Series (Numbers) The Engine Series designation is being set up with four digits
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 4
ENGINE DESIGNATION, continued
3 Cylinder Arrangements (Letter) The Cylinder Arrangement is assigned directly behind the engine series designation. L In Line Cylinder arrangement= IN LINE ENGINE V V-configuration Cylinder arrangement= V ENGINE 4 Number of Cylinders (Numbers) The Numbers of Cylinders is arranged directly behind the cylinder arrangement. 5 Special Engine Designation (Number/Letter combination) Special Engine Designation will be indicated by two digits. P Increased power output 6 Piston Stroke in cm (Numbers) The Piston Stroke is a part of the engine series designation and is identified with a two digit number. The piston travel is specified in approximate centimeters. 7 Basic Variants (Numbers) The Basic Variants identify the cooling method of the engine and is laid out with two BSC-7-5 digits. 20 Medium cooled 90 Air cooled The term High Speed Engines that has been used until now, will not be used any DC-BSC-7-5 longer. With the above introduction the engines with a piston stroke < 150,00mm (including 1015and 2015 ) will be declared as Compact Engines.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 5
BSC-7-6
ENGINE DESIGNATION NEW (1) DC-BSC-7-6
1 T C D 2 ENGINE DESIGNATION CODE Turbo Charged Charge Air Cooling Diesel Engine Series 2013 Cylinder Arrangement In line engine Number of Cylinders 6 Cylinders Special Engine Designation 7 20 Basic Variants Medium Cooled
3 L 4 06 5
6 13
Piston Stroke 13 cm
TITLE: BASICS SECTION: 7 PAGE: 6
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
BSC-7-7
ENGINE DESIGNATION NEW (2) DC-BSC-7-7
1 T C D 2 ENGINE DESIGNATION CODE Turbo Charged Charge Air Cooling Diesel Engine Series 2015 Cylinder Arrangement V-ENGINE Number of Cylinders 8 Cylinders Special Engine Designation Power (increased output) Piston Stroke 14.5 cm
TITLE: BASICS SECTION: 7 PAGE: 7
7 20
Basic Variants Medium Cooled
3 V 4 08 5 P 6 15
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
BSC-7-8
NAME PLATE DC-BSC-7-8
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 8
BSC-7-9
NAME PLATE DC-BSC-7-9
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Engine Type Engine Certification Engine Serial Number Total Power Output / Blower disengaged Total Power Output / Blower engaged Rated engine Speed Fuel Injection Timing 8. 9/10 11 12 13 14 15 Additional Power Absorption Free Space for Information ISO Power Indication Power reduction kW (G) Power reduction kW (s) Power reduction kW (Temperature) Power reduction kW (Altitude)
For internal combustion engines, the power is always indicated with reference to a standard (ISO). These standards specify the engines power output settings as indicated on the nameplate. The performance of the engine is essentially influenced by the environmental conditions at its working site. Such as temperature and density of combustion air and cooling air. (14 and 15) 1 2 3 4 Engine type e.g.: BF4M 2011 Code: For engines certification according EPA Engine number: Serial number of engine kW (G) 1) "Total power" (T-power), fan not running. T-power as per ISO standard (The engine is equipped with a controlled blower. The indication on the name plate is the total power output including
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 9
NAME PLATE, continued
power absorption of the cooling blower. During total power output, the blower is not engaged or running at maximum slippage. )
kW (S) "Continuous power" (C-power), fan continuous running C-power as per ISO standard (The engine can be equipped with a controlled or rigid driven cooling blower. The indication on the name plate is the engines power output when the cooling blower is fully engaged.) 1/min 3) ) kW (W) Rated speed of the engine. Commencement of injection in C/A. Effective power absorption (fan/blower)
7 8
Indication for power absorption of cooling fan for additional cooling, when a transmission oil cooler, charge air cooler (intercooler) is installed. 9+10 11 Free space (for additional information). Abbreviation of ISO power indication. Indication of the standard and/or acceptance regulation taken as a basis to determine the engines performance. To all performance standards, the following reference standard conditions apply: DC-BSC-7-10 Ambient air pressure, total: dry: Ambient air temperature : 12 kW (G) red. 2) kW (S) red. 2) 100 kPa 99 kPa 298 K ( 25 C )
BSC-7-10
Reduced "total power" for the ambient conditions prevailing at the place of installation / on site. (see 14/15)
13
Reduced "continuous power" for the ambient conditions prevailing at the place of installation / on site. (see14/15)
14 15 16 17
Ambient air temperature in C 2) Ambient conditions at the place of installation 2) Ambient conditions at the place of installation Altitude above sea level in m Not applicable for series 2011 K Piston classification
1)
The letter S or G according to Deutz Standard H 0172 defines the value of the net brake power in kW on the nameplate.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 10
NAME PLATE, continued
Increasing air temperature and lower air pressure result in a reduced air density and a reduction in the amount of oxygen. Lower oxygen content and lower density have negative effects on the engine's combustion process and cooling. The result is a power loss and higher component temperatures. If, for a longer time, an engine is operated at clearly less favourable ambient conditions, premature wear must be expected due to thermal overload. Therefore, upon extended operation or stationary operation under unfavourable ambient conditions, the power output must be reduced by lowering the fuel injection rate as specified in power reduction tables. When reducing the power, it must be distinguished between the applications (stationary or non-stationary or transient engine operation) and between naturally aspirated and turbo charged engines. To establish the power reduction a) the rated power indicated on the nameplate and BSC-7-11 b) the ambient conditions at the location of installation must be taken as a basis. 1. 2. Altitude in metres above sea level Air temperature in Celsius *)
2)
*) The air temperature is defined as "normal maximal day temperature"; this is the average value of the highest day temperature of the last years in the hottest month. Rated speed, as indicated on the name plate, is the speed at which the engine develops its highest or rated power output. The engines high idle no load speed can be 3-14% higher than the rated speed. The difference between rated and high idle no load sped and is called DROOP. Generator application: Industrial application: Automotive application: 1800 rpm 2300 rpm 2500 rpm +4%= +7%= + 12%= 1872 High idle rpm 2461 High idle rpm 2800 High idle rpm
DC-BSC-7-11
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 11
BSC-7-12
EPA PLATE DC-BSC-7-12
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) approved large nonroad compression ignition engines must be equipped with an engine information plate. The following information can be found on the plate. ENGINE FAMILY EPA standardized engine family designation 4 Engine model year DZX Letter combination assigned to DEUTZ L Large non road diesel engine 03.1 Largest piston displacement in this engine family 039 Engine manufacturers assigned number to differentiate engine design POWER Declared engines power out put in kW and HP VALVE LASH Engine specific valve clearance in mm INJECTION TIMING Engine specific commencement of injection before top dead center MODEL DEUTZ engine nomenclature RPM Rated engine speed ENGINE DISPLACEMENT Engine piston displacement in Liters INJECTION RATE Fuel injection rate in mm3 / Stroke SERIAL NUMBER DEUTZ engine serial number REM Remarks (empty for)
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 12
BSC-7-13
MSHA PLATE DC-BSC-7-13
MSHA = Mine Safety Health Administration
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 13
BSC-7-14
HORSE POWER DC-BSC-7-14
The unit of power used in mechanical engineering is the Horsepower. A metric horsepower is the power required to move 75 kp through 1 m in the time of 1 sec. In English speaking countries the the unit of measurement HP means the following A SAE horsepower is equal to the lifting a weight of 550 lbs through one foot in the time of 1 sec.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 14
BSC-7-15
SAE HP DC-BSC-7-15
DIN PS
KW
For several years the new international unit of power has been the kilowatt (kW). The power units DIN* PS, SAE HP and kW are related to each other as shown in the graphic.
*DIN = German Industrial Standards (metric)
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 15
BSC-7-16
ROTATION AND CYLINDER NUMBERING DC-BSC-7-16
1 OBSERVER 6 FREE END 2 DIRECTION OF VISION 7 RIGHT HAND SIDE 3 DIRECTION OF ROTATION 8 ENGINE BOTTOM 4 LEFT HAND SIDE 9 DRIVING END 5 ENGINE TOP In the Workshopmanuals for the DEUTZ engine series, the ISO (International Organization for Standardization) method is being used to designate engine rotating direction and other locations on the engine. Position of the Observer. (1) A The position of the observer in relation to an engine is considered to be the extension of the axis of the shaft which provides the main power take off. The observer should direct his view (2) towards this driving extremity. Designation of Cylinders B It is assumed that in all the mechanisms described from here on, the cylinders areI identical in design. The designation of each individual cylinder of a reciprocating engine shall be effected by using a number (numbering consecutively 1, 2, 3, etc.) or by using a combination of a capital letter (lettering consecutively A, B, C etc.) and a number.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 16
BSC-7-17
ROTATION AND CYLINDER NUMBERING DC-BSC-7-17
Individual cylinders of an engine with more than one bank shall be designated by combinations of a capital letter and a number. C The letters shall be allocated by placing an imaginary semi plane (P) centered through the axis of the driving crankshaft. The crankshaft is to be assumed to be in horizontal position. The semi plane P is imagined to be rotating in clockwise direction. The starting position of this semi plane shall be horizontal and to the left (at 9 oclock position) of the observer. The first bank through which the clockwise rotating semi plane moves, including the bank if it is the starting position, shall be designated by the capital letter A the following bank by the capital letter B. Each individual cylinder shall be designated by combination a capital letters followed by a number (A1; A2 etc. B1; B2 etc.) starting with the cylinder unit nearest to the observer. Direction of rotation (3) (Counter clockwise ) The direction of rotation of an internal combustion engine is the direction of rotation of the shaft that provides the main power take off as viewed from the position of the observer.
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 17
ROTATION AND CYLINDER NUMBERING, continued
Left side (4) The portion of the engine which is on the left of the engine as viewed by the observer. Top (5) The portion of the engine which is on the top of the engine as viewed by the observer. Free end (6) The portion of the engine which is the most remote from the observer. Right hand side (7) The portion of the engine which is on the right of the engine as viewed by the observer. Driving end (8) The portion of the engine which is the nearest to the observer Bottom (9) BSC-7-18 The portion of the engine which is on the bottom of the engine as viewed by the observer.
The above specifications are an extract of the, International Standards, ISO 1204 (counter clockwise, flywheel end, blower end) are specifications that have been used by DEUTZ
DC-BSC-7-18
DEUTZ CORPORATION Product Support Training Center Atlanta All rights reserved
TITLE: BASICS
SECTION: 7 PAGE: 18
También podría gustarte
- Thomson Electrac HD Linear Actuator Motion Control per CAN BusDe EverandThomson Electrac HD Linear Actuator Motion Control per CAN BusAún no hay calificaciones
- Install - Deutz EURO 6 AdBlue EmulatorDocumento2 páginasInstall - Deutz EURO 6 AdBlue EmulatorValentin AndrenoiuAún no hay calificaciones
- Brochure Abg7820b Abg8820b t3 en 21 20000048 CDocumento12 páginasBrochure Abg7820b Abg8820b t3 en 21 20000048 CKurniawan100% (1)
- AGC 242 With Cummins DG Set 750Documento3 páginasAGC 242 With Cummins DG Set 750José David Barrios PadrónAún no hay calificaciones
- BW 219 DH 5Documento2 páginasBW 219 DH 5Hữu Dũng Nguyễn0% (1)
- BW24RH / BW27RHDocumento4 páginasBW24RH / BW27RHVlad SuteuAún no hay calificaciones
- SUPER 1603-3: Universal ClassDocumento22 páginasSUPER 1603-3: Universal ClassBurazBurazAún no hay calificaciones
- ECU-9988N Cut Sheet 22JULY08 PDFDocumento2 páginasECU-9988N Cut Sheet 22JULY08 PDFJosé David Barrios PadrónAún no hay calificaciones
- Operation & Maintenance: Paver Finisher Dynapac SD1800WDocumento468 páginasOperation & Maintenance: Paver Finisher Dynapac SD1800WKrzysztof BrękAún no hay calificaciones
- Deutz 2012 LDA-replacement of Diaphragm-1Documento10 páginasDeutz 2012 LDA-replacement of Diaphragm-1Luís Fernando OliveiraAún no hay calificaciones
- PM2000 SchematicsDocumento18 páginasPM2000 SchematicsThilina JayasingheAún no hay calificaciones
- TL470 6990102 enGB OmDocumento194 páginasTL470 6990102 enGB Ommetin bulatAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Finisoare de Asfalt Pe Senile Volvo p7820c p8820c 47543Documento16 páginas7 Finisoare de Asfalt Pe Senile Volvo p7820c p8820c 47543Farkas PalAún no hay calificaciones
- Installation Guide For Diesel EnginesDocumento250 páginasInstallation Guide For Diesel EnginesJose FavaAún no hay calificaciones
- DX420LCA-K: Construction EquipmentDocumento15 páginasDX420LCA-K: Construction EquipmentHaidar SareeniAún no hay calificaciones
- Atlas Copco 300 CFM XATS 156 DDDocumento4 páginasAtlas Copco 300 CFM XATS 156 DDusman zafarAún no hay calificaciones
- Valvula MixproofDocumento66 páginasValvula MixproofVazter BI100% (1)
- Crankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDocumento5 páginasCrankcase Pressure SM019901095211 - en PDFDavy GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- MWM Geg TCG 2020Documento5 páginasMWM Geg TCG 2020absahkah100% (1)
- 150 7121 Deutz Operation Manual PDFDocumento62 páginas150 7121 Deutz Operation Manual PDFduongpnAún no hay calificaciones
- SUPER700-3 - EN - 2513779 - 0216 - MPW - VOGELEDocumento18 páginasSUPER700-3 - EN - 2513779 - 0216 - MPW - VOGELERobinson GuanemeAún no hay calificaciones
- 2954 4960 01 - Branded EU Lighting Tower - ENDocumento50 páginas2954 4960 01 - Branded EU Lighting Tower - ENIlarion Ciobanu100% (1)
- DF145CS PLC Omm03 GBDocumento180 páginasDF145CS PLC Omm03 GBhitman7788Aún no hay calificaciones
- PERKINS ENGINE Identification Serial Number 35Documento1 páginaPERKINS ENGINE Identification Serial Number 35wilsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Cummins QSX15 Spec & PartsDocumento12 páginasCummins QSX15 Spec & Partskevinsims11100% (1)
- Load Rate: Test ReportDocumento1 páginaLoad Rate: Test ReportluvfearAún no hay calificaciones
- Backhoe Loader: Stage II CompliantDocumento20 páginasBackhoe Loader: Stage II CompliantTamquadistu AlexAún no hay calificaciones
- FCE60 Ignition Box: User ManualDocumento34 páginasFCE60 Ignition Box: User ManualSony Hermawan100% (1)
- Instruction Manual: Hako-Trac 1950 DA (8084)Documento62 páginasInstruction Manual: Hako-Trac 1950 DA (8084)Aleksandra HreščakAún no hay calificaciones
- DG 04 003-E 08-04 Formular Communication OrderDocumento17 páginasDG 04 003-E 08-04 Formular Communication OrderLuis JesusAún no hay calificaciones
- z45-25j Mantenimiento 2Documento255 páginasz45-25j Mantenimiento 2jonny david martinez perezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cat DP40 55N Diesel Forklift BrochureDocumento12 páginasCat DP40 55N Diesel Forklift BrochureAdrian FerreyraAún no hay calificaciones
- SG72 PDFDocumento6 páginasSG72 PDFnhocti007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Robin Generator r600Documento78 páginasRobin Generator r600cbeckdorf100% (1)
- TCD2015 PDFDocumento67 páginasTCD2015 PDFRosa ChAún no hay calificaciones
- Catalogo Generador Olimpian 150-200 KWDocumento5 páginasCatalogo Generador Olimpian 150-200 KWlujes99Aún no hay calificaciones
- DYNAPAC F 150 C 769130 - SpecificationDocumento254 páginasDYNAPAC F 150 C 769130 - Specificationhoan100% (2)
- Operation & Maintenance: Paver Finisher F 121 W/D F 141 W/DDocumento266 páginasOperation & Maintenance: Paver Finisher F 121 W/D F 141 W/DAliTronic1972Aún no hay calificaciones
- Silentpiler f101Documento3 páginasSilentpiler f101Nguyen The PhatAún no hay calificaciones
- BOMAG Finisher BF 800. The Heavy Weight ChampionDocumento20 páginasBOMAG Finisher BF 800. The Heavy Weight ChampionVany LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- ZX210W-3 Technical Manual (Troubleshooting)Documento632 páginasZX210W-3 Technical Manual (Troubleshooting)derekpalang1003100% (1)
- Atlas Copco XATS 156-BrochureDocumento4 páginasAtlas Copco XATS 156-BrochureramseyAún no hay calificaciones
- @perkins: Diagnostic Code ReaderDocumento2 páginas@perkins: Diagnostic Code ReaderM. ShaatAún no hay calificaciones
- Omm PC800,850-8R - Pen00419-00Documento399 páginasOmm PC800,850-8R - Pen00419-00Andri Assoi100% (1)
- Perkins 1106D PJDocumento96 páginasPerkins 1106D PJcrash2804Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3705 Brochure Bf800 CDocumento4 páginas3705 Brochure Bf800 CAbdul Khaliq100% (1)
- MGE Series Generators Model MGE2901FOU Parts BreakdownDocumento34 páginasMGE Series Generators Model MGE2901FOU Parts BreakdownZaki AnwerAún no hay calificaciones
- BPR 100 80dDocumento112 páginasBPR 100 80dBane RadovicAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 Finisor de Asfalt Pe Senile Volvo Abg9820 47542Documento6 páginas6 Finisor de Asfalt Pe Senile Volvo Abg9820 47542Farkas Pal100% (1)
- Operator & Parts Manual: Serial Numbers 1010-1070Documento45 páginasOperator & Parts Manual: Serial Numbers 1010-1070Євген ЗаліщукAún no hay calificaciones
- JT30AT Operator Manual (3152)Documento243 páginasJT30AT Operator Manual (3152)Luke FosterAún no hay calificaciones
- BODAS-service: RE 95086/2021-04-19 Replaces: 2020-03-02Documento10 páginasBODAS-service: RE 95086/2021-04-19 Replaces: 2020-03-02Vinod HegdeAún no hay calificaciones
- Deutz 1011 Spec SheetDocumento6 páginasDeutz 1011 Spec SheetJulian Alberto AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Deutz Fahr BFM 2012 Engine Service Repair ManualDocumento16 páginasDeutz Fahr BFM 2012 Engine Service Repair ManuallaopaodunAún no hay calificaciones
- Reuse and Salvage For 3500 Engine Cylinder BlocksDocumento96 páginasReuse and Salvage For 3500 Engine Cylinder Blocksma.powersource100% (1)
- 1221 - 1010KVA DG Set SpecificationDocumento36 páginas1221 - 1010KVA DG Set SpecificationKhiem Le100% (1)
- Commonrail XeMAN PDFDocumento47 páginasCommonrail XeMAN PDFsasa oljacaAún no hay calificaciones
- Base Engine Data Sheet D383045CX03Documento3 páginasBase Engine Data Sheet D383045CX03jbsb2Aún no hay calificaciones
- I. Models CF34-10E5 CF34-10E5A1 CF34-10E6 CF34-10E6A1: Maximum ContinuousDocumento6 páginasI. Models CF34-10E5 CF34-10E5A1 CF34-10E6 CF34-10E6A1: Maximum ContinuousEstevam Gomes de AzevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Imo ACGDocumento16 páginasImo ACGMiguel Ponce100% (1)
- 75 CC 88Documento17 páginas75 CC 88jonasrodon1624Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aviation Piston EngineDocumento20 páginasAviation Piston EngineGiannisAún no hay calificaciones
- Hemi EnginesDocumento18 páginasHemi EnginesSano SanojAún no hay calificaciones
- WankelDocumento24 páginasWankelKunchala SaiAún no hay calificaciones
- E660FL Product Brochure-EnglishDocumento2 páginasE660FL Product Brochure-EnglishLorre HuAún no hay calificaciones
- PumpsDocumento35 páginasPumpsMuhammad Ahmed Saleem100% (2)
- 115135150175-OptiMax-Direct Fuel Injection Starting Model Year 2000-Starting Serial Number OG960500Documento653 páginas115135150175-OptiMax-Direct Fuel Injection Starting Model Year 2000-Starting Serial Number OG960500LeandroLeiteAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 1610 - Gri LectureDocumento65 páginasSection 1610 - Gri LectureCaringal Christelle MaeAún no hay calificaciones
- Automobile EngineeringDocumento142 páginasAutomobile Engineeringprem pravashAún no hay calificaciones
- Air CompressorDocumento2 páginasAir CompressorAli AimranAún no hay calificaciones
- Machine Foundation-Calculation of Unbalance ForceDocumento6 páginasMachine Foundation-Calculation of Unbalance Forcesathiyaseelann.sAún no hay calificaciones
- Design and Fabrication of Mini-Air EngineDocumento33 páginasDesign and Fabrication of Mini-Air EngineMadhan KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal Engineering Question BankDocumento33 páginasThermal Engineering Question BankmechgokulAún no hay calificaciones
- Reciprocating & Rotary CompressorDocumento64 páginasReciprocating & Rotary Compressorraghu.entrepreneur100% (1)
- Spare Part Pulsar P200NSDocumento55 páginasSpare Part Pulsar P200NSdidin MuhidinAún no hay calificaciones
- Reciprocating Compressors For Industrial Refrigeration Series Grasso VDocumento56 páginasReciprocating Compressors For Industrial Refrigeration Series Grasso VVadimAún no hay calificaciones
- B.E (Iv/Iv) - Mechanical - B: Rotary EngineDocumento25 páginasB.E (Iv/Iv) - Mechanical - B: Rotary EngineFaiz Naeem Sait100% (1)
- 0 - Solenoid Engine Report-2Documento29 páginas0 - Solenoid Engine Report-2Deepak KV ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 9 GAS Power CycleDocumento87 páginasChapter 9 GAS Power CyclezabidullahAún no hay calificaciones
- Reciprocating Piston Engine Lubrication SystemDocumento39 páginasReciprocating Piston Engine Lubrication SystemSolomon MehretAún no hay calificaciones
- Tom AssignmentDocumento21 páginasTom AssignmentAbhimechAún no hay calificaciones
- Ae Lab ManualDocumento48 páginasAe Lab Manualसंकेत कलगुटकर100% (1)
- Limbach l2400 Only Ef DF Et DT Operatingandmaintenancemanual enDocumento44 páginasLimbach l2400 Only Ef DF Et DT Operatingandmaintenancemanual enabidparipurnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mechanical MaintanenceDocumento311 páginasMechanical MaintanenceSandeep VijayakumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Flywheel & Camshaft PDFDocumento43 páginasFlywheel & Camshaft PDFMatthew Smith0% (1)
- Piston EngineDocumento6 páginasPiston EngineanandAún no hay calificaciones
- FEA and Material Optimization of Diesel Engine PistonDocumento59 páginasFEA and Material Optimization of Diesel Engine PistonRakshith M100% (1)
- Guideline For Field Testing of Reciprocating Compressor PerformanceDocumento173 páginasGuideline For Field Testing of Reciprocating Compressor PerformanceSean Clark100% (2)
- Nomenclature of IC EnginesDocumento10 páginasNomenclature of IC EnginesSurjit Kumar GandhiAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 TrainingDocumento16 páginas12 Trainingfranz.xoithAún no hay calificaciones