Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
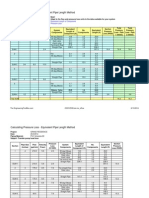
Recommended velocities and pressure drops for common process pipelines
Cargado por
ger80Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Recommended velocities and pressure drops for common process pipelines
Cargado por
ger80Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Recommended Mean Velocities in Pipe From Various Sources Fluid Velocity Dry Gas 100 fps Wet Gas
80 fps High Pressure Steam (150 psig+) 150 fps Low Pressure Steam (< 50 psig) 100 fps Air 100 fps Vapor Lines, General Max velocity 0.3 mach or 0.5 psi/100 ft Light Volatile Liquid near Bubble Point, Pump Suction 0.5 ft head total suction line Pump Discharge, Tower Reflux 3 to 5 psi/100 ft Hot Oil Headers 1.5 psi/100 ft Vacuum Vapor Lines below 50 MM Abs Pressure Allow max of 5% absolute pressure for friction loss Source: Branan, "Rules of Thumb for Chemicl Engineers", 2nd ed., Page 5
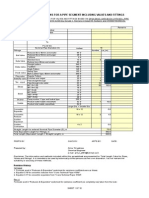
Typical Design Velocities for Process System Applications Service Average liquid process Pump suction, supercooled fluid Pump suction, boiling fluid Boiler feed water Gravity liquid drain lines Liquid to reboiler (no pump) Vapor-liquid mixture out of reboiler Vapor to condenser Gravity separator flows
Velocity, ft/sec 4 - 6.5 1-5 0.5 - 3 4-8 1.5 - 4 2-7 15 - 30 15 - 80 0.5 - 1.5
Liquid Fluid Ammonia, liquid Benzene Bromine, liquid Calcium chloride Carbon tetrachloride Chlorine, dry liquid Chloroform, liquid Ethylene dibromide Ethylene dichloride Ethylene glycol Hydrochloric acid, liquid Methyl chloride, liquid Oils, lubricating Perchlorethylene Propylene glycol Sodium chloride solution Sodium chloride sol'n w/solids Sodium hydroxide, 0-30% Sodium hydroxide, 30-50%
Pipe Material Steel Steel Glass Steel Steel Steel, Schedule 80 Copper, steel Glass Steel Steel Rubber-lined Steel Steel Steel Steel Steel Monel, Ni Steel, Ni Steel, Ni
Velocity, ft/sec 6 6 4 4 6 5 6 4 6 6 5 6 6 6 5 5 6 min; 15 max 6 5
Sodium hydroxide, 50-73% Styrene Sulfuric acid, 88-93% Sulfuric acid, 93-100% Trichlorethylene Vinyl chloride Vinylidene chloride Water, average service Water, pump suction Water, usual maximum economical Water, sea and brackish Water, sea and brackish
Steel, Ni Steel 316 SS, lead Cast iron; Steel, Sched 80 Steel Steel Steel Steel Steel Steel Rubber-lined, Saran Concrete-lined
4 6 4 4 6 6 6 3 to 8; 6 avg 3 to 8 ; 6 avg 7 to 10 5 to 8 5 to 12
Gaseous or Vapor Fluid Acetylene Air, 0 to 30 psig Ammonia Bromine Chlorine, dry Chloroform Ethylene Hydrochloric acid Hydrogen Methyl chloride Natural gas Oxygen (ambient temp.) Oxygen (low temp.) Steam, 0-30 psi, sat. Steam, 15 psi up, superheated Steam, 30-150 psi, sat or superheated Sulfur dioxide
Pipe Material Steel Steel Steel Glass Steel, Schedule 80 Copper, steel Steel Rubber-lined, Saran Steel Steel Steel Steel 304 SS Steel Steel Steel Steel
Velocity, ft/sec 30 (max) 65 100 35 30 to 80 35 100 65 65 65 100 75 (Max) 65 0.1 to 100 0.1 to 250 0.1 to 165 65
Velocity
h or 0.5 psi/100 ft
olute pressure for friction loss
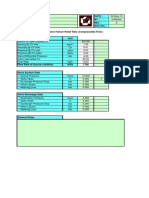
Recommended velocities or frictional P / 100 ft (physical length) of pipelines
Recommen ded Recommended (mass) velocity v, ft/s psi/100 ft Note all pipe diameters Nominal pipe size lower 3" or 4" 6" 8" or higher 1 Liquid in centrifugal pump suction line 3 to 5 3 to 5 3 to 5 up to 6 1.0 () As above, but 1 to 3 at boiling point (e.g. LPG, LNG) 3 liquid 1 to 3 1 to 3 1 to 0.3 to 0.5 () 2 Liquid in pumpto 7 5 dischargeto 7 5 line up to 10 up to 12 1.0 () 3 Flashing condensate 1 to 2 1 to 2 1 to 2 1 to 2 as required () Notes () Satisfy both recommendations (velocity and P / 100 psi), e.g. if P/100 ft=2 in 4" pipe with v=4 m/s, you have to chose 6" to lo () Velocity can be higher on the condition that NPSHa of the pump (with all safety margins) is satisfied. () Value of psi / 100 ft can be higher for short lines, up to 3 psi / 100 ft for total length up to 250 m = 820 ft (physical + e Sized by "Cameron hydraulic data" cooling water lines can have 1.5 (instead of 1) psi /100 ft for long lines as above. () Recommended velocity as if all condensate remained liquid
Note
, you have to chose 6" to lower P/100 ft.
0 m = 820 ft (physical + equivalent). t for long lines as above.
También podría gustarte
- 6206 Guide For Selection Installation andDocumento32 páginas6206 Guide For Selection Installation andakbavra80% (5)
- Restriction Orifice Calculation SheetDocumento2 páginasRestriction Orifice Calculation Sheetparykoochak50% (2)
- Steam Silencer DesignDocumento3 páginasSteam Silencer DesignDaan BrenisAún no hay calificaciones
- Reference For Sizing of Vacuum Breaker Valve PDFDocumento2 páginasReference For Sizing of Vacuum Breaker Valve PDFLcm Tnl50% (2)
- 4.47 The Expansion Factor, Y: P, AP P, P2Documento18 páginas4.47 The Expansion Factor, Y: P, AP P, P2Enrico GambiniAún no hay calificaciones
- Equivalent Length MethodDocumento3 páginasEquivalent Length MethodSharon LambertAún no hay calificaciones
- LOS Sizing Calcs - API 614 Chapter2 Upload VersionDocumento1 páginaLOS Sizing Calcs - API 614 Chapter2 Upload VersionZoebair100% (2)
- A106-B Pipe Temperature CalculatorDocumento8 páginasA106-B Pipe Temperature CalculatorAksheyAún no hay calificaciones
- Rupture Disc SizingDocumento8 páginasRupture Disc Sizing이가람100% (1)
- Acceleration Head For Reciprocating PumpsDocumento2 páginasAcceleration Head For Reciprocating PumpsEng Alf100% (1)
- Entrainment Vortex BreakerDocumento3 páginasEntrainment Vortex Breakerzorro21072107Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sly Venturi ScrubberDocumento2 páginasSly Venturi Scrubberzguy360Aún no hay calificaciones
- CV - Orifice Diameter PDFDocumento8 páginasCV - Orifice Diameter PDFManuelAún no hay calificaciones
- TEMA Shell Bundle Entrance and Exit AreasDocumento3 páginasTEMA Shell Bundle Entrance and Exit AreasArunkumar MyakalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Api 526-2009Documento1 páginaApi 526-2009고희숙Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vertical Separator SizingDocumento4 páginasVertical Separator SizingnemprrAún no hay calificaciones
- A New Approach For Sizing Finger Slug CatcherDocumento15 páginasA New Approach For Sizing Finger Slug CatcherHaryadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Jet Mixing CalculationDocumento3 páginasJet Mixing CalculationRachel FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Tank Static Head CalculationDocumento3 páginasTank Static Head CalculationrohitkushAún no hay calificaciones
- PSV Capacity ConversionDocumento4 páginasPSV Capacity Conversionaw_aeAún no hay calificaciones
- Steam Out of VesselsDocumento1 páginaSteam Out of Vesselsanon_293243615Aún no hay calificaciones
- Deaerator Volume Calculation ReportDocumento1 páginaDeaerator Volume Calculation Reportpsk.pranesh5520Aún no hay calificaciones
- EXAMPLE SIZING OWS Calculation Per API 421 PDFDocumento1 páginaEXAMPLE SIZING OWS Calculation Per API 421 PDFarnel_ado4412Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relief Load Calculation For Fire Case - As Per API 521Documento1 páginaRelief Load Calculation For Fire Case - As Per API 521ktejankarAún no hay calificaciones
- Suction Heaters and Heating Coils Suction Heaters and Heating CoilsDocumento3 páginasSuction Heaters and Heating Coils Suction Heaters and Heating CoilsDaysianne100% (1)
- Modern steam trap monitoring and steam leakage calculation Excel sheetDocumento3 páginasModern steam trap monitoring and steam leakage calculation Excel sheetvazzoleralex6884Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vacuum Pump SizingDocumento1 páginaVacuum Pump SizingMuhammad HassamAún no hay calificaciones
- Crane TP-410 Flow of FluidsDocumento135 páginasCrane TP-410 Flow of FluidsAbid Ur Rehman100% (1)
- PP Lined Pipe PDFDocumento27 páginasPP Lined Pipe PDFNILADRI BHATTACHARYYAAún no hay calificaciones
- Vent StackDocumento6 páginasVent Stackiuiuiooiu0% (1)
- Orifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and VaporsDocumento2 páginasOrifice Flow Calculator For Gases, Steam, and Vaporsbakhtyar21Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% ofDocumento3 páginasPipe Sizing Steam Supply and Condensate Return Lines Sizing Charts Chart CG-25, page CG-51, is the basic chart for determining the flow rate and velocity of steam in Schedule 40 pipe for various values of pressure drop per 100 ft, based on 0 psig saturated steam. Using the multiplier chart (Chart CG-24), Chart CG-25 can be used at all saturation pressures between 0 and 200 psig (see Example). These Charts are based on the Moody Friction Factor, which considers the Reynolds number and the roughness of the internal pipe surfaces. Notes: Based on Moody Friction Factor where flow of condensate does not inhibit the flow of steam. See Chart CG-24 for obtaining flow rates and velocities of all saturation pressures between 0 to 200 psig: see Example. Pipe Sizing Two principal factors determine pipe sizing in a steam system: 1. The initial pressure at the boiler and the allowable pressure drop of the total system. The total pressure drop in the system should not exceed 20% of1970acoAún no hay calificaciones
- API Verses Non APIDocumento19 páginasAPI Verses Non APIsandeshAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Drop CalculationsDocumento28 páginasPressure Drop Calculationshicham100% (1)
- PSV Sizing - API-520 PDFDocumento8 páginasPSV Sizing - API-520 PDFAnonymous da6X60VpII100% (1)
- Estimate Valve Pressure DropDocumento3 páginasEstimate Valve Pressure DropFranklin Santiago Suclla PodestaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dense Phase PR Drop & Pipe SizingDocumento32 páginasDense Phase PR Drop & Pipe SizingyoyoAún no hay calificaciones
- The GPSA 13th Edition Major ChangesDocumento2 páginasThe GPSA 13th Edition Major Changespatrickandreas77Aún no hay calificaciones
- Restriction Orifice PlatesDocumento9 páginasRestriction Orifice PlatesparykoochakAún no hay calificaciones
- Stirred Tank Heat ExchangerDocumento4 páginasStirred Tank Heat ExchangerMiguel OjedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Loss Insulated PipeDocumento3 páginasHeat Loss Insulated PipeKatie BensonAún no hay calificaciones
- What is pressure drop in pipesDocumento4 páginasWhat is pressure drop in pipesKartik ChaddarwalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Equivalent Length Calculator - RevADocumento10 páginasEquivalent Length Calculator - RevArkrajan1502Aún no hay calificaciones
- Control Valve Failure Relief Rate - Gas ServiceDocumento3 páginasControl Valve Failure Relief Rate - Gas ServiceSaeid Rahimi Mofrad100% (1)
- Small Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFDocumento4 páginasSmall Bore Orifice For Gas Flow PDFManufacturer VerifyAún no hay calificaciones
- Roark Mast CalculationsDocumento1 páginaRoark Mast Calculationsjamil voraAún no hay calificaciones
- Steam Pipe Size Calculation PDFDocumento16 páginasSteam Pipe Size Calculation PDFkhairul1989100% (5)
- PHE As CondensersDocumento50 páginasPHE As CondensersHelga Ines BenzAún no hay calificaciones
- Line Sizing Guideline EssentialsDocumento33 páginasLine Sizing Guideline EssentialsDavid Gustavo Duran TangoAún no hay calificaciones
- IR HL Heatless DryerDocumento1 páginaIR HL Heatless DryerYing Kei ChanAún no hay calificaciones
- Restriction Orifice Sizing CalculationDocumento2 páginasRestriction Orifice Sizing CalculationSiLan Subramaniam100% (1)
- Vacuum PresentationDocumento277 páginasVacuum Presentationavinashpatil2408100% (2)
- PSV Sizing CalculationsDocumento53 páginasPSV Sizing CalculationsAMITH OK93% (28)
- High Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesDe EverandHigh Pressure Phase Behaviour of Multicomponent Fluid MixturesAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid Velocities - RecommendationDocumento3 páginasFluid Velocities - RecommendationjnmanivannanAún no hay calificaciones
- Recommended velocities or frictional ΔP / 100 ft (physical length) of pipelinesDocumento2 páginasRecommended velocities or frictional ΔP / 100 ft (physical length) of pipelinesPham TinAún no hay calificaciones
- Recommended velocities or frictional ΔP / 100 ft (physical length) of pipelinesDocumento2 páginasRecommended velocities or frictional ΔP / 100 ft (physical length) of pipelinesImtinan MohsinAún no hay calificaciones
- Microsoft PowerPoint - PCM Vulcain TMDocumento22 páginasMicrosoft PowerPoint - PCM Vulcain TMDouglas A. RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Line Sizing Calculations for Water Distribution LoopsDocumento25 páginasLine Sizing Calculations for Water Distribution LoopsSharon LambertAún no hay calificaciones
- Sizing Steam Pipes & Steam VelocitiesDocumento3 páginasSizing Steam Pipes & Steam VelocitiesMacarthur B. MonsantoAún no hay calificaciones
- cz501 ManualDocumento34 páginascz501 Manualger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- NTL No. 2009-G33 Well Naming and Numbering StandardsDocumento24 páginasNTL No. 2009-G33 Well Naming and Numbering Standardsger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Treatment of Osteoarthritis of The Knee With Bracing: A Scoping ReviewDocumento7 páginasTreatment of Osteoarthritis of The Knee With Bracing: A Scoping Reviewger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- NTL 2009-g18Documento3 páginasNTL 2009-g18ger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- NASA MarginOfSafetyDocumento42 páginasNASA MarginOfSafetyger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Arc Flash Mitigation TechniquesDocumento4 páginasArc Flash Mitigation Techniquesger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment of CorrosionDocumento30 páginasAssessment of Corrosionamin110110Aún no hay calificaciones
- Interior Department Guidance on Pipeline Alternate Compliance RequestsDocumento4 páginasInterior Department Guidance on Pipeline Alternate Compliance Requestsger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- PTJ 6 2018Documento68 páginasPTJ 6 2018ger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- NTL 2011-n11Documento9 páginasNTL 2011-n11ger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- NTL 2009-g36Documento16 páginasNTL 2009-g36ger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Casing Pressure 30 CFR 250.517 (A)Documento5 páginasCasing Pressure 30 CFR 250.517 (A)azareiforoushAún no hay calificaciones
- Preprocessing Time Series Data Tips and TricksDocumento1 páginaPreprocessing Time Series Data Tips and TricksPradeep SinglaAún no hay calificaciones
- API Subcommittee 17 Industry Standards For Subsea Equipment: John M. Bednar - BP API SC17 ChairmanDocumento13 páginasAPI Subcommittee 17 Industry Standards For Subsea Equipment: John M. Bednar - BP API SC17 ChairmanSOURAV KARAún no hay calificaciones
- Interior Department Releases Notice on Offshore Production Safety SystemsDocumento8 páginasInterior Department Releases Notice on Offshore Production Safety Systemsger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- IT Project Delivery & Business Engagement ModelDocumento37 páginasIT Project Delivery & Business Engagement Modelger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Margin of SaftyDocumento15 páginasMargin of Saftybhanu25Aún no hay calificaciones
- O3 PURE Fridge Deodorizer ManualDocumento7 páginasO3 PURE Fridge Deodorizer Manualger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- InstructionSheet W11033125 RevADocumento2 páginasInstructionSheet W11033125 RevAger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Engineering Quiz Questions and AnswersDocumento155 páginasElectrical Engineering Quiz Questions and AnswersPimentel HaroldAún no hay calificaciones
- The PID Control Algorithm How It Works, How To Tune It, and How To Use It. 2nd EdDocumento68 páginasThe PID Control Algorithm How It Works, How To Tune It, and How To Use It. 2nd EdmiroperAún no hay calificaciones
- IMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Documento223 páginasIMPORTANT QUESTION IN ELECTRICAL ENGG FOR ASSISTANT ENGINEER EXAMS OF UPRVUNL, UPPCL, MPPKVVNL, HPPSC, IES, GATE and Other State Psus.Rishi Kant Sharma100% (1)
- BCBS LA 2020IndividualSolutions PDFDocumento28 páginasBCBS LA 2020IndividualSolutions PDFger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Periodicidad de La Calibracion de Los Medidores Masicos Tipo CoriolisDocumento3 páginasPeriodicidad de La Calibracion de Los Medidores Masicos Tipo CoriolisJorge Kovach AlvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Eaton Arc Flash HandbookDocumento32 páginasEaton Arc Flash Handbookger80100% (1)
- IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Initiati PDFDocumento8 páginasIEEE Electric Ship Technologies Initiati PDFger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- InstructionSheet W11033125 RevA PDFDocumento2 páginasInstructionSheet W11033125 RevA PDFger80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mil e 7016FDocumento48 páginasMil e 7016FnicolasAún no hay calificaciones
- IEEE Color Books OverviewDocumento6 páginasIEEE Color Books Overviewbanjan0230100% (1)
- Mil STD 704Documento38 páginasMil STD 704Yang TaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Literature ReviewDocumento18 páginasLiterature ReviewRaymond Manalo Panganiban100% (1)
- Supreme Court Rules in Favor of TEC and TPC in Dispute Over Alleged Electric Meter TamperingDocumento8 páginasSupreme Court Rules in Favor of TEC and TPC in Dispute Over Alleged Electric Meter TamperingDiosa Mae SarillosaAún no hay calificaciones
- 00 - User Manual - Netsure 702IC4 - For ODUDocumento53 páginas00 - User Manual - Netsure 702IC4 - For ODUSameera MilindaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S0196890422012195 MainDocumento16 páginas1 s2.0 S0196890422012195 MainAlex SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Design Mech DryersDocumento5 páginasDesign Mech DryersBrandon DouglasAún no hay calificaciones
- COACHING SET 2 MergedDocumento17 páginasCOACHING SET 2 Mergedjohn-john castañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- PTK MateriDocumento101 páginasPTK MateriAnnisah MardiyyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydronic M-Ii: Technical Description, Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsDocumento42 páginasHydronic M-Ii: Technical Description, Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsjeevaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1006 Tag Engine Parts BookDocumento216 páginas1006 Tag Engine Parts BookNilupul WijeratneAún no hay calificaciones
- EEDC DetailDocumento21 páginasEEDC DetailAfrian HindrawijayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Defstan 91-91R7 Amendment2 PDFDocumento38 páginasDefstan 91-91R7 Amendment2 PDFlimhockkin3766Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wireless Mobile Networks - Ch2Documento16 páginasWireless Mobile Networks - Ch2Mohammed ZohlofAún no hay calificaciones
- Concept of Net Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) - A Literature ReviewDocumento16 páginasConcept of Net Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) - A Literature ReviewJaime PazAún no hay calificaciones
- Catalogo PNRDocumento115 páginasCatalogo PNRKaren Isabel Ambiado RivasAún no hay calificaciones
- NS1 Work Plan Procedure For Erection of Circulating Water Pump Rev.0 - Part 1 of 3Documento53 páginasNS1 Work Plan Procedure For Erection of Circulating Water Pump Rev.0 - Part 1 of 3namdq-1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Welding Workshop ReportDocumento12 páginasGas Welding Workshop ReportDuventhirenAún no hay calificaciones
- 9315 200-500kVA Installation and Initial Startup Parallel CabinetsDocumento3 páginas9315 200-500kVA Installation and Initial Startup Parallel CabinetsElvis Eliud HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 7 8 Synchronous MotorDocumento19 páginasLecture 7 8 Synchronous MotorCHATHURA MADURANGAAún no hay calificaciones
- Fracture MechanicsDocumento31 páginasFracture MechanicsDhany SSat100% (2)
- Assignment (1) Vibrations: Submitted ToDocumento11 páginasAssignment (1) Vibrations: Submitted ToMahmoud KassabAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 12: Alternator PowerDocumento7 páginasExperiment 12: Alternator Powerxjqpl0% (1)
- DC13 072A. 356-415 KW (408-471 kVA) : Fuel OptimizedDocumento2 páginasDC13 072A. 356-415 KW (408-471 kVA) : Fuel OptimizedbrayandparavicinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Engg Chemistry R13 Model Question PapersDocumento4 páginasEngg Chemistry R13 Model Question PapersBell P PedAún no hay calificaciones
- Microwave Oven Owner's ManualDocumento38 páginasMicrowave Oven Owner's ManualjoseaurelianoAún no hay calificaciones
- National Resilience - 2016Documento2 páginasNational Resilience - 2016my oneAún no hay calificaciones
- SolidWorks Simulation Professional TrainingDocumento104 páginasSolidWorks Simulation Professional TrainingAnonymous NonQwK3qL275% (4)
- 2017 Facilities Standards (P100) PDFDocumento358 páginas2017 Facilities Standards (P100) PDFBhingle Abellera100% (1)
- Request For Information: 8 June 2020Documento11 páginasRequest For Information: 8 June 2020Mhae PotAún no hay calificaciones
- DeforestationDocumento4 páginasDeforestationPeggopoulouAún no hay calificaciones