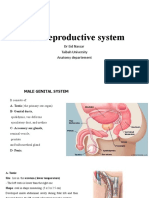
Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Bovine Repro
Cargado por
Chai YawatTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Bovine Repro
Cargado por
Chai YawatCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
3/10/2010
Bovine reproduction: problems during pregnancy
1
DONAL OTOOLE DEPT VET SCI DISEASES OF FOOD ANIMALS AND HORSES
3/10/2010
Putting it in perspective
2
Value of selected US commodities (2007)
11.4% swine 27% poultry 30.5% cattle 30.2% milk Cattle Milk Poultry Swine Sheep Catfish Others
Note: sheep less valuable than catfish (as a commodity companionship issues are separate)
Source: USDA NAHMS 2007-08 survey
3/10/2010
Typical production cycle
3
Breed late spring - early summer
Cow rebred 45-90 days after calving Natural service Bulls turned out for 3 months to ensure cows are bred L Less labor l b Own or lease bulls
Pregnancy check Vaccinate cows 1. when open; 2. at preg. check; 3. in
late gestation
Vaccinate calves: branding; pre-weaning/weaning
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
USDA NAHMS May 2009 4
3/10/2010
Goals
National average Pregnancy rate Abortion rate Calf losses Net calf crop 87% 3% 7% 77% Your target 94 96% <2% <5% 87 89%
Of breeding age females exposed to bulls/AI, national average producing calf (alive or dead): 91.5% (2007-08 numbers)
5
3/10/2010
Illness and death in calf crop (beef)
6
Calf mortality:
50 70
60% within one day of birth 80% in first 3 weeks of post-natal life S Scours > pneumonia > other problems i h bl
Management:
Pre-calving Calving Post-partum
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Record keeping in cow-calf operations
7
1992- 1993
2007 - 2008
67%
83%
USDA NAHMS May 2009
3/10/2010
Getting there
8
Proper nutrition of brood cows/replacement heifer Minimize calf death loss Use healthy, fertile bulls healthy Cull non-breeding cows and heifers Breed heifers >21 days earlier than cow cohort Disease prevention in cows and heifers: ID cattle and keep records of health status
3/10/2010
USDA NAHMS May 2009
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Disease in periparturient period
10
1. 2. 3. 3 4.
Dystocia Failure to ingest colostrum Hypoglycemia/hypothermia Environmental contamination, esp. damp crowding
Infectious disease influenced by these four factors
3/10/2010
Replacement heifers
11
Smaller mean pelvic size dystocia
Differences in measurement Importance of calf birth weight Feed to allow modest weight gain (0.5kg/day) Restricting feed does not reduce dystocia rates Third trimester weight loss = dystocia Ensure well vaccinated sentinel group Conception rates: ~60% first 21 day cycle ~80% first 3 cycles Heifers bred at ~15 months 60-65% mature body weight Calve at 24 months Use bulls with low birth weight/moderate weaning or yearling rate EPDs
3/10/2010
Target weight for puberty in heifers (2/3 mature weight)
Breed Angus Hereford Charolais
12
Weight 650 lb 700 lb 750 lb
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Effect of condition on estrus
Cycling 80 days post-partum
Body condition score 4 5 6 Percent cycling 62% 88% 98%
13
3/10/2010
Dystocia in heifers vs. cows
14
Heifers
Cows
11%
5% 0 4% 0.4%
0.9% 1.8% 0.1%
Easy pull Hard pull C-section Normal
Easy pull Hard pull C-section Normal
USDA NAHMS May 2009
3/10/2010
Bulls
Sire selection
15
Calving ease EPD (expected progeny differences)
>15-18 months old Breeding soundness examination:
Distinguishes satisfactory from unsatisfactory bulls Observation for physical problems Ob i f h i l bl Palpation of testis, and reproductive glands per rectum Observation of penis/prepuce; feet and leg conformation; eyes and periocular pigment Classification of semen: Sperm motility MOST important property - >30% motile
Sperm morphology - >70% normal Scrotal circumference
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
USDA NAHMS May 2009
16
3/10/2010
Scrotal Circumference
17
All testicles produce same number of sperm/gm
Bigger testicles = more spermatozoa
SC predicts earlier puberty in daughters 15 18 month old bulls: >31 cm
Adjust for age, breed, age of dam, breed, diet
3/10/2010
Diseases detected by BSE
18
Small, asymmetrical, inflamed or degenerate testes Absent or defective epididymis Persistent frenulum ( tied penis ) >12 months (tied penis Short, deviated or corkscrew penis Penile hematoma ruptured penis Seminal vesiculitis common In WY and other range states: trichomoniasis
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Poor penile conformation
Persistent frenulum
Preputial abscess Penile hematoma
19
3/10/2010
Seminal vesiculitis
20
Noah F20301
Esp. common in young bulls Ascending infection Various bacteria P i or asymmetry Pain Recovery unpredictable Control:
energy diet Antibiotics for 2 weeks
3/10/2010
Bull soundness BSE libido and mating ability
21
Feet and legs check while walking Body condition too fat or too thin Ocular its how he finds the ladies Libido, Libido mating ability, social dominance ability If he cant find cows in heat and will not mate, or is dominated by other bulls, good BSE is immaterial Bull: cow ratio
Allow for terrain Young bulls: 1:15 20; older bulls: 1:20 - 30
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Artificial insemination
22
More labor intensive Better disease control:
Trichomoniasis Campylobacteriosis (vibrio) py ( ) Poor nutritional development in replacement heifers Inadequate body condition of cows after calving Failure to identify cows in heat Failure to breed cows at proper time
3/10/2010
Poor results when:
Campylobacteriosis in cattle
23
Now RARE Venereal Bacterial Persists on penis and in
female tract
EED or abortion Sterility Effective killed vaccines
e.g., Virbin venerealis
Campylobacter fetus ssp.
3/10/2010
Trich Tritrichomonas fetus
24
Natural service bulls Venereal disease due to protozoan Recurring problem in WY, esp. in grazing associations Reportable to WLSB Test bulls during BSE InPouch test 3 times is best PCR once is adequate coming into increased use (mandated) Early returns to service and abortion (esp. early) Vaccine ineffective Cull bulls
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
Confirmed venereal trichomoniasis in Wyoming
Sept 1, 2008 July 15, 2009 (7,550 bulls tested) Affected bulls/affected ranches
1/1
7/3 21/4 34/12
20/9
7/3
WLSB
<2% is normal
Abortion
Spontaneous abortions
Trauma, genetic and starvation uncommon Intoxications rare: ponderosa pine; locoweed; nitrates in WY Most unlikely to go through herd:
Opportunistic infections per vagina Twins Exceptions: BVD TRICHOMONIASIS Campylobacteriosis Leptospirosis Neosporosis BRUCELLOSIS Any systemic disease where fever-endotoxemia occurs
26
3/10/2010
ABORTION in a beef state
Viral 11%
Clyde Kirkbride, JVDI 1992
Bacte rial 14%
No diagnosis 51% Fungal 5% Othe r 2% No diagnosis, le sions pre se nt 17%
27
3/10/2010
3/10/2010
ABORTION in a dairy-beef state
Dr. Mark Anderson 2003 AAVLD meeting
Protozoal 23% No diagnosis 40% Bacterial 17% No diagnosis, lesions present 16%
28
Viral Other 3% 1%
3/10/2010
Neosporosis
29
Rare in WY Most important cause of
abortion in dairy industry
Protozoan Dog-transmitted Vertical AND horizontal
spread
Vaccine so-so Post-natal CNS disease
Noah F19900
3/10/2010
Brucellosis
30
GYA Eliminated in US Feb 2008 Bacterial B. abortus Late term abortion storms Elk and bison in western WY Spatial separation Vaccinate heifers Lifetime infection Testing at slaughter Zoonotic USDA regulated
Noah F19900
3/10/2010
10
3/10/2010
Leptospirosis
31
Underdiagnosed? Bacterial disease:
Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar Hardjo strain hardjobovis Leptospira interrogans serovar Hardjo strain hardjoprajitno
In urine Zoonotic Some reports of high rates of infection in herds, esp. dairy Diagnosis by serology Avoid by vaccination conventional vs. SpirovacTM Full spectrum disease: return to service; early embryonic
death; abortion/stillbirth; weak calves
3/10/2010
Systemic fever
32
Underdiagnosed Recognized with febrile viral diseases Bacterial BRD? Oth ? Others? Difficult to confirm: No lesions in fetus No lesions in placenta
3/10/2010
Ponderosa pine abortion
33
Isocupressic acid Associated with hard winters
and shelter-seeking
3rd trimester 2 14 days post ingestion Weak contractions Retained fetal membranes Weak calves Difficult to confirm Supplement in 3rd trimester Keep out of slash piles
3/10/2010
11
3/10/2010
Mummies
34
Fetal death Autolysis in absence of
putrefactive bacteria
Dried out May be dead for months Minimal diagnosis value in
cattle and sheep
Various causes
3/10/2010
Twins and abortion
35
Can be ~10% of pregnancies Many early spontaneous abortions Recognized as <2.5% Complications: Death of one twin, esp. in unilateral pregnancies Freemartins Retained placentas Ketosis Dystocia
3/10/2010
In event of abortion storm
36
Isolate animal till you know what is going on Protect yourself Submit fetus + placenta, if available Serum from cow, and resample 3 weeks later:
antibody tests
History: Illness in cows AI vs. natural service Retained placenta Recent introductions Other illness in herd
3/10/2010
12
3/10/2010
37
3/10/2010
Take home
38
Attention to:
Bulls breeding soundness examination; venereal disease Heifers infectious disease crops up in this group first WHY? Cows records Opportunistic bacterial infections Regulated diseases: brucellosis and trich Toxic: pine needle abortion (regional in WY) Isolate dam Get tests run be patient, as it often takes multiple tries to figures out what may have occurred
Important diseases: p
In event of abortion storm:
3/10/2010
13
También podría gustarte
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2102)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Manhood - The Bare Reality (PDFDrive)Documento303 páginasManhood - The Bare Reality (PDFDrive)Memphis Kopa75% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Male Genitalia AbnormalitiesDocumento25 páginasMale Genitalia AbnormalitiesClaudette Kyle CornelioAún no hay calificaciones
- Science 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemDocumento12 páginasScience 5 DLP 1 - Human Reproductive SystemMark Cua89% (35)
- Successes and Failures With Animal Nutri PDFDocumento177 páginasSuccesses and Failures With Animal Nutri PDFFaisal MohommadAún no hay calificaciones
- Alimuddin Naseri Animal Nutrition ManualDocumento77 páginasAlimuddin Naseri Animal Nutrition ManualMohammad AmeenAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 1 Animal Welfare IntroductionDocumento26 páginasModule 1 Animal Welfare IntroductionChai Yawat100% (1)
- Ethics Animal EngDocumento6 páginasEthics Animal EngChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- CVWP Animals of All Shapes and Sizes BundleDocumento99 páginasCVWP Animals of All Shapes and Sizes BundleRaviAún no hay calificaciones
- Aged Animal Nutrition Student Ref PDFDocumento19 páginasAged Animal Nutrition Student Ref PDFIonela HoteaAún no hay calificaciones
- Recognition of Basic Cell Types and 2002 Veterinary Clinics of North AmericaDocumento27 páginasRecognition of Basic Cell Types and 2002 Veterinary Clinics of North AmericaChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Avian PathologyDocumento48 páginasAvian PathologyEric Cheah100% (1)
- Vet Sci Project GoalsDocumento1 páginaVet Sci Project GoalsChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts SkeletonDocumento9 páginasParts SkeletonChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Livestock Extension EducationDocumento88 páginasLivestock Extension EducationDustin SawyerAún no hay calificaciones
- Pet First AidDocumento56 páginasPet First AidRita RodriguesAún no hay calificaciones
- Vet Sci Vital 5 DayDocumento1 páginaVet Sci Vital 5 DayChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Kind of NutrientsDocumento3 páginasKind of NutrientsChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Feeding HorsesDocumento20 páginasFeeding HorsesChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Kind of NutrientsDocumento3 páginasKind of NutrientsChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Horse IdentificationDocumento12 páginasHorse IdentificationChai Yawat100% (1)
- Horse Digestive SystemDocumento5 páginasHorse Digestive SystemChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Eccv2012 Dog FinalDocumento14 páginasEccv2012 Dog FinalTaylor Made DonaldsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducing DogsDocumento50 páginasIntroducing DogsMorgan Clae Sanker100% (1)
- Hoof AnatomyDocumento4 páginasHoof AnatomyChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- F ConformDocumento25 páginasF ConformChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Genetics BookDocumento20 páginasGenetics BookChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Equine SkeletonDocumento1 páginaEquine SkeletonChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Hoof Problems 30211Documento2 páginasCommon Hoof Problems 30211Chai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Hoof Problems 30211Documento2 páginasCommon Hoof Problems 30211Chai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Breeds of Dogs Involved in Fatal Human AttacksDocumento5 páginasBreeds of Dogs Involved in Fatal Human AttacksChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal Breeds WorksheetDocumento1 páginaAnimal Breeds WorksheetChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- 4-Hparts of HorseDocumento2 páginas4-Hparts of HorseChai YawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Male Reproductive SystemDocumento121 páginasMale Reproductive SystemProf Lina RamliAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 19 Reproductive SystemDocumento36 páginasChapter 19 Reproductive SystemMacthalas QuiazonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4 VGO-1 PDFDocumento103 páginasChapter 4 VGO-1 PDFPankaj BeniwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Male Pelvic Viscera: NaeemiDocumento36 páginasMale Pelvic Viscera: Naeemijed larsen capulong gavinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Castration of Calves: Castration: Gettings The Best Results For Farm and Calf What Techniques Are Available?Documento5 páginasCastration of Calves: Castration: Gettings The Best Results For Farm and Calf What Techniques Are Available?WAQAS SHAHIDAún no hay calificaciones
- Sperm A ToDocumento16 páginasSperm A TogfujawatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 12 - Human Reproduction Health PDFDocumento137 páginasModule 12 - Human Reproduction Health PDFvarunAún no hay calificaciones
- Health Appraisal ProceduresDocumento5 páginasHealth Appraisal ProceduresAlex SampangAún no hay calificaciones
- Female and Male Reproductive OrgansDocumento2 páginasFemale and Male Reproductive OrgansPink EaintAún no hay calificaciones
- PubertyDocumento6 páginasPubertyNata LiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocumento21 páginasLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinAún no hay calificaciones
- Urology DossierDocumento166 páginasUrology DossierPeterAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocumento10 páginasAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemSerious LeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemDocumento7 páginasFinal Assessing Female and Male Genitourinary SystemJo Marchianne PigarAún no hay calificaciones
- Cobb MX CM10 11 Male SupplementDocumento28 páginasCobb MX CM10 11 Male SupplementernisitiwAún no hay calificaciones
- Human Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDocumento11 páginasHuman Reproductive System: Development of The Reproductive OrgansDhion Ardhian NugrohoAún no hay calificaciones
- Class 12 NEET Revision Notes - 7083332 PDFDocumento146 páginasClass 12 NEET Revision Notes - 7083332 PDFvengateshwaran kAún no hay calificaciones
- CastrationDocumento3 páginasCastrationLaura RosserAún no hay calificaciones
- NCERT Highlight - Human Reproduction by Seep PahujaDocumento16 páginasNCERT Highlight - Human Reproduction by Seep PahujaHarshit DevAún no hay calificaciones
- Kelly9e Ch03 Male Sexual-Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento19 páginasKelly9e Ch03 Male Sexual-Anatomy and Physiologysauloalberto6254Aún no hay calificaciones
- Male Reproductive System MLTDocumento12 páginasMale Reproductive System MLTAbdulrahman MohammedAún no hay calificaciones
- The Ultimate Alpha Male - How To Turn Your Intimacy Issues Into Ball Busting Superpowers and Become A Total Sexual Warrior (PDFDrive)Documento95 páginasThe Ultimate Alpha Male - How To Turn Your Intimacy Issues Into Ball Busting Superpowers and Become A Total Sexual Warrior (PDFDrive)Motivasyon PAMAún no hay calificaciones
- SCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveDocumento1 páginaSCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveJessa Tirambulo0% (1)
- Activity 1 Animal SciDocumento5 páginasActivity 1 Animal SciKylle BedisAún no hay calificaciones
- Male Reproductive System - PPTX NewDocumento7 páginasMale Reproductive System - PPTX NewSarilyn SimonAún no hay calificaciones
- Question SetDocumento140 páginasQuestion SetPiyush Ranjan BeheraAún no hay calificaciones
- Testicular TraumaDocumento25 páginasTesticular TraumaHuda HamoudaAún no hay calificaciones