Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Structure & Functions of the Cell
Cargado por
Harshit KumarTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Structure & Functions of the Cell
Cargado por
Harshit KumarCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
8.
Cell - Structure and Function
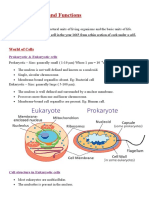
Cell Cells are the basic structural units and the building blocks of living organisms. Discovery of the cell Cell was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 after observing a piece of cork under a magnifying device. Hooke coined the term cell. Number of cells Organisms made of only a single cell are called unicellular organisms; for example: Amoeba and Paramecium Single cell in these organisms performs all the basic functions such as digestion, respiration, and excretion. Organisms made up of more than one cells are called multicellular organisms. For example: Humans, cow, etc. In these organisms, the cells show division of labour as particular set of cells are involved in performing a specific body function. Shape of the cells Most of the cells have a definite shape. Some cells such as Amoeba have no definite shape. The human red blood cells (RBC) are spherical in shape. The muscle cells in humans are spindle-shaped. The human nerve cells have elongated branched structure. In plants and bacteria, the cell is enclosed in a protective covering called cell wall, which gives shape and rigidity to the cells. Size of the cells The smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5 m in bacteria. The largest cell is the egg of an ostrich which is about 170 mm 130 mm in size. Size of a cell has no relation with the size of an organism. Cell structure and functions In multicellular organisms, each organ system is made up of several organs. Organs are further made up of tissues. Tissues are groups of similar cells performing a specific function. Components of the cell Cell membrane o It is the protective layer that surrounds the cell.
o Cell membrane selectively allows the entry of only some substances and prevents the movement of other materials. Hence, it checks the transport of substances in and out of the cell. Cell wall o In plants, an extra protective covering of a polysaccharide, cellulose is present. o It is called cell wall that protects plant cells from environmental variations. Cytoplasm o It is a jelly-like substance present between cell membrane and nucleus. o It contains various cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosomes etc. Nucleus o It is a dense spherical body located at the centre of the cell. o It is surrounded by porous nuclear membrane. o It contains spherical body called nucleolus. o It also contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. o Chromosomes are the structures that carry genes and play an important role in inheritance. o Genes are the structural and functional unit of inheritance. o The entire living substance in a cell is known as protoplast. Vacuoles o Vacuoles are fluid-filled membrane-bound structures in the cell. o In plant cells, a single large vacuole is present. o In animal cells, numerous small vacuoles are present. Plastids o They are present only in plant cells. o Plastid that contains green colour pigment called chlorophyll is known as chloroplasts. It is the chlorophyll that gives green colour to the leaves. o Chloroplast traps solar energy and utilizes this energy to manufacture food for the plant. Types of cell Prokaryotic cells - Cells having nuclear material without well defined nuclear membrane. For example - bacteria, blue green algae Eukaryotic cells - Cells having nucleus with well defined nuclear membrane. For example - plant and animal cells Differences between plant and animal cells Plant cell o Cell wall is present.
o Nucleus is located in the periphery of the cell. o Plastids are present. o A large single vacuole is present. Animal cells o Cell wall is absent. o Nucleus is located in the centre of the cell. o Plastids are absent. o Numerous small vacuoles are present in the cytoplasm. **
También podría gustarte
- The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocumento20 páginasThe Fundamental Unit of LifeShivansh Shrivastava100% (1)
- Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast ChromosomeDocumento17 páginasCytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Chromosomeardusias100% (1)
- Lec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesDocumento57 páginasLec 3,4,5-Cell and Cell OrganellesSatyam AryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocumento6 páginasCell - Structure and Functionssidhantm823Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cell - Structure and Functions PDFDocumento3 páginasCell - Structure and Functions PDFmaya__scribd100% (1)
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocumento5 páginasRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsArpit SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocumento10 páginasClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science NotesDocumento8 páginasChapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science Notesdeepti jainAún no hay calificaciones
- Science CH 8Documento3 páginasScience CH 8Mohammad HamzahAún no hay calificaciones
- CELLS For Class8Documento15 páginasCELLS For Class8cbseiscAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structure and Function - OutputDocumento5 páginasCell Structure and Function - OutputRaghav ChaudharyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsDocumento5 páginasCell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsPriyanshu Priyadarshi MeherAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes of Cell ChapterDocumento15 páginasNotes of Cell ChapterSudha SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- The Cell: Structure and Function of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento6 páginasThe Cell: Structure and Function of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsshaniahAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal and Plant CellsDocumento3 páginasAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinAún no hay calificaciones
- Plant and Animal Cell OrganellesDocumento4 páginasPlant and Animal Cell OrganellesRosalinda LappayAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell NotesDocumento10 páginasCell Notesofwargod769Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?Documento5 páginasChapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life: What Are Living Organisms Made Up Of?HeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento20 páginasCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio and PhysicsDocumento25 páginasBio and Physicsyasser yousriAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction to the Fundamental Unit of Life - the CellDocumento17 páginasIntroduction to the Fundamental Unit of Life - the Cellyashgodse kendriyavidyalayakoliwada.inAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocumento6 páginasCells: The Building Blocks of LifeDrexel DalaygonAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocumento24 páginasCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsJaspher Joshua CallangaAún no hay calificaciones
- SYLLABUS: Discovery of Cell, Modern Cell Theory, A Prokaryotic Cell, Unicellular and Multicellular Organism, Level ofDocumento12 páginasSYLLABUS: Discovery of Cell, Modern Cell Theory, A Prokaryotic Cell, Unicellular and Multicellular Organism, Level ofVijay KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell and Its Function Class 8 NotesDocumento4 páginasCell and Its Function Class 8 NotesNavyaAún no hay calificaciones
- The CellsDocumento4 páginasThe CellsSlaheddineAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1cell ConceptDocumento10 páginas1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayAún no hay calificaciones
- CELL AND TISSUE STRUCTUREDocumento11 páginasCELL AND TISSUE STRUCTUREAnand ClassesAún no hay calificaciones
- Science-Class 8_ Part 3Documento9 páginasScience-Class 8_ Part 3Arnav MalasiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Number. 8 Notes ScienceDocumento3 páginasLesson Number. 8 Notes ScienceVinod PursaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell is the structural and functional unit of lifeDocumento16 páginasCell is the structural and functional unit of lifeSathyabala BalamuruganAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocumento8 páginasUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocumento5 páginasChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Lecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQDocumento10 páginasLecture 1,2 - Plant Cell Structure - DFQUmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasClass 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesneilAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells: A Basic IntroductionDocumento18 páginasCells: A Basic IntroductionMuqadasAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesDocumento8 páginasFundamental Unit of Life Class 9 NotesMd AurangjebAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells: Building Blocks of LifeDocumento28 páginasCells: Building Blocks of LifeScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Unit of LifeDocumento5 páginasFundamental Unit of Lifechabalalalulama5Aún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Note About CellsDocumento17 páginasBiology Note About CellsEK TubeAún no hay calificaciones
- Structure of CellsDocumento14 páginasStructure of CellsTimothy JonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Structure and Nature of Living CellDocumento11 páginasStructure and Nature of Living CellKikiez PathanasriwongAún no hay calificaciones
- CellsDocumento31 páginasCellsPranav ShindeAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is A CellDocumento2 páginasWhat Is A Celljose de jesus sanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocumento7 páginasProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilAún no hay calificaciones
- The Cell: Life's Fundamental Building BlockDocumento8 páginasThe Cell: Life's Fundamental Building BlockQadirAún no hay calificaciones
- CellDocumento23 páginasCellridabatool151214Aún no hay calificaciones
- Structure of CellsDocumento14 páginasStructure of CellsTimothy JonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Cell StructureDocumento2 páginasBiology Cell StructureCut Rizka RahmiAún no hay calificaciones
- Plant Cells PDFDocumento7 páginasPlant Cells PDFMarcus Ben AlgerreAún no hay calificaciones
- Edulabz: InternationalDocumento1 páginaEdulabz: InternationaldarshnikddAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell-Structure and FunctionDocumento15 páginasCell-Structure and FunctionNILKAMAL CHAUDHARYAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Unit of Life Cell TheoryDocumento87 páginasFundamental Unit of Life Cell TheoryAryan SaxenaAún no hay calificaciones
- CellsDocumento26 páginasCellsNairita LetipoAún no hay calificaciones
- Reviewer in Science BDocumento5 páginasReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells - Structure and Function NotesDocumento26 páginasCells - Structure and Function NotesPrabal SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- The Cell Class VIIIDocumento28 páginasThe Cell Class VIIIShabab AlamAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of The Cell and Its FunctionDocumento24 páginasParts of The Cell and Its FunctionErnest De Mesa MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocumento5 páginasNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeAún no hay calificaciones
- The CellDocumento10 páginasThe CellAbeer Alnajjar عبير النجارAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksDe EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (2)
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomesDocumento20 páginasCell-The Fundamental Unit of Life: RibosomescbseiscAún no hay calificaciones
- As Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Documento21 páginasAs Biology: Unit 2 Notes (Edexcel)Charity Owo100% (1)
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniDocumento3 páginasCell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniSummer ValliniAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structures in Onion, Hydrilla and Cheek CellsDocumento8 páginasCell Structures in Onion, Hydrilla and Cheek CellsJachelle KateAún no hay calificaciones
- Darwin's Theory of EvolutionDocumento8 páginasDarwin's Theory of EvolutionRazelle Olendo100% (1)
- Lecture 2Documento32 páginasLecture 2alizeh amanAún no hay calificaciones
- Classification of OrganismDocumento35 páginasClassification of OrganismJnll JstnAún no hay calificaciones
- Classification PPT 1 Class 9Documento22 páginasClassification PPT 1 Class 9vidushi rathiAún no hay calificaciones
- snc2d Test ReviewDocumento2 páginassnc2d Test Reviewapi-265050003Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carl WoeseDocumento4 páginasCarl WoeseGabriel VenicioAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Structure AND Cell OrganisationDocumento54 páginasCell Structure AND Cell OrganisationAngel Cascayan Delos SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Origin of CellsDocumento15 páginasOrigin of CellsEmanuelah CuriAún no hay calificaciones
- 03 Unicellular EukaryotesDocumento14 páginas03 Unicellular EukaryotesALYSSA BEYONCE FERMINAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 2 Ultrastructure of Cells - Students NotesDocumento17 páginas1 2 Ultrastructure of Cells - Students Notesapi-289234696Aún no hay calificaciones
- Researchgate Publication on Morphology and Classification of BacteriaDocumento20 páginasResearchgate Publication on Morphology and Classification of Bacteriavineetvishal73100% (1)
- Science Exam ReviewerDocumento13 páginasScience Exam ReviewerManoli MontinolaAún no hay calificaciones
- General Biology 1: Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic CellsDocumento7 páginasGeneral Biology 1: Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic CellsGabrielle Alquizalas CincoAún no hay calificaciones
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 The Nature and Variety of Living Organisms - Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocumento4 páginasDetailed Notes - Topic 1 The Nature and Variety of Living Organisms - Edexcel Biology IGCSEpreet kaurAún no hay calificaciones
- IB Released Questions On 01 Cell BiologyDocumento50 páginasIB Released Questions On 01 Cell BiologyZuzanna BaligaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aakash Test PaperDocumento12 páginasAakash Test Paperajitha100% (1)
- Spelling Bee List of Words For 10th GradeDocumento2 páginasSpelling Bee List of Words For 10th GradeMel 8aAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Biology 5th Edition Robert Brooker Eric Widmaier Linda Graham Peter StilingDocumento29 páginasTest Bank For Biology 5th Edition Robert Brooker Eric Widmaier Linda Graham Peter StilingJanice Linder100% (32)
- Salters Nuffield Advanced Biology AS Revision SummaryDocumento23 páginasSalters Nuffield Advanced Biology AS Revision SummaryBenAún no hay calificaciones
- Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells and Kingdoms ClassificationDocumento4 páginasProkaryote vs Eukaryote Cells and Kingdoms Classificationdani abrahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbe Mission WIKIDocumento4 páginasMicrobe Mission WIKINur Banu Simsek100% (3)
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: ObjectivesDocumento39 páginasFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: ObjectivesAndrian SiscarAún no hay calificaciones
- Cells, Tissues and OrgansDocumento6 páginasCells, Tissues and OrgansatheelAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureDocumento22 páginasChapter 2 Summary and Model Answers:: 3.2.1 Cell StructureteeeAún no hay calificaciones