Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
NCP (Ideal) Nursing Diagnosis
Cargado por
Silinna May Lee SanicoTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
NCP (Ideal) Nursing Diagnosis
Cargado por
Silinna May Lee SanicoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
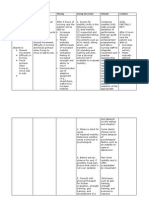
NCP (Ideal) Nursing Diagnosis Impaired Physical Mobility related to bed rest and fractured posterior wall of the
acetabulum
Subjective cues Objective cues
-
Di jud ko kalihok tungod aning akong bat-ang, as verbalized by client. Received lying on bed, awake With bandage on left hip Limited range of motion Slowed movement and delayed responses Decreased muscle strength
Short term Goal
Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the client will demonstrate passive/active ROM and isometric exercises and increase intake of nutritious foods and fluids.
Long term Goal
Within two weeks of nursing interventions, the client will increase strength and functioning and be able to perform self-care activities independently.
Nursing Interventions
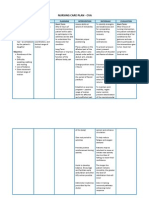
I: Encourage participation in diversional/recreational activities. Maintain stimulating environment, e.g., radio, TV, newspapers. R: Provides opportunity for release of energy, refocuses attention, enhances patients sense of self-control/selfworth, and aids in reducing social isolation. I: Instruct patient in/assist with active/passive ROM exercises of affected and unaffected extremities. R: Increases blood flow to muscles and bone to improve muscle tone I: Encourage use of isometric exercises starting with the unaffected limb. R: Isometrics contract muscles without bending joints or moving limbs and help maintain muscle strength and mass. I: Provide diet high in proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, limiting protein content until after first bowel movement. R: Nutrients required for healing are rapidly depleted, often resulting in a weight loss during skeletal traction. This can have a profound effect on muscle mass, tone, and strength. I: Place in supine position periodically if possible. R: Reduces risk of flexion contracture of hip. I: Assist with/encourage self-care activities (e.g., bathing, shaving). R: Enhances patient control in situation, and promotes self-directed wellness. I: Reposition periodically and encourage coughing/deep-breathing exercises. R: Prevents/reduces incidence of skin and respiratory complications. I: Auscultate bowel sounds. Monitor elimination habits and provide for regular bowel routine. R: Bed rest, use of analgesics, and changes in dietary habits can slow peristalsis and produce constipation. I: Encourage increased fluid intake to 20003000 mL/day. R: Keeps the body well hydrated, decreasing risk of urinary infection, stone formation, and constipation. I: Consult with physical/occupational therapist and/or rehabilitation specialist. R: Useful in creating individualized activity/exercise program. Nursing Diagnosis Acute Pain related to movement of bone fragments and injury to the soft tissue secondary to surgery
Subjective cues
Reports of pain
Objective cues
-
With bandage on left hip Guarding and protective behaviour Grimaced face Wincing upon movement Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the client will verbalize relief from pain or reduced pain score.
Short term Goal Long term Goal
Within two week of nursing interventions, the client will be able to participate in self-care activities independently and sleep and rest comfortably without reports of pain.
Nursing Interventions
I: Evaluate/document reports of pain/discomfort, noting location and characteristics, including intensity (010 scale), relieving and aggravating factors. R: Influences choice of/monitors effectiveness of interventions. I: Maintain immobilization of affected part by means of bed rest. R: Relieves pain and prevents bone displacement/extension of tissue injury. I: Explain procedures before beginning them. R: Allows patient to prepare mentally for activity and to participate in controlling level of discomfort. I: Medicate before care activities. Let patient know it is important to request medication before pain becomes severe. R: Promotes muscle relaxation and enhances participation. I: Perform and supervise active/passive ROM exercises. R: Maintains strength/mobility of unaffected muscles and facilitates resolution of inflammation in injured tissues. I: Provide alternative comfort measures, e.g., massage, position changes. R: Improves general circulation; reduces areas of local pressure and muscle fatigue. I: Provide emotional support and encourage use of stress management techniques, e.g., progressive relaxation, deep-breathing exercises, visualization/guided imagery. R: Refocuses attention, promotes sense of control, and may enhance coping abilities in the management of the stress of traumatic injury and pain I: Identify diversional activities appropriate for patient age, physical abilities, and personal preferences. R: Prevents boredom, reduces muscle tension, and can increase muscle strength; may enhance coping abilities. I: Administer medications as prescribed. R: Given to reduce pain and/or muscle spasms. I: Investigate any reports of unusual/sudden pain or deep, progressive, and poorly localized pain unrelieved by analgesics. R: May signal developing complications; e.g., infection, tissue ischemia, compartmental syndrome.
También podría gustarte
- Nursing Care for Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento3 páginasNursing Care for Impaired Physical MobilityMeljonesDaan100% (1)
- ACL Tear & Knee Arthroplasty Nursing CareDocumento2 páginasACL Tear & Knee Arthroplasty Nursing CareEd Pascasio100% (2)
- The ShelfDocumento18 páginasThe Shelfsowcowdd100% (5)
- Surgical Case Study: CranioplastyDocumento50 páginasSurgical Case Study: Cranioplastyrhia casinillo100% (8)
- NCP For Impaired MobilityDocumento4 páginasNCP For Impaired MobilityBettinaFernandoAún no hay calificaciones
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Nsg. Research Betty NeumannDocumento9 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN For Nsg. Research Betty NeumannFlor SabaysabayAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientDocumento9 páginasNursing Care Plans for Neurological PatientJam AbantaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Spinal Surgery Rehab ProtocolDocumento5 páginasSpinal Surgery Rehab ProtocolDanijela DragovicAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Diagnosis for Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 páginasNursing Diagnosis for Impaired Physical MobilitySilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan for Immobility and Pain ManagementDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for Immobility and Pain ManagementClariss Alota100% (2)
- Impaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Documento3 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility RT Neuromuscular Skeletal Impairment.Abegail Abaygar100% (2)
- NCP Inc.Documento2 páginasNCP Inc.Franklin A. Salaum III100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired MobilityDocumento3 páginasNursing Care Plan for Impaired MobilityEvan SmixAún no hay calificaciones
- NCPDocumento10 páginasNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP Sicu!Documento6 páginasNCP Sicu!joanne190Aún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Crib Com Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain Surgery AMB IncisionDocumento5 páginasNursing Crib Com Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain Surgery AMB IncisionKevin YangsonAún no hay calificaciones
- NCPDocumento8 páginasNCPJose Benit DelacruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem:: TherapiesDocumento2 páginasProblem:: TherapiesDhine Dhine ArguellesAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing DiagnosisDocumento4 páginasNursing DiagnosisEnzo DyAún no hay calificaciones
- Li Satri Materi Bing - IIIDocumento9 páginasLi Satri Materi Bing - IIILi SatryAún no hay calificaciones
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 páginasImpaired Physical MobilityAl-Qadry NurAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento15 páginasDrug StudyMariz Joy Gonzales Guillermo100% (1)
- Activities 1-2 Week 9Documento5 páginasActivities 1-2 Week 9api-338926820Aún no hay calificaciones
- Discharge Planning for Amputation RecoveryDocumento4 páginasDischarge Planning for Amputation Recoveryalynnavictoria100% (4)
- AssessmentDocumento2 páginasAssessmentBriggette AnnangaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcomes Interventions Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective CueDocumento3 páginasCues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcomes Interventions Rationale Implementation Evaluation Subjective CuefabtaciousVeelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Impaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortDocumento2 páginasImpaired Physical Mobility Related To Pain and DiscomfortRis NapolisAún no hay calificaciones
- Acute PainDocumento5 páginasAcute PainBrix ValdrizAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP ImmobiltyDocumento4 páginasNCP ImmobiltyAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasNursing Care PlanJoyce AnglubenAún no hay calificaciones
- HEalth Education Plan CVADocumento4 páginasHEalth Education Plan CVAJoenaCoy ChristineAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction PhysiotherapistDocumento12 páginasIntroduction Physiotherapistapi-371068989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Diagnosis: Chronic Pain Related To Tissue Distension byDocumento4 páginasNursing Diagnosis: Chronic Pain Related To Tissue Distension byAj AquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Spina Bifida NCPDocumento3 páginasSpina Bifida NCPCarpz Darpz100% (2)
- Cues Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento6 páginasCues Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationAndrea BroccoliAún no hay calificaciones
- Icu ReqDocumento9 páginasIcu Reqzygote_23100% (1)
- IMPAIRED MOBILITY RT Insufficient Muscle StrengthDocumento2 páginasIMPAIRED MOBILITY RT Insufficient Muscle StrengthMj Lina TiamzonAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 páginaNursing Care Planlaehaaa67% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN RealDocumento3 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN RealJorossMabantaMarayanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pain Management Nursing InterventionsDocumento6 páginasPain Management Nursing InterventionsJeffrey Richmond AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPAldrece CastroverdeAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care Plan (CVA)Documento2 páginasNursing Care Plan (CVA)Mel Rodolfo50% (2)
- LCPDDocumento7 páginasLCPDakoismeAún no hay calificaciones
- Rehabilitation of Patients After StrokeDocumento47 páginasRehabilitation of Patients After StrokeRogerAún no hay calificaciones
- Tugas RiaDocumento16 páginasTugas RiaSafitri SampulawaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento8 páginasNursing Care PlanCatherine Joy VillapandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessing mobility and activity intoleranceDocumento4 páginasAssessing mobility and activity intoleranceSteffi Muriel100% (1)
- Activity intolerance nursing care cervical cancer chemotherapyDocumento4 páginasActivity intolerance nursing care cervical cancer chemotherapyIvy MinaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Actual NCPsDocumento4 páginas2 Actual NCPsSittie Rohaina SabanAún no hay calificaciones
- Intervention EdwardsDocumento19 páginasIntervention EdwardsChamCham AquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Management of CVA and NIDDMDocumento12 páginasNursing Management of CVA and NIDDMKaloy KamaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Therapy Rehabilitation ProgramDocumento3 páginasPhysical Therapy Rehabilitation ProgramSriAún no hay calificaciones
- Fracture Mobility NursingDocumento10 páginasFracture Mobility NursingLea TanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ransverse Myelitis TM: by Rusu DumitritaDocumento16 páginasRansverse Myelitis TM: by Rusu DumitritaBraga MihaelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Prep 2Documento9 páginasClinical Prep 2Colin FraleyAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP Risk For FallDocumento20 páginasNCP Risk For FallRen Ren Determinado86% (7)
- Holistic Home Remedies for Acute Low Back Pain: Incorporating Stretching and the McKenzie MethodDe EverandHolistic Home Remedies for Acute Low Back Pain: Incorporating Stretching and the McKenzie MethodAún no hay calificaciones
- Incontinence a Time to Heal with Yoga and Acupressure: A Six Week Exercise Program for People with Simple Stress Urinary IncontinenceDe EverandIncontinence a Time to Heal with Yoga and Acupressure: A Six Week Exercise Program for People with Simple Stress Urinary IncontinenceAún no hay calificaciones
- Injury Rehab with Resistance Bands: Complete Anatomy and Rehabilitation Programs for Back, Neck, Shoulders, Elbows, Hips, Knees, Ankles and MoreDe EverandInjury Rehab with Resistance Bands: Complete Anatomy and Rehabilitation Programs for Back, Neck, Shoulders, Elbows, Hips, Knees, Ankles and MoreAún no hay calificaciones
- Releasing the Rotator Cuff: A complete guide to freedom of the shoulderDe EverandReleasing the Rotator Cuff: A complete guide to freedom of the shoulderAún no hay calificaciones
- ControllingDocumento21 páginasControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- ControllingDocumento21 páginasControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- RN Heals JournalDocumento2 páginasRN Heals JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnesium SulfateDocumento1 páginaMagnesium SulfateSilinna May Lee Sanico0% (1)
- DR JournalDocumento2 páginasDR JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisDocumento2 páginasNCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Surgical ProceduresDocumento4 páginasSurgical ProceduresSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- CHEST PROCEDURESDocumento10 páginasCHEST PROCEDURESSilinna May Lee SanicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Assessment of Diverse Frenum Morphology in Permanent DentitionDocumento7 páginasClinical Assessment of Diverse Frenum Morphology in Permanent DentitionBayu Aji KurniawanAún no hay calificaciones
- Sigmoidoscopy and Colonoscopy Request FormDocumento2 páginasSigmoidoscopy and Colonoscopy Request FormAbdullahi AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Bowel Preparation: Penyusun: Nicholas David Marcellis Pembimbing: Dr. Mangalindung O, SPBDocumento18 páginasBowel Preparation: Penyusun: Nicholas David Marcellis Pembimbing: Dr. Mangalindung O, SPBbocah_britpopAún no hay calificaciones
- Ichthyosis Vulgaris: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocumento3 páginasIchthyosis Vulgaris: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureJames Czar Fontanilla IlaganAún no hay calificaciones
- Graded Exercise Testing (GXT) NewDocumento8 páginasGraded Exercise Testing (GXT) Newf3rd110Aún no hay calificaciones
- Legal Med FinalDocumento59 páginasLegal Med FinalCriminology Criminology CriminologyAún no hay calificaciones
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocumento412 páginasInflammatory Bowel DiseaseSabbra CadabraAún no hay calificaciones
- Disease Symptoms and Patient Profile DatasetDocumento6 páginasDisease Symptoms and Patient Profile Datasetnavyalohitha49Aún no hay calificaciones
- Yemisi Chapter ThreeDocumento10 páginasYemisi Chapter ThreeAbimbola OyarinuAún no hay calificaciones
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocumento7 páginasChest PhysiotherapyNikhil Mohan100% (1)
- Acupressure Meridian TherapyDocumento4 páginasAcupressure Meridian Therapynikanor1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tech MagDocumento44 páginasTech Magcarambola88Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pendekatan Klinis Penurunan PendengaranDocumento29 páginasPendekatan Klinis Penurunan PendengaranHeather PorterAún no hay calificaciones
- Interpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileDocumento8 páginasInterpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileAndre NgoAún no hay calificaciones
- MAPC 2nd Year Assignments 2019-20Documento13 páginasMAPC 2nd Year Assignments 2019-20Jayee's GalleryAún no hay calificaciones
- Kheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Documento5 páginasKheir 31st Anniversary Dinner Sponsorship Packet 20171012Anonymous wnCXWd3Aún no hay calificaciones
- DepEd Medical CertificateDocumento1 páginaDepEd Medical CertificateMaria Eleonor C. BañaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmaco VigilanceDocumento31 páginasPharmaco VigilanceRasika NatuAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice TestDocumento6 páginasPractice TestJulie May SuganobAún no hay calificaciones
- Anesth Analg-1970-ALDRETE-924-34 PDFDocumento11 páginasAnesth Analg-1970-ALDRETE-924-34 PDFYudiSiswantoWijaya100% (2)
- KETOCONAZOLEDocumento22 páginasKETOCONAZOLEAbdul khodir jaelaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Step Eugenic Programmed Murder of Myra Snyder ScottDocumento23 páginasStep Eugenic Programmed Murder of Myra Snyder ScottRally The PeopleAún no hay calificaciones
- ACCESORIOS MONITOREO DragerDocumento112 páginasACCESORIOS MONITOREO DragerRene Gonzales VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac Complications in Diphtheria Predict OutcomesDocumento12 páginasCardiac Complications in Diphtheria Predict OutcomesPratiwi Indah PalupiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sanford Resume 3 21 18Documento2 páginasSanford Resume 3 21 18api-329968843Aún no hay calificaciones
- ECOG/WHO/Zubrod Score (: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group WHO C. Gordon ZubrodDocumento7 páginasECOG/WHO/Zubrod Score (: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group WHO C. Gordon ZubrodsuehandikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Recommendation Letter Maria HurtadoDocumento1 páginaRecommendation Letter Maria Hurtadoapi-641781710Aún no hay calificaciones
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDocumento36 páginasAcute Flaccid ParalysisArun George100% (1)