Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Book-Keeping:-: Chapter # 01 Accounting
Cargado por
Jehangir AfridiDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Book-Keeping:-: Chapter # 01 Accounting
Cargado por
Jehangir AfridiCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
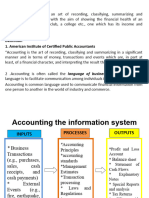
Chapter # 01 ACCOUNTING: Accounting is process of analyzing, recording, classification, summarizing and prepared report of business.
USERS OF ACCOUNTING: Owners, Creditors, Manager, Employees, Government, Public
BOOK-KEEPING:The process of recording business transactions in books of accounting are called Book Keeping. Book-Keeping is an art of recording in books of accounts, transactions in money or moneys terms. The systematic recording of financial transaction of an enterprise is known as Book-Keeping. Book-Keeping may be defined as an art of recording business transactions in terms of money under appropriate heads.
Page 1 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
TYPES OF BOOK-KEEPING SYSTEM: There are two systems of book keeping (1) Single Entry System (2) Double Entry system
Explanation: (1) Single Entry System: Under this system we records only one aspect (side) of transaction and ignore the other aspects (sides). It is incomplete system Double Entry system: Under this system we record all aspects (sides) of transaction. It is complete system. Difference between Accounting and Book-keeping Book-keeping Scope of book keeping is limitted Book keeper is low knowledge and skill We cant take any decision from the work of book keeper Accounting Its scope is wider from book keeping Accountant have more knowledge & skill We can take decision from the work of accountant
(2)
Scope Knowledge & skill
Decisions
Page 2 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
ACCOUNT:It is a device which contains an increase or decrease in an item for a particular period. TYPES OF ACCOUNT:There are two approaches in accounting. 1. American approach. 2. British Approach Under American there are five types of account. Asset, Capital, liability, revenue, expenses Under British there are three types of account. Real, Personal, Nominal. Accounting Cycle: Step by step process of Accounting is called accounting cycle.
A CCOU N TIN G C YCLE
TR AN S ACTION
F IN AN CIAL S TATE ME N TS
J OU R N AL
ACCOU N TI N G CYCLE
AD J U S TE D TR AIL B ALAN CE
LE D GE R
TR IAL B ALAN CE
18
Page 3 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
Accounting Basic Terminologies
Business: It includes all those legal activities for the purpose of earning profit. Proprietor: A person who invests money or things in business is called owner or proprietor. Voucher: Any written evidence in support of a transaction is called voucher e.g. invoice, bill and cash memo etc. Cash memo: Any written proof for the goods purchased on cash. Invoice: Bill prepared by a seller of goods or services and submitted to the buyer. The invoice describes such items as date, customer, vendor, quantities, prices, freight, and credit terms of a transaction. Account: It is a device which contains an increase or decrease in an item for a particular period. Merchandise: The things purchased by a business organization for the purpose of reselling them in the same condition are called merchandise or goods. Purchases: The cost of merchandise is called purchases. It may be cash or credit. Sales: The amount earned from sale of goods is called sales. It may be cash sales or credit sales Revenues: All types of income received or accrued as Revenue. Expenses: For the achievement of business objective, certain payments are made. These are called expenses. Profit: The amount earned by a business organization after deducting the cost of the product from the revenues.
Page 4 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
Loss: If the expenses or the cost of the product is higher than the revenue. It is called as loss. Trade Discount: When concession or allowance or rebate is given by seller to buyer on listed or scheduled price of goods at the time of sale is called trade discount. Cash Discount: a discount, which is allowed or received at the time of cash payment on credit sale or purchase, is called cash discount. e.g. 2% 10 Net 30: This means that discount of 2% will be allowed or received if payment/receipt is made within 10 days, otherwise the total amount is payable within 30 days. Cash discount has two types Discount Received Discount Allowed Commission: Remuneration for services performed by one person to another, normally on the percentage basis is called commission. Stock(Inventory): Goods or merchandise on hand, that is goods remaining unsold, is called stock (inventory) or stock in trade. Turnover: It means the total amount of sales during a particular period. It is called as inventory turnover or stock turnover. Balance: Balance means the difference. In accounting, it means the difference between the debit and credit sides of an account. Account Receivable/Debtor: A person to whom goods are sold on credit is called account receivable or debtor. Account Payable/Creditor: A person from whom goods are purchased on credit is called creditor, or Account Payable. Note Payable: A written document on which certain amount is to be paid on specific date is called Note or Bill Payable.
Page 5 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
Notes Receivable: A written document on which certain amount is receivable on specific date is called as note/bill receivable. Cash Book: A book of original entry in which all cash receipts and payments are recorded as is called cash book. Bad Debts/Uncollectable: The amount which cannot be recovered from debtors and as such finally treated as loss is called bad debts or uncollectable. Assets: Resources that are owned by a business and are expected to benefit future operations, anything valuable possessed by a firm. E.g. cash, building, land, Account Receivable and furniture etc. Equity: The rights possessed by owners or outsiders against the assets of firm are called as equities. Internal Equity/owner fund Liabilities Drawings/Withdrawals: The cash or commodities withdrawn by the owner for his personal uses from business are known as drawings. Financial Statements: It means the statements prepared to show the financial positions of a business organization after a year are called financial statements. Income Statement: A statement which is prepared for the objective that how much profit is earned or how much loss is suffered by the organization for a specific period. Balance sheet: Balance sheet represents the financial position of a firm on a certain fixed date. Usually at the close of financial period. It has two sides, on one side the whole assets are written and on the other side Liabilities and owner equity is written
Page 6 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
Page 7 SAJID ALI Ms Finance
También podría gustarte
- Accounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesDocumento3 páginasAccounting:: Capital Assets - LiabilitiesashAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter: 1 Meaning, Objectives and Basic Accounting TermsDocumento19 páginasChapter: 1 Meaning, Objectives and Basic Accounting TermsGudlipAún no hay calificaciones
- AccountDocumento37 páginasAccountGaurang MakwanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Terms and Elements of Accounting - Chapter 2Documento3 páginasBasic Terms and Elements of Accounting - Chapter 2Sheharyar AwanAún no hay calificaciones
- An Introduction To AccountingDocumento20 páginasAn Introduction To AccountingRocket SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- The Original Attachment: BasicsDocumento32 páginasThe Original Attachment: BasicsVijayGogulaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter # 1 Business TransactionDocumento22 páginasChapter # 1 Business TransactionWaleed NasirAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.introduction To AccountingDocumento14 páginas1.introduction To AccountingBhuvaneswari karuturiAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting BasicsDocumento7 páginasAccounting BasicsGovind SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting Training OverviewDocumento74 páginasAccounting Training Overviewzee_iitAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 11 Accounting Exam BreakdownDocumento9 páginasGrade 11 Accounting Exam BreakdownAli SiddiquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting and Financial MangementDocumento25 páginasAccounting and Financial MangementSHASHIAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction to Accounting FundamentalsDocumento73 páginasIntroduction to Accounting FundamentalsSneha ChhabraAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 TAPDocumento19 páginasUnit 1 TAPchethanraaz_66574068Aún no hay calificaciones
- RH Consult - Training AcctDocumento13 páginasRH Consult - Training Acctjoseph borketeyAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is AccountingDocumento13 páginasWhat Is AccountingFaridullah MohammadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Download the original attachment - The complete basics of accountingDocumento32 páginasDownload the original attachment - The complete basics of accountingvijayAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting PDFDocumento10 páginasAccounting PDFRI AZAún no hay calificaciones
- Principles of AccountsDocumento7 páginasPrinciples of AccountsJadeja ChatrieAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To AccountingDocumento45 páginasIntroduction To AccountingPravin Kumar RajakAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding basic accounting concepts and termsDocumento10 páginasUnderstanding basic accounting concepts and termsshakaday ShokshokAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting Basics in 40 CharactersDocumento78 páginasAccounting Basics in 40 CharactersSandya SlideshareAún no hay calificaciones
- Tally Lesson 1Documento13 páginasTally Lesson 1kumarbcomca100% (1)
- Accounting - DefinitionsDocumento4 páginasAccounting - DefinitionsYashi SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Powerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceDocumento40 páginasPowerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceChris Iero-Way100% (1)
- Accounting Interview QuestionsDocumento6 páginasAccounting Interview QuestionsSahana GAún no hay calificaciones
- Break-Even Point:c: CC CC CCCCCCCCC CCC CCCCCCCCC C C CCC C CCCC CCCCC C CCCCC CCCCCCCCC C CCCDocumento8 páginasBreak-Even Point:c: CC CC CCCCCCCCC CCC CCCCCCCCC C C CCC C CCCC CCCCC C CCCCC CCCCCCCCC C CCCchanduanu2007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basics of Accounting and Book KeepingDocumento16 páginasBasics of Accounting and Book KeepingPuneet DhuparAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting Terms - Basic DefinitionsDocumento7 páginasAccounting Terms - Basic DefinitionsSourav JaiswalAún no hay calificaciones
- CRT - Accounting BasicsDocumento28 páginasCRT - Accounting BasicsSiddarth Hari AnantaneniAún no hay calificaciones
- F & A - Basic Accounting TermsDocumento3 páginasF & A - Basic Accounting TermsAbdul Azeez 312Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Financial AccountingDocumento118 páginasBasic Financial AccountingSaleem Javed100% (1)
- All Basic Terms of AccountingDocumento20 páginasAll Basic Terms of AccountingpoornapavanAún no hay calificaciones
- Finance and AccountsDocumento10 páginasFinance and AccountsvijayAún no hay calificaciones
- SITXFIN002 Interpret Financial InformationDocumento12 páginasSITXFIN002 Interpret Financial Informationsampath lewkeAún no hay calificaciones
- LEARNING THE BASICS OF ACCOUNTING WITH TALLY ERP 9 CHAPTER 1Documento385 páginasLEARNING THE BASICS OF ACCOUNTING WITH TALLY ERP 9 CHAPTER 1Samuel Zodingliana100% (2)
- Foundation Course NotesDocumento29 páginasFoundation Course NotesPriya DharshiniAún no hay calificaciones
- Al-Samnan Academy of Commerce and ScienceDocumento7 páginasAl-Samnan Academy of Commerce and ScienceMian NajamAún no hay calificaciones
- 60+ Basic Accounting Terms Dictionary: Free Online ManagementDocumento1 página60+ Basic Accounting Terms Dictionary: Free Online ManagementEhsan ElahiAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting PresentationDocumento68 páginasAccounting PresentationGibzy D100% (1)
- accountancy III yr.docDocumento24 páginasaccountancy III yr.docdrismailkm20Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tally ERP9Documento68 páginasTally ERP9sah100% (10)
- VIVADocumento15 páginasVIVAAlex MoonAún no hay calificaciones
- Session 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlDocumento10 páginasSession 1: Overview of Financial Accounting and ControlYamu HiadeenAún no hay calificaciones
- Functional AccountingDocumento9 páginasFunctional Accountingayesha shafaqatAún no hay calificaciones
- Viva AccountingDocumento15 páginasViva Accountingsakib990Aún no hay calificaciones
- NC-III Bookkeeping ReviewerDocumento33 páginasNC-III Bookkeeping ReviewerNovelyn Gamboa92% (52)
- Bank Financial Management BasicsDocumento78 páginasBank Financial Management BasicsAksAún no hay calificaciones
- Tally Notes Computer Training - Sscstudy PDFDocumento49 páginasTally Notes Computer Training - Sscstudy PDFfreelancertech Nepal100% (1)
- Accounting Principles Lecture-3Documento5 páginasAccounting Principles Lecture-3shivani chhipaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Accounting BasicsDocumento25 páginasIntroduction To Accounting BasicsBaktash Ahmadi100% (1)
- Faa IDocumento18 páginasFaa Iabhiseknanda82495Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basics of AccountingDocumento82 páginasBasics of AccountingDivyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Accounting TermsDocumento12 páginasBasic Accounting TermsAnkur AryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Accountancy Notes PDF Class 11 Chapter 3 and 4Documento5 páginasAccountancy Notes PDF Class 11 Chapter 3 and 4Rishi ShibdatAún no hay calificaciones
- Tally Erp.9Documento50 páginasTally Erp.9Jancy Sunish100% (1)
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?De EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionDe EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Governance Issues Regarding Transfer PriDocumento17 páginasCorporate Governance Issues Regarding Transfer PriShelviDyanPrastiwiAún no hay calificaciones
- Assign 5 Chapter 7 Cash Flow Analysis Answer Cabrera 2019-2020Documento6 páginasAssign 5 Chapter 7 Cash Flow Analysis Answer Cabrera 2019-2020mhikeedelantar50% (2)
- Integrated Strategy Optimisation for Complex Mining OperationsDocumento8 páginasIntegrated Strategy Optimisation for Complex Mining OperationsCarlos A. Espinoza MAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting in Action: Assignment Classification TableDocumento50 páginasAccounting in Action: Assignment Classification TableChi IuvianamoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lessons Learned From World Cup Trading ChampionsDocumento8 páginasLessons Learned From World Cup Trading Championsandy6688Aún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study - Financial Statement AnaysisDocumento8 páginasCase Study - Financial Statement Anaysisssimi137Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Compensation and Benefits 1Documento31 páginasChapter 8 Compensation and Benefits 1Jeremie ArgoncilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Cash FlowDocumento60 páginasChapter 3 Cash FlowKate Albay100% (2)
- Salary Slip Template V12Documento5 páginasSalary Slip Template V12Amas OnrAún no hay calificaciones
- EssaDocumento3 páginasEssaridwantpAún no hay calificaciones
- PCNC List of Requirements For AccreditationDocumento4 páginasPCNC List of Requirements For AccreditationNCREAún no hay calificaciones
- BSBFIM501 Assessment Leadership and ManagementDocumento23 páginasBSBFIM501 Assessment Leadership and ManagementAmanda Pires100% (1)
- 17 Engineering EconomicsDocumento7 páginas17 Engineering EconomicsM Hadianto WaruwuAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 3 Admission of A Partner QuestionsDocumento4 páginasUnit 3 Admission of A Partner QuestionsMitesh SethiAún no hay calificaciones
- Applied Corporate Finance TVM Calculations and AnalysisDocumento3 páginasApplied Corporate Finance TVM Calculations and AnalysisMuxammil IqbalAún no hay calificaciones
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles Refer To TheDocumento55 páginasGenerally Accepted Accounting Principles Refer To TheVimala Selvaraj VimalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 5 - Cost Systems and Accumulation Job Order CostingDocumento9 páginasModule 5 - Cost Systems and Accumulation Job Order CostingJulie Ann Marie BernadezAún no hay calificaciones
- Agriculture BussinessDocumento5 páginasAgriculture BussinessaronAún no hay calificaciones
- Improve Your Skills For Advanced - Listening and Speaking Skills For Advanced pp14-18 PDFDocumento5 páginasImprove Your Skills For Advanced - Listening and Speaking Skills For Advanced pp14-18 PDFAlejandra GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- ITC Research ReportDocumento4 páginasITC Research ReportMrRishabh97Aún no hay calificaciones
- Public Notice: New NSSF Member ContributionsDocumento1 páginaPublic Notice: New NSSF Member ContributionsDiana Dekatrinah KatrineAún no hay calificaciones
- Gregorio Sancianco's 1881 Treatise on Economic Reforms for the PhilippinesDocumento1 páginaGregorio Sancianco's 1881 Treatise on Economic Reforms for the PhilippinesCarol Ferreros PanganAún no hay calificaciones
- Deters Motion For Contempt 02032014Documento10 páginasDeters Motion For Contempt 02032014Nathaniel Livingston, Jr.Aún no hay calificaciones
- DRS Business Case - Barnet CouncilDocumento161 páginasDRS Business Case - Barnet CouncilMisterMustardAún no hay calificaciones
- Solved Twelve Years Ago Marilyn Purchased Two Lots in An UndevelopedDocumento1 páginaSolved Twelve Years Ago Marilyn Purchased Two Lots in An UndevelopedAnbu jaromiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting Formulas 21Documento2 páginasAccounting Formulas 21Nouman MujahidAún no hay calificaciones
- L1 Book-Keeping S2 2000Documento21 páginasL1 Book-Keeping S2 2000Fung Hui YingAún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting For AttorneysDocumento160 páginasAccounting For AttorneyschueneAún no hay calificaciones
- Dividend: HistoryDocumento20 páginasDividend: Historyanup bhattAún no hay calificaciones
- Bus 215 NotesDocumento18 páginasBus 215 Notesctyre34Aún no hay calificaciones