Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
FM
Cargado por
princess_camarilloDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
FM
Cargado por
princess_camarilloCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
FINAL PAPER ON FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
PROF. E. AURELLADO CPA, MBA, PhD
SUBMITTED BY: PRINCESS I. CAMARILLO
HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL ANALYSIS: STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
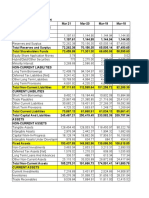
Globe Telecom, Inc. and Subsidiaries Consolidated Statements of Financial Position December 31, 2011 2011 2010 (In Thousand Pesos) ASSETS Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Receivables - net Inventories and supplies Derivative assets Prepayments and other current assets net Assets classified as held for sale Total Current Assets Noncurrent Assets Property and equipment - net Investment property - net Intangible assets and goodwill - net Investments in joint ventures Deferred income tax - net Other noncurrent assets - net Total Noncurrent assets TOTAL ASSETS LIABILITIES AND EQUITY Current Liabilities Accounts payable and accrued expenses Notes payable Unearned revenues Derivative liabilities Income tax payable Provisions Current portion of long-term debt 23,042,514 1,756,760 2,474,142 208,247 1,157,927 166,773 9,597,367 22,115,203 2,402,749 93,336 1,098,492 224,388 8,677,209 99,267,780 191,645 3,591,514 249,000 765,670 3,209,477 107,275,086 130,839,333 101,837,254 214,192 3,248,376 197,016 670,594 2,875,686 109,043,118 130,627,967
HORIZONTAL INC (DEC) %
VERTICAL 2011 2010
5,159,046 10,119,505 1,911,190 9,766 5,586,419 22,785,926 778,321 23,564,247
5,868,986 8,374,123 1,839,333 19,888 4,704,198 20,806,528 778,321 21,584,849
-709,940 1,745,382 71,857 -10,122 882,221 1,979,398 0 1,979,398
-12% 21% 4% -51% 19% 10% 0% 9%
4% 8% 1% 0% 4% 17% 1% 18%
4% 6% 1% 0% 4% 16% 1% 17%
-2,569,474 -22,547 343,138 51,984 95,076 333,791 -1,768,032 211,366
-3% -11% 11% 26% 14% 12% -2% 0%
76% 0% 3% 0% 1% 2% 82% 100%
78% 0% 2% 0% 1% 2% 83% 100%
927,311 1,756,760 71,393 114,911 59,435 -57,615 920,158
4% 0% 3% 123% 5% -26% 11%
18% 1% 2% 0% 1% 0% 7%
17% 2% 0% 1% 0% 7%
38,403,730 Liabilities directly associated with the assets classified as held for sale Total Current Liabilities Noncurrent Liabilities Deferred income tax - net Long-term debt - net of current portion Derivative liabilities Other long-term liabilities Total Noncurrent Liabilities Total Liabilities Equity Paid-up capital Cost of share-based payments Other reserves Retained earnings Total Equity Total Liabilities and Equity 3,929,414 37,324,579 58,370 2,111,719 43,424,082 82,411,177 583,365 38,987,095
34,611,377 697,729 35,309,106
3,792,353 -114,364 3,677,989
11% -16% 10%
29% 0% 30%
26% 1% 27%
4,620,490 41,694,261 152,529 1,982,453 48,449,733 83,758,839
-691,076 -4,369,682 -94,159 129,266 -5,025,651 -1,347,662
-15% -10% -62% 7% -10% -2%
3% 29% 0% 2% 33% 63%
4% 32% 0% 2% 37% 64%
33,967,476 573,436 -124,902 14,012,146 48,428,156 130,839,333
33,946,004 544,794 -88,310 12,466,640 46,869,128 130,627,967
21,472 28,642 -36,592 1,545,506 1,559,028 211,366
0% 5% 41% 12% 3% 0%
26% 0% 0% 11% 37% 100%
26% 0% 0% 10% 36% 100%
HORIZONTAL ANALYSIS: CONCENTRATION ON THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS In reviewing Globe Telecom, Inc. and Subsidiaries Statements of Financial Position as of December 31, 2011, the horizontal analysis indicates that the percentage of increase in total current assets (9%) was lower than the percentage of increase in total current liabilities (10%). It can be observed that derivative liabilities (123%) increased significantly. Derivative assets (-51) decreased dramatically, and the same goes for cash and cash equivalents (-12%) and investment property (-11%). The book value of property, plant and equipment (-3%) declined because of the depreciation provision for the year. Total liabilities decreased by 2% whereas shareholders equity increased by 3%. Overall, there were little or very minimal changes in total assets, total liabilities and equity.
VERTICAL ANALYSIS: SIGNIFICANT CHANGES AND IMPLICATIONS Most of the items in the statement of financial position incurred insignificant changes and others did not change even a little increase or decrease.
PROBLEMS AND OPPORTUNITIES On the other hand, the company needs to take a look at the 12% decrease in cash since this could greatly affect the companys ability to meet its short term obligations and pay dividends. And also, the decrease has a significant impact on the companys ability to generate positive future net cash flows. Further, the company is engaged in communications services. It might be necessary to review the movements and conditions of these cash transactions. As shown in 2011 data , the company need to focus on reducing liquidity risk ( cash ) and credit risk ( receivables) to maintain a balance between continuity of funding and flexibility in operations. Controls and procedures should be in place to ensure sufficient cash is maintained to run the company operations. Also, management needs to monitor the derivative liabilities since it has the greatest impact on the substantial increase in the total liabilities.
HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL ANALYSIS: INCOME STATEMENT
Globe Telecom, Inc. and Subsidiaries Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income For the year ended December 31, 2011 HORIZONTAL 2011 2010 INC (DEC) % VERTICAL 2011 2010
(In Thousand Pesos) Service revenues Cost of sales Gross profit General, selling and administrative Depreciation and amortization Financing costs Impairment losses and others Equity in net losses of joint ventures Nonservice revenues Interest income Gain on disposal of property and equipment - net Other income - net INCOME BEFORE TAX PROVISION FOR (BENEFIT FROM) INCOME TAX: Current Deferred Total NET INCOME OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) Transactions on cash flow hedges - net Changes in fair value of available-for-sale investment in equity securities Exchange differences arising from translations of foreign investments Tax effect relating to components of other comprehensive income Total Other Comprehensive Income TOTAL COMPREHENSIVE INCOME 67,811,301 5,887,589 61,923,712 29,304,463 18,941,227 2,579,714 1,918,583 27,345 3,753,283 297,388 319,250 574,768 14,097,069 62,554,689 4,238,960 58,315,729 26,692,104 18,085,839 2,068,401 1,529,534 2,968 2,993,301 218,532 32,535 856,941 14,038,192 5,256,612 1,648,629 3,607,983 2,612,359 855,388 511,313 389,049 24,377 759,982 78,856 286,715 -282,173 58,877 8% 39% 6% 10% 5% 25% 25% 821% 25% 36% 881% -33% 0% 100% 9% 91% 43% 28% 4% 3% 0% 6% 0% 0% 1% 21% 100% 7% 93% 43% 29% 3% 2% 0% 5% 0% 0% 1% 22%
5,049,479 -784,215 4,265,264 9,831,805
4,187,625 105,933 4,293,558 9,744,634
861,854 -890,148 -28,294 87,171
21% -840% -1% 1%
7% -1% 6% 14%
7% 0% 7% 16%
-53,194 1,269 -625 15,958 -36,592 9,795,213
-133,257 20,150 -33,698 39,977 -106,828 9,637,806
80,063 -18,881 33,073 -24,019 70,236 157,407
-60% -94% -98% -60% -66% 2%
0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 14%
0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 15%
HORIZONTAL ANALYSIS: CONCENTRATION ON THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Globe Telecom, Inc. and Subsidiaries Statements of Comprehensive Income for the year ended December 31, 2011 showed that Equity in net losses of joint ventures increased by 821% while Gain on disposal of property and equipment net accounts for 881% increase. Most of the costs and expenses increase gradually while total other comprehensive income (loss) decreased significantly. Sales accounts for 8% increase only compare to the cost of sales that increase by 39%. VERTICAL ANALYSIS: SIGNIFICANT CHANGES AND IMPLICATIONS Unfavorable changes could be observed in the gross margin percentage in relation to net sales. The decrease in percentage could be due to a higher cost of sales of year 2011 compare to year 2010. The data to support the increase in cost of sales was taken from the companys notes to financial statements as shown below:
General, administrative and selling expenses had more or less remained constant. Better control over the cost of sales and the general, administrative and selling expenses should be instituted to further improve the profitability of the company.
PROBLEMS AND OPPORTUNITIES Service revenues increased by 8% while cost of sales increases by 39%. This is so unfavorable because this could indicate that the company was unable to adjust the selling price of the service commensurate to the increase in cost of sales or it was unable to control the price factor of its cost of sales. These changes resulted to the reduction in the gross profit which is unfavorable. It is noteworthy that the company allots expenditure for selling expenses where they can always use as an avenue to promote, keep and make their services known in the market.
FINANCIAL RATIO ANALYSIS LIQUIDITY RATIOS 1. CURRENT RATIO = TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS / TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES 2010
21,584,849 35,309,106
1:0.61
2011
23,564,247 38,987,095
1:0.60
2. ACID TEST RATIO = TOTAL CASH + TRADE SECURITIES + TRADE RECEIVABLE / TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES 2010
14,243,109 35,309,106
1:0.40
2011
15,278,551 35,309,106
1:0.43
3. NET WORKING CAPITAL = CURRENT ASSETS - CURRENT LIABILITIES
2010 2011
21,584,849 23,564,247
35,309,106 38,987,095
= =
13,724,257 15,422,848
The acid test ratio indicates a favorable trend for the company since it is showing a positive growth if data in 2011 is compared to the data in 2010. But the current ratio and the net working capital most especially, indicate an unfavorable trend. The liquidity risk is being blown up and whatever control or procedures placed by the management needs to seek a high attention in order to keep these ratios on a progressive trend. ACTIVITY RATIOS 1. ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE TURN OVER = NET CREDIT SALES / TRADE RECEIVABLES
2010
62,554,689 8,374,123
7.47
2011
67,811,301 10,119,505
6.70
2. DAYS IN RECEIVABLE = 365 DAYS / RECEIVABLE TURN OVER
2010
365 7.47
49
2011
365 6.70
54
3. INVENTORY TURN OVER = COST OF SALES / INVENTORY
2010
4,238,960 1,839,333
2.30
2011
5,887,589 1,911,190
3.08
4. OPERATING CYCLE = DAYS IN RECEIVABLE + DAYS IN INVENTORY
2010
49 + 158 = 207 DAYS
2011
54 + 118 = 172 DAYS
5. ASSET TURN OVER = NET SALES / AVERAGE TOTAL ASSETS
2010
62,554,689 130,627,967
0.48
2011
67,811,301 130,839,333
0.52
The company needs to work certain mechanism or control procedure to improve its receivable turn over. The company credit term average of 60 120 days is being achieved but compare to 2010, 2011 receivable has a much lower turnover. Fortunately, there was an improvement in operating cycle in 2011.
SOLVENCY RATIOS 1. TIMES INTEREST EARNED = NET INCOME BEFORE INTEREST AND TAXES / INTEREST EXPENSE
2010
16,019,977 1,981,785 16,156,729 2,059,660
8.08
2011
7.84
2. DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO = TOTAL LIABILITIES / TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY ****
2010
83,758,839 46,869,128
1.79
2011
82,411,177 48,428,156
1.70
3. EQUITY MULTIPLIER = TOTAL ASSETS / TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS EQUITY
2010
3,966,840,779 3,931,620,720
2.79
2011
3,863,788,755 4,362,580,082
2.70
The companys debt to equity ratio has decreased between 2010 and 2011, implying a less slightly risky capital structure. Times interest earned has also decreased as well as the equity multiplier. PROFITABILITY RATIOS 1. GROSS MARGIN PERCENTAGE = GROSS MARGIN / SALES
2010
58,315,729 62,554,689 61,923,712 67,811,301
93%
2011
91%
2. RETURN ON ASSETS = NET INCOME / TOTAL ASSETS
2010
9,744,634 130,627,967 9,831,805 130,839,333
0.07
2011
0.08
3. RETURN ON EQUITY = NET INCOME/ TOTAL EQUITY 2010 1,050,602,374 3,931,620,720 2011 429,613,213 4,362,580,082 4. EARNINGS PER SHARE ( COMMON ) = NET INCOME - PREFERRED DIVIDENDS / COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING 2010 1,050,602,374 1,834,915,200 2011 429,613,213 1,834,915,200 5. PRICE EARNING PER SHARE = MARKET VALUE PER SHARE / EARNINGS PER SHARE *** MARKET VALUE PER SHARE is not given/available 6. PROFIT MARGIN PERCENTAGE = NET PROFIT / NET SALES 2010 1,050,602,374 6,315,541,028 2011 429,613,213 7,330,316,246 The profitability ratios also are something to look at since both the gross and operating margin percentages indicated a regressive trend. The same is true with the return on equity data. 14% 16% 74.02 73.29 0.10 0.27
También podría gustarte
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Catholic Prayer and WorshipDocumento68 páginasCatholic Prayer and Worshipprincess_camarillo100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Greek CivilizationDocumento22 páginasGreek Civilizationprincess_camarillo100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Sample Articles of PartnershipDocumento4 páginasSample Articles of PartnershipUmma Mie ZY83% (112)
- Teresita Buenaflor ShoesDocumento23 páginasTeresita Buenaflor ShoesRonnie Lloyd Javier78% (32)
- Cartwright Lumber Company Forecast Analysis (38Documento9 páginasCartwright Lumber Company Forecast Analysis (38Douglas Fraser0% (1)
- Manage risks from asset-liability mismatches in banksDocumento50 páginasManage risks from asset-liability mismatches in banksAbhishek Kumar100% (4)
- Sample Engagement LetterDocumento5 páginasSample Engagement Letterprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- The Book of HaggaiDocumento5 páginasThe Book of Haggaiprincess_camarillo0% (1)
- Case AnalysisDocumento9 páginasCase Analysisprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Study On Strengthening The Withholding Tax System On Individual Taxpayers 48tijve7Documento21 páginasStudy On Strengthening The Withholding Tax System On Individual Taxpayers 48tijve7princess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Biblical Accounts of Human OriginsDocumento9 páginasBiblical Accounts of Human Originsprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Cpa Review School of The Philippines Auditing TheoryDocumento16 páginasCpa Review School of The Philippines Auditing Theoryprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Globe TelecomDocumento3 páginasGlobe Telecomprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- StewardshipDocumento1 páginaStewardshipprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- StewardshipDocumento1 páginaStewardshipprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Yearning For Your LearningDocumento16 páginasYearning For Your Learningprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- StewardshipDocumento1 páginaStewardshipprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Globe TelecomDocumento3 páginasGlobe Telecomprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Globe TelecomDocumento3 páginasGlobe Telecomprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Prehistoric PeopleDocumento9 páginasPrehistoric Peopleprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- OpMan LPDocumento11 páginasOpMan LPprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Systems Analysis and Design Kendall and Kendall Fifth EditionDocumento27 páginasSystems Analysis and Design Kendall and Kendall Fifth Editionprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Production and Operations ManagementDocumento5 páginasProduction and Operations Managementprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Biblical Accounts of Human OriginsDocumento9 páginasBiblical Accounts of Human Originsprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOGENESISDocumento10 páginasBIOGENESISprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- FCL 102 Course IntroDocumento12 páginasFCL 102 Course Introprincess_camarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Namma Kalvi 12th Accountancy Unit 5 Sura English Medium Guide PDFDocumento15 páginasNamma Kalvi 12th Accountancy Unit 5 Sura English Medium Guide PDFAakaash C.K.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocumento100 páginasAnalysis of Financial Statementsidont100% (1)
- AFAR.3101 Partnership (Drill) : D. Advanced Financial AccountingDocumento1 páginaAFAR.3101 Partnership (Drill) : D. Advanced Financial Accountingvane rondinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Books of Rishi Trading CoDocumento3 páginasBooks of Rishi Trading CoHoney GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Acctg 41 DepartmentalDocumento12 páginasAcctg 41 DepartmentalMelrose Eugenio ErasgaAún no hay calificaciones
- Depreciation: Disposal of Fixed AssetsDocumento13 páginasDepreciation: Disposal of Fixed AssetsHassan AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation Slides of Credit AnalysisDocumento117 páginasPresentation Slides of Credit AnalysisDamotAún no hay calificaciones
- BBA13Documento283 páginasBBA13Ishwar PadwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Far160 (CT October 2018) QuestionDocumento4 páginasFar160 (CT October 2018) QuestionFarah HusnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Information: (Agensi Di Bawah KPDNHEP)Documento6 páginasCorporate Information: (Agensi Di Bawah KPDNHEP)Leow Zi Liang100% (1)
- Tata Steel FinancialsDocumento8 páginasTata Steel FinancialsManan GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- AS Marathon (TRG) PDFDocumento84 páginasAS Marathon (TRG) PDFMahendraAún no hay calificaciones
- I Semester MCQDocumento8 páginasI Semester MCQJoshva FranklinAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 18Documento6 páginasChapter 18Xynith Nicole RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Income Statement and Balance Sheet QDocumento12 páginasBasic Income Statement and Balance Sheet QJahanzaib ButtAún no hay calificaciones
- PARTNERSHIP LIQUIDATION AND JOINT VENTURESDocumento20 páginasPARTNERSHIP LIQUIDATION AND JOINT VENTURESapremsAún no hay calificaciones
- Capital Budgeting IIDocumento28 páginasCapital Budgeting IIy64d54mkh5Aún no hay calificaciones
- 780 MS Financial Accounting XIIDocumento9 páginas780 MS Financial Accounting XIIAjay YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Example of BusinessPlan For Your ReferenceDocumento113 páginasExample of BusinessPlan For Your ReferenceSiti Rafidah DaudAún no hay calificaciones
- LiquidationDocumento18 páginasLiquidationSamaica MontemayorAún no hay calificaciones
- AP.3403 Audit of Intangible AssetsDocumento3 páginasAP.3403 Audit of Intangible AssetsMonica GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Intangible Assets Asset Useful Lif Recognized Acquisition Acquirer Balance SheetDocumento4 páginasIntangible Assets Asset Useful Lif Recognized Acquisition Acquirer Balance SheetMuhammad Arslan QadirAún no hay calificaciones
- SYBcom Eco 1 PDFDocumento80 páginasSYBcom Eco 1 PDFUrmila DeoAún no hay calificaciones
- AFR Revision - Qns-AnsDocumento63 páginasAFR Revision - Qns-AnsDownloder UwambajimanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic: Cash Flow Statement Subject: Accounting For ManagersDocumento25 páginasTopic: Cash Flow Statement Subject: Accounting For Managersamartya tiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- Consolidation Subsequent To Acquisition Date: AFM491 Advanced Financial AccountingDocumento46 páginasConsolidation Subsequent To Acquisition Date: AFM491 Advanced Financial AccountingIzzy BAún no hay calificaciones
- Company Alembic Pharmaceuticals LTD.: Name Deepankar Tiwari Roll No 24 Class Mba HCMDocumento11 páginasCompany Alembic Pharmaceuticals LTD.: Name Deepankar Tiwari Roll No 24 Class Mba HCMAryan RajAún no hay calificaciones