Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
UBD Lesson Plan - Science 3rd QRTR
Cargado por
Jean Acutillar PaguiaDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
UBD Lesson Plan - Science 3rd QRTR
Cargado por
Jean Acutillar PaguiaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Georgia International Academy SY 2011-2011 Subject: ____Science 5________________ Teacher: ___T.
Arlene_____________ Sem/Quarter: __3rd Quarter_____
Main Topic: Energy Why do we need to conserve energy? What will happen if we have exhausted our means to get energy? What are our responsibilities to maintain and preserve or sources of energy? I. Assessment Evidence A. Performance Task/s Oral Presentation Each child will be assigned a topic related to Renewable Energy 1) Solar bulb 2) Renewable Energy Act 3) Hydro electricity Slogan Making/Poster Making Each child will make a slogan/poster on how to conserve energy. Experiment: Electrical energy Materials: Small bulb Used cables Batteries switch
Lesson/Topics: A. Forms of Energy B. Electricity C. Machines
Time Frame: 6 weeks
Individual Oral Presentation Criteria
Richness and accuracy of information Originality in organization of ideas and visuals Creativity of presentatio n Mastery of content and clarity of presentatio n
Rating
Excellen t
Points Earned
4
Points Earned
Very Satisfact ory
Satisfact ory
Needs Improve ment
B. Other Evidences 1. Homework
- Observe what forms of energy is present in your home. Explain why you think so? - Collect pictures of Different kinds of simple machines and make a booklet with their description.
2. Summative Test 3. Quizzes
II. Vocabulary Words Terms, Translation, Definition, Picture (if needed) : 1. energy- the ability to make things move. 2. chemical energy- form of energy released from chemical reaction like burning, mixing solutions
3. electrical energy- movement of electrons through matter like electricity. 4. thermal energy- form of energy formed through the heat energy of an object that determines how active its atoms are. 5. mechanical energy- Energy due to a objects motion (kinetic) or position (potential). 6. Electromagnetic Energy- Includes energy from gamma rays, xrays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwave and radio bands 7. electricity- when electrons move quickly from one atom to another 8. static electricity- is the charge that stays on an object. Unlike charges attract each other, and like charges repel each other. 9. electric current- The steady flow of electricity is called an electric current. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. circuit- A current will move along a wire or a path called a circuit conductor- is a material that current can pass through easily, like metals. insulator- An insulator is a material that current cannot pass through easily, like plastic. series circuit- A series circuit is a circuit that has only one path for the current. parallel circuit- A parallel circuit has more than one path for current to travel. machines- are tools that make our work a lot easier.
References: Pacheco, M. (2010). Exploring and Protecting Our World. Quezon City:Vibal Publishing House, Inc. http://science.pppst.com/simplemachines.html http://science.pppst.com/electricity.html
Knowledge: After finishing this unit, the children are expected to : 1. Know the different forms of energy. 2. Learn the sources of energy and their importance. 3. Learn the how to conserve energy. 4. Make a connection between energy and electricity 5. Learn how electricity is produced. 6. Know about static and current electricity. 7. Tell the difference between parallel and series circuit. 8. Learn about simple and compound machines. 9. Tell how machines are important in
Skills: After finishing this unit, the children are able to : 1. Identify forms of energy and their sources 2. Identify the forms of energy they see in the house or school. 3. Express and apply ways to conserve energy. 4. Explain how energy is connected to the use of electricity. 5. Explain the path way of electricity in terms of parallel and series circuit. 6. Conduct an experiment to make electricity. 7. Explain about different machines. 8. Make their own simple or compound machine.
our daily lives.
También podría gustarte
- Ansi Ashrae Acca 183-2007 (Ra 2014)Documento10 páginasAnsi Ashrae Acca 183-2007 (Ra 2014)Ahmed Labib100% (3)
- Zick AnalysisDocumento12 páginasZick AnalysisrksahayAún no hay calificaciones
- Solar Photovoltaic Cells: Photons to ElectricityDe EverandSolar Photovoltaic Cells: Photons to ElectricityAún no hay calificaciones
- ScienceSLM G7 Q3 M6 ElectricityDocumento29 páginasScienceSLM G7 Q3 M6 ElectricityXemelle SuelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Self - Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Subject: Science Grade: 6 Level: Elementary Quarter: 3 Week: 3Documento6 páginasSelf - Learning Home Task (SLHT) : Subject: Science Grade: 6 Level: Elementary Quarter: 3 Week: 3Jesse100% (1)
- Applied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFDocumento204 páginasApplied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFdogclutchAún no hay calificaciones
- Driven Pile Design Methods in Weak Rock: September 2017Documento7 páginasDriven Pile Design Methods in Weak Rock: September 2017Anonymous I8nZsDqlmhAún no hay calificaciones
- Solution Manual For Nonlinear Control PDFDocumento11 páginasSolution Manual For Nonlinear Control PDFpranav natu17% (6)
- Power Transformer Tests Guide - Voltage Ratio, Turns Ratio, Polarity Vector GroupDocumento7 páginasPower Transformer Tests Guide - Voltage Ratio, Turns Ratio, Polarity Vector GroupsupermannonAún no hay calificaciones
- Critical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling ModesDocumento5 páginasCritical Axial Load For Torsional and Flexural Torsional Buckling ModesPang Sze Dai100% (1)
- Science 10 - Q2 - M4Documento15 páginasScience 10 - Q2 - M4MERCADER, ERICKA JAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Quarter: Computer Systems ServicingDocumento18 páginas4 Quarter: Computer Systems ServicingXanica HorcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Electric CircuitDocumento26 páginasScience: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Electric Circuitmarkjhuncarl caccam0% (1)
- Electricity Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasElectricity Lesson Planapi-278394742Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science 10 - Q2 - M3Documento16 páginasScience 10 - Q2 - M3MERCADER, ERICKA JAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit of WorkDocumento8 páginasUnit of Workapi-378962710Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pre-Planning: / Anchors PA/Common Core/StandardsDocumento10 páginasPre-Planning: / Anchors PA/Common Core/Standardsapi-278838777Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science 5-Electricity Unit Plan 1Documento21 páginasScience 5-Electricity Unit Plan 1api-302777648Aún no hay calificaciones
- Big Ideas of Electricity REVISEDDocumento2 páginasBig Ideas of Electricity REVISEDSarah SellAún no hay calificaciones
- Final CapstoneDocumento29 páginasFinal CapstoneJoey GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- HeidiprotocolrevisedDocumento13 páginasHeidiprotocolrevisedapi-302772510Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electricityunit 1Documento19 páginasElectricityunit 1api-288336054Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unitplanner ScienceDocumento9 páginasUnitplanner Scienceapi-361106677Aún no hay calificaciones
- Light The Bulb Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasLight The Bulb Lesson Planapi-296195922Aún no hay calificaciones
- SC2909 1Documento28 páginasSC2909 1LYDIA Villalon-AyingAún no hay calificaciones
- Edms 545-4th-Eclectriccurrent LPDocumento12 páginasEdms 545-4th-Eclectriccurrent LPapi-253399358Aún no hay calificaciones
- ScienceSLM G9 Q4 Module-7Documento21 páginasScienceSLM G9 Q4 Module-7Shanna Sophia PelicanoAún no hay calificaciones
- (April 11-12, 2023) LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 5Documento6 páginas(April 11-12, 2023) LESSON PLAN in SCIENCE 5clyde alfarasAún no hay calificaciones
- Learning Cycle Lesson Planning Form Science Topic/Content Area: Grade Level: Gles To Be Addressed: LPS: 4.2.1 Construct and Design Simple CircuitsDocumento4 páginasLearning Cycle Lesson Planning Form Science Topic/Content Area: Grade Level: Gles To Be Addressed: LPS: 4.2.1 Construct and Design Simple Circuitsapi-302655114Aún no hay calificaciones
- (Author) : Walking As A Source of Electricity Through The Use of Piezoelectric Plated ShoesDocumento5 páginas(Author) : Walking As A Source of Electricity Through The Use of Piezoelectric Plated ShoesBrave MitraAún no hay calificaciones
- Walking As A Source of Electricity Through The Use of Piezoelectric Plated ShoesDocumento5 páginasWalking As A Source of Electricity Through The Use of Piezoelectric Plated ShoesBrave MitraAún no hay calificaciones
- s5fe Iiif 6 s5fe III f 6 and g 6Documento10 páginass5fe Iiif 6 s5fe III f 6 and g 6LARRY FABIAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Plan (Electricity Bell)Documento9 páginasLesson Plan (Electricity Bell)Yolanita Septiana100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 2Documento12 páginasLesson Plan 2api-373383732Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science Lesson Plan 2Documento4 páginasScience Lesson Plan 2Sarah SellAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Circuits An Introduction Grade 4 Jessica DutcherDocumento42 páginasElectrical Circuits An Introduction Grade 4 Jessica Dutcherapi-302628627Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sci Pptq3 w5 Day 1 5Documento72 páginasSci Pptq3 w5 Day 1 5Shielanie EsclandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Science 9 Q4 SML17 V2Documento15 páginasScience 9 Q4 SML17 V2HotdogAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 Grade Intro To Industrial Tech: Unit Title: Power & Energy Lesson Title: Part 2Documento4 páginas8 Grade Intro To Industrial Tech: Unit Title: Power & Energy Lesson Title: Part 2api-405568948Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Electricity: Grade Level: Written By: Length of UnitDocumento33 páginasIntroduction To Electricity: Grade Level: Written By: Length of UnitChEnta YAnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 9 - Q3 - Module 8Documento17 páginasGrade 9 - Q3 - Module 8MELAIDA CASTANAR GARIBAYAún no hay calificaciones
- Detailes Lesson PlanDocumento6 páginasDetailes Lesson PlanRuwill Lyn PonferradaAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Electricity: Lesson Plan SectionsDocumento4 páginasUnderstanding Electricity: Lesson Plan SectionsrezhabloAún no hay calificaciones
- SCIENCE 10-Q2 Module 9 Week 9 REVISEDDocumento30 páginasSCIENCE 10-Q2 Module 9 Week 9 REVISEDBuenavides P. Gerundio Jr.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Students &WIDA Level:: Teacher Candidate Julia Biasi Grade Level 5 Title CircuitDocumento8 páginasStudents &WIDA Level:: Teacher Candidate Julia Biasi Grade Level 5 Title Circuitapi-252675552Aún no hay calificaciones
- m8 TCEW & Electronic CircuitDocumento18 páginasm8 TCEW & Electronic CircuitMarilou AcalAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson TemplateDocumento7 páginasLesson Templateapi-279875556Aún no hay calificaciones
- Explaining How Electric Circuits WorkDocumento52 páginasExplaining How Electric Circuits WorkK.s.AarvindSundarAún no hay calificaciones
- Teacher Solar 2006Documento16 páginasTeacher Solar 2006basura12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 2 Final DraftDocumento7 páginasLesson 2 Final Draftapi-239996848Aún no hay calificaciones
- 5th U2 ElectricityMagnetism 2011-2012 GuideDocumento4 páginas5th U2 ElectricityMagnetism 2011-2012 GuideKristal Jane OjerioAún no hay calificaciones
- Written ReportDocumento45 páginasWritten ReportowenAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 5 Unit 1 - 2 Parent GuideDocumento3 páginasGrade 5 Unit 1 - 2 Parent GuideKathlyn VerdaderoAún no hay calificaciones
- TVL CSS8 Q3 M14Documento14 páginasTVL CSS8 Q3 M14glyza joy mercadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit Plan - ScienceDocumento11 páginasUnit Plan - Scienceapi-282413899Aún no hay calificaciones
- Solar Energy Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasSolar Energy Lesson Planapi-270356197Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electroscope Activity Cep LPDocumento10 páginasElectroscope Activity Cep LPapi-285382578Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pathways Final PDFDocumento11 páginasPathways Final PDFLucienAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Scince Lesson Plans ps2Documento5 páginasSample Scince Lesson Plans ps2api-268585214Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1 English Everything You Wanted To Know About Electric MotorDocumento11 páginas1 English Everything You Wanted To Know About Electric MotorRoan FranciscoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Plan 1Documento9 páginasLesson Plan 1api-373383732Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Circuit Fundamentals Course OutlineDocumento68 páginasElectric Circuit Fundamentals Course OutlineJames TonyAún no hay calificaciones
- Learning Pack For Electrical Principles and Technologies - Unit 4 (Science in Action 9) 1Documento47 páginasLearning Pack For Electrical Principles and Technologies - Unit 4 (Science in Action 9) 1ayesha ameedAún no hay calificaciones
- Q3 - Science5 - Week 8Documento5 páginasQ3 - Science5 - Week 8Maria Ronavie Davalos MantesAún no hay calificaciones
- 6-8 Science MakingAnElectromagnetDocumento5 páginas6-8 Science MakingAnElectromagnetSamraida MamucaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Teaching Electrostatics: A Teacher's Resource for Increasing Student EngagementDe EverandTeaching Electrostatics: A Teacher's Resource for Increasing Student EngagementAún no hay calificaciones
- Electromagnetics in Power Engineering SimulationDocumento8 páginasElectromagnetics in Power Engineering SimulationSamuel NóbregaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diesel Engine PracticalDocumento3 páginasDiesel Engine PracticalSamAún no hay calificaciones
- First Year Phyiscs Ipe Imp Q.bank 2020-2021 - (Hyderad Centres)Documento26 páginasFirst Year Phyiscs Ipe Imp Q.bank 2020-2021 - (Hyderad Centres)Varun Sai SundalamAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Machine Elements 2 6Documento25 páginasDesign of Machine Elements 2 6sasikskAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 2Documento6 páginasLab 22023498288Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gr8s Gravity Simulation Lab 2014-11-14Documento3 páginasGr8s Gravity Simulation Lab 2014-11-14Suman LayekAún no hay calificaciones
- WORKSHEETS GRADE 4 SciDocumento8 páginasWORKSHEETS GRADE 4 SciQurrat-Ul-Ain - 47255/TCHR/BMBAún no hay calificaciones
- GE 6163 - Physics Lab Manual PDFDocumento21 páginasGE 6163 - Physics Lab Manual PDFsatya_vanapalli3422Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 24Documento27 páginasLecture 24Abhishek vermaAún no hay calificaciones
- Solid Liquid and GasesDocumento46 páginasSolid Liquid and Gasesjoudiahmed604Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unit Viib Fans and BlowersDocumento8 páginasUnit Viib Fans and BlowersRaffy Calamonte CanoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Analytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsDocumento20 páginasAnalytical Methods - Trigonometric MethodsSteven GoddardAún no hay calificaciones
- Radiation and ScienceDocumento2 páginasRadiation and ScienceBobAún no hay calificaciones
- Multivariable Calculus Lecture on Distance in 3-Space and SpheresDocumento16 páginasMultivariable Calculus Lecture on Distance in 3-Space and SpheresDanyal NasirAún no hay calificaciones
- Slope Stability of Road EmbankmentDocumento7 páginasSlope Stability of Road Embankmentpraveen latharAún no hay calificaciones
- Phy 1206Documento5 páginasPhy 1206Sujan ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- RF SlabDocumento8 páginasRF Slabcheligp1981Aún no hay calificaciones
- All About Waves NotesDocumento1 páginaAll About Waves NotesRusherAún no hay calificaciones
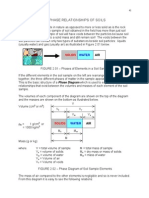
- Phase Relationships of SoilsDocumento19 páginasPhase Relationships of SoilsSelah Abdulahi100% (2)
- Fabrication of Quantum Dots PDFDocumento2 páginasFabrication of Quantum Dots PDFMelanieAún no hay calificaciones
- PHY103 MidSem SolutionsDocumento9 páginasPHY103 MidSem SolutionsShreyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics XII CH 8 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electromagnetic WavesDocumento4 páginasPhysics XII CH 8 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electromagnetic WavesNjan KL16么PorottaAún no hay calificaciones
- Iso Plate Bending StiffnessDocumento29 páginasIso Plate Bending StiffnesslapuAún no hay calificaciones