Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Concept Map 6 - Alkenes: Saturday, November 13, 2010
Cargado por
aminmasruriDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Concept Map 6 - Alkenes: Saturday, November 13, 2010
Cargado por
aminmasruriCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Saturday, November 13, 2010
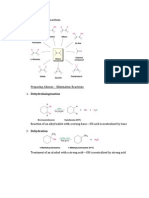
CONCEPT MAP 6 ALKENES
Objectives:
describe the chemistry of alkenes as exemplified, where relevant, by the following reactions of ethene: addition of hydrogen, steam, hydrogen halides and halogens oxidation by cold, dilute, acidified manganate(VII) ions to form the diol oxidation by hot, concentrated, acidified manganate(VII) ions leading to the rupture of the carbon-to-carbon double bond in order to determine the position of alkene linkages in larger molecules describe the mechanism of electrophilic addition in alkenes.
BOX 6A: REACTIONS OF ALKENES Carbon-to-carbon double bond broken. Used to determine the position of the double bond in a molecule.
hydrogen halide
Hot, concentrated, acidified KMnO4
Halogenoalkanes
Electrophilic addition
Alkenes
Cold, dilute, acidified KMnO4
Diol
H2
Alkane
Electrophilic addition
halogen
heat, Ni catalyst
Oxidation
dihalogenoalkane
Electrophilic addition
BOX 6B: THE MECHANISM OF ELECTROPHYLIC ADDITION
Consider the addition of bromine to propene.
H H3 C C
H C Br Br H
The + end of the halogen molecule is electrophilic, and can attack the electron rich -bond. Meanwhile, the end of the halogen molecule will accept both of the bond pair of electrons, forming a negative anion.
The electrons in the double bond repel the electrons in the approaching Br2 molecule, causing a dipole.
H H3 C C Br Br C
H H3 C H
H C Br
H C Br H H3 C
H C Br
H C Br H
También podría gustarte
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookDe EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- 13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021Documento14 páginas13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021raziabegum03761Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl Compound-2Documento20 páginasCarbonyl Compound-2fishindasea00Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl Compounds: A2 Chemistry Unit 4Documento45 páginasCarbonyl Compounds: A2 Chemistry Unit 4Faddy Oraha100% (1)
- Oxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDocumento5 páginasOxidation of Alkenes With Potassium Manganate - Chemistry LibreTextsDannyelle BaileyAún no hay calificaciones
- 30 08 2021 Alkanes Introduction Lec IIDocumento32 páginas30 08 2021 Alkanes Introduction Lec IIVaibhav PriyadarshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesDocumento58 páginasCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes KetonesNur Aliyah Abdul RazakAún no hay calificaciones
- HydrocarbonsDocumento30 páginasHydrocarbonsSneha AunttyAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocumento9 páginasOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- ATOOCV1 12 0 Addition To Carbon Hetero Multiple BondsDocumento65 páginasATOOCV1 12 0 Addition To Carbon Hetero Multiple BondsSIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrocarbons Dps AssignmentDocumento6 páginasHydrocarbons Dps AssignmentharshillbhartiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento26 páginasChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDipankar YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- EXPE8Documento5 páginasEXPE8K-yanVehraaYomomaAún no hay calificaciones
- of HydrocarbonsDocumento45 páginasof HydrocarbonsSneha KediaAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkene 2Documento16 páginasAlkene 2Nadzirah YusopAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento29 páginasCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento29 páginasCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes IVDocumento8 páginasNotes IVAmahAún no hay calificaciones
- 12.alkynes HybridizationDocumento10 páginas12.alkynes HybridizationSgt-Zephie OdeckAún no hay calificaciones
- Done By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim PapersDocumento10 páginasDone By: Kaijie, Elias, Chenxi, Ashwini, Sahana, Kelly From 0901 and 0914 Compiled From 2007 and 2008 H2 Chemistry Prelim Papersdiejunqs sAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydroxy Cpds Tut (Ans)Documento6 páginasHydroxy Cpds Tut (Ans)DomAún no hay calificaciones
- NamereactionorganicDocumento13 páginasNamereactionorganicdeykrishna654100% (1)
- Alkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentDocumento25 páginasAlkanes Paraffins: Preparation (I) From Grignard ReagentShivam GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap# 8 Short QuestionsDocumento8 páginasChap# 8 Short QuestionsMUKARAM AHMAD JOIYAHAún no hay calificaciones
- Gist 2 Xii Chemistry 2023Documento15 páginasGist 2 Xii Chemistry 2023sroy191006Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Aldehydes and KetonesDocumento42 páginasAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Aldehydes and KetonesVicky VigneshAún no hay calificaciones
- Edexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDocumento8 páginasEdexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMaliha Ishrat JarinAún no hay calificaciones
- Anic Compounds Containing CHO PDFDocumento12 páginasAnic Compounds Containing CHO PDFGunnu NarayanAún no hay calificaciones
- Alcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2Documento18 páginasAlcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2PrakharAún no hay calificaciones
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction Mechanisms.Documento32 páginasNucleophilic Substitution Reaction Mechanisms.hey ur momgqwy lolAún no hay calificaciones
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocumento5 páginasAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiAún no hay calificaciones
- HydrocarbonDocumento33 páginasHydrocarbonaleenashaji.abraham1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aldehydes & KetonesDocumento104 páginasAldehydes & KetonesCharin Kadian75% (4)
- AlkenesDocumento120 páginasAlkenesVidhan PatniAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem Pre Prelim PaperDocumento5 páginasChem Pre Prelim PaperSuvadip SanyalAún no hay calificaciones
- General DescriptionDocumento12 páginasGeneral DescriptionMariel VillaAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocumento40 páginasUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Org 2Documento30 páginasOrg 2rearachel25Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wa0005.Documento39 páginasWa0005.amaandeshmukh4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Organic MaterialDocumento15 páginasOrganic MaterialAditya GathwalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocumento7 páginasHydrocarbon Notesl8627352Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aldehydes and Ketones .NotesDocumento32 páginasAldehydes and Ketones .NotesvishalAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkene: This Article Is About The Chemical Compound. For The Material, See - Not To Be Confused With orDocumento19 páginasAlkene: This Article Is About The Chemical Compound. For The Material, See - Not To Be Confused With orRAMAKRISHNA PARJANYAAún no hay calificaciones
- Reactivity of Aldehydes & KetonesDocumento1 páginaReactivity of Aldehydes & KetonesKala IwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Theory of The Aldol Condensation ReactionDocumento9 páginasTheory of The Aldol Condensation ReactionaizatAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 7 Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento7 páginasChapter 7 Carbonyl CompoundsJacqueen0330Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 05Documento31 páginasCH 05nayan159Aún no hay calificaciones
- 202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFDocumento14 páginas202004032240234952abha Carbonyl Compounds PDFSrikeshav BAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkene Synthesis & ReactionsDocumento11 páginasAlkene Synthesis & ReactionsStanley ChuAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxylDocumento26 páginasNotes Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes Ketones and CarboxyltcbrihzllmkmkvxfovAún no hay calificaciones
- Aldehydes Ketone Carboxylic AcidsDocumento4 páginasAldehydes Ketone Carboxylic AcidspoornaAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbonyl compounds-II S-1Documento5 páginasCarbonyl compounds-II S-1sciencewing rbiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Documento16 páginasHydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Soham NagAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem-12. Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento17 páginasChem-12. Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsJitendra kumarAún no hay calificaciones
- AldehydeandketoneDocumento15 páginasAldehydeandketoneDj Arts Tarpaulin PrintingAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Flow Chart 16Documento3 páginasOrganic Flow Chart 16Kshitiz JoshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Upper 6 Organic Chemistry Chapter 7: Carboxylic Acid & Its DerivativesDocumento65 páginasChemistry Upper 6 Organic Chemistry Chapter 7: Carboxylic Acid & Its DerivativesChin Bao ErAún no hay calificaciones
- Structural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesDocumento20 páginasStructural Chemistry Organic Chemistry Summary: Alkynes: Structure, Conformations, PropertiesMohanraj ShanmugamAún no hay calificaciones
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Teacher OrientationDocumento9 páginasAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: Teacher OrientationAnand RawatAún no hay calificaciones