Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Java Cheat Sheet
Cargado por
api-3744988Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Java Cheat Sheet
Cargado por
api-3744988Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
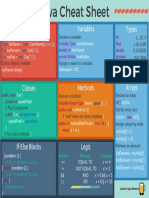
HP JAVA Cheat Sheet
INPUT with JOptionPane if with multiple actions (braces)
import javax.swing.*; if ( xCoord > 800 )
{
public class TriangleArea xAddition = -5;
{ forwards = true; //Boolean variable
public static void main(String[] args) }
{
String baseString,heightString;
double base; // base of triangle.
double height; // height of the triangle
if with else
if ( hungry) //hunger is Boolean variable – must be true
double area; // area of triangle
System.out.println("Buy the cookie!" );
else
baseString = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter base:");
System.out.println("Buy the apple!" );
heightString = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter height:");
base = Double.parseDouble( baseString ); if
height = Double.parseDouble( heightString ); if ( (hunger + look + smell ) > 15 )
area = (.5)*base*height; // Compute the area. System.out.println("Buy the cookie!" );
else if (hunger + look + smell)>20
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "The base was "+ base System.out.println("Buy the cake!" );
+ "The height was "+ height else
+ "The area of the triangle is " + area); System.out.println("Buy the apple!" );
} // end of main()
} // end of class TriangleArea
for
for (countDown=3;countDown>=0;countDown--)
{
Java Primitives/Variables System.out.println(countDown);
System.out.println("and counting.");
Integers
}
int= -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
Real Numbers: while
Double = +1038 (15 significant figures) while ( dollars < 1000000.00 )
{
dollars = dollars*1.05;
Single Characters: year++;
Char letter=’A’; }
Boolean values (true or false) do looping
Boolean isPrime= true;
do
{
String Values: System.out.println(x);
String name = “Erin”; }
while (x>10);
Arrays (see Java Array Class):
int theArray[] = new int[10]; 1 dimensional HTML for APPPLET
int theArray[][]=new int[6][6]; 2 dimensional <html>
<body>
<applet code="HappyFace" width="800" height="600">
Standout Output Methods </applet>
System.out.print(“Enter the score”); (same line) </body>
System.out.println(“Try again”); (new line) </html>
System.out.println(“The answer is “+ 42);
APPLET
Branching Structures import javax.swing.*;
“and” is represented in Java as && import java.awt.*;
“or” is represented in Java as | |
“not” is represented in Java as ! public class HappyFace extends JApplet
{
public void paint(Graphics canvas)
if {
if ( xCoord > 800 ) canvas.drawOval(100, 50, 200, 200);
addition = -5; canvas.fillOval(155, 100, 10, 20);
canvas.fillOval(230, 100, 10, 20);
canvas.drawArc(150, 160, 100, 50, 180, 180);
}
}
HP JAVA Cheat Sheet
Useful Math Class Methods Result
Math.abs(-7)
Math.ceil(6.2)
7
7
Increment and Decrement Operators
count++; //increase the value of count by 1
Math.floor(6.8) 6
count--; // decrease the value of count by 1
Math.max(5,6) 6
count+2; // increase the value of count by 2
Math.min(5,6) 5
count-2 // decrease the value of count by 2
Math.pow(2.0,3.0) 8.0
Math.random() number between 0 less than 1
Math.round(6.5) 7
Math.sqrt(4.0) 2.0 Switch and Case Statements
int month = 8;
switch (month) {
Assignment Statements case 1: System.out.println("January"); break;
double pi; case 2: System.out.println("February"); break;
int x = 1; case 3: System.out.println("March"); break;
String empty = ""; case 4: System.out.println("April"); break;
double pi = 3.14159; case 5: System.out.println("May"); break;
case 6: System.out.println("June"); break;
case 7: System.out.println("July"); break;
x == y // x equals y case 8: System.out.println("August"); break;
x != y // x is not equal to y case 9: System.out.println("September"); break;
x>y // x is greater than y case 10: System.out.println("October"); break;
x<y // x is less than y case 11: System.out.println("November"); break;
x >= y // x is greater than or equal to y case 12: System.out.println("December"); break;
x <= y // x is less than or equal to default: System.out.println("Not a month!");break;
}
String Methods
(assume stringVariable is name) Java Escape Characters
\n new line – position cursor to the beginning of next line
length stringVariable.length();
\t horizontal tab
equals stringVariable.equals(otherStringVariable);
\r position cursor to beginning of current line
stringVariable.equalsIgnoreCase(otherStringVariable);
\\ backslash – prints a backslash
lowercase stringVariable.toLowerCase();
\” prints a double quote
uppercase stringVariable.toUpperCase();
trim stringVariable.trim()
System.out.println("Hello\nnext\nLine");
charAt(Position) stringvariable.charAt(Position);
Simple OOP example
class BoxTester
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
Box cube = new Box( 2.0, 2.0, 2.0 ) ;
System.out.println( "Area: " + cube.area() );
System.out.println(“Volume:” +cube.volume());
}
}
class Box
{
private double width, height, length;
//constructors
Box( double W, double H, double L)
{ height = H ;
width = W ; Input with EasyReader
length = L ;
} // console is an EasyReader Object you create below
// methods EasyReader console = new EasyReader();
double volume()
{ //EasyReader Method Calls are below
return length*width*height ; change = console.readInt();
} discountRate = console.readDouble();
También podría gustarte
- Java Cheat SheetDocumento6 páginasJava Cheat SheetMike Lyons80% (5)
- Java Cheat SheetDocumento18 páginasJava Cheat SheetRahul Das100% (1)
- Js Cheatsheet PDFDocumento13 páginasJs Cheatsheet PDFGabri Dinw100% (8)
- Core JavaDocumento6 páginasCore JavaVanda AzevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Video Games Industry FinalDocumento44 páginasVideo Games Industry FinalZee100% (4)
- Java Cheat Sheet 100 Plus PDFDocumento129 páginasJava Cheat Sheet 100 Plus PDFchristopherAún no hay calificaciones
- The Essential Java Cheat SheetDocumento16 páginasThe Essential Java Cheat Sheetsankalp.ims2931Aún no hay calificaciones
- Java OOP-Cheat SheetDocumento1 páginaJava OOP-Cheat SheetzanandAún no hay calificaciones
- JavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms: An Introduction to Understanding and Implementing Core Data Structure and Algorithm FundamentalsDe EverandJavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms: An Introduction to Understanding and Implementing Core Data Structure and Algorithm FundamentalsAún no hay calificaciones
- Java Programming Cheat SheetDocumento13 páginasJava Programming Cheat SheetYogesh232350% (4)
- JAVA NotesDocumento36 páginasJAVA NotesRAVIKRISHNA SUKHAVASIAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Java MaterialDocumento56 páginasCore Java MaterialRaghavendra GupthaAún no hay calificaciones
- JavaDocumento162 páginasJavaUtkrusht LaloriaAún no hay calificaciones
- AR Porta CabinDocumento2 páginasAR Porta CabinVp SreejithAún no hay calificaciones
- Learn SQLDocumento11 páginasLearn SQLJae Li ChangAún no hay calificaciones
- 061 Java Cheat SheetDocumento1 página061 Java Cheat Sheetag1tatorAún no hay calificaciones
- rc024 Corejava PDFDocumento10 páginasrc024 Corejava PDFAditya ChendwankarAún no hay calificaciones
- Corejava PDFDocumento250 páginasCorejava PDFsai srinivasAún no hay calificaciones
- Important Programs in JavaDocumento35 páginasImportant Programs in JavaKaral Marx S0% (1)
- B777 ChecklistDocumento2 páginasB777 ChecklistMarkus Schütz100% (1)
- Java Notes Of25sessionsDocumento318 páginasJava Notes Of25sessionsSourav SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Core JavaDocumento6 páginasCore JavaSajal NigamAún no hay calificaciones
- JEE CompleteDocumento443 páginasJEE Completeprakash_02009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Java CheatsheetDocumento7 páginasJava Cheatsheetdinesh3434Aún no hay calificaciones
- Java ProgramsDocumento157 páginasJava ProgramsDurgesh Tripathi0% (1)
- Core JavaDocumento10 páginasCore JavaSharath SharuAún no hay calificaciones
- Java ProgrammingDocumento111 páginasJava ProgrammingCarolina SilviaAún no hay calificaciones
- Spring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration CRUD Example TutorialDocumento17 páginasSpring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration CRUD Example Tutorialswapnil dafAún no hay calificaciones
- Java ProgramsDocumento62 páginasJava ProgramsMahek FatimaAún no hay calificaciones
- Apex CheatsheetDocumento4 páginasApex CheatsheetAmit GangwarAún no hay calificaciones
- Core JavaDocumento314 páginasCore Javasakshi aggarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Tank TacticsDocumento241 páginasTank TacticsSlobodan Petrovic100% (1)
- Core Java: - Sharad BallepuDocumento56 páginasCore Java: - Sharad BallepuyacobaschalewAún no hay calificaciones
- Refcardz Core Java PDFDocumento6 páginasRefcardz Core Java PDFAshishJaiswalAún no hay calificaciones
- Concentric-Valves-API-609-A (Inglés)Documento12 páginasConcentric-Valves-API-609-A (Inglés)whiskazoo100% (1)
- Poster SIL PDFDocumento1 páginaPoster SIL PDFvgogulakrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- Javascript: Javascript Programming For Absolute Beginners: Ultimate Guide To Javascript Coding, Javascript Programs And Javascript LanguageDe EverandJavascript: Javascript Programming For Absolute Beginners: Ultimate Guide To Javascript Coding, Javascript Programs And Javascript LanguageAún no hay calificaciones
- Java - by ManishDocumento110 páginasJava - by ManishRahul singh100% (1)
- Java GenericsDocumento5 páginasJava GenericsincognitozaelusAún no hay calificaciones
- JavaScript NotesDocumento30 páginasJavaScript NotesSudheer Reddy PothuraiAún no hay calificaciones
- Java: Advanced Guide to Programming Code with Java: Java Computer Programming, #4De EverandJava: Advanced Guide to Programming Code with Java: Java Computer Programming, #4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Java Collections TutorialDocumento38 páginasJava Collections Tutorialpaulrulez3157100% (1)
- Java Collections in DepthDocumento26 páginasJava Collections in DepthPawan KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Plant Improves C3 Recovery With Lean Six Sigma ApproachDocumento9 páginasGas Plant Improves C3 Recovery With Lean Six Sigma ApproachganeshdhageAún no hay calificaciones
- String Methods in JavaDocumento24 páginasString Methods in JavaJerold FerreiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Java 8 Programmer II Study Guide: Exam 1Z0-809De EverandJava 8 Programmer II Study Guide: Exam 1Z0-809Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Object Oriented Programming Through JavaDocumento16 páginasObject Oriented Programming Through JavaRevanth AbhyudayAún no hay calificaciones
- JavaCheatSheet PDFDocumento7 páginasJavaCheatSheet PDFJake Jarvis0% (1)
- JAVA GlossaryDocumento17 páginasJAVA Glossaryrebson100% (1)
- What Is Java? Java Syntax BasicsDocumento29 páginasWhat Is Java? Java Syntax BasicsJaya BalakrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- K V Rao Adv Java PDFDocumento151 páginasK V Rao Adv Java PDFFeleke AfeworkAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes On JAVA 10.2005.3: Syntax of CommandsDocumento3 páginasNotes On JAVA 10.2005.3: Syntax of CommandsJonas SingboAún no hay calificaciones
- HTML5 CSS3 Training Course, Best HTML5 CSS3 Training Institute Hyderabad, India - NareshITDocumento7 páginasHTML5 CSS3 Training Course, Best HTML5 CSS3 Training Institute Hyderabad, India - NareshITAnand Dhanalakota0% (1)
- Index of Programs: S. No Program Name Page NoDocumento28 páginasIndex of Programs: S. No Program Name Page NoJemal GutemaAún no hay calificaciones
- Inheritance Vs ContainershipDocumento2 páginasInheritance Vs ContainershipManas SrivasatavaAún no hay calificaciones
- JAVA ProgrammingDocumento66 páginasJAVA ProgrammingSuguna100% (2)
- JavaDocumento260 páginasJavaRulz Andrei100% (1)
- Java Lecture NotesDocumento128 páginasJava Lecture Notesdivakartripleh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Java Interview QuestionsDocumento80 páginasBasic Java Interview QuestionsArvind SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- JavaPrograms PDFDocumento11 páginasJavaPrograms PDFRadhe Raman KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Jquery: Study Guide For Module No. 6Documento9 páginasIntroduction To Jquery: Study Guide For Module No. 6Dhan CabugaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Modern Web Applications with Next.JS: Learn Advanced Techniques to Build and Deploy Modern, Scalable and Production Ready React Applications with Next.JSDe EverandModern Web Applications with Next.JS: Learn Advanced Techniques to Build and Deploy Modern, Scalable and Production Ready React Applications with Next.JSAún no hay calificaciones
- Omni III User's Manual Va.1.0-20140124Documento130 páginasOmni III User's Manual Va.1.0-20140124Reuel TacayAún no hay calificaciones
- Lector: Aleksandar Karamfilov Skype: Sanders - Kar E-Mail: Aleksandar - Karamfilov@Pragmatic - BG Linkedin: 2013 - 2014Documento19 páginasLector: Aleksandar Karamfilov Skype: Sanders - Kar E-Mail: Aleksandar - Karamfilov@Pragmatic - BG Linkedin: 2013 - 2014Diana DikovaAún no hay calificaciones
- HGU User ManualDocumento72 páginasHGU User Manuallomayani100% (1)
- Oracle Secure BackupDocumento294 páginasOracle Secure BackupCarlos ValderramaAún no hay calificaciones
- Whose Online Video Lectures Are Best For The IIT JEE?Documento6 páginasWhose Online Video Lectures Are Best For The IIT JEE?Buzz PriyanshuAún no hay calificaciones
- Toshiba NB520 Compal LA-6859PDocumento38 páginasToshiba NB520 Compal LA-6859Pash thonAún no hay calificaciones
- Weg CFW500 Enc PDFDocumento32 páginasWeg CFW500 Enc PDFFabio Pedroso de Morais100% (1)
- Family Surveyed 2017 - TimberDocumento26 páginasFamily Surveyed 2017 - TimberAlibasher Macalnas0% (1)
- ZzzsaDocumento4 páginasZzzsanikzperaltaAún no hay calificaciones
- Reynolds EqnDocumento27 páginasReynolds EqnSuman KhanalAún no hay calificaciones
- Weapon Lights and Targeting LasersDocumento3 páginasWeapon Lights and Targeting LasersバラモスまさゆきAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematical Modelling of Gear Tooth Stiffness: Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical EngineeringDocumento40 páginasMathematical Modelling of Gear Tooth Stiffness: Bachelor of Technology in Mechanical EngineeringVishal ShasiAún no hay calificaciones
- InternshipDocumento14 páginasInternshipMohammed Shaheeruddin0% (1)
- Ric RG90 y RG60Documento1 páginaRic RG90 y RG60GabrielConsentidoAún no hay calificaciones
- Camsco Breaker PDFDocumento12 páginasCamsco Breaker PDFMichael MaiquemaAún no hay calificaciones
- Roxtec CatalogDocumento41 páginasRoxtec Catalogvux004Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ne40 Ne80 PDFDocumento192 páginasNe40 Ne80 PDFณัชชา ธนปัญจาภรณ์Aún no hay calificaciones
- Phase ShifterDocumento7 páginasPhase ShifterNumanAbdullahAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 Candidate Quiz Buzzer Using 8051Documento33 páginas8 Candidate Quiz Buzzer Using 8051prasadzeal0% (1)
- CatalogDocumento42 páginasCatalogOnerom LeuhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Fault and Alarm Indicators: Planning and Installation Guide For Trident v2 SystemsDocumento27 páginasFault and Alarm Indicators: Planning and Installation Guide For Trident v2 SystemsDeepikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment No.7 Study of Disc Pelletizer: ObjectivesDocumento4 páginasExperiment No.7 Study of Disc Pelletizer: ObjectivesPrafulla Subhash SarodeAún no hay calificaciones
- Rcfe Contract SSHDocumento240 páginasRcfe Contract SSHJeanne MarshAún no hay calificaciones