Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Theory of Structures Problems Solved by DK Mamonai
Cargado por
Darya MemonTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Theory of Structures Problems Solved by DK Mamonai
Cargado por
Darya MemonCopyright:
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
A. Supports :
Supports are provided to resist the loads.
There are three types of Supports 1. Hinge Support: It is always in clockwise or Anti-clockwise not horizontal or vertical
2. Fixed Support: Horizontal or Vertical or Clockwise
3. Circular or Roller Support: Always normal to the surface.
B. Loads :
Dead Loads Uniformity Disturbed Load Uniformly Varying Load Point Load
Live Loads Moving Load Wind Load Snow Load
09CE37
1|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Beams
(i) Determinate Beam or Simply Supported Beam:
(ii) Continuous Beam : One or more span is said as Continuous Beam.
(iii) Cantilever Beam : In Sindhi it is said as CHAJA!
09CE37
2|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem:1 :
Determinate Forms
Free Body Diagram
Ma
Ra Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0,
Ha
+ve Fy = 0 Ra P = 0 Ra= P
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 Ma+ Ra * L =0 Ma + PL = 0 Ma = - PL
09CE37
3|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem:2 :
Determinate Forms
P= 80lb
L = 10
Free Body Diagram
P = 80 lb
Ma
L = 10
Ra Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0,
Ha
+ve Fy = 0 Ra P = 0 Ra= 80 lb
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 Ma+ Ra * L =0 Ma + PL = 0 Ma = - 800 lb-ft ( Anti-clockwise )
09CE37
4|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem:3 :
Uniformly disturbed Load
W v/v
L WL Free Body Diagram A Ma L/2 C L L/2 B
Ra
Ha
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra WL = 0 Ra= WL Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point C Ma+ Ra * L/2 =0 Ma = - ( Ra * L / 2 ) Ma = - ( WL * L / 2) Ma= - W L 2 / 2
09CE37
5|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem:4 :
Uniformly disturbed Load
3 kip/m
2m 6 kip Free Body Diagram A Ma 1.5 C 2m 1.5 B
Ra
Ha
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra WL = 0 Ra= 6 Kip Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point C Ma+ Ra * L/2 =0 Ma= - W L 2 / 2 Ma= - 3 (2)2 / 2 Ma= - 6 kip. m
09CE37
6|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
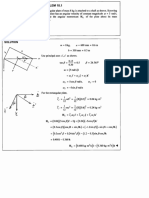
Problem:5:
60k 4
60k
Free Body Diagram
60k
Fx Fy
60k
A Ma Ra Ha 6
53.30
B Rb
First of all changing Tangent into Degree = Tan-1 4/3 = 53.30 Now, finding X-Y co-ordinates of the Inclined Force Fx= F Cos = 60 Cos 53.3 = 60 (0.59)= 36K ; Fy = F Sin = 60 Sin 53.3 = 60 (0.801)=48.10K
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha Fx = 0, Ha=Fx ,
Ha= 36 K,
+ve Fy = 0 Ra + Rb P - Fy = 0 Ra + Rb -60 -48 =0
Ra + Rb = 108 -------------------------(i)
09CE37
7|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 60 * 6 + Fy * 12 Rb *18 = 0 60 * 6 + 48 * 12 = 18 Rb Rb = 52 K Putting Value of Rb in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 108 Ra + 25 = 108 Ra = 56 K
09CE37
8|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem:6:
12 k 16k 16k 3 k / ft
2 K / ft
8 Free Body Diagram 16 k A Ra Ha 4 4
12 k C D
16 k E
16 k F G
9k B Rb
2 2
As there is V.D.L = 1/2 * 6 * 3 = 9 k For U.D.L = 2* 8 = 16 K
; ;
X = L / 3 = 6 / 3 = 2 X= L / 2 = 8 / 2 = 4
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 16k 12k 16k 16k + Rb 9k = 0 Ra + Rb = 69 --------------------------------(i) Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A (16 * 4) + (12 * 12) + (16 *16) + (16 * 20) - (Rb * 24) + (9 * 26)= 0 1018 24Rb = 0 Rb = 42.41 K Putting Value of Rb in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 69 Ra + 42.41 = 69 Ra = 26.6 K
09CE37 9|Page
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 7
Point Load
40 K
50K 3/4
30 K
A 4
E 5
C 3
F 3
D 8
G 3
H 3
(PART 1 ) We Disturb this Diagram into two A Point to C Point Free Body Diagram 40 k
A Ha 4 Ra
C Hc 5 Rc
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha - Hc = 0, Ha= Hc Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Rc * 90 + 40 *4 = 0 +ve Fy = 0 Ra 40 + Rc = 0 Ra + Rc = 40 --------------------------------(i)
0 = -9 Rc + 160 Rc = 18 K Putting Value of Rc in Equation (i) Ra + Rc = 40 Ra + 18 40 = 0
09CE37
Ra = 22 K
10 | P a g e
Theory of Structures (Part 2) 50k 32 K 30 K
Sir Dr.Zubair
Hc 3
F 3
D 4 4
G 3
H 3
= Tan-1 3/4 36.86 Fx = F Cos 50 * Cos 36.86 40K Fy= F Sin 50 * Sin 36.86 30 K
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Hc + Fx = 0, Hc = - 40 k Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Rc * 18 - Fy * 15 + Rd *12 32*8 30*2 = 0 +ve Fy = 0 - Rc Fy + Rd 32 -30 + Rb = 0 Rb + Rd = 110 --------------------------------(i)
12 Rd = 1090 Rd = 91 K Putting Value of Rd in Equation (i) Rb + Rd = 110 Rb + 91 110 = 0 Rb = 19 K
09CE37
11 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 8 :
Rk 6k 3 k /ft
8 Free Body Diagram 48k Rk
2 6k
Ma
Ra
Ha 8
8 6
8 2
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra -48 37 - 6 = 0 Rb + Rd = 143 --------------------------------(i) Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Ma + Ra *16 ( 48 + 37 ) * 8 - 6 * 2= 0 0 = Ma + 143 *16 1096 - 12 Ma = -1180 K. ft Hence the direction of Moment A should be taken as reversed.
09CE37
12 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 9 :
R K /ft
A 20
Free Body Diagram R*20 k Ha 6.66 Ra 6.66 6.66 Ra
Point Load = 1/2 * 37 * 20 890 k Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 890 + Rb = 0 Ra + Rb = 890 --------------------------------(i) Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 890 * 6.66 - Rb * 20 = 0 20 Rb = 5927.4 Rd = 296.37 K Putting Value of Rd in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 890 Ra + 296.37 890 = 0 Rb = 593.63 K
09CE37
13 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 10: Find Unknown Reactions
Rk 2.5 k/ft 4 k/ft
8k
A 4
C 8
D 6
Free Body Diagram
10 k
Rk
32 k
8k
Ra Ma
A Ha 2
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 10 - 37 32 -8 = 0 Ra = 139 k Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Ma + Ra * 18 10* 16 37 * 14 32 * 10 = 0 0 = Ma + 2502 -1724 Ma = -778 K . ft
The direction should be reversed
09CE37
14 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 11:
8K (0.2+R ) K RK 20 k
4 8 5 5 9 5
Free Body Diagram: 8k C Rc Hc 4 8 9 32 5 9 5 Ra (R +0.2 )K A RK 20k B Rb Hb
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Hb = 0, +ve Fy = 0 8 160 37 + Ra 20 + Rb = 0 Ra + Rb = 1722.6 -----------------------------(i) Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A - 8 * 28 - 1605.6 * 23 20 * 5 + Ra -24 = 0 24 Ra = 27252.8 Rd = 1552.2 K Putting Value of Rd in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 890 Ra + 1552.2 1722.6 = 0
09CE37
Rb = 170.4 K
15 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 12:
( 10+ R/2) K/ft
20 We break this triangle into two parts PART : 1
(10+R/2) K
Free Body Diagram (1/2 * 10 * [10+R/2] ) A Ra
V.D.L = 1/ 2 * 10 * 54.5 = 272.5 k
Ha 3.33 3.33 3.33
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 272.5 = 0 Ra = 272.5
09CE37
16 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Part 2:
( 1/2 * 10 * [10+R/2] ) B
Rb 3.33 3.33 3.33
V. D.L = 1/2 * 10 * 54.5 = 272. 5 k
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Fx = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 272.5 = 0 Ra = 272.5 k
09CE37
17 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 13:
10 k
20 k
Rk 1/2
A 8 Disturbing into 3 parts 4
B 6
E 4 5
C 5
F 4 6
Part 1
10 k
Free Body Diagram
10 k
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha - He = 0, Ha = 79.60 k Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 10 * 8 - Rb * 12 Re * 18 = 0 -12 Rb = - 2.12 *18 Rb = 3.65 K Putting Value of Ra in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 12.12 Ra + 3.65 12.12 = 0
09CE37
+ve Fy = 0 Ra -10 + Rb + Re = 0 Ra + Rb = 12.12 -----------------------------(i)
Rb = 8.47 K
18 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Part 2 : 20 k Free Body Digram: 20 k
Sir Dr.Zubair
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, He - Hf = 0, He = 79.60 k Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point E 20*4 Rc * 9 + Rf * 14 = 0 -9 Rc = - 414.236 Rc = 46 K Putting Value of Rc in Equation (i) Re + Rc = 43.874 Re + 46 43.874 = 0 Re = -2.124 K +ve Fy = 0 Re + -20 +Rc -Rf = 0 Re + Rc = 43.874 -----------------------------(i)
09CE37
19 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Part 3: Rk
Free Body Diagram: Rk
= tan -1 1 / 2 26.56 Fx = F Cos 37 Cos 26.56 79.60 k Fy = F Sin 37 Sin 26.56 39.79 k Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Hf - Fx = 0, Hf = 7960 k Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point F Fy * 4 Rd * 10 =0 39.79 * 4 10 Rd = 0 Rd = 15.916 K +ve Fy = 0 Rf - Fy + Rd = 0 Rf + Rd = 39.79 -----------------------------(i)
Putting Value of Rd in Equation (i) Rf + Rd = 39.79 Re + 15.916 39.79 = 0 Re = 23.874 K
09CE37
20 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 14:
0.6 k / ft
2.4 k /ft
16
It is disturbed like that
16
Free Body Diagram: 14.4 k 14.4 9.6 k A Ha 8 5.33 B
Ra
Rb
09CE37
21 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Point Load of U.D.L = 16 * 0.6 9.6 k 14.4 k
Sir Dr.Zubair
Point Load of V.D.L = 1/2 * 16 * ( 2.4 0.6 )
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra - 9.6 14.4 + Rb = 0 Ra + Rb = 24 -----------------------------(i) Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 9.6 * 8 + 14.4 * 10.66 - Rb * 16 = 0 Putting Value of Rb in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 24 Ra + 14.39 24 = 0 Re = 9.61 K 0 = 76.8 + 153.59 15 Rb Rb = 14.39 K
09CE37
22 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 15 :
RK
200 lb /ft
100 lb/ft A C D
Solving this equation by parts . Part 1: 1200 k C 6 2 4 D 600 k
Solution: By solving the above figure: First convert the U.D.L and V.D.L into single point loads. For U.D.L = 12 * 100 = 1200 k For V.D.L = 1/2 * 12 * 100 = 600 k
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Rc -1200 600 + Rd = 0 Ra + Rb = 1800 -----------------------------(i)
09CE37
23 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point C 1200 * 6 + 600 * 8 Rd * 12 = 0 Putting Value of Rb in Equation (i) Rc + Rd = 1800 Ra + 1000 1800 = 0 Re = 800 K 0 = 7200 + 4800 12 Rd Rd = 1000 K
Part 2:
R k
800 k
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra - 89 800 + Rb = 0 Ra + Rb = 889 -----------------------------(i)
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 89 * 4 + 800 * 8 Rb * 12 = 0 0 = 356 + 6400 -12 Rb Rb = 563 K
Putting Value of Rb in Equation (i) Ra + Rb = 889 Ra + 563 889 = 0 Re = 326 K
09CE37
24 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Shear Force and Bending Moment Shear Force :
The Shear force at a cross- sectional of a beam is the unbalanced vertical force to the tight or left of the section.
Bending Moment:
The bending moment at a cross-section of a beam is the algebraic sum of the moments of the forces to the right or left of the section. OR Algebraic sum of the clockwise and anti-clockwise moment is called Bending Moment.
Shear Force & Bending Moment Diagram:
The shear force and bending moment will be different at different cross sections depending upon the loading on the beam. The variation in the there can be shown graphically by plot the S.F and B.M diagram.
Shear Force Diagram for Different Types of Loading: CASE-I :
For any concentrated / Point Load shear force is straight line.
CASE-II :
For U.D.L the shear force diagram will be inclined line. Or Triangular Form
09CE37
25 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
CASE - III :
For U.V.L uniform varying load 20 Curve will be there in its diagram
20
SIGN CONVERSION :
An upward force to the right of a section contributes to a Positive Shearing force in upward L.H.S +VE -VE
R.H.S
+VE
-VE
09CE37
26 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Bending Moment Diagram for Different Loads CASE-I
For Concentrated Force ( Point Load ) the bending moment diagram will be inclined line.
CASE-II
For UDL the shape of B.M diagram will be parabolic at 20 curve
20
CASE-III
The shape for V.D.L of B.M will be at 30 curve.
30
SIGN CONVERSION: A clockwise moment to the right of then section or an anticlockwise
moment to the left of the section contributes to positive bending moment. L.H.S: R.H.S :
+VE
-VE
-VE
+VE
Positive Bending Moment is also known as Hogging Bending Moment and Negative B.M is also known as sagging B.M
09CE37
27 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 1
Sir Dr.Zubair
2.5 k
1.5 k
2k
0.6 m
0.6 m
0.6 m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 - 2.5 + Ra 1.5 - 2 = 0 Ra = 6 k -----------------------------(i)
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point B Ma + Ra * 0.18 - 2.5 * 0. 12 1.5 * 0.6 = 0 0 = Ma + 10.8 3 0.9 Ma = - 6.9 K
Hence the direction of moment will be reversed to which we have taken .
09CE37
28 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Shear force 1 2.5k 2 1.5 k 3 2k
Sir Dr.Zubair
Ra Ha 0.6 m X1 X2
0.6 m
0.6 m
X3
Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra
+ 6 t ----------- (i)
If = 0 @ A + 6 t If = 0.6 @ ( A-C) + 6 t Section ( 2-2)
V2 = Ra 2.5
6 2.5
+ 3.5 t ----------- (ii)
If = 0.6 @ C + 3.5 t If = 1.2 @ ( A -D ) + 3.5 t Section ( 3-3)
V3 = Ra 2.5 1.5
If = 1.2 @ D + 2 t
6 2.5 1.5
+ 2 t ----------- (iii)
If = 1.8 @ ( A - B ) + 3.5 t
09CE37
29 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment :
Sir Dr.Zubair
1 2.5 k
2 1.5 k
3 2k
Ma
Ra 0.5 m X1 X2 X3 0. 6 m 0.6 m
Section ( 1-1)
B.M1 = Ra * + Ma
1
6 1 6.9
----------- (i) - 6.9 t.m
If 1 = 0 @ A Section ( 2-2)
6 ( 0) 6.9
B.M2 = Ra *
Section ( 3-3)
+ Ma 2.5 * ( 2 0.6) 6 2 69 2.5( 2 0.6 ) 6 2 6.9 2.5 2 1.5 (ii) - 3.3 tm
If 2 = 0.6 @ C 6 * 0.6 6.9 2.5 * 0.6 + 1.5
B.M3 = Ra * + Ma 2.5 * ( 0.6) 1.5 ( 1.2)
3 3 3
6 3 69 2.5( 3 0.6 ) 1.5 ( 3 1.2 ) ----------- (iii) - 1.2 t.m
If 3 = 1.2 @ D 6 * 1.2 69 2.5 ( 1.2 0.6 ) 1.5 ( 1.2 1.2 ) If 3 = 1.8 @ B 0 t.m
09CE37
30 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Shear and Bending Moment Diagram 2.5 k 1.5 k 2k
Sir Dr.Zubair
0.6 m
0.6 m
0.6 m
+6t
+ 3.5t
+ 2.1 t
-6.9 tm
-3.3 tm
-1.2 tm
09CE37
31 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 2
Sir Dr.Zubair
W lb/ft
A L
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra WL = 0 Ra = WL -----------------------------(i)
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point B Mn + W * L/2 0 = Ma + WL2 / 2 Ma = - WL2 / 2 K
09CE37
32 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Free Body Diagram of Shear force
Sir Dr.Zubair
Ra Ha L
X1 Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra - W
WL - W ----------- (i)
If = 0 @ A WL W (0) + WL If = L @ ( B ) WL W (L) 0 Bending Moment
A Ma
Ra
X1
B.M1 = Ma + Ra * W * /2
If 1 = 0 @ A If 1 =L @ B
Ma + Ra * W2 /2 Ma + 0 - WL2 / 2 + WL2 WL2/2
----------- (i) - WL2 / 2 t.m 0 t.m
09CE37
33 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Shear and Bending Moment Diagram
Sir Dr.Zubair
W lb/ft
A L
+WL
0 0 -WL2 /2 20
09CE37
34 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 3
Sir Dr.Zubair
A cantilever beam AB 2m long carrying a uniform disturbed load of 2.5 Kn/m over a length of 1.6 m frin free hand . draw the S.F and B.M diagram for the beam. 2.5 Kn/m
A 0.4 m 1.6 m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 4 = 0 Ra = 4 KN
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Ma = Ma + 4 * 1.6 / 2 0 = Ma + 4.8 Ma = - 4.8 KN . m
09CE37
35 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Free Body Diagram of Shear force 1 4 Kn 2
Sir Dr.Zubair
A B Ra Ha 0.4 m 0.8 m 0.8 m
X1 X2 Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra
4 KN ----------- (i)
If = 0 @ A 4 KN
Section ( 2-2)
V2 = Ra 2.5 *( 2 0.4 )
Ra 2.5 2 + 1
If 2 = 0.4 @ C 4 2.5 ( 0.4) + 1 4 KN ----------- (ii) If 2 = 2 @ ( B ) 4 2.5 (2) + 1 0 ----------- (iii)
09CE37
36 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment 1 4 Kn 2
Sir Dr.Zubair
A Ra 0.4 m Ma X1 0.8 m 0.8 m
Section ( 1-1)
B.M1 = Ma +
If 1 = 0 @ A Section ( 2-2)
* Ra
----------- (i)
Ma + 0
- 4.8 t.m
B.M2 = Ra
* 2 + Ma 2.5 * ( 2 0.4) { ( 2 0.4)/2 }
Ma + Ra 2 - 1.25 ( 2 0.4 )2 - 4.8 + 4 2 - 1.25 ( 2 - 0.4 ) 2
If 2 = 0.4 @ C - 4.8 + 1.6 - 0 If 2 = 2 m @ B 0 KN. m
- 3.2 KN. m
09CE37
37 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Shear and Bending Moment Diagram 2.5 Kn/m
Sir Dr.Zubair
A 0.4 m 1.6 m
+4 Kn
+ 4 Kn
-4.80 kn.m
-3.2 Kn.m 2o
09CE37
38 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 4
Sir Dr.Zubair
A cantilever beam of 1.8 m is loaded as shown in figure . Draw the shear force and bending moment diagram. 2 Kn 1.5 Kn 2.5 Kn/m 1 KN
A 0.3 m
B 0.6 m
C 0.3m 0.6 m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 2 1.5 ( 0.8 * 0.6 ) -1 = 0 Ra = 4.98 KN
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A Ma = Ma + 2 * 0.3 + 1.5 * 0.9 + 0.48 * 1.5 0 = Ma + 0.6 + 1.35 + 0.72 + 1.8 Ma = - 4.47 KN . m
09CE37
39 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Free Body diagram and Shear Force 1 2 kn 2 3 1.5 kn 4 0.48 Kn
Sir Dr.Zubair
1 Kn
A Ra Ha 0.3 m
0.6 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
X1 X2 X3 X4 Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra
Section ( 2-2)
+ 4.98 KN ----------- (i)
If 1 = 0 @ A +4.98 KN
V2 = Ra 2
Section ( 3-3)
4.98 2 +2.98 KN
If 2 = 0.3 @ B + 2.98 KN
V3 = Ra 2 1.5
Section ( 4-4)
4.98 3.5 1.48 KN
If 3 = 0.9 @ C
+ 1.48 KN
V4 = Ra 2 1.5 0.8( 2 1.2 )
If 4 = 1.2 @ D + 1.48 KN
1.48 - 0.8 ( 2 1.2 )
If 4 = 1.8 @ E 1.48 0.8 ( 1.8 1.2 )
1 KN
09CE37
40 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment
Sir Dr.Zubair
1 2 kn Ma A Ra 0.3 m
3 1.5 kn
4 0.48 Kn 1 Kn
0.6 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
X1 X2 X3 X4
Section ( 1-1)
B.M1 = Ra *
If 1 = 0 @ A Section ( 2-2)
+ Ma
----------- (i)
Ma + 0
-4.47 Kn.m
B.M2 = Ra
* 2 + Ma 2 * ( 2 0.3 )
4.98 2 4.4 - 2 2 + 0.6 If 2 = 0.3 @ B 4.98 ( 0.3) - 4.4 2 ( 0.3) + 0.6 - 2.97 KN. m
09CE37
41 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Section ( 3-3)
B.M3 = Ra
* 3 + Ma 2 * ( 3 0.3 ) 1.5 (3 0.9 )
-4.47 + 4.98 3 - 2 3 + 0.6 1.5 3 +1.35 1.48 3 2.52 If 3 = 0.9 @ C 1.48 ( 0.9 ) - 2.52 - 1 .188 KN. m
Section ( 4-4)
B.M4 = Ra
* 4 + Ma 2 * ( 4 0.3 ) 1.5 (4 0.9 ) 0.8 (4 1.2) (4 -1.2 / 2)
-4.47 + 4.98 3 - 2 3 + 0.6 1.5 3 +1.35 0.4 (4 1.2)2 - 2.52 + 1.48 4 0.4 (4 1.2) 2 If 4 = 1.2 @ D -2.52 + 1.48 (1.2 ) 0.4 ( 1.2 1.2 ) 2 If 4 = 1.8 @ E -2.52 + 1.48 (1.8 ) 0.4 ( 1.8 1.2 ) 2 - 0.744 KN. m 0 KN. m
09CE37
42 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Shear and Bending Moment Diagram 2 Kn 1.5 Kn 2.5 Kn/m 1 KN
A 0.3 m
B 0.6 m
C 0.3m 0.6 m
+4.98 kn
+2.98 kn
+1.48 kn
+1.48 kn
1kn
- 4.47 kn.m
-2.97 kn.m -1.18 kn.m 20
- 0.744 knm
09CE37
43 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem : 5 A 5m long cantilever bream carries a point load of R t at the free hand and a UDL of ( 1+ 0.2 R ) t /m over a length of 3m from the free end . Draw the shear force and bending moment diagram. Rt 18.8 t
A 2m
B 3m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 56.4 89 = 0 Ra = 145.4 t
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 0 = Ma + 56.4 * 3.5 +89* 5 0 = Ma + 197.4 + 445 Ma = - 642.4 t . m
09CE37 44 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Free Body diagram and Shear force
Sir Dr.Zubair
(1+0.2 R )*3
Rt
A Ra Ha 2m
1.5 m
1.5 m
X1
X2
SHEAR FORCE
Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra
Section ( 2-2)
+ 145.4 t ----------- (i)
If 1 = 0 @ A +145.4 t
V2 = Ra 18.8 (2 -2 )
If 2 = 2 @ B If 2 = 5 @ C
145.4 18.8 (2 -2 ) 145.4 18.8 ( 2 - 2 ) 145.4 18.8 ( 5 - 2 ) + 145.4 t + 89 t
09CE37
45 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment : 1 2
Sir Dr.Zubair
(1+0.2 R )*3 Ma A Ra 2m 1.5 m 1.5 m B
Rt
X1
X2
Section ( 1-1)
B.M1 = Ra *
If 1 = 0 @ A Section ( 2-2)
+ Ma 145 1 - 624.4
----------- (i)
Ma + 0
- 642.4 t.m
B.M2 = Ra
* 2 + Ma + 18.8 * ( 2 2 ) ( 2 2 / 2 )
145.4 2 624.4 - 9.4 ( 2 + 2) 2 If 2 = 2 @ B 145.4 * 2 642.4 9.4 ( 2- 2 ) 2 If 2 = 5 @ C 145.4 * 5 642.4 9.4 ( 5- 2 ) 2 - 351.6 t. m 0 t. m
09CE37
46 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Shear and Bending Moment Diagram:
Sir Dr.Zubair
Rt 18.8 t
A 2m
B 3m
+145.4 t
+145.4t
89t
0 -642.4 tm 20 -351.6 tm
09CE37
47 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 6
Sir Dr.Zubair
A cantilever beam of 150 cm span carries a load of 2t at 60 cm from the fixed end , a load of 1t at the free end and a load of 4 ton UDL over 60 cm from 2 ton load towards the free end . Draw S.F and B,M diagram
2t 6 t /m
1t
A 0.6 m
B 0.6 m
C 0.3 m
Load intensity = Load / Length = 4 / 0.66 = 6 t/m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 2 (4) - 1 = 0 Ra = 7 t
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 0 = Ma + 2 * 0.66 + 4 * 0.99 + 1 * 1.5 0 = Ma + 1.33 + 3.99 + 1.5 Ma = - 6.33 t . m
09CE37
48 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Free Body diagram and Shear force
Sir Dr.Zubair
1 2t 4t
1t
A Ra Ha 0.6 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
X1
X2
Section ( 1-1)
V1 = Ra
Section ( 2-2)
+ 7 t ----------- (i)
If 1 = 0 @ A + 7 t
V2 = Ra 6 ( 2 0.66 )
Section ( 3-3)
If 2 = 0.66 @ B + 7 t
V3 = Ra 6 (2 0.66 ) - 2
If 3 = 1.33 @ C If 3 = 1.5 @ D
74-2 1 t
+1t +1 t
09CE37
49 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment :
Sir Dr.Zubair
1 2t Ma 4t
1t
A Ra 0.6 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
0.3 m
X1
X2
Section ( 1-1)
B.M1
= Ra * 1 + Ma
----------- (i) Ma + 0 - 6.33 t.m
If 1 = 0 @ A Section ( 2-2)
B.M2 = Ra
* 2 + Ma 2 * ( 2 0.6 ) 6 * ( 2 0.6 ) ( 2 0.6 )/2
7 2 6.33 2 (2 0.6 ) 3 (2 - 0.6 ) 2 If 2 = 0.66 @ C 7 * 0.66 6.33 Section ( 3-3) - 2.16 t. m
B.M3 = Ra
* 3 + Ma 2 * ( 3 0.6 ) 4 * ( 3 0.9)
7 3 6.33 2 (3 - 0.6 ) 4 (3 0.9 ) - 0.6 t . m 0 t.m
If 3 = 0.9 @ D 7 * 0.9 6.3 2 ( 0.9 0.6 ) 0
If 3 = 1.5 @ B 7 * 1.5 6.3 2 ( 1.5 0.6 ) 4 ( 1.5 - 0)
09CE37
50 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Bending Moment and Shear Diagram 2t 6 t /m
Sir Dr.Zubair
1t
A 0.6 m
B 0.6 m
C 0.3 m
+ 7t
+7t
1t
1t
-6.31 t.m
-21.6 t.m
20
-0.6 t.m
09CE37
51 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
TRUSSES
09CE37
52 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem 1 :
20 k 15 k
60o A 5 10 5
600 C
60o 5 10 5
60o E
Ra
Rb
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, +ve Fy = 0 Ra 20 15 + Re = 0 Ra + Re = 35 ---------------------- (i)
Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 0 = 20 * 5 + 15 * 15 20 Re = 0 0 = 325 20 Re Re = 16. 25 k Ra = 18.75 k
09CE37
53 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
B A 60o
C
Joint A : Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, -F ac F ab x = 0,
Ra = 18.75
+ve Fy = 0 Ra F ab y = 0 F ab y = 18.75 k
F ac = - F ab x ------------------------(i) As Fx = F Cos and Fy = F Sin F ab y = F ab Sin 60 0 Equation (i) will be 20 k
F ab = 21.65 ( C ) , F ab x = F ab Cos 60 0 F ac = - 10.82 ( C )
F ab x = 10.82
A Joint B : Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, F ab x F bd + F cb x = 0,
+ve Fy = 0 F ab y 20 F cb y = 0 18.75 20 F cb
y
10.82 + F cb x - F bd ------------------------(ii) F cb y = F cb Sin 60 0
= 0 F cb
= 1.25
F cb = 1.44 ( C ) , F cb x = F cb Cos 60 0
F cb x = - 0.721
Equation (ii ) will be 10.82 F bd 0. 721 F bd = - 10.82 ( C )
09CE37
54 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
B C Joint C : A 60o 60o
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, F bc x F ac - F cd x - F ce = 0, Fce + F cd x = -10.1 F cd y = F cd Sin 60 0 ------------------------(iii) +ve Fy = 0 - F bc y - F cd y = 0 -1.25 F cd
y
= 0 F cd
= - 1.25
F cd = 1.43 ( T ) , F cb x = F cb Cos 60 0
F cb x = -0.721
Equation (iii ) will be F ce 0.721 = - 10.1 15 K
F ce = - 9.378 ( C ) or Fce = 9.378 ( T )
C E
Joint D : Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, F bd F cd x - F de x = 0, Fde x = - 9.379 F de x = F de Cos 60 0
F de = - 18.75 k ( C )
09CE37
55 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem # 2 : 3k
2k F 3k
C A 30o 3 Ra Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha = 0, 60o 60o 3
D 60o 60o 3 Rb 30o B
+ve Fy = 0 Ra 3 2 3 + Rb = 0 Ra + Rb = 8 ---------------------- (i)
By applying Sine Law Sin 60 / AG = Sin 90 / 3 AG = 3 Sin 60 AG = 2.59 Cos 30 = AC / AG AC = 2.59 Sin 60 / 3 = Sin 60 / CF Cos 60 = CD / 3 Moment, +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 0 = 3 * AC + 2 * ( 3 + CD ) + 3 * ( 6 + DB ) Rb * 9 0 = 28.46 9 Rb CF = 3
CD = 1.5
Rb = 4.27 k
09CE37
Ra = 4 k
56 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
60o
Ra Joint A : Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, - F ag x + F ac = 0, F ag x = F ac ------------------------(i) F ag y = F ag Sin 60 0 Equation (i ) will be +ve Fy = 0 Ra - F ag y = 0 F ag
y
= 4k
F ag = 8 k ( C ) , F ag x = F ag Cos 60 0 F ac = 6.92 k ( T )
F ag x = 6.92 k
F ac = F ag x 3k F
Here if we solve it directly it will be more different for us to get the assumes beacuase 2 unknown will come in each equation of equilibrium. So we rotate it as
09CE37
57 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
y 30 k 300
A G
Joint G : Fx = F Cos 60 3 Cos 60 1.5 Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, F ag + F gf F x = 0, F gf = 6.5 N ( C ) +ve Fy = 0 F gc - Fy = 0 F gc = 2.6 ( C )
Note denotes the values which are already known to us
Fy = F Sin 60 3 Sin 60 2.6
09CE37
58 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Joint C : Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, - F ac Fcd + F cg x + F cf x = 0, ----( ii ) F cg y = F cg Sin 60 0
F ag y = 2.251 , F cg x = F cg Cos 60 0
F cg x = 1.3 k
Equation (ii ) will be - F ac Fcd + F cg x + F cf x = 0 - 6.9 F cd + 1.3 + F cf x = 0 F cf x - F cd = 5.6 -------------- ( iii)
+ve Fy = 0 F cf y - F cg y = 0 F cf
y
= 4k
F cf
= F cf Sin 60 0
F cf = 2.59 ( T ) , F cf x = F cf Cos 60 0
F cf x = 1.295 k
Equation (iii) will be 1. 295 F cd = 5.6 - Fcd = 4.3 ( C ) Fcd = 4.3 ( T)
Joint F From Figure We have indentify that F fg = F bf = 6. 5 F cf = F fd = 2.59 G C
2k
F B D
09CE37
59 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Method of Sections
Previously we have studied methods of joints for analysis of trusses In this methods we can directly analysis a truss force without calculating from initial point .
Here condition of moment is used rather than condition of statistics ( except in exceptional cases ) Need to cut a section where maximum unknown members force becomes zero or can be neglected.
PROCEDURE Cut a section Draw a free body diagram Assume compression and tension Apply co-planer applications of forces and equation of moment to determine members force
09CE37
60 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem : 1 D m =1/3 B m=3/2 F
Sir Dr.Zubair
12
12
12
12
Ra
1200
1200
1200
Rh
+ve Fy = 0
Taking momet at A.
Ra + Rh 1200 -1200 1200 = 0
Ra + Rh = 3600---- ( i )
Ma = 0 1200 *12 + 1200 * 24 + 1200 * 36 - Rh * 48 = 0 48 Rh = 86400 Rh = 1800 lb D B Ra = 1800 lb
Ra=1800
1200
Take the point where maximum unknowns can be neglected. Taking moment at B. Taking moment at E 1800 * 12 F ce * 8 = 0 F ce = 2700 lb ( T ) Fbd y = 2400 lb
1800 * 24 1200 * 12 F bd y * 12 = 0
Fbd y = F bd * Sin 18.45 Fbd = 7583.4 lb ( C ) Taking moment at D F be x * 12 F ce * 12 + 1800 * 24 = 0 F be x= 2400 lbs
F be x = F be * Cos 33.69 F be = 2884.43 ( C )
09CE37
61 | P a g e
Theory of Structures Problem # 2:
Sir Dr.Zubair
Required needed forces Rce = ? , Rbd= ? , Rcd= ? , R gf= ?
For Fce , we take moment at D. F ce * 20 + Ra * 40 20 * 20 = 0 20 Fce =- -30 * 40 + 400 Fce = 40 k ( C ) or Fce = 40 k ( T )
For Fbd taking moment at C. Fbd * 20 + 30 * 20 = 0 Fbd = - 30 ( T ) or 30 ( C )
For Fcd we take moment at B. Fcd y * 20 + Fce * 20 + 30 * 20 = 0 20 Fcd y = 200 Fcd y = 10 k ( C)
Fcd y = F cd * Sin 45 10 = Fcd * Sin 45
Fcd = 14.14 k
09CE37
62 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Here Equation of moment fails so we have apply direct method which is to apply equation of statics.
+ve Fy = 0
F gf + 30 = 0 F gf = - 30 ( C ) or 30 ( T )
09CE37
63 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
ARCHES
09CE37
64 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem 1 : 3 hinge parabolic arch of 20 ft and standardize of 5 caring a concentrate load of 20 kips at 6 from the left side support. Draw the bending moment diagram for the arch, position and magnitude of maximum bending moment for the arch also find the value of the reaction forces C 20 kips yc=5 A 20 ft DATA: Yc = 5 P = 20 kips L = 20 B.M = ? B
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha - Hb = 0, Ha = Hb +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 20* 6 Vb * 20 = 0 Vb = 6 kips R.H.S +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point C Vb * 10 + Hb * 5 = 0 Hb= 12 kips RESULTANT Ra = Ha2 + Va 2 18.44 kips Rb= Hb2 + Vb 2 13.4 kips as Hb=Ha , So , Ha = 12 kips putting this value in eq(i) Va = 14 kips +ve Fy = 0 Va + Vb = 20 ------ ( i )
09CE37
65 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
B.M max ( +ve ) Using Formula Y = 4 Yc ( L ) / L2 Y = 4 * 5* 6 ( 20 6 ) / (20)2 Y = 4 .2 s.ft
Va * 6 Ha * Y = 14 * 6 12 * 4.2
33. 6 k.ft
B.M max ( -ve ) Hb * Y Vb * --------------- (iii) Using Formula Y = 4 Yc ( L ) / L2 Y = 4 * 5 * ( 20 ) / L2 Y = - 2 / 20----(iv) putting Y value in equation (iii) 12 * ( 2 / 20) 6 * 12 12 2/20 6 6 12 2/20 Differentiating w.r.t = 5 p putting this value in eq (iv)
09CE37
Y = - 15
66 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem 2 : 3 hinge parabolic arch of 20 m and standardize of 4 m caring a concentrate U.D.L of 2 ton/m from the left side support over the length of 8 m . Draw the bending moment diagram for the arch, position and magnitude of maximum bending moment for the arch also find the value of the reaction forces
A DATA: Yc = 4 m P = 2 to / m L = 20 m B.M = ?
8m 20 m
Equilibrium, +ve Fx = 0, Ha - Hb = 0, Ha = Hb +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point A 16 * 4 Vb * 20 = 0 Vb = 3.2 t R.H.S +ve Clockwise M = 0 at point C Va * 16 + Ha * 4 16 * 6 = 0 Hb= 8 t RESULTANT Ra = Ha2 + Va 2 15.094 t Rb= Hb2 + Vb 2 8.61 t
09CE37 67 | P a g e
+ve Fy = 0 Va + Vb = 16 ------ ( i )
putting this value in eq(i)
Va = 12.8 t
as Hb=Ha , So ,
Ha = 8 t
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
B.M max ( +ve ) Va * Ha * Y 2 * * /2 -------- (v) Using Formula Y = 4 Yc ( L ) / L2 Y = 4 * 4 * ( 20 ) / (20)2 Y = 0.8 0.04 2 Putting Value of Y in eq ( v) B.M= 12.8 * 8 * ( 0.8 0.04 2 ) - 2 B.M = 12.8 6.4 + 0.32 2 2 B.M = 6.4 0.68 2 ---- ( vi) Differentiating w.r.t. 0 = 6.4 ( 0.68 ) ( 2 ) = 4.7 m from left hand side support Putting value of in eq ( vi ) B.M = 6.4 * 4.7 0.68 * ( 4.7)2 B.M ( max) = 15.05 t.m
09CE37
68 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
B.M max ( -ve ) Vb * Hb * Y --------------- (vii) Using Formula Y = 4 Yc ( L ) / L2 Y = 0.08 0.04 2 put in equation (vii) 3.2 * 8 * ( 0.8 2 0.04 2 ) B.M = - 3.2 + 0.32 2 ---------------- ( viii) Differentiating w.r.t 0 = - 3.2 + 0.64 =5m putting this value in eq (viii) B.M = -3.2 * 5 + 0.32 * ( 5 )2 = - 8 t.m
09CE37
69 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
COLUMNS
09CE37
70 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem 1 : 1.5 m long column and has a circular cross-section of 5m diameter one of the ends of the column is fixed and other end is free . Find the Rakiens formula and Find the Eulers Crippling load .
Assume: Rakiens Constant = 1 / 1600 Modulus of Elasticity : 1.2 x 106 kg / cm2 Crushing Stress = 5600 kg/cm2
Rakiens Formula: P = Fc * A / 1 + a ( L/K)2 DATA: L = 1.5 m = 150 cm E = 1.2 * 106 kg / cm2 fc= 5600 kg/cm2 Finding Area = / 4 (d)2 As one head is fixed = L = 2l Finding Inertia = / 64 (d)4 Finding K = i/A / 4 ( 5) 2 19.63 cm2 2 ( 150 ) 300 cm 3.14 / 64 ( 5) 2 30.67 cm4 , , d = 5 cm a = 1 / 1600 K = I /A
30.67 / 19.63 12.4 cm
Putting Value in formula P = 5600 * 19.63 / 1 + { 1 / 1600 ( 300 / 12.4 ) 2 } P = 2971.78 kg Finding Eulers Formula P = 2 E I / 4 L 2 ----------------------- As one end is fixed other is free P = (3.14)2 * (1.2 * 10 6) ( 30.67 ) / 4 ( 300 ) 2 P = 362.87 * 10 6 kg
09CE37
71 | P a g e
Theory of Structures
Sir Dr.Zubair
Problem 2 : A cast iron 3 m in length when hinged at both ends has a critical pickling load of P kilogram when the column is fixed at both the ends its critical load rises to P + 30,000 kilogram . if ratio of external diameter is 1.25 and E is equal to 1 * 10 6 . Determine the external and internal diameter of column.
L = 3000 cm
do/di = 1.25 do = 1.25 di
Load when both ends are hinged : P kg Load when both ends are fixed : P + 30,000 E = 1 * 10 6 Using Eulers theorem when both ends are hinged P = 2 E I / L 2 -------------------------- ( i ) Finding interia ( i) = i = / 64 ( do2 di2 ) Putting value of do i= / 64 ( 1.25 di )2 - ( di ) 2 i= / 64 ( 0.25 di ) 4 ----------------------------- (ii) putting value of i P=2EI/L2 in equation (i) P = 2 E ( / ( 0.25 di ) 4 ) / 64 * L 2 P = 3 (0.25 di) 4 -------------------------- (iii) L = l / 2 3000 / 2 1500 cm L =l
Using Eulers theorem when both ends are fixed. P + 30, 000 = 4 2 E I / L 2 Putting value of i P + 30 , 000 =
4 2 E { / ( 0.25 di ) 4 } / 64 * L 2 3 ( di ) 4
P + 30,000 = 3 ( di ) 4 ------------------------------ (iv) Putting value of P from eq (iii) into eq ( iv) 3 (0.25 di) 4 + 30,000 = 3 ( di ) 4
30,000 = ( 31 0.121 ) di4 Di = 5.58 cm as we know, do = 1.25 * di do = 7.5 cm
09CE37
72 | P a g e
También podría gustarte
- Structures Theory Textbook and Lecture NotesDocumento67 páginasStructures Theory Textbook and Lecture Notesjoyce_mabitasan67% (3)
- Area of Tension SteelDocumento13 páginasArea of Tension Steelnoli90Aún no hay calificaciones
- Reinforced Concrete Design Solution Manual 9th McCormacDocumento38 páginasReinforced Concrete Design Solution Manual 9th McCormacFerly May Zabala VillezaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - Elastic Behaviour of RC BeamsDocumento25 páginasChapter 2 - Elastic Behaviour of RC BeamsVincent NavaAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 9-Design and Analysis of Beams Bending in Both AxisDocumento18 páginasModule 9-Design and Analysis of Beams Bending in Both AxisRosechelle NodadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 4 Analysis & Design of Doubly-Reinforced BeamsDocumento12 páginasLesson 4 Analysis & Design of Doubly-Reinforced Beamsrose ann claveriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Double Integration MethodDocumento35 páginasDouble Integration MethodPuma Tychingco Rañeses96% (27)
- Structural Theory 1 (Part 1)Documento14 páginasStructural Theory 1 (Part 1)GinoOcampoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 5 Analysis and Design of T-Beams and Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocumento199 páginasChap 5 Analysis and Design of T-Beams and Doubly Reinforced BeamsSetsumii Shiizukaa50% (2)
- Double Integration MethodDocumento56 páginasDouble Integration MethodJigar Soni88% (8)
- 08 New Format Effective Stresses in SoilsDocumento3 páginas08 New Format Effective Stresses in SoilsHomer Batalao0% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Sample Problems PDFDocumento5 páginasReinforced Concrete Sample Problems PDFSevy100% (4)
- Lab No 8Documento5 páginasLab No 8LO Ver JG100% (1)
- Orifice QuestionsDocumento5 páginasOrifice QuestionsCamille Joy Cucio100% (1)
- RCCRDocumento154 páginasRCCRRommel Villaroman EstevesAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 5-PermeabilityDocumento2 páginasAssignment 5-Permeabilitytushar gautamAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam 2 StructuralDocumento20 páginasExam 2 StructuralMs. Engr100% (1)
- FLUID MECHANICS ENHANCEMENT REVIEWDocumento3 páginasFLUID MECHANICS ENHANCEMENT REVIEWᜎᜒᜌᜓᜈᜒᜎ᜔ ᜄ᜔ᜏᜇᜒᜈ᜔100% (1)
- Geotechnical Engineering Problem Set 2: SolutionsDocumento7 páginasGeotechnical Engineering Problem Set 2: SolutionsTabbyAún no hay calificaciones
- Structural Theory Lecture NotesDocumento151 páginasStructural Theory Lecture NotesCharizza Montarin CEAún no hay calificaciones
- Elementary Structural Analysis - by Wilbar NorrisDocumento349 páginasElementary Structural Analysis - by Wilbar Norrisajay72% (18)
- Properties of FluidsDocumento6 páginasProperties of Fluidsmon2x20% (1)
- Structural Framing SystemDocumento6 páginasStructural Framing SystemMelchor Jaramilla Oronos100% (3)
- Soil Weight-Volume RelationshipsDocumento60 páginasSoil Weight-Volume RelationshipsJonniel De Guzman100% (1)
- Steel Module 2 Part 1Documento33 páginasSteel Module 2 Part 1Pyro Villanueva100% (1)
- Soil Mechanics Problems on Compressibility and Shear StrengthDocumento4 páginasSoil Mechanics Problems on Compressibility and Shear Strengthrmle100% (1)
- Module 1Documento20 páginasModule 1John Aparicio100% (1)
- Geo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti DanDocumento13 páginasGeo - Technical Engineering Question Bank by MR Sukriti Dansukritidan1990100% (1)
- REINFORCED BEAM DESIGNDocumento18 páginasREINFORCED BEAM DESIGNrose ann claveriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Geotechnical Engineering ModuleDocumento5 páginasGeotechnical Engineering ModuleFeigyl Faith Lanit Miro100% (3)
- Hydraulics Geotech2Documento101 páginasHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ce Correl Soil Mechanics (A)Documento6 páginasCe Correl Soil Mechanics (A)Glenn Frey Layug100% (2)
- RCD Chapter 3Documento58 páginasRCD Chapter 3jereck loquisoAún no hay calificaciones
- Shear Strength SoilDocumento22 páginasShear Strength SoilJommarVocalTagalog100% (1)
- CE November 2016 Exams PDFDocumento46 páginasCE November 2016 Exams PDFAngela Mae Francisco100% (2)
- Chapter 3 T BeamDocumento31 páginasChapter 3 T BeamEarl Rajim RiogelonAún no hay calificaciones
- List of Symbols. ap Ca Cp Ct Cv Fp Ft hn I Na Nv R Rp S T V W Z Ωo ΔsDocumento20 páginasList of Symbols. ap Ca Cp Ct Cv Fp Ft hn I Na Nv R Rp S T V W Z Ωo ΔsAnton_Young_1962Aún no hay calificaciones
- Besavilla Past Board Exam Past Board Exam Bookspdf Free Civil Engineering Board PDFDocumento2 páginasBesavilla Past Board Exam Past Board Exam Bookspdf Free Civil Engineering Board PDFLuz MirasolAún no hay calificaciones
- EXAMPLE Cantilever MethodDocumento11 páginasEXAMPLE Cantilever MethodNany Nektod100% (7)
- Mech 2Documento82 páginasMech 2Erwin100% (1)
- Module 7-Combined Axial and BendingDocumento55 páginasModule 7-Combined Axial and BendingPeter Harold Maducdoc67% (3)
- Timber Design ReviewDocumento4 páginasTimber Design ReviewRoben Casano78% (9)
- PROBLEM 3.120: SolutionDocumento10 páginasPROBLEM 3.120: SolutionPedro Noe CMAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3, Solution 136.: COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization SystemDocumento4 páginasChapter 3, Solution 136.: COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization Systemmiguel_maahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 18Documento260 páginasChapter 18Gabriela Sequeira100% (1)
- Iit Jee 2012 Paper2-Final SolnDocumento8 páginasIit Jee 2012 Paper2-Final Solnvarun303gr8Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vector and force calculationsDocumento7 páginasVector and force calculationsjhanedAún no hay calificaciones
- MechanicalDocumento36 páginasMechanicalAyale MnAún no hay calificaciones
- Precalculus ch4 ReviewDocumento3 páginasPrecalculus ch4 Reviewapi-213604106Aún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis Struktur Portal Tiga SendiDocumento17 páginasAnalisis Struktur Portal Tiga SendiWidayat AbzarihAún no hay calificaciones
- Solution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Documento18 páginasSolution of Engineering Mechanics For UCER Students 1995976039Gulshan KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- IIT-JEE-2011 Chemistry Paper Ii Solution Paper Code 4: Detailed AnswersDocumento10 páginasIIT-JEE-2011 Chemistry Paper Ii Solution Paper Code 4: Detailed Answerssanits591Aún no hay calificaciones
- Most Important Question Cbse X AnsDocumento29 páginasMost Important Question Cbse X AnsSoniya LullaAún no hay calificaciones
- University of Basrah: Collage of Engineering Petroleum DepartmentDocumento6 páginasUniversity of Basrah: Collage of Engineering Petroleum DepartmentNarjes WalidAún no hay calificaciones
- Mec Rac Mer Cap 03Documento7 páginasMec Rac Mer Cap 03Ricardo PilcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 3.138Documento2 páginasEjercicio 3.138EDWIN-GARCIA100% (1)
- Reactor WorkDocumento13 páginasReactor WorkMalak HindiAún no hay calificaciones
- Dynamics - Solutions Chapter R2Documento40 páginasDynamics - Solutions Chapter R2holverson2Aún no hay calificaciones
- ME101 Tutorial 03 Solution PDFDocumento13 páginasME101 Tutorial 03 Solution PDFalex albAún no hay calificaciones
- C++ Basic NotesDocumento44 páginasC++ Basic NotesDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Soil Mechanics PracticalDocumento35 páginasSoil Mechanics PracticalDarya Memon100% (1)
- Lec # 48 Composting of MSWDocumento36 páginasLec # 48 Composting of MSWDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 39 Hazardous WasteDocumento8 páginasLec # 39 Hazardous WasteDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Green House Effect and Global WarmingDocumento8 páginasGreen House Effect and Global WarmingDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 40 Hazardous WastesDocumento92 páginasLec # 40 Hazardous WastesDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ozone Layer Depletion, Its Causes and Its EffectsDocumento24 páginasOzone Layer Depletion, Its Causes and Its EffectsDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 51 A.pollution and Its Effects and SourcesDocumento21 páginasLec # 51 A.pollution and Its Effects and SourcesDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 52 Ozone and Fine Particles Effect and FormationDocumento13 páginasLec # 52 Ozone and Fine Particles Effect and FormationDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 52 Noise Pollution and Effects of Noise PollutionDocumento11 páginasLec # 52 Noise Pollution and Effects of Noise PollutionDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 52 Air and Noise PollutionDocumento34 páginasLec # 52 Air and Noise PollutionDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec # 28-29 Solid Waste and Its ImpactDocumento37 páginasLec # 28-29 Solid Waste and Its ImpactDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 FlownetsDocumento23 páginas4 FlownetsDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Drainage and Design of Drainage System-1Documento65 páginasDrainage and Design of Drainage System-1Darya Memon100% (2)
- Green House Effect, Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocumento25 páginasGreen House Effect, Global Warming and Climate ChangeDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 5-Runoff and Factors Affecting ....Documento30 páginas5-Runoff and Factors Affecting ....Darya Memon95% (20)
- AcidRain and Its EffectDocumento29 páginasAcidRain and Its EffectDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Hydraulic ConductivityDocumento31 páginas7 Hydraulic ConductivityDarya Memon100% (2)
- 7 HydrographDocumento6 páginas7 HydrographDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 5-Hydraulic Boundary ConditionsDocumento12 páginas5-Hydraulic Boundary ConditionsDarya Memon100% (1)
- 3-GW Flow EquationsDocumento7 páginas3-GW Flow EquationsDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 6-Water LoggingDocumento11 páginas6-Water LoggingDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-Volume Elasticity of AquifersDocumento13 páginas2-Volume Elasticity of AquifersDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 - Computation of RunoffDocumento19 páginas6 - Computation of RunoffDarya Memon100% (3)
- 1-Darcy's LawDocumento25 páginas1-Darcy's LawDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 3-Measurement of RainfallDocumento14 páginas3-Measurement of RainfallDarya Memon100% (1)
- 8 - Estimation of Peak Flood DischargeDocumento29 páginas8 - Estimation of Peak Flood DischargeDarya Memon89% (9)
- 2-Hydrologic Cycle and PrecipitationDocumento18 páginas2-Hydrologic Cycle and PrecipitationDarya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- 4-Computation of Average RainfallDocumento15 páginas4-Computation of Average RainfallDarya Memon100% (9)
- Class 16Documento8 páginasClass 16Darya MemonAún no hay calificaciones
- Aga 3 - 2000 RevisionDocumento57 páginasAga 3 - 2000 RevisionAnonymous XV4AlTzUAún no hay calificaciones
- Iec 60287-2-3-2017Documento54 páginasIec 60287-2-3-2017xandergadielAún no hay calificaciones
- Gazetas 1991Documento41 páginasGazetas 1991RAUL HANDERAún no hay calificaciones
- Mechanical Supervisor Vol 4Documento62 páginasMechanical Supervisor Vol 4AyanAnandAún no hay calificaciones
- Enhancement of Heat Transfer Coefficient Through Helical CoilDocumento5 páginasEnhancement of Heat Transfer Coefficient Through Helical CoilNaqqash SajidAún no hay calificaciones
- Hargreaves 2007Documento15 páginasHargreaves 2007Sam GonçalvesAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermal Engineering-CondenserDocumento17 páginasThermal Engineering-CondenserJayAún no hay calificaciones
- Vol 11 No 1 P 31Documento9 páginasVol 11 No 1 P 31viswamanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Air MixingDocumento2 páginasAir MixingJom SanzAún no hay calificaciones
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark QuestionsDocumento43 páginasMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Syllabus, 2&16 Mark Questionsdellibabu509Aún no hay calificaciones
- HCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP2 MergedDocumento29 páginasHCUY CE17 (Hydraulics) LP2 MergedGleanna NiedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsDocumento50 páginasLecture 3-1 - Heat Exchanger CalculationsBilal AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- TOS 5 Unit 2a Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsDocumento7 páginasTOS 5 Unit 2a Design of Doubly Reinforced BeamsKshitija100% (1)
- Review - Structural AnalysisDocumento31 páginasReview - Structural AnalysisShayne Rose OrtegaAún no hay calificaciones
- KS3 States of Matter Practice Exam QuestionsDocumento5 páginasKS3 States of Matter Practice Exam Questionsgzm yldz0% (1)
- Strength of Materials ExamDocumento1 páginaStrength of Materials ExamAndrew PortugalAún no hay calificaciones
- Fan Coil 3rowsDocumento1 páginaFan Coil 3rowsJunior VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Modeling of The Yield Strength of A Stainless Maraging SteelDocumento4 páginasModeling of The Yield Strength of A Stainless Maraging SteelFernando HenriqueAún no hay calificaciones
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSDocumento13 páginasKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DEHRADUN REGION SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER (2022-23) CLASS XI PHYSICSAmythAún no hay calificaciones
- All Sheets ConcreteDocumento72 páginasAll Sheets ConcreteSulaiman Mohsin AbdulAziz100% (1)
- Flow Measurement Lecture 1Documento37 páginasFlow Measurement Lecture 1Rahul KalraAún no hay calificaciones
- Resonant Behaviour of Base-Isolated High-Rise Buildings Under Long-Period Ground MotionsDocumento14 páginasResonant Behaviour of Base-Isolated High-Rise Buildings Under Long-Period Ground MotionstrimenoneAún no hay calificaciones
- Steel Bearing PlatesDocumento4 páginasSteel Bearing Platessebastian9033Aún no hay calificaciones
- Brinch Hansens MethodDocumento5 páginasBrinch Hansens MethodahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- ExtraProbPhys2Ch2 HeatTempLaw0Documento3 páginasExtraProbPhys2Ch2 HeatTempLaw0NaHuynJungAún no hay calificaciones
- Amende 2007Documento6 páginasAmende 2007Warren PuthAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch-2-2 Thermal Power PlantDocumento48 páginasCh-2-2 Thermal Power Planthussen belewAún no hay calificaciones
- Antoine EquationDocumento2 páginasAntoine EquationAlfrets Marade SianiparAún no hay calificaciones
- The Effects of Geometric, Flow, and Boiling Parameters On Bubble Growth and Behavior in Subcooled Flow Boiling PDFDocumento242 páginasThe Effects of Geometric, Flow, and Boiling Parameters On Bubble Growth and Behavior in Subcooled Flow Boiling PDFLuthfi Ady Farizan HaryokoAún no hay calificaciones