Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
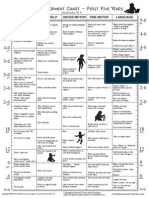
Chart - Summary of Stages of Child Development: Compares Piaget and Erikson
Cargado por
lwood06Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Chart - Summary of Stages of Child Development: Compares Piaget and Erikson
Cargado por
lwood06Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Comparative Summary of Child Development
Piaget (cognitive) and Erikson (social/emotional)
Ages birth through twelve+
Piaget Erikson
Birth – 2 years Sensory-motor Stage Trust Vs. Mistrust (bonding)
Birth to 2 years Birth to 1 year
Reflex physical action physical needs are met and the
repeats and learns to control baby then learns to trust
imitation of actions and ◦ crying, smiling, cooing,
sounds reaching
repetition ◦ parents receptive
social interaction reliable
gain control of physical “warm” interactions w/adults
movements safe
object permanence basis for hope
2 – 7 years Pre-operational Stage Autonomy vs. Shame and doubt
2-7 years 1 to 3 years (toddlers)
egocentric given the emotional support,
perception based thinking they are free to explore
symbolic play physically on their own (do it
generalize in illogical ways by myself...)
animism adults support rather than fuss
artificialism when accidents happen
perpetual motion stage
potty training
starting to talk and explore
their world.
Initiative and belonging vs.Guilt and
alienation
3 and 4 years
language development is key
for interactions & initiative
their questions are looking for
“purpose of” answers
parallel play, then cooperative
play
importance of frames
7-11 years Concrete Operational Industry and competence vs.
7-11 years Inferiority and helplessness
reversibility 5-11 years
conservation ages 5-7ish play still important
transitivity/ unit for learning
sense/concept begin to develop work habits
logical thinking (post competence
concrete and pre-abstract) manipulative & fundamental
classify and categorize learning
rules enjoy global, permeable,
social cooperation hands-on, learning
like skills & facts (trivia)
social comparison
need to feel
success/accomplishments/achi
evements (but have to be true
ones)
12 - 18 Formal Operational Stage Identity vs. role confusion
11+ 12-18 years
abstract thinking Social Identity (Who am I?)
hypothetical gender development reemerges
bigger world because they delineation of identity separate
are able to have broader from parents begins
ideas create and identify values
También podría gustarte
- Human Growth and Development TheoriesDocumento8 páginasHuman Growth and Development TheoriesThuganamix86% (29)
- Stages of Child Development and The Importance of PlayDocumento12 páginasStages of Child Development and The Importance of Playlwood06100% (5)
- Developmental Milestones ChartDocumento13 páginasDevelopmental Milestones ChartPsydoc100% (3)
- Child Development Milestone Chart: Birth to 6 YearsDocumento2 páginasChild Development Milestone Chart: Birth to 6 YearsWheng Alcabedas100% (11)
- Understanding Children's DevelopmentDocumento65 páginasUnderstanding Children's DevelopmentDoodah2100% (9)
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento23 páginasDevelopmental Milestonesshh_ayye100% (1)
- Growth and Development of ChildDocumento58 páginasGrowth and Development of ChildBasant karn100% (51)
- Milestone Chart For BabiesDocumento8 páginasMilestone Chart For BabiesKaypee BorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento4 páginasDevelopmental Milestonesdomskun18100% (1)
- Primitive ReflexesDocumento3 páginasPrimitive ReflexesMio NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Child Development ChartDocumento1 páginaChild Development ChartDevelopmentChart100% (4)
- Understanding Child Development StagesDocumento6 páginasUnderstanding Child Development StagesdomikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento3 páginasDevelopmental MilestonesCharis Mae Dimaculangan0% (2)
- PD Sensory Room TrainingDocumento35 páginasPD Sensory Room Trainingapi-393264699Aún no hay calificaciones
- Reflex Testing Method For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentDocumento55 páginasReflex Testing Method For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentPJHG100% (6)
- Child Development TheoristsDocumento19 páginasChild Development TheoristsFady Jehad ZabenAún no hay calificaciones
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders GuideDocumento45 páginasNeurodevelopmental Disorders Guidenico ValenzonaAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrating NDT and SI-Theory and PracticeDocumento7 páginasIntegrating NDT and SI-Theory and PracticePaulinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Preschool Developmental MilestonesDocumento21 páginasPreschool Developmental MilestonesOnika75% (4)
- Sensory History QuestionnaireDocumento6 páginasSensory History Questionnaireİpek OMUR100% (1)
- Milestone FinalDocumento21 páginasMilestone FinalFransric TinampayAún no hay calificaciones
- Principles of Growth and DevelopmentDocumento15 páginasPrinciples of Growth and DevelopmentAbigail MangaoangAún no hay calificaciones
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento14 páginasDevelopmental MilestonessilverapAún no hay calificaciones
- Child Development: Prof. Rachelle Gay R. Pacial, MSN, RN Saint Louis University School of NursingDocumento26 páginasChild Development: Prof. Rachelle Gay R. Pacial, MSN, RN Saint Louis University School of NursingRachelle Gay PacialAún no hay calificaciones
- Sensory Processing BrochureDocumento3 páginasSensory Processing Brochureapi-383884645Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tactile Defensiveness PDFDocumento7 páginasTactile Defensiveness PDFCristi BacuAún no hay calificaciones
- Prevalence of Dyslexia Among Primary School ChildrenDocumento19 páginasPrevalence of Dyslexia Among Primary School ChildrenJubie MathewAún no hay calificaciones
- Child Development Milestone ChartDocumento21 páginasChild Development Milestone ChartPhilip SimanganAún no hay calificaciones
- Primitive Reflexes and How They Affect PerformanceDocumento3 páginasPrimitive Reflexes and How They Affect Performancemohitnet1327100% (1)
- Denver Developmental Screening TestDocumento5 páginasDenver Developmental Screening Testrampy86100% (1)
- Cranial Nerve Assessment GuideDocumento5 páginasCranial Nerve Assessment GuideBAdz TanAún no hay calificaciones
- Stages of Growth & DevelopmentDocumento2 páginasStages of Growth & DevelopmentRamlah Idris100% (7)
- Piaget Stage of DevelopmentDocumento5 páginasPiaget Stage of Developmentjedisay1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Psychosocial DevelopmentDocumento68 páginasPsychosocial DevelopmentDonita BinayAún no hay calificaciones
- Infant ReflexesDocumento41 páginasInfant ReflexesamwriteaAún no hay calificaciones
- Classic Reflex Hierarchy and ReflexesDocumento8 páginasClassic Reflex Hierarchy and ReflexesJaclyn ArpinAún no hay calificaciones
- Sensory Processing PowerpointDocumento39 páginasSensory Processing Powerpointitikjawa100% (2)
- Cognitive TheoryDocumento14 páginasCognitive TheoryRiya Joy100% (4)
- Growth and Development of ChildrenDocumento144 páginasGrowth and Development of ChildrenShihon Dml100% (1)
- Five Domains For Early Childhood DevelopmentDocumento57 páginasFive Domains For Early Childhood Developmentemil_masagca1467100% (1)
- Primitive ReflexesDocumento3 páginasPrimitive Reflexesicrs_aamirAún no hay calificaciones
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento22 páginasDevelopmental MilestonesSillmark Bacason100% (3)
- Newborn ReflexesDocumento35 páginasNewborn ReflexesCitra Dwi Lestari100% (1)
- The 4 Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocumento10 páginasThe 4 Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDevera GinalynAún no hay calificaciones
- Physical and Motor Development of Children and AdolescentsDocumento4 páginasPhysical and Motor Development of Children and AdolescentsTenIs ForMeAún no hay calificaciones
- Developmental MilestonesDocumento8 páginasDevelopmental Milestones3aces100% (1)
- Developmental AssessmentDocumento13 páginasDevelopmental AssessmentIsaac Tan100% (1)
- Play is Essential for Child DevelopmentDocumento8 páginasPlay is Essential for Child Developmentmarkus_danusantosoAún no hay calificaciones
- A Powerpoint Presentation On The Autism SpectrumDocumento16 páginasA Powerpoint Presentation On The Autism SpectrumJane GilgunAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 - Study of Human DevlopmentDocumento10 páginasChapter 1 - Study of Human DevlopmentfuqthisAún no hay calificaciones
- A Review of Pediatric Assessment Tools For Sensory Integration AOTADocumento3 páginasA Review of Pediatric Assessment Tools For Sensory Integration AOTAhelenzhang888Aún no hay calificaciones
- Primitive Reflexes in New Born DevelopmentDocumento4 páginasPrimitive Reflexes in New Born DevelopmentSadaf RizwanhumayoonAún no hay calificaciones
- Brochure !Documento2 páginasBrochure !api-291329856Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cerebral Palsy and EducationDocumento14 páginasCerebral Palsy and EducationDatin Lianawati IdayuAún no hay calificaciones
- Behavior-Checklist StudentReferralLetterDocumento4 páginasBehavior-Checklist StudentReferralLetterAna MallariAún no hay calificaciones
- Home Plan For Hemiplegic CPDocumento13 páginasHome Plan For Hemiplegic CPMaira PervezAún no hay calificaciones
- Making Sense Sensory Processing Disorder103114Documento61 páginasMaking Sense Sensory Processing Disorder103114Branislava Jaranovic Vujic100% (5)
- Theory BheDocumento4 páginasTheory BheKhryss Paula BaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Go To Page Word 2022 CompleteDocumento17 páginasGo To Page Word 2022 Completeapi-659980878Aún no hay calificaciones
- SW GDLoader GettingStarted v3-0 enDocumento41 páginasSW GDLoader GettingStarted v3-0 enEduardo QuispeAún no hay calificaciones
- "Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of TortsDocumento4 páginas"Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of Tortsaridaman raghuvanshiAún no hay calificaciones
- 015-Using Tables in ANSYSDocumento4 páginas015-Using Tables in ANSYSmerlin1112255Aún no hay calificaciones
- Inbound Delivery ProcessDocumento5 páginasInbound Delivery ProcessDar Pinsor50% (2)
- Voice of The RainDocumento4 páginasVoice of The RainShriya BharadwajAún no hay calificaciones
- Well Logging 1Documento33 páginasWell Logging 1Spica FadliAún no hay calificaciones
- Summary and RecommendationsDocumento68 páginasSummary and Recommendationssivabharathamurthy100% (2)
- Cost-effective laboratory thermostats from -25 to 100°CDocumento6 páginasCost-effective laboratory thermostats from -25 to 100°CCynthia MahlAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementDocumento24 páginasChapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementEsmira Melić ŠutkovićAún no hay calificaciones
- The Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasDocumento10 páginasThe Benefits of Radio Broadcasting As Perceived by The People in Rural AreasMaeAún no hay calificaciones
- SPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseDocumento2 páginasSPM Literature in English Tips + AdviseJessica NgAún no hay calificaciones
- Newsletter April.Documento4 páginasNewsletter April.J_Hevicon4246Aún no hay calificaciones
- Controversial Aquatic HarvestingDocumento4 páginasControversial Aquatic HarvestingValentina RuidiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Differential Aptitude TestsDocumento2 páginasDifferential Aptitude Testsiqrarifat50% (4)
- Constructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersDocumento32 páginasConstructed Wetland Design Guidelines for DevelopersBere QuintosAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Environmental Science For A Changing World Canadian 1St Edition by Branfireun Karr Interlandi Houtman Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasTest Bank For Environmental Science For A Changing World Canadian 1St Edition by Branfireun Karr Interlandi Houtman Full Chapter PDFelizabeth.martin408100% (16)
- IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. COM-34, NO. 5 , MAY 1986A BPSK/QPSK Timing-Error DetectorDocumento7 páginasIEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. COM-34, NO. 5 , MAY 1986A BPSK/QPSK Timing-Error DetectorFahmi MuradAún no hay calificaciones
- Detection of Self-Mutating Computer VirusesDocumento17 páginasDetection of Self-Mutating Computer VirusesVMads3850Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aspen TutorialDocumento33 páginasAspen TutorialSarah RasheedAún no hay calificaciones
- SplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFDocumento103 páginasSplunkCloud-6 6 3-SearchTutorial PDFanonymous_9888Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyDocumento4 páginasVocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyRosa MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideDocumento84 páginasFractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideSassie LadyAún no hay calificaciones
- Alphabet of LinesDocumento46 páginasAlphabet of LinesNancy Cordero AmbradAún no hay calificaciones
- Critical Thinking Portfolio AssignmentDocumento8 páginasCritical Thinking Portfolio Assignmentapi-334295481Aún no hay calificaciones
- Developing and Validating a Food Chain Lesson PlanDocumento11 páginasDeveloping and Validating a Food Chain Lesson PlanCassandra Nichie AgustinAún no hay calificaciones
- K-12 Grade 9 Science Roll Roll AwayDocumento20 páginasK-12 Grade 9 Science Roll Roll AwayMeya Jhana Navidad75% (8)
- (Genus - Gender in Modern Culture 12.) Segal, Naomi - Anzieu, Didier - Consensuality - Didier Anzieu, Gender and The Sense of Touch-Rodopi (2009)Documento301 páginas(Genus - Gender in Modern Culture 12.) Segal, Naomi - Anzieu, Didier - Consensuality - Didier Anzieu, Gender and The Sense of Touch-Rodopi (2009)Anonymous r3ZlrnnHcAún no hay calificaciones
- The Cultural Diversity Phenomenon in Organisations and Different Approaches For Effective Cultural Diversity Management - A Literary Review PDFDocumento21 páginasThe Cultural Diversity Phenomenon in Organisations and Different Approaches For Effective Cultural Diversity Management - A Literary Review PDFeugene123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cbcs Syllabus 2016-17 Admn Batch 30.07.16Documento23 páginasCbcs Syllabus 2016-17 Admn Batch 30.07.16Sushree sonali NayakAún no hay calificaciones
- Soft Start - Altistart 48 - VX4G481Documento2 páginasSoft Start - Altistart 48 - VX4G481the hawakAún no hay calificaciones