Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Wheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature Etc
Cargado por
r005w3lt0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
9 vistas6 páginasWheatstone's bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown resistance (Rx) by balancing the bridge until the current (IG) is zero. When balanced, R2 is adjusted to cancel out Rx, allowing Rx to be calculated if the bridge is unbalanced. Strain gauges, which are thin wire conductors glued to an object, are a common application and work by changing resistance when force is applied, unbalancing the bridge. Strain gauge measurements involve balancing the bridge with no force and measuring the voltage change when a force is applied. Different strain gauge configurations like having dummy gauges or full bridges can improve sensitivity.
Descripción original:
9
Título original
ELT M1 S14 - 9
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoWheatstone's bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown resistance (Rx) by balancing the bridge until the current (IG) is zero. When balanced, R2 is adjusted to cancel out Rx, allowing Rx to be calculated if the bridge is unbalanced. Strain gauges, which are thin wire conductors glued to an object, are a common application and work by changing resistance when force is applied, unbalancing the bridge. Strain gauge measurements involve balancing the bridge with no force and measuring the voltage change when a force is applied. Different strain gauge configurations like having dummy gauges or full bridges can improve sensitivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
9 vistas6 páginasWheatstone's Bridge: Typical Applications: Strain Gauges (Stress Measurements), Temperature Etc
Cargado por
r005w3ltWheatstone's bridge is a circuit used to measure an unknown resistance (Rx) by balancing the bridge until the current (IG) is zero. When balanced, R2 is adjusted to cancel out Rx, allowing Rx to be calculated if the bridge is unbalanced. Strain gauges, which are thin wire conductors glued to an object, are a common application and work by changing resistance when force is applied, unbalancing the bridge. Strain gauge measurements involve balancing the bridge with no force and measuring the voltage change when a force is applied. Different strain gauge configurations like having dummy gauges or full bridges can improve sensitivity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 6
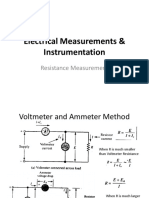
Wheatstones Bridge
Rx unknown to be measured. If R2 is variable
this can be changed until IG=0 A -the bridge is
then called balanced, thus
If R2 is not variable the current flow and
voltage difference can be used to calculate the
value of Rx (bridge unbalanced)
Typical applications: Strain gauges (stress measurements), temperature etc.
Strain gauges
Smaller than a poststamp and very thin glued onto the element to be measured
Conductor a thin wire app. 0,02-0,03 mm in diameter
Typical resistance values from 30 to 3 k (unstressed)
Strain gauge base type
Strain gauge measurement at its simplest form:
With no forces applied the reading of V-meter is zero (bridge balanced)
With forces applied strain gauge resistance will either decrease or increase, thus
unbalancing the bridge and producing a reading on the V-meter.
Strain gauge different types
With wire resistance put on
(Inaccuracy due to temperature changes)
With wire resistance put on
Inaccuracy partly eliminated with separate
wire to V-meter (top wire bypassed)
Strain gauge different types
With dummy strain gauge put on
(identical strain gauges) only one strain
gauge active
With wire resistance put on
Wire resistance tends now to be cancelled
due to same resistance in strings
Strain gauge different types
With all applied strain gauges made active the system will be more responsive/sensitive to
the applied force either by a half-bridge configuration and even a full bridge configuration
También podría gustarte
- LAB # 12 Wheatstone Bridge and Ohmmeter: ObjectiveDocumento3 páginasLAB # 12 Wheatstone Bridge and Ohmmeter: ObjectiveSardar Hamid ullahAún no hay calificaciones
- 1a-Sensor Resistif-1 PDFDocumento45 páginas1a-Sensor Resistif-1 PDFSat SatrioAún no hay calificaciones
- R1 and R2 Are Variable Resistors in The Wheatstone Bridge ExperimentDocumento1 páginaR1 and R2 Are Variable Resistors in The Wheatstone Bridge ExperimentBerk DağAún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone AbDocumento10 páginasWheatstone AbkartheesanvAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3Documento124 páginasChapter 3Endalk SimegnAún no hay calificaciones
- WheitStone Bridge For Temperature MeasurementDocumento6 páginasWheitStone Bridge For Temperature MeasurementrajeshAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 3Documento6 páginasUnit 3dhub324Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 eDocumento50 páginasChapter 3 eEndalk SimegnAún no hay calificaciones
- Stain Gage Measurements YsDocumento9 páginasStain Gage Measurements YsAnonymous RJtBknAún no hay calificaciones
- The Basic Bridge CircuitDocumento8 páginasThe Basic Bridge CircuitMuhammad QasimAún no hay calificaciones
- RecoveredDocumento33 páginasRecoveredmahmoudsaeb10Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 9Documento16 páginasLecture 9Aravindan SivanandanAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit IIDocumento67 páginasUnit IIonhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Principle of The Strain GaugeDocumento6 páginasPrinciple of The Strain Gaugeapi-3706095100% (1)
- Loadcells Quarter Half and Full BridgeDocumento25 páginasLoadcells Quarter Half and Full BridgeCharles le MagneAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT-2: Strain GaugesDocumento51 páginasUNIT-2: Strain GaugesRafi Rebal ShaikAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 FinalDocumento15 páginasChapter 2 FinalPandimadevi SelvakumarAún no hay calificaciones
- EIM Manual 6 Wheatstone BrdigeDocumento9 páginasEIM Manual 6 Wheatstone BrdigeMaha RaufAún no hay calificaciones
- M&I UNIT III Notes - Downloaded From EEEexclusive - BlogspotDocumento8 páginasM&I UNIT III Notes - Downloaded From EEEexclusive - BlogspotJi La BaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Three-Wire Quarter-Bridge CircuitDocumento4 páginasThe Three-Wire Quarter-Bridge CircuitNoita EnolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Measurements & Instrumentation: Resistance MeasurementDocumento35 páginasElectrical Measurements & Instrumentation: Resistance MeasurementNikeREVIEWSAún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone BridgeDocumento7 páginasWheatstone BridgeSilvio MadetyAún no hay calificaciones
- Potentiometer PDFDocumento59 páginasPotentiometer PDFRajaa HusseinAún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone BridgeDocumento8 páginasWheatstone BridgeThiaga RajanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3Documento123 páginasChapter 3SriramAún no hay calificaciones
- Bef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeDocumento19 páginasBef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeMuhammad Izz IzzuddinAún no hay calificaciones
- Duo Range Type PotentiometerDocumento19 páginasDuo Range Type Potentiometersaikarthick023Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone BridgeDocumento16 páginasWheatstone Bridgedivyansh0% (1)
- LU1.2.Use Basic Electric MetersDocumento23 páginasLU1.2.Use Basic Electric Metersnguemaabraham1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone Bridge: Operational AmplifiersDocumento8 páginasWheatstone Bridge: Operational AmplifiersNida KhairiyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Wheatstone BridgeDocumento6 páginasWheatstone BridgeaniketkadekarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ece014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 3Documento10 páginasEce014 - Electronics 3 - Experiment 3John Wilfredd CurimoAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Instrumentation - Bridge CircuitsDocumento17 páginas3 Instrumentation - Bridge CircuitsWanjala WilliamAún no hay calificaciones
- S2 Temperature SensorsDocumento3 páginasS2 Temperature SensorsAnonymous AK2M4TE4Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Wire Quarter Bridge Circuit PDFDocumento3 páginas3 Wire Quarter Bridge Circuit PDFJosé GomesAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsDocumento21 páginasAnalog Electrical Devices and MeasurementsGabriel MarzinottoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mi Unit - IiiDocumento54 páginasMi Unit - IiiJayaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Three-Wire Quarter-Bridge Circuit: Strain Gages and InstrumentsDocumento4 páginasThe Three-Wire Quarter-Bridge Circuit: Strain Gages and InstrumentsCesar Adolfo Ortega VivasAún no hay calificaciones
- Resistance Measurement and Digital MultimeterDocumento10 páginasResistance Measurement and Digital Multimetervipranshu0308Aún no hay calificaciones
- BTMR1313 Assignment: Department of Electrical &electronic Engineering Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocumento9 páginasBTMR1313 Assignment: Department of Electrical &electronic Engineering Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyKAI ZHI LIMAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Documento41 páginasElectrical and Electronics Measurement 4th Sem B.Tech.Saksham KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement Sensors and InstrumentDocumento60 páginasMeasurement Sensors and InstrumentKarthik MathavenAún no hay calificaciones
- Potential Dividers: You Will Be Familiar With The Use of A Variable Resistor To Vary CurrentDocumento16 páginasPotential Dividers: You Will Be Familiar With The Use of A Variable Resistor To Vary CurrentMuhammad Amirul AkbarAún no hay calificaciones
- MR - KK PhyDocumento25 páginasMR - KK PhychaitupcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Multimeter - Basic GuideDocumento4 páginasDigital Multimeter - Basic GuidetowfiqeeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Temperature Detectors Temperature Detection Circuitry: Balanced Bridge CircuitDocumento1 páginaTemperature Detectors Temperature Detection Circuitry: Balanced Bridge CircuitharizazrinoordinAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 Electrodynamic SP21Documento29 páginas05 Electrodynamic SP21Luckily LuckyAún no hay calificaciones
- An117-Basic Bridge CircuitsDocumento6 páginasAn117-Basic Bridge Circuitsmsdn12000Aún no hay calificaciones
- Current Voltage MeasurementDocumento35 páginasCurrent Voltage MeasurementAaqib AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTDocumento7 páginasLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRajeev ValunjkarAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment No - Measurement of ResistanceDocumento5 páginasExperiment No - Measurement of ResistanceAppu ParoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Temperature Control Utilizing SSRDocumento2 páginasTemperature Control Utilizing SSRAtakan OzturKAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement TipsDocumento14 páginasMeasurement TipsFarah DianaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter OneDocumento12 páginasChapter OneSofiyat AbdulrasakAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement of ResistanceDocumento20 páginasMeasurement of ResistanceWanjala WilliamAún no hay calificaciones
- Student Notes On (Wheatstone Bridge)Documento7 páginasStudent Notes On (Wheatstone Bridge)rajeevAún no hay calificaciones
- Strain Gauge Presentation PPTXDocumento32 páginasStrain Gauge Presentation PPTXArun Raja K KAún no hay calificaciones
- Capacitor Transient Response RC Circuits ExamplesDocumento10 páginasCapacitor Transient Response RC Circuits Examplesr005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Independent Voltage SourceDocumento10 páginasIndependent Voltage Sourcer005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Blooms TaxonomyDocumento22 páginasBlooms Taxonomyr005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Recap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - PowerDocumento17 páginasRecap: - The Coulomb Force (Fundamental Force) - Voltage - Ohm's Law - Resistance - Powerr005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Mme M1: Lesson 8Documento17 páginasMme M1: Lesson 8r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Mme M1: Lesson 7Documento23 páginasMme M1: Lesson 7r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Mme M1: Lesson 6Documento17 páginasMme M1: Lesson 6r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Mme M1: Lesson 4Documento19 páginasMme M1: Lesson 4r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- L3Documento22 páginasL3r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Mme M1: Lesson 2Documento24 páginasMme M1: Lesson 2r005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th MarchDocumento1 páginaAssignment MME # 1 To Be Handed in Tuesday 11'th Marchr005w3ltAún no hay calificaciones