Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Ranking de Competitividad Perú
Cargado por
Carlos Alexander Espinoza HDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ranking de Competitividad Perú
Cargado por
Carlos Alexander Espinoza HCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
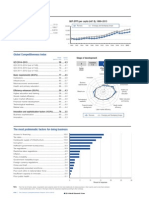
2: Country/Economy Profiles
Peru
Key indicators, 2014
GDP (PPP) per capita (intl $), 19902014
Population (millions) ........................................ 31.4
GDP (US$ billions) ........................................ 202.9
GDP per capita (US$) ................................... 6,458
GDP (PPP) as share (%) of world total ............ 0.34
Peru
20,000
Latin America and the Caribbean
15,000
10,000
5,000
0
Global Competitiveness Index
Rank
(out of 140)
Score
(17)
Institutions
7
Innovation
GCI 20152016 ...................................................... 69 ..... 4.2
GCI 20142015 (out of 144) ..................................... 65 ......4.2
GCI 20132014 (out of 148) ..................................... 61 ......4.3
GCI 20122013 (out of 144) ..................................... 61 ......4.3
Infrastructure
6
5
Business
sophistication
Macroeconomic
environment
4
3
2
Basic requirements (40.0%) .......................................76 ......4.5
Market size
1st pillar: Institutions ............................................... 116 ......3.3
2nd pillar: Infrastructure ............................................ 89 ......3.5
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic environment .................... 23 ......5.9
4th pillar: Health and primary education ................. 100 ......5.3
Health and
primary
education
Higher education
and training
Technological
readiness
Financial market
development
Efficiency enhancers (50.0%) .....................................60 ......4.2
Goods market
efficiency
Labor market efficiency
5th pillar: Higher education and training ................... 82 ......4.1
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency ............................ 60 ......4.4
7th pillar: Labor market efficiency ............................. 64 ......4.3
8th pillar: Financial market development ................... 30 ......4.5
9th pillar: Technological readiness ............................ 88 ......3.4
10th pillar: Market size.............................................. 48 ......4.4
Peru
Latin America and the Caribbean
Stage of development
Innovation and sophistication factors (10.0%) .........106 ......3.3
11th pillar: Business sophistication .......................... 81 ......3.8
12th pillar: Innovation ............................................. 116 ......2.8
Transition
12
Factor
driven
Transition
23
Efficiency
driven
Innovation
driven
The most problematic factors for doing business
Score*
Inefficient government bureaucracy ...................................18.7
Restrictive labor regulations ...............................................16.6
Corruption .........................................................................14.1
Inadequate supply of infrastructure ......................................9.9
Policy instability ...................................................................7.4
Crime and theft ...................................................................6.8
Inadequately educated workforce ........................................6.8
Complexity of tax regulations...............................................6.0
Tax rates..............................................................................5.5
Access to financing .............................................................2.5
Poor work ethic in labor force..............................................2.0
Insufficient capacity to innovate ...........................................1.9
Poor public health ...............................................................1.0
Government instability/coups ..............................................0.7
Foreign currency regulations ................................................0.0
Inflation ................................................................................0.0
0
*
10
15
20
25
From the list of factors, respondents were asked to select the five most problematic for doing business in their country and to rank them between 1 (most problematic) and 5. The score
corresponds to the responses weighted according to their rankings.
294 | The Global Competitiveness Report 20152016
2015 World Economic Forum
30
2: Country/Economy Profiles
Peru
The Global Competitiveness Index in detail
INDICATOR
VALUE RANK/140
INDICATOR
1st pillar: Institutions
VALUE RANK/140
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency (contd.)
1.01
1.02
1.03
1.04
1.05
1.06
1.07
1.08
1.09
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
1.16
1.17
1.18
1.19
1.20
1.21
Property rights ....................................................... 3.8 ..........104
Intellectual property protection ............................... 3.3 ..........104
Diversion of public funds ........................................ 2.5 ..........114
Public trust in politicians ......................................... 1.8 ..........130
Irregular payments and bribes ................................ 3.9 ............72
Judicial independence............................................ 2.8 ..........112
Favoritism in decisions of government officials ....... 2.5 ..........109
Wastefulness of government spending ................... 2.4 ..........117
Burden of government regulation ........................... 2.4 ..........133
Efficiency of legal framework in settling disputes .... 2.6 ..........130
Efficiency of legal framework in challenging regs. ... 2.7 ..........118
Transparency of government policymaking............. 3.9 ............82
Business costs of terrorism .................................... 4.2 ..........123
Business costs of crime and violence..................... 2.9 ..........129
Organized crime ..................................................... 3.0 ..........133
Reliability of police services .................................... 2.6 ..........135
Ethical behavior of firms ......................................... 3.5 ..........106
Strength of auditing and reporting standards ......... 5.1 ............41
Efficacy of corporate boards .................................. 5.2 ............39
Protection of minority shareholders interests ......... 4.2 ............57
Strength of investor protection, 010 (best)* .......... 6.2 ............39
2.01
2.02
2.03
2.04
2.05
2.06
2.07
2.08
2.09
Quality of overall infrastructure ............................... 3.2 ..........112
Quality of roads ...................................................... 3.0 ..........111
Quality of railroad infrastructure .............................. 1.9 ............94
Quality of port infrastructure ................................... 3.6 ............86
Quality of air transport infrastructure....................... 4.1 ............82
Available airline seat km/week, millions* ............. 533.3 ............42
Quality of electricity supply ..................................... 4.7 ............70
Mobile telephone subscriptions/100 pop.* ......... 102.9 ............93
Fixed-telephone lines/100 pop.* ............................. 9.9 ............84
3.01
3.02
3.03
3.04
3.05
Government budget balance, % GDP*................. 0.1 ............24
Gross national savings, % GDP* .......................... 22.7 ............53
Inflation, annual % change* .................................... 3.2 ............62
General government debt, % GDP* ..................... 20.7 ............16
Country credit rating, 0100 (best)* ...................... 66.3 ............41
4.01
4.02
4.03
4.04
4.05
4.06
4.07
4.08
4.09
4.10
Malaria cases/100,000 pop.* ............................. 190.1 ............37
Business impact of malaria .................................... 5.8 ............15
Tuberculosis cases/100,000 pop.* ..................... 124.0 ............98
Business impact of tuberculosis ............................. 5.0 ............92
HIV prevalence, % adult pop.* ............................... 0.4 ............74
Business impact of HIV/AIDS ................................. 5.4 ............76
Infant mortality, deaths/1,000 live births* .............. 12.9 ............67
Life expectancy, years*......................................... 74.8 ............60
Quality of primary education ................................... 2.2 ..........136
Primary education enrollment, net %* .................. 91.8 ............85
5.01
5.02
5.03
5.04
5.05
5.06
5.07
5.08
Secondary education enrollment, gross %* .......... 94.0 ............59
Tertiary education enrollment, gross %*................ 40.6 ............66
Quality of the education system ............................. 2.5 ..........130
Quality of math and science education .................. 2.2 ..........137
Quality of management schools ............................. 4.1 ............71
Internet access in schools ...................................... 3.7 ............95
Availability of specialized training services .............. 4.1 ............73
Extent of staff training ............................................ 3.7 ............92
2nd pillar: Infrastructure
6.06
6.07
6.08
6.09
6.10
6.11
6.12
6.13
6.14
6.15
6.16
No. procedures to start a business* .......................... 6 ............57
No. days to start a business* ............................... 26.0 ..........106
Agricultural policy costs.......................................... 3.7 ............83
Prevalence of non-tariff barriers .............................. 4.1 ..........101
Trade tariffs, % duty* .............................................. 1.8 ............35
Prevalence of foreign ownership............................. 5.0 ............46
Business impact of rules on FDI ............................. 4.9 ............40
Burden of customs procedures .............................. 3.8 ............76
Imports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 24.6 ..........127
Degree of customer orientation .............................. 4.8 ............56
Buyer sophistication ............................................... 3.5 ............55
7.01
7.02
7.03
7.04
7.05
7.06
7.07
7.08
7.09
7.10
Cooperation in labor-employer relations ................. 4.3 ............69
Flexibility of wage determination ............................. 5.7 ............21
Hiring and firing practices ....................................... 2.7 ..........133
Redundancy costs, weeks of salary* .................... 11.4 ............43
Effect of taxation on incentives to work .................. 3.2 ..........112
Pay and productivity............................................... 3.8 ............83
Reliance on professional management ................... 4.3 ............64
Country capacity to retain talent............................. 3.8 ............42
Country capacity to attract talent ........................... 3.7 ............47
Women in labor force, ratio to men* ..................... 0.80 ............74
8.01
8.02
8.03
8.04
8.05
8.06
8.07
8.08
Availability of financial services ............................... 4.7 ............53
Affordability of financial services ............................. 4.1 ............68
Financing through local equity market .................... 3.7 ............58
Ease of access to loans ......................................... 3.2 ............43
Venture capital availability ....................................... 3.1 ............43
Soundness of banks .............................................. 5.7 ............30
Regulation of securities exchanges ........................ 5.1 ............27
Legal rights index, 012 (best)* ................................. 8 ............17
9.01
9.02
9.03
9.04
9.05
9.06
9.07
Availability of latest technologies ............................ 4.5 ............84
Firm-level technology absorption ............................ 4.5 ............77
FDI and technology transfer ................................... 4.9 ............33
Individuals using Internet, %* ............................... 40.2 ............88
Fixed-broadband Internet subscriptions/100 pop.* .. 5.7 ............80
Intl Internet bandwidth, kb/s per user* ................ 36.4 ............66
Mobile-broadband subscriptions/100 pop.* ......... 13.7 ..........106
10.01
10.02
10.03
10.04
Domestic market size index, 17 (best)*................. 4.3 ............45
Foreign market size index, 17 (best)* .................... 4.8 ............62
GDP (PPP$ billions)* .......................................... 371.3 ............46
Exports as a percentage of GDP* ........................ 22.2 ..........120
11.01
11.02
11.03
11.04
11.05
11.06
11.07
11.08
11.09
Local supplier quantity ........................................... 4.7 ............49
Local supplier quality.............................................. 4.3 ............61
State of cluster development.................................. 3.2 ..........104
Nature of competitive advantage ............................ 2.8 ..........112
Value chain breadth................................................ 3.4 ..........104
Control of international distribution ......................... 3.6 ............92
Production process sophistication.......................... 3.6 ............89
Extent of marketing ................................................ 4.4 ............59
Willingness to delegate authority ............................ 3.8 ............64
12.01
12.02
12.03
12.04
12.05
12.06
12.07
Capacity for innovation........................................... 3.6 ..........105
Quality of scientific research institutions ................. 2.9 ..........117
Company spending on R&D................................... 2.7 ..........115
University-industry collaboration in R&D ................. 3.1 ..........108
Govt procurement of advanced tech products ...... 2.7 ..........123
Availability of scientists and engineers .................... 3.2 ..........117
PCT patents, applications/million pop.* .................. 0.3 ............84
7th pillar: Labor market efficiency
8th pillar: Financial market development
3rd pillar: Macroeconomic environment
4th pillar: Health and primary education
5th pillar: Higher education and training
6th pillar: Goods market efficiency
6.01
6.02
6.03
6.04
6.05
Intensity of local competition .................................. 5.2 ............58
Extent of market dominance .................................. 3.5 ............84
Effectiveness of anti-monopoly policy ..................... 3.8 ............64
Effect of taxation on incentives to invest................. 3.4 ............88
Total tax rate, % profits* ....................................... 36.0 ............65
9th pillar: Technological readiness
10th pillar: Market size
11th pillar: Business sophistication
12th pillar: Innovation
Notes: Values are on a 1-to-7 scale unless otherwise annotated with an asterisk (*). For further details and explanation, please refer to the section How to Read
the Country/Economy Profiles on page 89.
2015 World Economic Forum
The Global Competitiveness Report 20152016 | 295
También podría gustarte
- Print World ForumPortugalDocumento2 páginasPrint World ForumPortugalbiles1234Aún no hay calificaciones
- Groth Competitiveness IndexDocumento2 páginasGroth Competitiveness IndexsulthanhakimAún no hay calificaciones
- Romania Global Competitive IndexDocumento2 páginasRomania Global Competitive IndexAnda MărășescuAún no hay calificaciones
- COmpetitividad España 2013 PDFDocumento2 páginasCOmpetitividad España 2013 PDFcroquetoideAún no hay calificaciones
- Singapore: Key Indicators, 2014Documento2 páginasSingapore: Key Indicators, 2014Siddhant AgarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Taiwan, China: Key Indicators, 2012Documento4 páginasTaiwan, China: Key Indicators, 2012Santiago MilesAún no hay calificaciones
- Hong Kong SAR: Key Indicators, 2013Documento2 páginasHong Kong SAR: Key Indicators, 2013huznmh8334Aún no hay calificaciones
- QatarDocumento2 páginasQatarshabina921Aún no hay calificaciones
- Romania: Key Indicators, 2011Documento2 páginasRomania: Key Indicators, 2011Cata FrincuAún no hay calificaciones
- Profil SR 2012Documento2 páginasProfil SR 2012Dennik SMEAún no hay calificaciones
- JapanDocumento2 páginasJapanarchitectofskinAún no hay calificaciones
- Argentina: Key Indicators, 2010Documento2 páginasArgentina: Key Indicators, 2010Stephen HartantoAún no hay calificaciones
- FinlandDocumento2 páginasFinlandFrancesco SaviozziAún no hay calificaciones
- Albania: Key Indicators, 2010Documento2 páginasAlbania: Key Indicators, 2010Marlind3Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sri LankaDocumento2 páginasSri LankaHarshadewa AriyasingheAún no hay calificaciones
- Indice de Competitividad Mundial: Bolivia Cerca de Etiopía... Lejos de SuizaDocumento2 páginasIndice de Competitividad Mundial: Bolivia Cerca de Etiopía... Lejos de SuizaBernardo PradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Egypt: Key IndicatorsDocumento4 páginasEgypt: Key IndicatorstemozAún no hay calificaciones
- Sector Statistics Report Q4 2021 2022Documento28 páginasSector Statistics Report Q4 2021 2022iganjo mutahiAún no hay calificaciones
- GWI March 2020 - Multi-Market DataDocumento49 páginasGWI March 2020 - Multi-Market DataSiew Siew LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Malaysia: Key IndicatorsDocumento2 páginasMalaysia: Key Indicatorszindagi5323Aún no hay calificaciones
- Do e 04 VGR 01Documento115 páginasDo e 04 VGR 01Parag Thakare100% (1)
- Mexico InnovationDocumento1 páginaMexico InnovationgabyrdmAún no hay calificaciones
- UnitedStates PDFDocumento2 páginasUnitedStates PDFMark Valvas RoblesAún no hay calificaciones
- Economic Review Volumes Vol.59 No1 2018-2019Documento149 páginasEconomic Review Volumes Vol.59 No1 2018-2019Islam HamdyAún no hay calificaciones
- BMI Vietnam Consumer Electronics Report Q3 2013Documento52 páginasBMI Vietnam Consumer Electronics Report Q3 2013chip12384Aún no hay calificaciones
- Kenya Facts 2012Documento83 páginasKenya Facts 2012mutindamarkAún no hay calificaciones
- Edprs 2008Documento166 páginasEdprs 2008Emmanuel HabumuremyiAún no hay calificaciones
- tdr2022 enDocumento72 páginastdr2022 enCaptain ChemicalAún no hay calificaciones
- U.S. Gulf of Mexico Oil and Natural Gas Industry Economic Impact AnalysisDocumento156 páginasU.S. Gulf of Mexico Oil and Natural Gas Industry Economic Impact AnalysisEnergy TomorrowAún no hay calificaciones
- The Rise and Fall of Neoliberal Capitalism (PDFDrive)Documento288 páginasThe Rise and Fall of Neoliberal Capitalism (PDFDrive)Zahra AdhaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2019 Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA) ReportDocumento39 páginas2019 Debt Sustainability Analysis (DSA) ReportsenohiAún no hay calificaciones
- Israel: Global Innovation Index (Out of 142) ................................. 56.0 14Documento1 páginaIsrael: Global Innovation Index (Out of 142) ................................. 56.0 14yairAún no hay calificaciones
- United Arab Emirates: Key IndicatorsDocumento4 páginasUnited Arab Emirates: Key IndicatorsequitytraderAún no hay calificaciones
- Qatar: Key Indicators, 2011Documento1 páginaQatar: Key Indicators, 2011shabina921Aún no hay calificaciones
- Consumer Appliances in The PhilippinesDocumento29 páginasConsumer Appliances in The PhilippinesHexeneAún no hay calificaciones
- Global Macro TrendsDocumento82 páginasGlobal Macro Trendsmaruan_trascu5661Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileDocumento2 páginasCyprus Travel Tourism Competitiveness Report 2011 - Country ProfileetourismforumAún no hay calificaciones
- Tanzania Governance Review 2012Documento122 páginasTanzania Governance Review 2012Policy ForumAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4 - European Index of Housing Exclusion 2020Documento54 páginasChapter 4 - European Index of Housing Exclusion 2020MarioAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Global Macro Trends For The Next Five Years PDFDocumento82 páginas10 Global Macro Trends For The Next Five Years PDFJAMAún no hay calificaciones
- The Political Economy of Vietnam's Industrial TransformationDocumento126 páginasThe Political Economy of Vietnam's Industrial TransformationLe TamAún no hay calificaciones
- Azerbaijan: Key Indicators, 2012Documento2 páginasAzerbaijan: Key Indicators, 2012Prassy PrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Philosophy 136Documento148 páginasPhilosophy 136jack sparowAún no hay calificaciones
- China Productivity Measures Web 22july06Documento286 páginasChina Productivity Measures Web 22july06redha craftAún no hay calificaciones
- Commercial Bank of Ethiopia: Business Development DivisionDocumento43 páginasCommercial Bank of Ethiopia: Business Development DivisionZenebe ZelelewAún no hay calificaciones
- Rela Tori of Mi PortugalDocumento77 páginasRela Tori of Mi PortugalRuben Samoel Barros RochaAún no hay calificaciones
- B. Consumer Lifestyles in Norway - Passport Oct 2014Documento43 páginasB. Consumer Lifestyles in Norway - Passport Oct 2014rimmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mdg2011 Book EngDocumento151 páginasMdg2011 Book Engabriti2003Aún no hay calificaciones
- Final Draft ITL ProjectDocumento34 páginasFinal Draft ITL ProjectDeepa TiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- Pet Care in Vietnam: Euromonitor International May 2020Documento48 páginasPet Care in Vietnam: Euromonitor International May 2020Tran NguyenAún no hay calificaciones
- Q2FY23 Press ReleaseDocumento9 páginasQ2FY23 Press ReleasercossichAún no hay calificaciones
- Mrunal Mains Eco Airpods Pill3 BoP Intl Trade WTODocumento26 páginasMrunal Mains Eco Airpods Pill3 BoP Intl Trade WTOScienceGramAún no hay calificaciones
- Financial Stability ReportDocumento44 páginasFinancial Stability ReportFan SijingAún no hay calificaciones
- Unilever Global Business StrategyDocumento31 páginasUnilever Global Business StrategyRameesha IshtiaqAún no hay calificaciones
- Note 11. Federal Debt Securities Held by The Public and Accrued InterestDocumento4 páginasNote 11. Federal Debt Securities Held by The Public and Accrued InterestLokiAún no hay calificaciones
- Moldova CEMDocumento122 páginasMoldova CEMOlga SicoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Switzerland: Global Innovation Index (Out of 142) ................................. 66.6 1Documento1 páginaSwitzerland: Global Innovation Index (Out of 142) ................................. 66.6 1yairAún no hay calificaciones
- The WTO Global Trade Model: Technical Documentation: Center For Global Trade Analysis (GTAP), Purdue UniversityDocumento39 páginasThe WTO Global Trade Model: Technical Documentation: Center For Global Trade Analysis (GTAP), Purdue UniversityOscar MilmoAún no hay calificaciones
- CAMPERDOWN HIGH SCHOOL - Accounting Grade 9 TestDocumento6 páginasCAMPERDOWN HIGH SCHOOL - Accounting Grade 9 TestLatoya SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Tenant Consent FormDocumento1 páginaTenant Consent FormChen LoAún no hay calificaciones
- Harvesting The Business Venture Investment Chapter 14Documento20 páginasHarvesting The Business Venture Investment Chapter 14Trang TranAún no hay calificaciones
- Audit of Receivables Lecture NotesDocumento10 páginasAudit of Receivables Lecture NotesDebs Fanoga100% (1)
- Final PPT Adr-GdrDocumento71 páginasFinal PPT Adr-Gdr24_anuAún no hay calificaciones
- Does IT Pay Off HSBC and Citi Case StudyDocumento8 páginasDoes IT Pay Off HSBC and Citi Case StudyIIMnotesAún no hay calificaciones
- Internship Report Veena - Copy of VeenaDocumento32 páginasInternship Report Veena - Copy of VeenaBhuvan MhAún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet FABM2 Q1 M1 SFPDocumento5 páginasWorksheet FABM2 Q1 M1 SFPMarjun AbogAún no hay calificaciones
- 1588756021-1693-Allegis Servicses Final PrintDocumento9 páginas1588756021-1693-Allegis Servicses Final PrintDehradun MootAún no hay calificaciones
- Black-Scholes The Easy Way: John NorstadDocumento6 páginasBlack-Scholes The Easy Way: John NorstadRuchita AgrawalAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Corporate Finance 2Documento4 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Corporate Finance 2Mrittika SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nada Gamal Youssef - AssignmentDocumento3 páginasNada Gamal Youssef - AssignmentNada YoussefAún no hay calificaciones
- True Smart Money ConceptsDocumento24 páginasTrue Smart Money ConceptsDikgang Malaka92% (13)
- ISJ017Documento84 páginasISJ0172imediaAún no hay calificaciones
- SSRN Id3140837Documento133 páginasSSRN Id3140837Mumu PilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Goodwill 23.3.23Documento1 páginaGoodwill 23.3.2308 Ajay Halder 11- CAún no hay calificaciones
- My Courses: Home BAED-FABM2112-2012S Week 10: Quarterly Exam 1st. Quarter ExamDocumento14 páginasMy Courses: Home BAED-FABM2112-2012S Week 10: Quarterly Exam 1st. Quarter Examjohn75% (8)
- SNGPL - Web BillDocumento1 páginaSNGPL - Web BillNazeer Ahmed100% (1)
- Drill 2 (1-24) FSUU AccountingDocumento12 páginasDrill 2 (1-24) FSUU AccountingRobert CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Commodities: User GuideDocumento9 páginasCommodities: User GuideDaer M Peña CrespoAún no hay calificaciones
- My StatementDocumento9 páginasMy StatementAjayAún no hay calificaciones
- SAP FICO FresherDocumento3 páginasSAP FICO FresherAnudeep ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes Insurable InterestDocumento58 páginasNotes Insurable Interestolofuzyatotz50% (2)
- Chapter 13 Financial Statement Analysis SolutionsDocumento3 páginasChapter 13 Financial Statement Analysis Solutionsbhardwajvn100% (3)
- Macro Tut 4 - With AnsDocumento11 páginasMacro Tut 4 - With AnsNguyen Tra MyAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 09 Paper 2 Mid-Term ExaminationDocumento7 páginasGrade 09 Paper 2 Mid-Term ExaminationSarrah ShabbirAún no hay calificaciones
- Buffet Bid For Media GeneralDocumento21 páginasBuffet Bid For Media Generalshivam chughAún no hay calificaciones
- AdaDocumento8 páginasAdaperapericprcasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax InvoiceDocumento1 páginaTax InvoicePintu ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of Fintech in IndiaDocumento22 páginasRise of Fintech in IndiaSukhmanpreet SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Think Like Amazon: 50 1/2 Ideas to Become a Digital LeaderDe EverandThink Like Amazon: 50 1/2 Ideas to Become a Digital LeaderCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (62)
- Having It All: Achieving Your Life's Goals and DreamsDe EverandHaving It All: Achieving Your Life's Goals and DreamsCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (65)
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryDe EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (26)
- 12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurDe Everand12 Months to $1 Million: How to Pick a Winning Product, Build a Real Business, and Become a Seven-Figure EntrepreneurCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (3)
- The Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeDe EverandThe Millionaire Fastlane, 10th Anniversary Edition: Crack the Code to Wealth and Live Rich for a LifetimeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (91)
- Summary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesDe EverandSummary of The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses by Eric RiesCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (99)
- Every Tool's a Hammer: Life Is What You Make ItDe EverandEvery Tool's a Hammer: Life Is What You Make ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (249)
- When the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachDe EverandWhen the Heavens Went on Sale: The Misfits and Geniuses Racing to Put Space Within ReachCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (6)
- Summary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizDe EverandSummary of The Four Agreements: A Practical Guide to Personal Freedom (A Toltec Wisdom Book) by Don Miguel RuizCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (112)
- Summary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe EverandSummary of The Subtle Art of Not Giving A F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good Life by Mark Manson: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (38)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsDe EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (48)
- Your Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyDe EverandYour Next Five Moves: Master the Art of Business StrategyCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (806)
- Rich Dad's Before You Quit Your Job: 10 Real-Life Lessons Every Entrepreneur Should Know About Building a Multimillion-Dollar BusinessDe EverandRich Dad's Before You Quit Your Job: 10 Real-Life Lessons Every Entrepreneur Should Know About Building a Multimillion-Dollar BusinessCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (407)
- Expert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceDe EverandExpert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (365)
- Buffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorDe EverandBuffettology: The Previously Unexplained Techniques That Have Made Warren Buffett American's Most Famous InvestorCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (132)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDe EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelDe EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Summary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureDe EverandSummary of Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (100)
- Built to Serve: Find Your Purpose and Become the Leader You Were Born to BeDe EverandBuilt to Serve: Find Your Purpose and Become the Leader You Were Born to BeCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (25)
- Be Fearless: 5 Principles for a Life of Breakthroughs and PurposeDe EverandBe Fearless: 5 Principles for a Life of Breakthroughs and PurposeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (49)
- Get Scalable: The Operating System Your Business Needs To Run and Scale Without YouDe EverandGet Scalable: The Operating System Your Business Needs To Run and Scale Without YouCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Summary of The 33 Strategies of War by Robert GreeneDe EverandSummary of The 33 Strategies of War by Robert GreeneCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (20)
- WEALTH EXPO$ED: This Short Argument Made Me a Fortune... Can It Do The Same For YouDe EverandWEALTH EXPO$ED: This Short Argument Made Me a Fortune... Can It Do The Same For YouCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (87)
- The Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelDe EverandThe Science of Positive Focus: Live Seminar: Master Keys for Reaching Your Next LevelCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (52)
- Summary of The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work and What to Do About It by Michael E. GerberDe EverandSummary of The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work and What to Do About It by Michael E. GerberCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (39)
- Take Your Shot: How to Grow Your Business, Attract More Clients, and Make More MoneyDe EverandTake Your Shot: How to Grow Your Business, Attract More Clients, and Make More MoneyCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (22)
- The Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersDe EverandThe Master Key System: 28 Parts, Questions and AnswersCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (62)
- Summary of $100M Offers: How To Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoDe EverandSummary of $100M Offers: How To Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)