Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Basic Chemistry 3 1 - Part 3
Cargado por
api-272358521Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Basic Chemistry 3 1 - Part 3
Cargado por
api-272358521Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Unit 3: Basic Chemistry
Content Outline: Chemical Bonding (3.1) - Part 3
I.
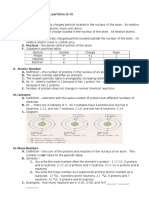
Ionic Bonds One or more electrons from one atom are transferred to another atom,
and the resulting positive or negative ion then attract each other
A. Ionic bonds usually result in crystalline solids
B. Occur between metal atoms, which tend to lose electrons and nonmetal atoms,
which tend to gain the electrons lost by the metal atoms.
C. Ionic compounds usually are crystalline solids, hard, have high melting points,
conduct electricity when melted, and may be soluble water but not nonpolar liquids.
II.
Covalent Bonds two adjacent atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The
electrons spend more time between the two atoms than anywhere else.
A. Covalently bonded atoms are often called molecules because the atoms are held
together so tightly that they behave as a single particle.
B. Covalent bonds are shared between two or more nonmetals.
C. Covalent compounds are can be gases, liquids, or solids, have low melting points,
are poor conductors in all phases, and are soluble in nonpolar liquids but not in
water.
D. When the atoms of covalently bonded compounds share paired electrons unevenly
to compounds are called polar covalent.
III.
Metallic Bonds - force that holds atoms together in a metallic substance.
A. Metallic bonds usually consist of closely packed metal atoms.
B. The outermost electron shell of each of the metal atoms overlaps with a large
number of atoms in close proximity. Therefore, the valence electrons continually
move from one atom to another and are not associated with any specific pair of
atoms.
C. The atoms that the electrons leave behind become positive ions, and the interaction
between such ions and valence electrons gives rise to the cohesive or binding force
that holds the metallic crystal together.
IV.
Hydrogen Bonds is a force of attraction between a hydrogen atom in one molecule
and a small atom of high negativity in another molecule.
A. When hydrogen atoms have their electron unequally shared with the other attached
atom, the partial positive charge on the hydrogen is highly concentrated because of
its small size. The other atom will carry a negative charge. Positive charges are
attracted to negative charges, but no actual physical connection occurs between
adjacent molecules.
B. Hydrogen bonding is also very important effect on the properties of water, proteins,
and nucleic acids.
También podría gustarte
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- 5 3 Characteristics of GasesDocumento1 página5 3 Characteristics of Gasesapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- 5 1 Math - The Language of ScienceDocumento2 páginas5 1 Math - The Language of Scienceapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Unit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. ElectromagnetismDocumento1 páginaUnit 10: Electricity & Magnetism Content Outline: Electromagnetism (10.4) I. Electromagnetismapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Work, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The SourceDocumento1 páginaWork, Then Out of The Device by A Wire, and Back To The Sourceapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- 5 4 Pressure and GasesDocumento1 página5 4 Pressure and Gasesapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- 4 7 Solubility 1Documento1 página4 7 Solubility 1api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- 4 4 Acids Bases BuffersDocumento2 páginas4 4 Acids Bases Buffersapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- 4 5 Molarity 1Documento1 página4 5 Molarity 1api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Reactions 3 4Documento2 páginasChemical Reactions 3 4api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Rates of Reactions 3 5Documento1 páginaRates of Reactions 3 5api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Properties of Matter NotesDocumento2 páginasProperties of Matter Notesapi-272358521100% (2)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Optics 9 7Documento1 páginaOptics 9 7api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Atomic Theory Project 2 1Documento2 páginasAtomic Theory Project 2 1api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- Subatomic Particles 2 4 1Documento2 páginasSubatomic Particles 2 4 1api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (345)
- Chemical Nomenclature 3 2Documento1 páginaChemical Nomenclature 3 2api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Atomic Model 2 2Documento2 páginasAtomic Model 2 2api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sound Waves 9 2Documento2 páginasSound Waves 9 2api-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- RubegoldbergprojectDocumento2 páginasRubegoldbergprojectapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Fluids OutlineDocumento3 páginasFluids Outlineapi-272358521Aún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)