Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Comparison of Major Animal Phyla - Sheet1 1
Cargado por
api-272860178Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Comparison of Major Animal Phyla - Sheet1 1
Cargado por
api-272860178Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
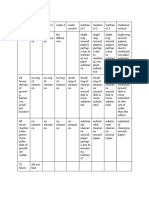
Porifera (Sponges)
Cnidaria
(Jellyfish,Anemones,Hydra)
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) Nematodes
Annelids (Earthworms)
Germ Layers
No true germ layers
2 germ layers: ectoderm >epidermis, endoderm ->
inner gastrodermis
3 germ layers: ectoderm,
mesoderm, endoderm
Three
3 germ layers: ecto-, meso-, 3 germ layers: ecto-,
endoderm
meso-, endoderm
3 germ layers: ecto-, meso-,
endoderm
3 germ layers: ecto-, meso-, endoderm
3 germ layers: ecto-, meso-,
endoderm
Symmetry
Asymmetrical or Radial
Radial, about the axis of the
mouth surface
Bilateral
Bilateral
Bilateral
Bilateral
Bilateral
Radial; but larvae bilateral
Bilateral
Present
limited cephalization in
nervous system
Mollusca (Squid)
Arthropoda (Grasshopper)
Echinodermata (Sea Urchin)
Chordata (Fishes, etc.)
Cephalization
None
None
some cephalization with
sensory, association, and
motor neurons
limited cephalization
extensive cephalization
none
extensive cephalization
Body Cavity
None
none other than gut
none
Pseudoceol
Coelom
Coelom
Coelom
Coelom
Coelom
Segmentation
none
none
none
Absent
Present
Absent
Present
Absent
Present (but reduced)
Mouth on oral surface leads to cardiac
stomach (everted during feeding), then
to pyloric stomach with hepatic
(digestive, pyloric) ceca extending into
each arm; short intestine with outbranching rectal ceca leads from pyloric
stomach to anus on aboral surface
Complete; pharynx with three
regions,
esophagus, stomach, small
intestine with three regions,
liver, pancreas, cecum, large
intestine
Suspension feeders
Specialized cells called
chaonocytes contain flagella
that produce a current
through pores in body;
chaonocytes ingest food by
phagocytosis Specialized
amoebocytes distribute food
Digestive System throughout body
Circulation
Respiration
GVC consists of mouth,
pharynx, and three branched
intestines; pharynx extends
tentacles gather food;
through mouth during
nutritive muscular cells engulf feeding and secrete digestive
partially digested food and
enzymes; muscular
specialized for filtering
transport to vacuoles for final contractions of pharynx pull Separate mouth complete system (mouth and small food particles from
digestion
food into mouth
and anus
anus)
water
complete system
chaonocytes contain flagella
that produce a current
Gastrovascular cavity (GVC);
moving water through pores Cilia lining cavity move fluid
in body
and food
Gastrovascular cavity (GVC) Absent
Closed circulatory system
(blood
contained within vessels);
dorsal
blood vessel and ring-like
hearts
contract rhythmically
Open circulatory system;
dorsal vessel carries
hemolymph anteriorly, into
cavities surrounding organs, Open circulatory system; poorly-defined channels
then flows posteriorly and
in coelomic cavity; lack heart; cilia associated with dorsal, hollow nerve cord; often
Open circulatory system back into dorsal vessel
water vascular system circulate coelomic fluid
protected by vertebrae
Diffusion
Use hemoglobin as
respiratory pigment
dissolved in blood (no red
blood cells)
Sinuses collect
hemolymph and transport
to ctenidia for gas
exchange
Air enters lateral spiracles,
through trachea, into
Gases diffuse via dermal branchiae; soluble
tracheoles throughout body; wastes released by simple diffusion across
no respiratory pigment
surface epithelium
Gills, functionally replaced by
lungs in higher vertebrates;
use blood to transport O2 and
CO2; respiratory pigment is
hemoglobin
Nitrogenous waste filtered by
pair of kidneys
Diffusion
Diffusion
Diffusion and out pores
Diffusion
Waste diffuses into
surrounding environment;
undigested food expelled out excretory gland empties into exterior by pore
of mouth
cells
in ventral wal
wastes excreted into
excurrent siphon by pair
of kidneys; some
ammonia eliminated by
ctenidia
Malpigian tubules at junction
of mid- and hind-gut function
in removal of nitrogenous
wastes from hemolymph in
coelom for transfer to
hindgut for excretion
no excretory glands
Nervous System
No cephalization or
specialized sensory cells
Primitive; forms irregular net
Responds to stimuli in a
coordinated fashion (outer
tentacle engulf while inner
tentacles contract); Limited
sensory capabilities
Organized like a ladder with
two lateral cords connected
by transverse cords;
pigmented eyespots but no
imaging
have giant nerve cells,
complex sensory system
with image forming eyes
and complex behavior
flattened, double, ventral
nerve cord; ganglia along
length of cord have strandlike nerves branching
outward
Reproduction
sperm released into water
current with internal
fertilization;some asexual
both sexual and asexual;
assexual: regeneration when
Hydra can be either dioecious cut; sexual: hermaphroditic sexual (somee Hermaphroditic with crossor hermaphroditic
with cross fertilization
hermaphroditic) fertilization
Sexual; dioecious
Sexual, dioecious; Male has
pair of testes, vas deferens,
accessory gland Female has Sexual; dioecious Gonads near base of each arm
pair of ovaries with 8
under hepatic ceca Some starfish can reproduce
ovarioles, accessory glands asexually by regeneration
Sexual; dioecious
Mesoglea: space between
epidermis and gastrodermis;
filled with extracellular matrix.
Functions like endoskeleton,
but is not considered cellular
layer
Hard exoskeleton; outer
organic layer rests on
layers of calcium
carbonate; exoskeleton
reduced or absent in
most cephalopods
Chitinous exoskeleton
secreted by underlying
epidermis; limits growth;
requires molting
Excretion
diverse elements depending
on types including
calcareous laminae, organic
filaments, and siliceous and
Support (Skeleton) calcium carbonate spicules;
Hydraulic skeleton gastrovascular fluid;
longitudinal and circular
muscles
Absent
head ganglia
with dorsal and connects to ventral nerve
ventral nerve
cord; nerves branch out to
cords
adjacent tissues
Hydrostatic
skeleton
Hydraulic skeleton coelomic cavity filled with
fluid
nerves distributed throughout arms and central
disk; no special sense organs (except starfish and
brittle stars have light-sensing eyes on end of
dorsal, hollow nerve cord; often
each arm)
protected by vertebrae
Calcareous endoskeleton made up of small plates Bony or cartilaginous
joined by connective tissue
endoskeleton
También podría gustarte
- Agri 22.leon 3Documento55 páginasAgri 22.leon 3Jackelene TumesaAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Unikonta - Deuterostomes & ChordatesDocumento5 páginas7 Unikonta - Deuterostomes & ChordateskahiauAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio 320 Practical 7Documento12 páginasBio 320 Practical 7MuhammadAsyraf50% (2)
- The Acoelomates (Continued) : - Trploblastic Animals Without A CoelomDocumento74 páginasThe Acoelomates (Continued) : - Trploblastic Animals Without A CoelomADRIANO MANUEL ALVAREZ PACHECOAún no hay calificaciones
- EchinodermsDocumento5 páginasEchinodermsAlyssa Marie CamayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal Systematics: Classification and Evolution of LifeDocumento45 páginasAnimal Systematics: Classification and Evolution of Lifekingbanakon0% (1)
- Phylum Annelida (Newer Annelid)Documento10 páginasPhylum Annelida (Newer Annelid)Jara RogacionAún no hay calificaciones
- AschelminthesDocumento25 páginasAschelminthesOmah AsriAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Notes Animal KingdomDocumento6 páginasClass Notes Animal Kingdomdevu sinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Phylum CnidariaDocumento37 páginasPhylum CnidariaMadhavAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal Kingdom: Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Organ System LevelDocumento16 páginasAnimal Kingdom: Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Organ System LevelRahul RavteAún no hay calificaciones
- Animals ChartDocumento2 páginasAnimals ChartShervin MortazaviAún no hay calificaciones
- Platyhelminthes Flukes Trematoda Life CyclesDocumento29 páginasPlatyhelminthes Flukes Trematoda Life CyclesRajkumar MandalAún no hay calificaciones
- Sbio - Phylum NematodaDocumento16 páginasSbio - Phylum NematodammballesterosAún no hay calificaciones
- ProtochordataDocumento7 páginasProtochordataricoghofarAún no hay calificaciones
- XI 4 Animal KingdomDocumento58 páginasXI 4 Animal KingdomDeepti KashyapAún no hay calificaciones
- Cestoidea:: CharactersDocumento20 páginasCestoidea:: CharactersConAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal Diversity SummaryDocumento24 páginasAnimal Diversity SummaryAna Melissa BarsalloAún no hay calificaciones
- Zoology Classification ProjectDocumento67 páginasZoology Classification ProjectArionnaAún no hay calificaciones
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Questions and Their Ideal AnswersDocumento17 páginasQuestions and Their Ideal AnswersHamzaShabaka100% (2)
- General Characteristics: NematodesDocumento27 páginasGeneral Characteristics: NematodesJaica Mangurali Tumulak100% (1)
- Animal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationDocumento15 páginasAnimal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationChaitali DeshmukhAún no hay calificaciones
- Sea Stars, Urchins, and Their RelativesDocumento9 páginasSea Stars, Urchins, and Their RelativesRiyah Zuhriyah TokappaAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal KingdomDocumento5 páginasAnimal KingdomArthav KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Characters of ChordatesDocumento5 páginasCharacters of ChordatesAnonymous J6r3IlQzQxAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 7 - Intro. To Arthropods Moulting Crustaceans ChelicerataDocumento81 páginasLecture 7 - Intro. To Arthropods Moulting Crustaceans ChelicerataJordan LewisAún no hay calificaciones
- Animals Classification and CharacteristicsDocumento23 páginasAnimals Classification and CharacteristicssrishtiAún no hay calificaciones
- (JR., Cleveland P Hickman, Larry S Roberts, Allan OrgDocumento58 páginas(JR., Cleveland P Hickman, Larry S Roberts, Allan Orgalem010Aún no hay calificaciones
- Acelomate Bilateral AnimalsDocumento59 páginasAcelomate Bilateral AnimalsLiz HackettAún no hay calificaciones
- Protochordates-WPS OfficeDocumento6 páginasProtochordates-WPS OfficeOgualu FavourAún no hay calificaciones
- PoriferaDocumento39 páginasPoriferaabhishek.ajmaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Mollusca (Mollusks) Definition: Molluscs (Also Know As Mollusks) Are Soft-Bodied, Bilaterally Symmetrical, SegmentedDocumento12 páginasMollusca (Mollusks) Definition: Molluscs (Also Know As Mollusks) Are Soft-Bodied, Bilaterally Symmetrical, SegmentedRica NorcioAún no hay calificaciones
- Phylum ChordataDocumento20 páginasPhylum Chordatanitsirkfm09Aún no hay calificaciones
- Phylum HemichordataDocumento11 páginasPhylum HemichordataRushana SadaqatAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Animal DiversityDocumento27 páginas2 Animal DiversityKochu NediyavilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Flatworms 1Documento63 páginasFlatworms 1Budi AfriyansyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Insect Morphology BreakdownDocumento9 páginasInsect Morphology Breakdownjyc roseAún no hay calificaciones
- Kingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALDocumento9 páginasKingdom Animalia by DR - SHAHID IQBALTaimoor Qadeer100% (1)
- Class - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4Documento20 páginasClass - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4Anshu RajAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal Evolution - The Invertebrates: Chapter 25 Part 1Documento73 páginasAnimal Evolution - The Invertebrates: Chapter 25 Part 1Kevin Contreras MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Simion Ana-MariaDocumento8 páginasSimion Ana-MariaAna-Maria SimionAún no hay calificaciones
- 6b. Nematode AnatDocumento5 páginas6b. Nematode AnatsenjicsAún no hay calificaciones
- PhylumtableDocumento1 páginaPhylumtableapi-238745558Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFDocumento59 páginasFish Pathology - Anatomy Histology PDFvinimoja100% (1)
- ChordataDocumento28 páginasChordatatinchu guptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nematode StructureDocumento31 páginasNematode StructureShadab HanafiAún no hay calificaciones
- Phylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraDocumento21 páginasPhylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraYukimi SugitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Phylum Annelida: Group. 5 - BSMT-2ADocumento22 páginasPhylum Annelida: Group. 5 - BSMT-2AMarie Christy Blancaflor JuanitoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ana Histo MaleDocumento4 páginasAna Histo MaleCarlito RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Aurelia MaqniDocumento6 páginasAurelia MaqniEhm MelsAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Study Guide: Key Terms for Chapters 7-12Documento4 páginasBiology Study Guide: Key Terms for Chapters 7-12Charly TorosianAún no hay calificaciones
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocumento16 páginasAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah NagraAún no hay calificaciones
- Obelia: Habitat, Structure and DiagramDocumento24 páginasObelia: Habitat, Structure and DiagramSunil BundelaAún no hay calificaciones
- How animals survive and adapt to their environmentsDocumento25 páginasHow animals survive and adapt to their environmentsLean Cristian LlobreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal CharacteristicsDocumento24 páginasAnimal CharacteristicsRyan ClemonsAún no hay calificaciones
- Biol 233 Uofc Review PackageDocumento15 páginasBiol 233 Uofc Review PackagePeter KimAún no hay calificaciones
- General Chordate Characteristics and AnatomyDocumento19 páginasGeneral Chordate Characteristics and AnatomyKunica SurajAún no hay calificaciones
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.De EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideDe EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideAún no hay calificaciones
- HandwarmersDocumento9 páginasHandwarmersapi-272862164Aún no hay calificaciones
- BoardgamerulesDocumento2 páginasBoardgamerulesapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Biotechnology ProjectDocumento15 páginasBiotechnology Projectapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Digestive SystemDocumento11 páginasDigestive Systemapi-266801505100% (2)
- LittlemountainscriptDocumento1 páginaLittlemountainscriptapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- PlantthingyDocumento1 páginaPlantthingyapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Humanbodyprojectproposal 1Documento4 páginasHumanbodyprojectproposal 1api-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- SteminstrumentDocumento8 páginasSteminstrumentapi-272862164Aún no hay calificaciones
- EchinodermataDocumento10 páginasEchinodermataapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Energysourcesjustification 56periodDocumento6 páginasEnergysourcesjustification 56periodapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Coldframe WindowDocumento12 páginasColdframe Windowapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Car DesignDocumento7 páginasCar Designapi-272860178Aún no hay calificaciones
- A. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Documento1 páginaA. Pathway: (Lutfi, 2007 Smeltzer, 2000: 360)Yosef HidayatAún no hay calificaciones
- ABG Values, InR, PTT, PT, Heparin, Coumadin LevelsDocumento4 páginasABG Values, InR, PTT, PT, Heparin, Coumadin LevelssodiwoAún no hay calificaciones
- Goats and Donkeys ModuleDocumento64 páginasGoats and Donkeys ModuleNigel KanyesiAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratory Manual Leptospirosis WHO, 2007Documento81 páginasLaboratory Manual Leptospirosis WHO, 2007'aoe'Lia RahmawatiAún no hay calificaciones
- How Pandemics Spread and WebquestDocumento3 páginasHow Pandemics Spread and Webquestapi-405140390Aún no hay calificaciones
- Body Condition Score Dog PDFDocumento1 páginaBody Condition Score Dog PDFJairo Alfonso Angulo NegreteAún no hay calificaciones
- Pathogens 11 00715 v2Documento25 páginasPathogens 11 00715 v2Hizrah Harianto SembiringAún no hay calificaciones
- Sodium Chromate TetrahydrateDocumento6 páginasSodium Chromate TetrahydrateErika WidiariniAún no hay calificaciones
- NC Coyote Management PlanDocumento200 páginasNC Coyote Management PlanDevetta BlountAún no hay calificaciones
- Debelica2009 AtlasKeyHairTerrestTexasMammalsDocumento108 páginasDebelica2009 AtlasKeyHairTerrestTexasMammalsJorge Manuel Cardenas CallirgosAún no hay calificaciones
- Online Assignment - Divya MuraliDocumento9 páginasOnline Assignment - Divya Muralidivyamurali3105Aún no hay calificaciones
- Portfolio BeekeepingDocumento6 páginasPortfolio Beekeepingapi-320168204Aún no hay calificaciones
- General Medicine MCQDocumento11 páginasGeneral Medicine MCQsami1218100% (3)
- Inventory Control Sheet for Laboratory SuppliesDocumento12 páginasInventory Control Sheet for Laboratory SuppliesMohammed Babikir ElbashirAún no hay calificaciones
- Digestive SystemDocumento15 páginasDigestive SystemchinchuAún no hay calificaciones
- Chest Tube ModuleDocumento37 páginasChest Tube ModuleEdison Reyes100% (1)
- Neonatal and Paediatric Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento19 páginasNeonatal and Paediatric Anatomy and PhysiologyIonela ConstantinAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiovascular Surgery GuideDocumento84 páginasCardiovascular Surgery GuideAna Sylvia AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Moura Et Al. (2011)Documento8 páginasMoura Et Al. (2011)Callum BromleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Blood LecturesDocumento128 páginasBlood LecturessrhrenaissanceAún no hay calificaciones
- Manuscript Provisional PDF: An Unusual Cause of HypertensionDocumento3 páginasManuscript Provisional PDF: An Unusual Cause of HypertensionjoelrequenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 15 StomachDocumento129 páginasChapter 15 StomachMACON824Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Assessment DaraDocumento3 páginasPhysical Assessment DaraMichael Bon MargajaAún no hay calificaciones
- NCM - Leopold'sDocumento3 páginasNCM - Leopold'sYanna Habib-MangotaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Name: Victanyl Legal Class: Drug Class: How Supplied:: OpiatesDocumento55 páginasDrug Name: Victanyl Legal Class: Drug Class: How Supplied:: OpiatesLowis YanmaniarAún no hay calificaciones
- Term Paper On Processing of MeatDocumento12 páginasTerm Paper On Processing of MeaturbanusmatiluAún no hay calificaciones
- Anesthesia Management in CCAM Resection Pediatric PatientsDocumento10 páginasAnesthesia Management in CCAM Resection Pediatric PatientsHari ciptadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1: Transport: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengDocumento21 páginasChapter 1: Transport: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengJuliet LingAún no hay calificaciones
- Embryonic Development of The Cardiovascular and Respiratory System During The First TrimesterDocumento34 páginasEmbryonic Development of The Cardiovascular and Respiratory System During The First TrimesterDennis SukadanaAún no hay calificaciones
- LoRaWAN Compliant Rumen BolusDocumento20 páginasLoRaWAN Compliant Rumen BolusLuis Adrian Pesantes UlloaAún no hay calificaciones