Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
1.R, RC, UJT Firing
Cargado por
manojTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
1.R, RC, UJT Firing
Cargado por
manojCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
(Model No : PEC14M12)
User Manual
Version 1.0
Technical Clarification /Suggestion :
N/F
Technical Support Division,
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
Plot No :75, Electronics Estate,
Perungudi, Chennai - 600 096, INDIA.
Ph: 91- 44-2496 3142, 91-44-2496 1852
Mail : service@vimicrosystems.com,
Web : www.vimicrosystem
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Chapter-1
Introduction
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[1]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
1.1
PEC14M12
INTRODUCTION
Power electronics deals with the application of solid-state electronics for the control and
conversion of electric power. Conversion techniques require the switching ON/OFF of power
semi conductor devices.
Modern Power Electronics started with the invention of SCR commonly known as thyristor in
1956. At present, a number of power switching semiconductor devices are available namely
BJT, MOSFET, IGBT and GTO etc. All these devices are turned ON/OFF through control
terminal, either base or gate as the case may be. This makes simple power circuit.
This manual is intended to give you description of R, RC & UJT Firing Circuits. An SCR
can be switched from OFF state to ON state by means of triggering. Gate triggering is the
most common method of turning ON the SCRs, because it is an efficient and reliable method.
The gate control circuit is also called firing or triggering circuit. These gating circuits are
usually low power electronic circuits. A firing circuit should fulfil the following two functions.
(i).
If power circuit has more than one SCR, the firing circuit should produce gating pulses
for each SCR at the desired instant for proper operation of power circuit.
(ii).
The control signal generated by a firing circuit may not be able to turn-on an SCR. It
is therefore common to feed the voltage pulses to a driver circuit and then to gate
cathode circuit. A driver circuit consists of a pulse amplifier and a pulse transformer.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[2]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Chapter-2
About Our Trainer
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[3]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
2.2
SPECIFICATION
1.
Power Input
230V AC, 50 Hz.
2.
Transformer
230V/24V AC
3.
Load Rheostat
50E/4A
4.
Maximum Load Rheostat
2 Amps
5.
SCR (TYN612)
600V, 12A
6.
UJT
2N2646
7.
Zener Diode
18V/1 W
8.
Fuse
0.5 Amps
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[4]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
2.3
PEC14M12
FRONT PANEL VIEW
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[5]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
2.4
PEC14M12
FRONT PANEL DESCRIPTION
The front panel of R, RC & UJT Firing module consists of
i.
R Firing Circuit
ii.
RC Firing Circuit
iii.
UJT Firing Circuit
1.
Power ON/OFF switch is provided to control the input AC mains supply to the
module.
2.
AC ON/OFF switch is provided to control input AC voltage to the power circuit.
3.
The input supply to the R, RC & UJT firing circuit are given through the T7- T9, T12
-T13 and T1-T2 terminals respectively.
4.
Test points are provided to view different signals in the power circuit.
5.
P & N terminals are provided to apply 24V AC input to the firing circuits.
6.
Pulse output from each firing circuits are terminated at respective G and K terminals.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[6]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
TEST POINT DESCRIPTION
i.
UJT FIRING
T3 & T4
Test points to check the input DC current
T3 & T7
Test points to check the input DC voltage
T4 & T7
Test points to check the Zener diode voltage
T5 & T7
Test points to check the capacitor voltage
T6 & T7
Test points to check the output pulses.
Test points to check the output trigger pulse.
T15 & T16
Test points to check the output trigger pulse.
T14 & T16
Test points to check the capacitor voltage
ii.
R FIRING
T10 & T11
iii.
RC FIRING
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[7]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
2.5
PEC14M12
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
2.5.1 Block Diagram
230V AC
50 Hz
Step Down
Transformer
Diode Bridge
Rectifier
UJT Firing
circuit
Pulse
Transfomer
G
K
To G & K
of SCR
230/24V
R Firing
circuit
RC Firing
circuit
The block diagram consists of
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
v.
vi.
Step down transformer
Diode bridge rectifier
UJT Firing circuit
R Firing circuit
RC Firing circuit
Pulse Transformer
2.5.2 Block Diagram Description
i.
Step Down Transformer
The 230V AC input supply is step down to 24 V AC using step down transformer. This
voltage is given as input to the firing circuit.
ii.
Diode Bridge Rectifier
The diode bridge rectifier converts the input AC voltage into fixed dc voltage. The constant
rectified DC voltage is obtained through the zener diode. This dc voltage is given to UJT
Firing circuit.( This rectifier is only for the UJT Firing circuit).
iii.
UJT Firing Circuit
The resistor, charging circuit (RC) Zener diode (Z) & UJT (2N2646) forms the UJT firing
circuit. The input is DC voltage. It is used to generate triggering signals to SCR.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[8]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
iv.
PEC14M12
R Firing Circuit
R Firing circuit is made up of variable resistance which controls the firing angle of SCR in the
range of 0-90. This circuit controls the gate current to the SCR.
v.
RC Firing Circuit
RC Firing circuit is made up of resistance and capacitance. On varying the resistance, the
current through the gate varies and controls the firing angle in the range of 0-180. This
method also controls the gate current to the SCR.
vi.
Pulse transformer
The purpose of pulse transformer used in triggering circuit are
i.
The isolation of low voltage gate circuits from high voltage anode circuit.
ii.
The triggering of two or more devices from the same trigger source.
vii.
SCR Device (TYN612)
SCR Device along with RC Snubber protection circuit is provided in the module. Using the
device the study of SCR operation for different firing circuit can be done. Snubber circuit is
provided to limit the switching losses of the device.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[9]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
2.7
Protection
1.
Fuse is provided to protect the trainer from over current faults.
2.
Earthing is provided to protect the trainer module.
3.
RC Snubber circuit is provided to protect the SCR.
2.8
Precautions
1.
Before doing connections make all switches in OFF position.
2.
Load Rheostat should be kept in maximum position.
3.
Do not view the AC input waveform and pulse waveform in CRO with dual mode.
4.
24V input AC to the SCR device should not be connected directly.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 10 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Chapter-3
Experiment Section
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 11 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
Experiment 1:
PEC14M12
Study of R-Firing Circuit
Aim:
To study the operation of resistance triggering circuit using R, RC & UJT Firing module.
Apparatus Required:
1.
2.
PEC14M12 Module
Patch chords.
Accessories to be provided by the institution
1.
2.
3.
CRO
50E/4A Rheostat
Digital Multimeter - 01
Circuit Diagram
50E/4A
A
Load
Rheostat
24V AC
50 Hz
SCR
Rmin
Rv
(POT)
Rb
K
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 12 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection Diagram
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 13 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection procedure:
1.
Connect the input supply to the module.
2.
Connect P & N terminals to T7 & T9.
3.
Connect one end of load rheostat to anode (A) of SCR.
4.
Connect the other end of the load rheostat to the P terminal of 24V AC supply.
5.
Connect the cathode (K) of SCR to the N terminal of 24V AC supply.
6.
Connect the G & K terminals of firing circuit to G & K terminals of SCR.
7.
Connect the CRO groung to Anode of SCR. Connect channel 1 probe to T7 & channel
2 probe to cathode of SCR.
Experiment Procedure
1.
Verify the connection as per the connection diagram.
2.
Switch ON the power supply.
3.
Switch ON the power on/off switch.
4.
Switch ON the 24V AC S/W.
5.
Switch ON power supply to CRO & select suitable sensitivity and time settings. Use
line trigger module.
6.
Observe the waveform for input AC voltage & the load voltage.
7.
Study the waveform for various firing angle by varying the POT in R firing circuit.
8.
For a particular firing angle, plot the waveforms on a graph sheet to scale.
9.
Measure the average DC voltage across the load & rms value of the ac input voltage
using a Digital multimeter.
10.
Calculate the dc output voltage using the equation.
Vdc
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
2V
1 cos
2
[ 14 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
and compare the measured value.
Firing angle delay
RMS value of the ac input voltage.
Model Graph
es
Vak
VL,i L
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 15 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
Experiment 2:
PEC14M12
Study of RC-Firing Circuit
Aim:
To study the operation of resistance capacitance triggering circuit using R, RC & UJT Firing
module.
Apparatus Required:
1.
2.
PEC14M12 Module
Patch chords.
Accessories to be provided by the institution
1.
2.
3.
CRO
50E/4A Rheostat
Digital Multimeter - 01
Circuit Diagram
50E/4A
+
Load
Rheostat
24V AC
50 Hz
D2
SCR
Rv
(POT)
D1
G
C
K
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 16 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection Diagram
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 17 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection procedure:
1.
Connect the input supply to the module.
2.
Connect P & N terminals to T12 & T13.
3.
Connect one end of load rheostat to anode (A) of SCR.
4.
Connect the other end of the load rheostat to the P terminal of 24V AC supply.
5.
Connect the cathode (K) of SCR to the N terminal of 24V AC supply.
6.
Connect the G & K terminals of firing circuit to G & K terminals of SCR.
7.
Connect the CRO ground to Anode of SCR connect channel -1 probe to T12 &
channel 2 probe to the cathode.
Experiment Procedure
1.
Verify the connection as per the connection diagram.
2.
Switch ON the power supply.
3.
Switch ON the power on/off switch.
4.
Switch ON the 24V AC S/W.
5.
Switch ON power supply to CRO & select suitable sensitivity and time settings. Use
line trigger module.
6.
Observe the waveform for input AC voltage & the load voltage.
7.
Study the waveform for various firing angle by varying the POT in R firing circuit.
8.
For a particular firing angle, plot the waveforms on a graph sheet to scale.
9.
Measure the average DC voltage across the load & rms value of the ac input voltage
using a Digital multimeter.
10.
Calculate the dc output voltage using the equation.
Vdc
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
2V
1 cos
2
[ 18 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
and compare the measured value.
Firing angle delay
RMS value of the ac input voltage.
Model Graph
es
Vak
VL,i L
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 19 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
Experiment 3:
PEC14M12
Study of UJT Firing Circuit
Aim:
To study the operation of UJT triggering circuit using R, RC & UJT Firing module.
Apparatus Required:
1.
2.
PEC14M12 Module
Patch chords.
Accessories to be provided by the institution
1.
2.
3.
CRO
50E/4A Rheostat
Digital Multimeter - 01
Circuit Diagram
50V/4A
A
Load
Rheostat
R1
D1
D3
R
(POT)
24V AC
E
D4
D2
B2
B1
SCR
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 20 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection Diagram
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 21 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Connection procedure:
1.
Connect the input supply to the module.
2.
Connect one end of load rheostat to anode (A) of SCR.
3.
Connect the other end of the load rheostat to the P terminal of 24V AC supply.
4.
Connect the G1 & K1 terminals of the UJT firing circuit to gate(G) and cathode (K)
terminals of SCR.
Experiment Procedure
1.
Verify the connection as per the connection diagram.
2.
Switch ON the power supply.
3.
Switch ON the power on/off switch.
4.
Connect the CRO ground to ground terminal of UJT Firing circuit.
5.
Switch ON the power supply to CRO & select suitable sensitivity and time settings.
Use line trigger module.
6.
Observe the waveform for input ac voltage & pulsating DC output.
7.
Connect channel 2 probe to terminal T4 and to observe the zener diode voltage.
8.
Connect channel 2 probe to terminal T5 and to observe the capacitor voltage.
9.
Study the waveform for various firing angle.
10.
For a particular firing angle plot a waveform on a graph sheet to scale.
11.
Observe the capacitor voltage is zero at the end of every half cycle.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 22 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Model Graph
Vac
Vdc
Vz
0
Vc
0
Vg
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 23 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Chapter-4
Theoretical Concept
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 24 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
The following section is discussed about the various types of firing circuits.
4.1.
R Firing Circuit:
This is the simple method for varying the triggering angle upto 90. Instead of using gate
pulse, here gate current is used to trigger the SCR. The circuit diagram is shown in fig 4.a.
Vo
+
Load
A
Rmin
24V AC
50 Hz
SCR
Rv
Rb
K
Fig 4.a. R Firing circuit
The circuit operates as follows,
1.
When a gate current Ig is equal to Ig(min), SCR turns ON while es goes positive and eL
is approximately equal to es.
2.
As es goes negative, SCR turns OFF and the load voltage (eL) is zero during this
period.
3.
The purpose of the diode(D) in the gate circuit is to prevent the gate cathode reverse
bias during the negative half cycle.
4.
The same sequence is repeated, when eS again goes positive.
5.
By varying Rv, the load voltage can be controlled.
6.
If Rv increases, the firing angle will increase & vice versa.
7.
The limiting resistor Rmin is used to limit the gate current to a safe value while varying
Rv.
8.
The stabilizing resistor Rb should have such a value that maximum voltage drop across
it does not exceed maximum possible gate voltage Vgm. This can happen only when Rv
is zero.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 25 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
When the supply voltage has reached its peak, Emax
From the voltage distribution
The thyristor will trigger when the instantaneous anode voltage, es, is
where
Ig(min) =
Vd
=
Vg(min) =
Minimum gate current to trigger the thyristor
Voltage drop across the diode
gate-voltage to trigger, corresponding to Ig(min).
The waveform for R firing circuit is shown in Fig 4.b.
es
Vak
VL,i L
Fig. 4.b Waveform for R Firing circuit
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 26 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
4.2.
PEC14M12
RC Firing Circuit:
The RC firing circuit which is normally used for simple phase control gives variation of firing
angle beyond 90. The circuit diagram is shown in fig 4.c.
Vo
Load
A
D2
24V AC
50 Hz
SCR
Rv
D1
G
C
Fig. 4.c RC Firing circuit
The circuit operates as follows,
1.
When es goes positive and the capacitor voltage Vc equals to gate trigger voltage
Vgt(=Vg min + VD1), the SCR will turn ON.
2.
After this, the capacitor holds to a small positive voltage as shown in the waveform.
3.
During negative half cycle, capacitor c charges through D2 with lower plate positive to
the supply voltage Emax.
4.
The diode D1 prevents the break down of the gate to cathode junction during negative
half cycle.
5.
In the range of power frequencies, the RvC for zero output voltage is given by
137
.
Rv C
2
Where T= 1/f = period of AC line frequency in seconds
6.
The maximum value of Rv is given by,
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 27 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
Where
VD1
eS
=
Voltage drop across the diode D1
Supply voltage at which SCR turn ON
The waveform for RC firing circuit is shown in Fig 4.d.
Emax
es
Vg(min)
Vc
-Emax
e
t
V
AK
Fig. 4.d Waveform for RC Firing circuit
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 28 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
4.3. UJT FIRING CIRCUIT:
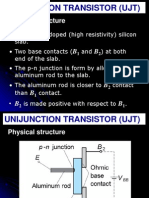
4.3.1. UNI JUNCTION TRANSISTOR:
UJT is commonly used to generate triggering signals for SCR. UJT has three terminals called
the Emitter E, Base one, B1 and Base two, B2. The basic structure and circuit symbol of UJT
is shown in Fig 4.e and 4.f.
B2
B2
R B2
P-type
E
R B1
N-type
B1
B1
Fig. 4.e. Basic Structure of UJT
Fig. 4.f. Circuit Symbol for UJT
Between B1 and B2 the unijunction has the characteristics of an ordinary resistance. This is
the interbase resistance RBB and has value in the range 4.7 to 9.1K. The VI characteristics
of UJT is shown in fig 4.g.
V
E
Negative
Resistance
Region
Cutoff
region
VP
Saturation
region
Peak Point
Valley Point
IP
IV
IE
Fig. 4.g. V-I Characteristics of UJT
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 29 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
4.3.2 Synchronized UJT Triggering [or Ramp Triggering
A synchronized UJT triggering circuit using an UJT is shown in fig 4.h. Diodes D1-D4
rectifies the input AC to DC. Zener diode Z is used to clip the rectified voltage to a standard
level Vz, which remains constant except near the Vdc zero.
R1
+
D1
+
i1
D3
R2
24V AC
Vdc
VZ
B2
G1
D4
D2
C
Vc
B1
K1
G2
Pulse
Transformer
K2
Fig. 4.h Synchronized UJT Triggering circuit
The zener voltage Vz is applied to charging circuit RC. So capacitor C charges by current i1.
When the capacitor voltage reaches threshold voltage Vz, the E-B1 junction of UJT breaks
down and C charges through primary of pulse transformer sending a current i2.
As the current i2 is in the form of pulse, SCR with positive anode voltage would turn ON.
Varying R can control rate of rise of capacitor voltage. This method of control is called ramp
control. The firing angle can be controlled up to 150. The waveform for generation of output
pulses for the given circuit is shown in fig 4.i.
Vdc
Vc
Vz
Vdc
Vz
Vc
Vc
Pulse
Voltage
t
Fig.4.i Waveform for synchronized UJT triggering circuit
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 30 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
PEC14M12
The period of oscillation, T, is independent of the dc supply voltage Vs, and is given by
(5.1)
The line synchronized UJT trigger circuit can be used for,
1.
Single phase AC controller
2.
Single phase half wave controlled converter
3.
Single phase controlled rectifier with center-tapped transformer (bi-phase half wave
converter)
4.
Single phase half controlled bridge rectifier.
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 31 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
2.6
1.
PEC14M12
DATA SHEETS
SCR (TYN612)
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 32 ]
R, RC & UJT FIRING MODULE
2.
PEC14M12
UJT (2N2646)
Vi Microsystems Pvt. Ltd.,
[ 33 ]
También podría gustarte
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsDe EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsAún no hay calificaciones
- Real-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsDe EverandReal-Time Simulation Technology for Modern Power ElectronicsAún no hay calificaciones
- O.C.C. & Load Test On Separately Excited D.C. GeneratorDocumento18 páginasO.C.C. & Load Test On Separately Excited D.C. GeneratorSuyash KothawadeAún no hay calificaciones
- EEET 205 Lab - 102Documento53 páginasEEET 205 Lab - 102Franch Maverick Arellano LorillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusDocumento6 páginasExperiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusNikhil BindalAún no hay calificaciones
- III Eee 05 Ee8501 Psa Unit 1Documento37 páginasIII Eee 05 Ee8501 Psa Unit 1BALAKRISHNANAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Electronics Lab Manual1Documento72 páginasPower Electronics Lab Manual1Harish SvAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Emitter UnbypassedDocumento38 páginasCommon Emitter Unbypassedaliffuden 123Aún no hay calificaciones
- ECE 424 - Assign3Documento2 páginasECE 424 - Assign3Amos Atandi0% (1)
- Edc Project Report: Prof. Garima SolankiDocumento32 páginasEdc Project Report: Prof. Garima SolankiAnime X100% (1)
- Chapter Five: Ac-Ac Conversion: Ac Voltage ControllerDocumento56 páginasChapter Five: Ac-Ac Conversion: Ac Voltage Controllerfor lifeAún no hay calificaciones
- Boost DesignDocumento4 páginasBoost DesignmuthukumartharaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Power System Stability - Unit 4 PSOCDocumento57 páginasPower System Stability - Unit 4 PSOChareesh.makesuAún no hay calificaciones
- Closed Loop Control of Separately Excited DC MotorDocumento13 páginasClosed Loop Control of Separately Excited DC MotorJAIRAJ MIRASHIAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Machine Example ProblemsDocumento4 páginasDC Machine Example ProblemsFemi Prince0% (1)
- Switch Mode InvertersDocumento22 páginasSwitch Mode InvertersVivek SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- 360 Topic 6 DC MachineDocumento33 páginas360 Topic 6 DC MachineAchsan ArfandiAún no hay calificaciones
- Alternators Connected To Infinite Bus BarDocumento9 páginasAlternators Connected To Infinite Bus BarbharatkAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocumento5 páginasPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Power Electronics Chapter#06Documento34 páginasPower Electronics Chapter#06Bilal HussainAún no hay calificaciones
- Design Considerations For An LLC Resonant ConverterDocumento29 páginasDesign Considerations For An LLC Resonant Converterbacuoc.nguyen356Aún no hay calificaciones
- Emf Equation of AlternatorDocumento2 páginasEmf Equation of AlternatorThe Engineers EDGE, CoimbatoreAún no hay calificaciones
- PCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveDocumento5 páginasPCEG 403 Lab No. 1 Title: Simulation of Single Phase Half Wave Converter DC DriveJanup PokharelAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Machine-1 Manual PDFDocumento40 páginasElectrical Machine-1 Manual PDFsoumencha80% (5)
- I DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationDocumento71 páginasI DT DT DT DT: Class Notes On Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationTia Nur AmaliahAún no hay calificaciones
- All Classroom Class ExamplesDocumento51 páginasAll Classroom Class ExamplesAhmed Sabri0% (1)
- Experiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodDocumento6 páginasExperiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Method61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- Basic Motor ControlDocumento17 páginasBasic Motor ControlHeizen BulanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter - 2 DC & AC BridgesDocumento18 páginasChapter - 2 DC & AC Bridgesvnyshreyas100% (2)
- Drives and Control Lab ManualDocumento36 páginasDrives and Control Lab ManualKabilanAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocumento5 páginasLab#2B: Half-Wave Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterHemanth GedelaAún no hay calificaciones
- EE2351Documento27 páginasEE2351Anonymous TJRX7C100% (1)
- CH 5 Full-Wave RectifierDocumento21 páginasCH 5 Full-Wave RectifierSYAFIQAH ISMAILAún no hay calificaciones
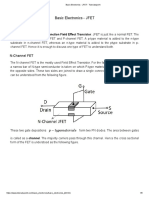
- Basic Electronics - JFET - TutorialspointDocumento6 páginasBasic Electronics - JFET - Tutorialspointgunasekaran k100% (1)
- Experiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip TestDocumento3 páginasExperiment No.5-Determination of XD and XQ of Synchronous Machine by Slip Test61EEPrabhat PalAún no hay calificaciones
- Ujt Relaxation OscillatorsDocumento47 páginasUjt Relaxation OscillatorsGeorge CamachoAún no hay calificaciones
- Glover 10 ExDocumento13 páginasGlover 10 ExAseel Bait MaditAún no hay calificaciones
- Viper 12s Buck Boost ConverterDocumento14 páginasViper 12s Buck Boost ConverterelkillyAún no hay calificaciones
- Speed Torque Characteristics of 3 Phase Induction MotorDocumento4 páginasSpeed Torque Characteristics of 3 Phase Induction MotorAdi AdnanAún no hay calificaciones
- TRIAC - CharacteristicsDocumento3 páginasTRIAC - CharacteristicsSri RamAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Controlled Rectifier DC DrivesDocumento25 páginas4 Controlled Rectifier DC DrivesshonmlrAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 1 - Single Phase TransformerDocumento9 páginasExperiment 1 - Single Phase TransformerKhairul Islam HimelAún no hay calificaciones
- Induction Motor Electric BrakingDocumento12 páginasInduction Motor Electric Brakingmastanamma.Y100% (1)
- Aim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpDocumento8 páginasAim: To Test Differentiator and Integrator Circuits Using Ua741op-AmpAvinash Nandakumar100% (1)
- 1.voltage Distribution Across String of InsulatorsDocumento3 páginas1.voltage Distribution Across String of Insulatorsarjuna4306Aún no hay calificaciones
- Thyristor ReportDocumento9 páginasThyristor ReportDhaval GamiAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch8 DC Machine FundamentalsDocumento29 páginasCh8 DC Machine FundamentalsalpizraAún no hay calificaciones
- Short Transmission LineDocumento18 páginasShort Transmission LineNaga AnanthAún no hay calificaciones
- BEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterDocumento38 páginasBEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterSaif KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics 1 Lab Manual PDFDocumento30 páginasElectronics 1 Lab Manual PDFAnonymous 7y7TeR0% (1)
- Hopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorDocumento5 páginasHopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorVarun VadluriAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignments StudentsDocumento2 páginasAssignments StudentsManju Chakraborty100% (1)
- EM2 - Lab - 10 - Synchronous Motor Part I - STD PDFDocumento7 páginasEM2 - Lab - 10 - Synchronous Motor Part I - STD PDFneonAún no hay calificaciones
- HV Impulse CurrentDocumento9 páginasHV Impulse CurrentEdward CullenAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFDocumento49 páginasCHAPTER 3 - Transducer and Sensors PDFROYALNEWSS100% (1)
- A Balanced Star Connected Load Takes 90 A From A Balanced 3-Phase, 4-Wire Supply. If The Fuses in The Y and B Phases Are Removed, Find The Symmetrical Components of The Line CurrentsDocumento1 páginaA Balanced Star Connected Load Takes 90 A From A Balanced 3-Phase, 4-Wire Supply. If The Fuses in The Y and B Phases Are Removed, Find The Symmetrical Components of The Line CurrentsممشطAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayDocumento5 páginasLab 13-Under Voltage and Over Voltage Monitoring Numerical RelayAliza Sharif100% (1)
- Tutorial1 (SynchronousMchines)Documento3 páginasTutorial1 (SynchronousMchines)Zamira JamilAún no hay calificaciones
- On AC Voltage ControllersDocumento25 páginasOn AC Voltage ControllersSahil ChoudharyAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog To DigitalDocumento5 páginasAnalog To DigitalmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Counselling Code:5530 Department of Auto Mobile EngineeringDocumento17 páginasCounselling Code:5530 Department of Auto Mobile EngineeringmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab QuestionsDocumento4 páginasLab QuestionsmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Assign 3Documento7 páginasAssign 3manojAún no hay calificaciones
- Moniga Mam Bank OfficerDocumento1 páginaMoniga Mam Bank OfficermanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Specify The ANFIS Software ToolDocumento1 páginaSpecify The ANFIS Software ToolmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Stepper MotorsDocumento9 páginasStepper MotorsmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Semi NorDocumento3 páginasSemi NormanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Regulations - 2013 First Semester Ge6162 Engineering Practices Laboratory Group B' (Electronics Engineering) SET-1Documento4 páginasRegulations - 2013 First Semester Ge6162 Engineering Practices Laboratory Group B' (Electronics Engineering) SET-1manojAún no hay calificaciones
- Proofs of The Real Existence of Illuminism 1802 - Payson, Seth, 1758-1820 Adams, John, 1735-1826, John Adams LibraryDocumento304 páginasProofs of The Real Existence of Illuminism 1802 - Payson, Seth, 1758-1820 Adams, John, 1735-1826, John Adams LibraryTruth1013 Brightstar2211Aún no hay calificaciones
- My Pan NumberDocumento1 páginaMy Pan NumbermanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Gim 2016Documento1 páginaGim 2016manojAún no hay calificaciones
- Sindalagundu Post, Dindigul - 624 002, Tamilnaduph: 0451-2448800 Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocumento2 páginasSindalagundu Post, Dindigul - 624 002, Tamilnaduph: 0451-2448800 Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Programme Calendar 2015 16Documento65 páginasProgramme Calendar 2015 16Reeta DuttaAún no hay calificaciones
- T.Ramya,: Project DetailsDocumento4 páginasT.Ramya,: Project DetailsmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Logarithmic Amplifier:) /R + I 0 Implies I V /RDocumento3 páginasLogarithmic Amplifier:) /R + I 0 Implies I V /RmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Duty Allotment Ct-1Documento1 páginaDuty Allotment Ct-1manojAún no hay calificaciones
- Duty Allotment Ct-1Documento1 páginaDuty Allotment Ct-1manojAún no hay calificaciones
- Igbt& MosfetDocumento28 páginasIgbt& MosfetmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- Speed Control of Induction Motor DrivesDocumento11 páginasSpeed Control of Induction Motor DrivesmanojAún no hay calificaciones
- GK Holiday Homework For Class 6Documento5 páginasGK Holiday Homework For Class 6ere50xvb100% (1)
- Excerscise 1 (C++ Syntax)Documento6 páginasExcerscise 1 (C++ Syntax)Muhammad Rafli FazalAún no hay calificaciones
- Call Letter 1-41Documento41 páginasCall Letter 1-41majeedkalavAún no hay calificaciones
- DatasheetDocumento13 páginasDatasheetJOSE MARIA DANIEL CANALESAún no hay calificaciones
- Accessories Cosasco Two-Inch System: Hollow Plug Assembly Solid Plug AssemblyDocumento2 páginasAccessories Cosasco Two-Inch System: Hollow Plug Assembly Solid Plug AssemblyFabricio Vega EstrellaAún no hay calificaciones
- Significant Zeros Worksheet AnswersDocumento6 páginasSignificant Zeros Worksheet AnswersEthan Heinzel100% (5)
- Aramid Yt510Documento4 páginasAramid Yt510Srinath SelvakumaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab - 03 Task On 2D ArrayDocumento3 páginasLab - 03 Task On 2D ArrayShantoAún no hay calificaciones
- BCG Hybrid Work Is The New Remote Work Sep 2020Documento8 páginasBCG Hybrid Work Is The New Remote Work Sep 2020khanhphamngoc1716Aún no hay calificaciones
- PanouDocumento2 páginasPanouMihaiNeacsuAún no hay calificaciones
- 329M Manual (English) 171027 SolventDocumento12 páginas329M Manual (English) 171027 SolventРадислав ЈовковићAún no hay calificaciones
- Minicargador 246D3Documento15 páginasMinicargador 246D3Carlos U. CallirgosAún no hay calificaciones
- A Novel Three-Phase Software Phase-Locked Loop Based On Frequency-Locked Loop and Initial Phase Angle Detection Phase-Locked LoopDocumento6 páginasA Novel Three-Phase Software Phase-Locked Loop Based On Frequency-Locked Loop and Initial Phase Angle Detection Phase-Locked LoopjunyeolAún no hay calificaciones
- 01chapter One-Introduction To OOPDocumento17 páginas01chapter One-Introduction To OOPYaikob KebedeAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 3 - NIST SP 800-63 Digital Identity GuidelinesDocumento3 páginasCapitulo 3 - NIST SP 800-63 Digital Identity GuidelinesCristiane LimaAún no hay calificaciones
- Standard Ib Clutch: Twin Disc Power Take-OffsDocumento2 páginasStandard Ib Clutch: Twin Disc Power Take-OffsLeonardo Jiménez CastellanosAún no hay calificaciones
- Summative Test 1 EnglishDocumento4 páginasSummative Test 1 EnglishIris KlenchAún no hay calificaciones
- PVAC Tie in Method of StatementDocumento8 páginasPVAC Tie in Method of StatementKAY UNAAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid SaturationDocumento54 páginasFluid SaturationRajat WadhwaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Answers: Warm-Up 1 Workout 1Documento29 páginasAnswers: Warm-Up 1 Workout 1Hassan mouslmaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Weight Per Meter of Weld MetalDocumento1 páginaWeight Per Meter of Weld MetalLuis SPAún no hay calificaciones
- HOW TO CASHOUT Remitly Method WCCDocumento3 páginasHOW TO CASHOUT Remitly Method WCCcody100% (8)
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 8-3: Practice Activities: Passing ParametersDocumento2 páginasDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 8-3: Practice Activities: Passing ParametersAlan V.B.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Harris Falcon Iii RF-7850S SPR: Advanced Wideband Secure Personal Radio (SPR)Documento2 páginasHarris Falcon Iii RF-7850S SPR: Advanced Wideband Secure Personal Radio (SPR)Jam LouizAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 8 SD Single Degree of Freedom System Periodic LoadingDocumento37 páginasLecture 8 SD Single Degree of Freedom System Periodic LoadingSarose PrajapatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Functional Programming: John Harrison University of CambridgeDocumento19 páginasIntroduction To Functional Programming: John Harrison University of Cambridgeceham66931Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8086 Lab ProgramsDocumento121 páginas8086 Lab ProgramsManjesh Kumar Kakade89% (27)
- Oracle 1Z0-071 Updated Page 1Documento3 páginasOracle 1Z0-071 Updated Page 1AljuanAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 - Mill Feed System With Gate Valves For POLYCOM®Documento49 páginas02 - Mill Feed System With Gate Valves For POLYCOM®CHRISTIAN ROJAS VALENZUELAAún no hay calificaciones
- Siga OshdDocumento4 páginasSiga OshdEduardo LópezAún no hay calificaciones