Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Comandos Ospf Virtual Link
Comandos Ospf Virtual Link
Cargado por
Carlos RafaelDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Comandos Ospf Virtual Link
Comandos Ospf Virtual Link
Cargado por
Carlos RafaelCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
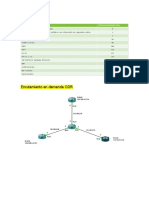
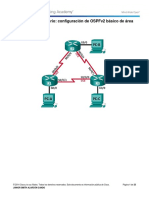
PARA CONFIGURAR VIRTUAL LINK USAR ROUTERS 1841
---------------------------------------------1.-INTERFACES Y DIRECCIONAMIENTO
-------------------------------R1(config)# interface loopback 1
R1(config-if)# description Engineering Department //ESTE NOMBRE VARIA DEPENDIEND
O DE LO QUE SE PIDA
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# interface loopback 30
R1(config-if)# ip address 172.30.30.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# clockrate 64000
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config)# interface loopback 2
R2(config-if)# description Marketing Department //ESTE NOMBRE VARIA DEPENDIENDO
DE LO QUE SE PIDA
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/0
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# clockrate 64000
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config)# interface loopback 3
R3(config-if)# description Accounting Department //ESTE NOMBRE VARIA DEPENDIENDO
DE LO QUE SE PIDA
R3(config-if)# ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 100
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.100.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 101
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.101.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 102
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.102.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 103
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.103.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# interface serial 0/0/1
R3(config-if)# ip address 10.1.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# no shutdown
2.-PROCESO OSPF
--------------R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 //DECLARACION DE REDES DIR
ECTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 0
R1(config-router)# network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 //DECLARACION DE REDES DIRE
CTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 0
R1(config-router)# exit
R1(config)# interface loopback 1
R1(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# network 10.1.12.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 //DECLARACION DE REDES DIR
ECTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 0
R2(config-router)# network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 //DECLARACION DE REDES DIRE
CTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 0
R2(config-router)# exit
R2(config)# interface loopback 2
R2(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
AGREGAR LA RED 10.1.23.0/24 A OSPF Y DECLARARLAS EN AREA 23
----------------------------------------------------------R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# network 10.1.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 23
AGREGAR LAS REDES 10.1.23.0/24 Y 10.1.3.0/24 A OSPF Y DECLARARLAS EN AREA 23
---------------------------------------------------------------------------R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# network 10.1.23.0 0.0.0.255 area 23 //DECLARACION DE REDES DI
RECTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 23
R3(config-router)# network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 23 //DECLARACION DE REDES DIR
ECTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 23
R3(config-router)# exit
R3(config)# interface loopback 3
R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
3.-CREAR VIRTUAL LINK
-----------------Son usados bsicamente para solucionar dos problemas:
Conectar una rea que no tiene conectividad fsica al backbone.
"Reparar" un backbone que ha perdido continuidad.
Son conexiones lgicas, que se parecen "vagamente" a un tnel.
No encapsulan el trfico.
Se configuran entre ABR, donde uno de ellos tiene "contacto" con el rea 0, no pue
den formarse usando reas "stub".
Esta conexin se convierte en un "link" point-to-point entre ellos y se generan LS
A de Tipo 1 para esa nueva conexin
en el rea 0. Los mensajes entre ellos son "Unicast"
El coste del virtual link depende del camino para conectar ambos ABR.
CONFIGURACION DE VIRTUAL LINK
----------------------------AADIR LOOPBACKS 100 a 103 EN R3 en el rea de 100.
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# network 192.168.100.0 0.0.3.255 area 100
ES DIRECTAMENTE CONECTADAS /24 Y AREA 100
R3(config-router)# exit
R3(config)# interface loopback 100
R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 101
R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 102
R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
R3(config-if)# interface loopback 103
R3(config-if)# ip ospf network point-to-point //PARA QUE LA
//DECLARACION DE RED
RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
RED QUE HAY EN LA LO
OPBACK SEA ANUNCIADA COMPLETA
OTRA FORMA DE CREAR UN VIRTUAL LINK ES CON EL AREA
-------------------------------------------------R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# area 23 virtual-link 192.168.103.1 //IP DE LA RED A LA QUE QU
EREMOS LLEGAR
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# area 23 virtual-link 10.1.2.1 //IP DE LA RED A LA QUE QUEREMO
S LLEGAR
Para asegurarse de que el ID del router de los enlaces extremos virtuales se man
tiene constante, se puede configurar
estticamente el ID del router OSPF del enlace terminales virtuales con el comando
router-id.
4.-SUMARIZACION POR AREA Y POR UN RANGO
--------------------------------------AQUI SE SUMALIZARA LA LOOPBACK DE LA 100 A LA 103 DEL R3 EN UNA SOLA PERO CON /2
2
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# area 100 range 192.168.100.0 255.255.252.0
VERIFICAR
--------R2# show ip route
5.-GENERAR RUTA POR DEFECTO EN OSPF
----------------------------------GENERALMENTE SE USA CUANDO EN UN ROUTER HAY UNA CONEXION A INTERNET, OSEA PARA T
RAFICO DESCONOCIDO
R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# default-information originate always
También podría gustarte
- Asterisk PBX: Aprende a crear y diseñar soluciones de telefonía IP desde ceroDe EverandAsterisk PBX: Aprende a crear y diseñar soluciones de telefonía IP desde ceroCalificación: 1 de 5 estrellas1/5 (1)
- Configuración de Voip en Switches Capa 3 CISCODocumento9 páginasConfiguración de Voip en Switches Capa 3 CISCOdenis0055100% (5)
- Laboratorio Conmutacion de CiruitosDocumento16 páginasLaboratorio Conmutacion de CiruitosTomás Hurtado CrassAún no hay calificaciones
- RIP y Las Rutas de DesplazamientoDocumento5 páginasRIP y Las Rutas de DesplazamientoGUTIERREZ AGUILAR MARCO DENNISAún no hay calificaciones
- Redes Punto A Punto OSPFDocumento14 páginasRedes Punto A Punto OSPFMau ChillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Configuracion RouterDocumento4 páginasTarea Configuracion RouterelizabethtaypemayhuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Kadr U2 Ea LupmDocumento22 páginasKadr U2 Ea LupmJhorge TerrezpAún no hay calificaciones
- Copia de 6 TroubleShooting OSPF. Caso 2Documento8 páginasCopia de 6 TroubleShooting OSPF. Caso 2NicProofAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica#2 Repaso-De-Enrutamiento-Estático PDFDocumento18 páginasPráctica#2 Repaso-De-Enrutamiento-Estático PDFLuisChaconAún no hay calificaciones
- PR06 OSPF Multiarea-2Documento8 páginasPR06 OSPF Multiarea-2Germán VillegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto Routing y ServerDocumento7 páginasProyecto Routing y ServerEsneider Juventud Compromiso DesarrolloAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de Laboratorio OSPFDocumento8 páginasPractica de Laboratorio OSPFCesar Alfredo GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Apunts CCNA4Documento6 páginasApunts CCNA4no pogas nombreAún no hay calificaciones
- Pasos Comandos RedDocumento3 páginasPasos Comandos RedEduardo Andrés LabrinAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 3 Enrutamiento EstáticoDocumento8 páginasPráctica 3 Enrutamiento EstáticoMOISÉS ARONAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features InstructionsDocumento3 páginas5.1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features InstructionszerosAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 10Documento10 páginasCapitulo 10drdaviidAún no hay calificaciones
- Este Post Muestra La Configuración Básica de OSPF en Una Única Área Utilizando Routers CiscoDocumento17 páginasEste Post Muestra La Configuración Básica de OSPF en Una Única Área Utilizando Routers CiscoRicardo FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Ospf 2022Documento19 páginasOspf 2022DavidFer DuraznoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio CCNPDocumento8 páginasEjercicio CCNPNacxhitl PereiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntes CCNPDocumento64 páginasApuntes CCNPmarcos aranedaAún no hay calificaciones
- UD5.2. Enrutamiento EstáticoDocumento17 páginasUD5.2. Enrutamiento EstáticoAmisa AjAún no hay calificaciones
- Router Configuracion OSPF NATDocumento20 páginasRouter Configuracion OSPF NATJose Arturo Sanchez RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- 8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2Documento23 páginas8.2.4.5 Lab - Configuring Basic Single-Area OSPFv2Marlon MontenegroAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 6Documento11 páginasCapitulo 6c2franco23Aún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen Del Capítulo 10Documento8 páginasResumen Del Capítulo 10Angel MartínezAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria, Explicacion Rip v2 y OspfDocumento36 páginasTeoria, Explicacion Rip v2 y Ospffelipe pinoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMDocumento8 páginas2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMjhon alexander yasno saenzAún no hay calificaciones
- PR6 Enrutamiento EstáticoDocumento8 páginasPR6 Enrutamiento EstáticoDavidFer DuraznoAún no hay calificaciones
- Configuración Básica de OSPFDocumento9 páginasConfiguración Básica de OSPFHahamitey Siempre El Pro100% (1)
- Grupo39 ABE2Documento56 páginasGrupo39 ABE2Indra GebAún no hay calificaciones
- Completado - G - 2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2Documento3 páginasCompletado - G - 2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2GIBRAN AARON LOEZA DE LA CRUZAún no hay calificaciones
- Comandos CCNPDocumento6 páginasComandos CCNPtool1234Aún no hay calificaciones
- Enrutamiento Dinamico RIPDocumento0 páginasEnrutamiento Dinamico RIPJC IreneoAún no hay calificaciones
- Todos Los Comandos de CcnaDocumento8 páginasTodos Los Comandos de CcnaRajardkt50% (2)
- informeNAT PatDocumento5 páginasinformeNAT PatLeimer GuambañaAún no hay calificaciones
- TARE - 1 - CCNA - 2 - Grupo - 2150507 - 27Documento200 páginasTARE - 1 - CCNA - 2 - Grupo - 2150507 - 27alexis pedrozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Comandos Ccna 4Documento11 páginasComandos Ccna 4franciscofvz16078Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2Documento5 páginas2.4.11 Packet Tracer - Modify Single-Area OSPFv2ADONIS DAMIAN ALCIVAR NIETOAún no hay calificaciones
- TAREA 2 - 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuración de OSPFv2 en Una Red de Accesos MúltiplesDocumento19 páginasTAREA 2 - 5.1.2.13 Lab - Configuración de OSPFv2 en Una Red de Accesos MúltiplesDiegoStivenRubioMorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Frame Relay Punto A MultipuntoDocumento5 páginasFrame Relay Punto A MultipuntoJavier Pablo ToctoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.5.1 Configuración Básica de PPP PDFDocumento21 páginas2.5.1 Configuración Básica de PPP PDFLuis Tovar100% (1)
- Configuracion Basica Router CiscoDocumento8 páginasConfiguracion Basica Router Ciscoismael GHAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Cisco Online CCNA4 V4.0 - "CAPITULO 3" - by Alen.Documento10 páginasExamen Cisco Online CCNA4 V4.0 - "CAPITULO 3" - by Alen.Alain Droguett LaredoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ericka Nava EVN-103 Cap10Documento11 páginasEricka Nava EVN-103 Cap10ericka navaAún no hay calificaciones
- GastoncraciaDocumento12 páginasGastoncraciaSamuel Pardo MesiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 6 - 18 May - FrameRelayDocumento6 páginasClase 6 - 18 May - FrameRelayfargotteAún no hay calificaciones
- Configuración Router ConsultaDocumento12 páginasConfiguración Router ConsultaAnthonny SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 7Documento32 páginasLab 7hi im adcAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILMDocumento23 páginas6.2.3.8 Lab - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv2 - ILMSergio TejedorAún no hay calificaciones
- PR10 AtributosBGPDocumento8 páginasPR10 AtributosBGPDarwin AlvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion PPPDocumento23 páginasSolucion PPPGeorge Yánez CajasAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 10Documento9 páginasCH 10Ferney ChicaAún no hay calificaciones
- UF1879 - Equipos de interconexión y servicios de redDe EverandUF1879 - Equipos de interconexión y servicios de redAún no hay calificaciones
- Prácticas de redes de datos e industrialesDe EverandPrácticas de redes de datos e industrialesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5)
- Asterisk PBX: Aprenda a crear y diseñar soluciones de telefonía IP desde ceroDe EverandAsterisk PBX: Aprenda a crear y diseñar soluciones de telefonía IP desde ceroCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Administración de servicios web: Anatomía del internetDe EverandAdministración de servicios web: Anatomía del internetAún no hay calificaciones
- Instalación y Configuración de SquirrelMailDocumento5 páginasInstalación y Configuración de SquirrelMailmjorquera1986Aún no hay calificaciones
- Las Derivadas 11 06Documento40 páginasLas Derivadas 11 06mjorquera1986Aún no hay calificaciones
- 037 - T05-Introducción Al Cálculo de Derivadas. AplicacionesDocumento27 páginas037 - T05-Introducción Al Cálculo de Derivadas. AplicacionesUlises Giancarlo Sánchez RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ospf Multi AreaDocumento4 páginasOspf Multi Areamjorquera1986Aún no hay calificaciones
- Seccion SDHDocumento123 páginasSeccion SDHIvan AlmironAún no hay calificaciones
- F.O. y SDHDocumento25 páginasF.O. y SDHmjorquera1986Aún no hay calificaciones
- UAM Marival II Foro Redes PresentacionDocumento16 páginasUAM Marival II Foro Redes Presentacionmaeritzaplazas0508Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3CBLSF50H 50 Puertos Gigabit 2PDocumento2 páginas3CBLSF50H 50 Puertos Gigabit 2PBrian AguirreAún no hay calificaciones
- Yeastar S Series VoIP PBX Datasheet EsDocumento2 páginasYeastar S Series VoIP PBX Datasheet Esandrosky2674Aún no hay calificaciones
- RDT - T Final - 2018-19Documento339 páginasRDT - T Final - 2018-19Jose Luis Carrillo GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen PEP 1 RedesDocumento13 páginasResumen PEP 1 RedesGabriela MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- El Estándar IEEE 802Documento8 páginasEl Estándar IEEE 802eglis13Aún no hay calificaciones
- VLAN (Red LAN Virtual)Documento18 páginasVLAN (Red LAN Virtual)lpiloaceAún no hay calificaciones
- Evolución de Los Protocolos de Enrutamiento DinámicoDocumento22 páginasEvolución de Los Protocolos de Enrutamiento DinámicoEiner Vasquez CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio VTP, Vlan, Troncal, Enrutamiento Inter - Vlan, STPDocumento4 páginasEjercicio VTP, Vlan, Troncal, Enrutamiento Inter - Vlan, STPNelson TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- MODULO 1 CCNA R&s ResumenDocumento21 páginasMODULO 1 CCNA R&s ResumenRoger LacosteAún no hay calificaciones
- Router de Servicios Integrados Cisco 4321 2 RoutersDocumento12 páginasRouter de Servicios Integrados Cisco 4321 2 RoutersdiegoAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduccion A Las Redes 1.1Documento63 páginasIntroduccion A Las Redes 1.1elkasadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Banco Preguntas Redes 2Documento20 páginasBanco Preguntas Redes 2sotogustavo27589Aún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen Capa de RedDocumento16 páginasResumen Capa de Redstefany0% (1)
- Esquemas y Diagramas de Red - Topologias XDSLDocumento2 páginasEsquemas y Diagramas de Red - Topologias XDSLjffm7147Aún no hay calificaciones
- Multiplexacion TDMDocumento4 páginasMultiplexacion TDMGabriel0% (1)
- Caracteristicas ICMPv6Documento3 páginasCaracteristicas ICMPv6Paul AstudilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Preguntas GPRSDocumento3 páginasPreguntas GPRSPedro LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen 1 - Revisión Del Intento PDFDocumento16 páginasExamen 1 - Revisión Del Intento PDFJefferson AlquingaAún no hay calificaciones
- Rdsi, Atm, Frame Relay, AdslDocumento9 páginasRdsi, Atm, Frame Relay, AdsljlAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTPDocumento8 páginas2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTPWesthly Jose Sarabia CarrilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Switch SEL 2730MDocumento8 páginasSwitch SEL 2730MReagan A Cohen GAún no hay calificaciones
- Franko Marchant Tera Semana6 Fundamentos de Redes y SeguridadDocumento7 páginasFranko Marchant Tera Semana6 Fundamentos de Redes y SeguridadFranko Andres Marchant CortezAún no hay calificaciones
- TelecomunicacionesDocumento64 páginasTelecomunicacionesEdwinRoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial 3Documento3 páginasParcial 3Carlos Monroy100% (1)
- Tecnologia WiDocumento5 páginasTecnologia WiBryan RigailAún no hay calificaciones
- 916-Texto Del Artículo-3289-1-10-20150601Documento6 páginas916-Texto Del Artículo-3289-1-10-20150601Francisco Joel CevallosAún no hay calificaciones
- E2 - FinalDocumento73 páginasE2 - FinalAlicia PeraltaAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.1.1.7 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDocumento8 páginas6.1.1.7 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesEricka Ordoñez0% (1)
- CS 1.2.1.7 JavierjhonycamposcrisostomoDocumento3 páginasCS 1.2.1.7 JavierjhonycamposcrisostomoJavier Jhony Campos CrisostomoAún no hay calificaciones