Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Uality of Ervice ART: Quality of Service Models IP Type of Service (TOS)
Cargado por
jhonvelsTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Uality of Ervice ART: Quality of Service Models IP Type of Service (TOS)
Cargado por
jhonvelsCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
packetlife.
net
by Jeremy Stretch v2.0
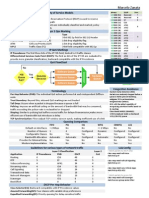
QUALITY OF SERVICE PART 1
Quality of Service Models
Layer 2 QoS Markings
Medium
Ethernet Class of Service (CoS)
Name Type
3-bit 802.1p field in 802.1Q header
Frame Relay Discard Eligibility (DE) 1-bit drop eligibility flag
Best Effort No QoS policies are implemented
Integrated Services (IntServ)
Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) is used to reserve bandwidth per-
flow across all nodes in a path
Differentiated Services (DiffServ)
Packets are individually classified and marked; policy decisions are made
independently by each node in a path
IP Type of Service (TOS)
Ver HL Len TOS
Precedence
DSCP
Precedence/DSCP
Binary
111000 Reserved
DSCP
56
Prec.
7
110000 Reserved 48 6
101110 EF 46 5
100000 32
4
100010 34
100100 36
100110 38
011000 24
3
011010 26
011100 28
011110 30
010000 16
2
010010 18
010100 20
010110 22
001000 8
1
001010 10
001100 12
001110 14
000000 BE 0 0
CS4
AF41
AF42
AF43
CS3
AF31
AF32
AF33
CS2
AF21
AF22
AF23
CS1
AF11
AF12
AF13
ATM
MPLS
Cell Loss Priority (CLP)
Traffic Class (TC)
1-bit drop eligibility flag
3-bit field compatible with 802.1p
IP QoS Markings
IP Precedence
The first three bits of the IP TOS field; limited to 8 traffic classes
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
The first six bits of the IP TOS are evaluated to provide more granular
classification; backward-compatible with IP Precedence
QoS Flowchart
Hardware
Queue
Queuing
Decision
S
c
h
e
d
u
l
e
r
Software Queue
No
Yes
Software Queue
Software Queue
HW
Queue
Full?
Terminology
Per-Hop Behavior (PHB)
The individual QoS action performed at each independent DiffServ node
Trust Boundary Beyond this, inbound QoS markings are not trusted
Tail Drop Occurs when a packet is dropped because a queue is full
Policing
Imposes an artificial ceiling on the amount of bandwidth that may be
consumed; traffic exceeding the policer rate is reclassified or dropped
Shaping
Similar to policing but buffers excess traffic for delayed transmission;
makes more efficient use of bandwidth but introduces a delay
DSCP Per-Hop Behaviors
Class Selector (CS) Backward-compatible with IP Precedence values
Assured Forwarding (AF) Four classes with variable drop preferences
Expedited Forwarding (EF) Priority queuing for delay-sensitive traffic
Congestion Avoidance
Random Early Detection (RED)
Packets are randomly dropped
before a queue is full to prevent tail
drop; mitigates TCP
synchronization
Weighted RED (WRED)
RED with the added capability of
recognizing prioritized traffic based
on its marking
TCP Synchronization
Flows adjust TCP window sizes in synch, making inefficient use of a link
Class-Based WRED (CBWRED)
WRED employed inside a class-
based WFQ (CBWFQ) queue
packetlife.net
by Jeremy Stretch v2.0
QUALITY OF SERVICE PART 2
Queuing Comparison
Default on Interfaces >2 Mbps
FIFO
Number of Queues 1
Configurable Classes
Bandwidth Allocation
Provides for Minimal Delay
Modern Implementation
No
Automatic
No
Yes
No
PQ
4
Yes
Automatic
Yes
No
No
CQ
Configured
Yes
Configured
No
No
<=2 Mbps
WFQ
Dynamic
No
Automatic
No
No
No
CBWFQ
Configured
Yes
Configured
No
Yes
No
LLQ
Configured
Yes
Configured
Yes
Yes
First In First Out (FIFO) Priority Queuing (PQ) LLQ Config Example
! Match packets by DSCP value
class-map match-all Voice
match dscp ef
!
class-map match-all Call-Signaling
match dscp cs3
!
class-map match-any Critical-Apps
match dscp af21 af22
!
! Match packets by access list
class-map match-all Scavenger
match access-group name Other
Class Definitions
policy-map Foo
class Voice
! Priority queue policed to 33%
priority percent 33
class Call-Signaling
! Allocate 5% of bandwidth
bandwidth percent 5
class Critical-Apps
bandwidth percent 20
! Extend queue size to 96 packets
queue-limit 96
class Scavenger
! Police to 64 kbps
police cir 64000
conform-action transmit
exceed-action drop
class class-default
! Enable WFQ
fair-queue
! Enable WRED
random-detect
Policy Creation
interface Serial0
! Apply the policy in or out
service-policy output Foo
Policy Application
LLQ Config Example
show policy-map [interface]
Show interface
show queue <interface>
High
Medium
Normal
Low
Hardware
Queue
Hardware Queue
Tx
Ring
Custom Queuing (CQ)
Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
Packets are transmitted in the
order they are processed
No prioritization is provided
Default queuing method on high-
speed (>2 Mbps) interfaces
Configurable with the tx-ring-
limit interface config command
Provides four static queues which
cannot be reconfigured
Higher-priority queues are
always emptied before lower-
priority queues
Lower-priority queues are at risk
of bandwidth starvation
Rotates through queues using
Weighted Round Robin (WRR)
Processes a configurable number
of bytes from each queue per turn
Prevents queue starvation but
does not provide for delay-
sensitive traffic
Queues are dynamically created
per flow to ensure fair processing
Statistically drops packets from
aggressive flows more often
No support for delay-sensitive
traffic
Class-Based WFQ (CBWFQ)
Low Latency Queuing (LLQ)
WFQ with administratively
configured queues
Each queue is allocated an
amount/percentage of bandwidth
No support for delay-sensitive
traffic
CBWFQ with the addition of a
policed strict-priority queue
Highly configurable while still
supporting delay-sensitive traffic
Flow 1
Flow 2
Flow n
...
Hardware
Queue
500 B/cycle
4500 B/cycle
1500 B/cycle
Queue A
Queue B
Queue C
Hardware
Queue
512 Kbps Min
1024 Kbps Min
Remainder
Queue A
Queue B
Default
Hardware
Queue
512 Kbps Min
1024 Kbps Min
Remainder
Queue A
Queue B
Default
512 Kbps Max Priority
Hardware
Queue
Show mls qos
También podría gustarte
- Configuring RSTPDocumento4 páginasConfiguring RSTPJose BenitezAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNP Studies - Configuring DHCP Snooping - Packet Pushers PDFDocumento10 páginasCCNP Studies - Configuring DHCP Snooping - Packet Pushers PDFKaymaynaijaAún no hay calificaciones
- WSA 9-2-0 UserGuide PDFDocumento286 páginasWSA 9-2-0 UserGuide PDFAnonymous RjuGfeQN7dAún no hay calificaciones
- CoreJava iNetSolv PDFDocumento191 páginasCoreJava iNetSolv PDFSubhabrata MishraAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 8 - Policy Based Routing: ISP/IXP Networking Workshop LabDocumento15 páginasModule 8 - Policy Based Routing: ISP/IXP Networking Workshop LabmaracyberstationAún no hay calificaciones
- Cisco WCCP Attacks Prevention - April 16 2008Documento7 páginasCisco WCCP Attacks Prevention - April 16 2008Sami WehbiAún no hay calificaciones
- C++ FAQ LITE - IndexDocumento214 páginasC++ FAQ LITE - Indexapi-3722217Aún no hay calificaciones
- MC7301 - Computer NetworksDocumento5 páginasMC7301 - Computer NetworksHari Kumar SAún no hay calificaciones
- C# DocsDocumento2288 páginasC# DocsKomal GawaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Master List of Companies Participating in Job Fair 2018 PDFDocumento144 páginasMaster List of Companies Participating in Job Fair 2018 PDFUsman FarooqAún no hay calificaciones
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Model Examinations, March 2018 Principles of Programming LanguagesDocumento4 páginasWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Model Examinations, March 2018 Principles of Programming Languageslucky lakshmiAún no hay calificaciones
- Policy Based Routing SIM (Formatted)Documento3 páginasPolicy Based Routing SIM (Formatted)Gossan AnicetAún no hay calificaciones
- Ccna 1) What Is An IP Address?Documento15 páginasCcna 1) What Is An IP Address?pankaj_subhedarAún no hay calificaciones
- Sun Java Training DayDocumento72 páginasSun Java Training DayJuan Flores MorocoAún no hay calificaciones
- DownloadDocumento68 páginasDownloadMuhammed A. Mahdi0% (1)
- 100+ Downloadable Courses GDrive LinksDocumento1 página100+ Downloadable Courses GDrive LinksHemantAún no hay calificaciones
- RIP Distance Vector Routing Protocol: Search..Documento17 páginasRIP Distance Vector Routing Protocol: Search..Ba DongAún no hay calificaciones
- Network Security NotesDocumento18 páginasNetwork Security NotesVinodh JeminiAún no hay calificaciones
- EIGRP NotesDocumento2 páginasEIGRP Noteschrisg1Aún no hay calificaciones
- OSPF - Quick Referce IsmailDocumento6 páginasOSPF - Quick Referce IsmailSai Kyaw HtikeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ethernet Switching User Guide PDFDocumento1678 páginasEthernet Switching User Guide PDFTrần Hoàng ThôngAún no hay calificaciones
- Spring Framework ReferenceDocumento847 páginasSpring Framework ReferencemyungoAún no hay calificaciones
- PortFast and UplinkFastDocumento8 páginasPortFast and UplinkFastKhaled ShimiAún no hay calificaciones
- Policy Based RoutingDocumento16 páginasPolicy Based RoutingAgbo Sunday ChukwuemekaAún no hay calificaciones
- Virtual Routing and ForwardingDocumento3 páginasVirtual Routing and Forwardingjim1234uAún no hay calificaciones
- Questions For Actionscript 3.0Documento28 páginasQuestions For Actionscript 3.0lalakis1431Aún no hay calificaciones
- Security ServicesDocumento1616 páginasSecurity ServicesColin FancesAún no hay calificaciones
- Juniper VPNDocumento386 páginasJuniper VPNRaunak AnandAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNA Security - 640-553 IINS Overview: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocumento5 páginasCCNA Security - 640-553 IINS Overview: o o o o o o o o o o o o o osrikanthchinthuAún no hay calificaciones
- Config Guide Vpns VplsDocumento486 páginasConfig Guide Vpns VplsCarlos GaldamezAún no hay calificaciones
- Question Bank For OSCDocumento9 páginasQuestion Bank For OSCprof_kt100% (1)
- OSPF LSA TypesDocumento9 páginasOSPF LSA TypesSyed Ali Raza GardeziAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choices Questions PDFDocumento141 páginasMultiple Choices Questions PDFceydaAún no hay calificaciones
- Student Notes CCNP Troubleshoot v1.2Documento9 páginasStudent Notes CCNP Troubleshoot v1.2edieealvitresAún no hay calificaciones
- Security VPN Ipsec@@@ PDFDocumento1678 páginasSecurity VPN Ipsec@@@ PDFAsif RazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Department Wise Book List FinalDocumento347 páginasDepartment Wise Book List FinalGajanan Shirke Author100% (1)
- User Access and Authentication User GuideDocumento1618 páginasUser Access and Authentication User GuideАлексей МаренковAún no hay calificaciones
- Madhavi NETDocumento9 páginasMadhavi NETKhader ShaikAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes On SET THEORYDocumento3 páginasNotes On SET THEORYDerren Nierras GayloAún no hay calificaciones
- MechanicsDocumento526 páginasMechanicsKuppa AkhilAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNP Route NotesDocumento7 páginasCCNP Route NotesunikdipAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Structures With C NotesDocumento118 páginasData Structures With C NotesDheeraj NambiarAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFDocumento14 páginas2.10-InterVLAN Routing PDFYureka MindsetAún no hay calificaciones
- Question Bank: Subject: Programming in Java 2 MarksDocumento6 páginasQuestion Bank: Subject: Programming in Java 2 MarksRam DeepakAún no hay calificaciones
- ADO.netDocumento64 páginasADO.netKumar AnupamAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNA Guide To Cisco Networking Fundamentals: Advanced Switching ConceptsDocumento41 páginasCCNA Guide To Cisco Networking Fundamentals: Advanced Switching ConceptsNaveed Khan AbbuAún no hay calificaciones
- BPDU Guard, BPDU Filter, Root Guard, Loop Guard & UDLD Eric LeahyDocumento10 páginasBPDU Guard, BPDU Filter, Root Guard, Loop Guard & UDLD Eric LeahyastonAún no hay calificaciones
- Using VBdotNET With PowerSolution ProductsDocumento74 páginasUsing VBdotNET With PowerSolution ProductsalipjsAún no hay calificaciones
- Programming On Java - NotesDocumento219 páginasProgramming On Java - NotesJASPER WESSLY100% (1)
- qfx10002 Juniper Core Switch PDFDocumento225 páginasqfx10002 Juniper Core Switch PDFMohd NazriAún no hay calificaciones
- 10263AD ENU TrainerHandbook Vol2 PDFDocumento446 páginas10263AD ENU TrainerHandbook Vol2 PDFrobertopeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced IPv6 Quick GuideDocumento245 páginasAdvanced IPv6 Quick Guidebomoarebun100% (1)
- RSTP MSTDocumento112 páginasRSTP MSTBarry GriffinAún no hay calificaciones
- MPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesDe EverandMPLS-Enabled Applications: Emerging Developments and New TechnologiesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (4)
- Qo SDocumento2 páginasQo SMonika MerenyiAún no hay calificaciones
- FactSheet - QoS v1Documento4 páginasFactSheet - QoS v1Jonathan ArandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Qos Protocols & Architectures: by Harizakis CostasDocumento30 páginasQos Protocols & Architectures: by Harizakis Costassantsj78Aún no hay calificaciones
- IP QoS PresentationDocumento44 páginasIP QoS PresentationSaji Kumar0% (1)
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 2) VRP System ArchitectureDocumento23 páginasMicrosoft PowerPoint - 2) VRP System ArchitectureRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 - Imanager U2000 MPLS LSP Deployment ISSUE1.00Documento16 páginas6 - Imanager U2000 MPLS LSP Deployment ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 4) TCPIP Basis ISSUE1.00Documento29 páginasMicrosoft PowerPoint - 4) TCPIP Basis ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- COPDDocumento32 páginasCOPDRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 - Imanager U2000 V100R002 Security and Data Management ISSUE1.01Documento43 páginas5 - Imanager U2000 V100R002 Security and Data Management ISSUE1.01Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Imanager U2000 Basic Operation ISSUE1.00Documento33 páginas2 - Imanager U2000 Basic Operation ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Imanager U2000-R V100R002 System Introduction ISSUE1.00Documento35 páginas1 - Imanager U2000-R V100R002 System Introduction ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 IP Network MPLS TE and TE Tunnel Availability IntroductionDocumento51 páginas3 IP Network MPLS TE and TE Tunnel Availability IntroductionRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-NE Series Products Routine Maintenance ISSUE 1.01Documento75 páginas2-NE Series Products Routine Maintenance ISSUE 1.01Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 3GPP (LTE) Course 3GPP (LTE) Course: Presented By: Eng - Karim Banawan. Eng - Yasser YoussryDocumento164 páginas3GPP (LTE) Course 3GPP (LTE) Course: Presented By: Eng - Karim Banawan. Eng - Yasser YoussryRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 1-ODR102005 NE5000E80E40E Product Feature Overview ISSUE 1.01Documento48 páginas1-ODR102005 NE5000E80E40E Product Feature Overview ISSUE 1.01Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- Imanager U2000 Performance ManagementDocumento55 páginasImanager U2000 Performance ManagementRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 MPLS TE Signaling Protocols ISSUE1.00Documento39 páginas4 MPLS TE Signaling Protocols ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- ODA062001 IP Multicast BasicsDocumento32 páginasODA062001 IP Multicast BasicsRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- ATN 910&910I&910B&950B V200R003C00 Product Description 01 (CLI)Documento119 páginasATN 910&910I&910B&950B V200R003C00 Product Description 01 (CLI)Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- ODA062006 PIM-SM Principle ISSUE1.01Documento39 páginasODA062006 PIM-SM Principle ISSUE1.01Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- ODA062002 IGMP Principle ISSUE1.01Documento32 páginasODA062002 IGMP Principle ISSUE1.01Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- Ethernet Service Complementary InformationDocumento59 páginasEthernet Service Complementary InformationRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- ODA062005 PIM-DM Principle ISSUE1.00Documento25 páginasODA062005 PIM-DM Principle ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones
- Erc Know Your Customer WebDocumento63 páginasErc Know Your Customer WebRandy DookheranAún no hay calificaciones