Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Tif 9780273761389 04
Cargado por
Anh NguyễnDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Tif 9780273761389 04
Cargado por
Anh NguyễnCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Exam
Name___________________________________
1.
B2B e-commerce refers to transactions between businesses that are conducted electronically over the public Internet only.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
2.
The availability of a secure broadband Internet platform is one of the key drivers of B2B EC.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
3.
B2B EC marketplaces that involve one seller selling to many buyers is called an exchange.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
4.
In one-to-many and many-to-one marketplaces, if all selling is done by one company, it is a buy-side market.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
5.
In company-centric marketplaces, the individual company has very little control over who participates in selling or
buying transactions.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
6.
E-marketplace exchanges are usually owned and run by a third party or by a consortium.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
7.
Market forecasters estimate that by 2012 the global B2B market, both online and ofine, could reach $1 trillion.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 182
AACSB:
Objective:
8.
Businesses deal with other businesses for purposes beyond just selling or buying. One example is that of collaborative
commerce, which includes communication, design, planning, and information sharing among business partners.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 182
AACSB:
Objective:
9.
Intermediaries in B2B commerce that broker transactions between buyers and sellers are third-parties that are either
virtual or brick-and-mortar.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 183.
AACSB:
Objective:
10.
Spot buying refers to the purchasing of goods and services according to a schedule, usually at prevailing market prices
that are determined by supply and demand.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 183
AACSB:
Objective:
11.
Stock exchanges and commodity exchanges (such as oil and sugar) are examples of spot buying.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 183
AACSB:
Objective:
12.
Strategic sourcing refers to purchasing involving long-term contracts that usually are based on private negotiations
between sellers and buyers.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 183
AACSB:
Objective:
13.
Computers and communication devices are two examples of direct materials for a food processing company.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 184
AACSB:
Objective:
14.
MRO, which stands for "maintenance, repair, and operation," refers to the indirect materials used in activities that support
production.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 184
AACSB:
Objective:
15.
Horizontal marketplaces are markets that concentrate on a service, material, or a product that is used in all types of
industries.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 184
AACSB:
Objective:
16.
Maverick buying refers to the planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities pertaining to the purchasing of
the goods and services necessary to accomplish the mission of an enterprise.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 196
AACSB:
Objective:
17.
Reverse auctions are one method of electronic procurement that is very popular with public organizations where
tendering is usually mandatory.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 203
AACSB:
Objective:
18.
Aggregating the catalogs of all approved suppliers and combining them into a single electronic catalog is an efective
solution for internal procurement because it minimizes maverick buying.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 203
AACSB:
Objective:
19.
Caltex, a multinational oil company, reduced the number of its suppliers from over 3,000 to 800 by implementing a central
catalog for internal purchasing, lowering the per unit prices.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 203
AACSB:
Objective:
20.
Exchanges can be vertical or horizontal.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 206
AACSB:
Objective:
21.
By law, exchanges cannot be owned by a consortium.
Answer:
True
False
Type: TF
Page Ref: 208
AACSB:
Objective:
22.
Anonymity is a key ingredient of dynamic pricing.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 209
AACSB:
Objective:
23.
A vertical portal is an exchange formed and operated by a group of major companies in an industry to provide industry-
wide transaction services.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 209
AACSB:
Objective:
24.
Dynamic pricing is the rapid movement of prices over time and possibly across customers, as a result of supply and
demand matching.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 209
AACSB:
Objective:
25.
Loss of customer service quality is a potential risk for buyers in B2B exchanges.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 210
AACSB:
Objective:
26.
Potential gains for sellers in B2B exchanges include less maverick buying.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 210
AACSB:
Objective:
27.
Corporate portals are major gateways through which employees, business partners, and the public can enter a corporate
website.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 211
AACSB:
Objective:
28.
Executive and supervisor portals are used for training, dissemination of company news, information, and discussion
groups.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 213
AACSB:
Objective:
29.
Mobile portals are accessible via mobile devices.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 213
AACSB:
Objective:
30.
Alibaba.com requires buyers to pay for sourcing.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 215
AACSB:
Objective:
31.
Creating brand awareness is an advantage of B2B social networking.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 216-217
AACSB:
Objective:
32.
Social networks are used extensively in the B2B marketplace.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 3
Type: TF
Page Ref: 217
AACSB:
Objective:
33.
Google's OpenSocial is a programming standard that lets developers create applications that can run on a wide range of
social networking platforms, which may increase B2B social networking.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 219
AACSB:
Objective:
34.
The marketing and advertising processes used for B2B and B2C are remarkably similar.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 2
Type: TF
Page Ref: 220
AACSB:
Objective:
35.
Afliate programs, infomediaries, and online data and text mining services are three popular B2B marketing and
advertising methods.
Answer:
True
False
Dif: 1
Type: TF
Page Ref: 221
AACSB:
Objective:
36.
Key business drivers for B2B include each of the following except
A)
the need for collaborations between suppliers and buyers.
B)
the willingness of companies to incur higher costs to improve collaboration.
C)
the ability to reduce delays.
D)
the availability of a secure broadband Internet platform.
Answer:
B
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 181
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
37.
E-commerce that focuses on a single company's buying needs or selling needs best defnes
A)
company-centric EC.
B)
private marketplace.
C)
computer exchange.
D)
business-to-business e-commerce.
Answer:
A
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
38.
Many-to-many e-marketplaces, usually owned and run by a third party or a consortium, in which many buyers and many
sellers meet electronically to trade with each other best describes
A)
spot purchases.
B)
public market.
C)
company-centric EC.
D)
exchanges.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 181
AACSB:
Objective:
39.
B2B transactions that involve communication, design, planning, information sharing, and activities beyond fnancial
transactions among business partners defnes
A)
collaborative commerce.
B)
public marketplaces.
C)
trading communities.
D)
exchanges.
Answer:
A
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 182
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
40.
An online third party that brokers a transaction online between a buyer and a seller best describes
A)
vertical marketplace.
B)
strategic source.
C)
online intermediary.
D)
horizontal marketplace.
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 183
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
41.
Types of B2B transactions include
A)
randomized buying.
B)
reverse purchasing.
C)
strategic sourcing.
D)
intermediation.
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 183
AACSB:
Objective:
42.
The purchase of goods and services as they are needed, usually at prevailing market prices, best defnes
A)
strategic sourcing.
B)
spot buying.
C)
direct materials.
D)
consolidation.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 183
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
43.
Purchases of goods and services based on long-term contracts best defnes
A)
consolidation.
B)
direct materials.
C)
strategic sourcing.
D)
spot buying.
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 183
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
44.
Which of the following can be supported more efectively and efciently through direct buyer-seller negotiations?
A)
spot buying
B)
B2C e-commerce
C)
strategic sourcing
D)
MRO
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 184
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
45.
Materials used in the production of a product best defnes
A)
MRO materials.
B)
indirect materials.
C)
production materials.
D)
direct materials.
Answer:
D
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 184
AACSB:
Objective:
46.
Two types of materials and supplies that are traded in B2B are
A)
commodities and nonproduction.
B)
horizontal and vertical.
C)
digital and physical.
D)
direct and indirect.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 184
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
47.
Materials used to support production are called
A)
direct materials.
B)
indirect materials.
C)
virtual materials.
D)
operational materials.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 184
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
48.
The major B2B service industries include each of the following except
A)
fnancial services.
B)
travel and hospitality services.
C)
banking and online fnancing.
D)
retail.
Answer:
D
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 185-186
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
49.
Which of the following is not one of the major benefts of B2B for both buyers and sellers?
A)
increases opportunities for collaboration
B)
expedites processing and reduces cycle time
C)
enables customized online catalogs with diferent prices for diferent customers
D)
reduces procurement costs
Answer:
D
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 187
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
50.
A business strategy that focuses on providing comprehensive quality service to business partners best defnes
A)
customer relationship management.
B)
supply chain management.
C)
supplier relationship management.
D)
partner relationship management.
Answer:
D
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 187
AACSB:
Objective:
51.
A comprehensive approach to managing an enterprise's interactions with the organizations that supply the goods and
services it uses best defnes
A)
supplier relationship management.
B)
customer relationship management.
C)
partnership relationship management.
D)
supply chain management.
Answer:
A
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 187
AACSB:
Objective:
52.
All are benefts of B2B except
A)
creates new sales or purchase opportunities.
B)
lowers search costs and time for buyers to fnd products and vendors.
C)
eliminates paper and reduces administrative costs.
D)
increases channel confict.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 187
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
53.
A Web-based marketplace in which one company sells to many business buyers from e-catalogs or auctions, frequently
over an extranet, describes
A)
refective e-commerce.
B)
sell-side e-commerce.
C)
single-side e-commerce.
D)
buy-side e-commerce.
Answer:
B
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 188
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
54.
Several benefts of Microsoft's ________ are that distributors can check inventory, make transactions, and look up the
status of their orders, signifcantly reducing the number of phone calls, e-mails, and incorrect product shipments.
A)
customized catalog
B)
electronic data interchange
C)
extranet-based order-entry tool
D)
auto-responder
Answer:
C
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 189
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
55.
High-quality bicycle manufacturer Gregg's Cycles does not sell its products online, nor do they allow their bicycles to be
sold online by others. By not selling online, Gregg's Cycles avoids ________ with its dealers and the independent bike
shops that sell its bikes.
A)
pricing confict
B)
disintermediation
C)
channel confict
D)
multichannel distribution
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 189
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
56.
Benefts of using a third-party hosting company for conducting B2B auctions instead of developing an auction site in-
house include all of the following except
A)
no redeployment of corporate resources.
B)
no need for additional resources such as hardware, bandwidth, or IT personnel.
C)
time-to-market of several weeks.
D)
no hiring costs.
Answer:
C
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 194
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
57.
Companies use ________ to sell their unneeded assets for quick disposal or to dispose of excess, obsolete, and returned
products.
A)
reverse auctions
B)
private auctions
C)
forward auctions
D)
liquidation
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 194
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
58.
A characteristic that describes customer loyalty to a site that eventually results in higher revenue best defnes
A)
attachment.
B)
retention.
C)
acquisition.
D)
stickiness.
Answer:
D
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 194
AACSB:
Objective:
59.
A corporate-based acquisition site that uses reverse auctions, negotiations, group purchasing, or any other e-procurement
method best defnes
A)
buy-side e-marketplace.
B)
desktop procurement method.
C)
aggregated catalog.
D)
intermediary.
Answer:
A
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 196
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
60.
The planning, organizing, and coordinating of all the activities relating to purchasing goods and services needed to
accomplish the organization's mission best defnes
A)
supply chain management.
B)
buy-side e-marketplace.
C)
procurement management.
D)
customer relationship management.
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 196
AACSB:
Objective:
61.
Unplanned purchases of items needed quickly, often at non-prenegotiated higher prices, best defnes
A)
maverick buying.
B)
free market.
C)
impulse purchases.
D)
MRO purchasing.
Answer:
A
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 196
AACSB:
Objective:
62.
Major procurement methods include
A)
buying directly from manufacturers, wholesalers, or retailers from their catalogs, and possibly by negotiation.
B)
buying at an exchange or industrial mall.
C)
buying at private or public auction sites in which the organization participates as one of the buyers.
D)
all of the above.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 197
AACSB:
Objective:
63.
The electronic acquisition of goods and services for organizations via the Internet or private network best defnes
A)
MRO planning.
B)
e-procurement.
C)
spot buying.
D)
resource acquisition.
Answer:
B
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 197
AACSB:
Objective:
64.
Using Internet technology to buy goods and services from a number of known or unknown suppliers best defnes
A)
e-tendering.
B)
e-reverse auctioning.
C)
e-sourcing.
D)
e-informing.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 199
AACSB:
Objective:
65.
Types of e-procurement include
A)
E-market sites.
B)
E-MRO.
C)
E-informing.
D)
all of the above.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 199-200
AACSB:
Objective:
66.
Gathering and distributing purchasing information both from and to internal and external parties using Internet
technology best defnes
A)
e-informing.
B)
e-tendering.
C)
e-MRO.
D)
e-sourcing.
Answer:
A
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 200
AACSB:
Objective:
67.
E-procurement benefts include each of the following except
A)
improving information fow and management.
B)
ensuring delivery on time, every time.
C)
reducing the number of suppliers.
D)
ease of internal and external integration.
Answer:
D
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 200
AACSB:
Objective:
68.
E-procurement limitations and challenges include each of the following except
A)
the system may be too complex.
B)
the ease of getting suppliers to cooperate electronically.
C)
the technology needs to be updated frequently.
D)
the cost may be too high.
Answer:
B
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 201
AACSB:
Objective:
69.
Which of the following is the unplanned, emergency-type buying where buyers usually pay more?
A)
extreme purchasing
B)
impulse purchasing
C)
maverick buying
D)
spot buying
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 203
AACSB:
Objective:
70.
Advantages of using internal catalogs include
A)
easy fnancial controls.
B)
decreasing the number of suppliers.
C)
using search engines to look through internal catalogs.
D)
all of the above.
Answer:
D
Dif: 1
Type: MC
Page Ref: 203
AACSB:
Objective:
71.
The aggregated catalogs of all approved suppliers combined into a single internal electronic catalog defnes
A)
internal procurement marketplace.
B)
buy-side e-marketplace.
C)
sell-side e-marketplace.
D)
bartering exchange.
Answer:
A
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 203
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
72.
An example of a successful aggregation of suppliers' catalogs is that of ________, which aggregates more than 10,000
items from the catalogs of approved suppliers into an internal electronic catalog.
A)
Google
B)
Priceline.com
C)
Amazon.com
D)
MasterCard International
Answer:
D
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 203
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
73.
Direct purchasing from internal marketplaces without the approval of supervisors and without the intervention of a
procurement department best defnes
A)
maverick buying.
B)
desktop purchasing.
C)
spot buying.
D)
renegade purchasing.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 204
AACSB:
Objective:
74.
With a bartering exchange, a company submits its surplus to the exchange and receives
A)
an equivalent amount of products or services.
B)
points of credit, which the company can then use to buy items that it needs.
C)
cash minus a small commission for services.
D)
interest payments until it buys something from the exchange.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 205
AACSB: Use of information technology
Objective:
75.
B2B portals that focus on a single industry or industry segment best describes
A)
collaborative portals.
B)
information portals.
C)
local portals.
D)
vortals.
Answer:
D
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 210
AACSB:
Objective:
76.
Portals that store data and enable users to navigate and query these data are
A)
MRO portals.
B)
information portals.
C)
mobile portals.
D)
collaborative portals.
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 213
AACSB:
Objective:
77.
The main uses of social networks include
A)
encouraging maverick purchases.
B)
reducing the number of suppliers.
C)
learning useful business intelligence.
D)
driving trafc to online Web properties.
Answer:
C
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 218
AACSB:
Objective:
78.
Which of the following companies uses viral videos to promote renewals of Care Pack Service agreements?
A)
Arketi Group
B)
Hewlett-Packard
C)
Reed Business Information
D)
Cisco Systems
Answer:
B
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 218
AACSB:
Objective:
79.
Marketing by manufacturers and wholesalers along the sell-side of the supply chain best defnes
A)
M2B purchasing.
B)
M2W marketing.
C)
B2C marketing.
D)
B2B marketing.
Answer:
D
Dif: 2
Type: MC
Page Ref: 219
AACSB:
Objective:
80.
Denver Boards, a B2B manufacturer of snowboard equipment, can reach and target new retail customers in order to grow
its online business by
A)
hiring an afliation service to drive trafc to its Web site.
B)
advertising in traditional media.
C)
mining data.
D)
reviewing POS data.
Answer:
A
Dif: 3
Type: MC
Page Ref: 221
AACSB:
Objective:
81.
List and briefy describe the four basic types of B2B transactions and activities.
Answer:
The four basic types of B2B transactions and activities are sell-side, buy-side, exchanges, and supply chain improvements
and collaborative commerce. While sell-side refers to one seller to many buyers, buy-side refers to one buyer from many
sellers. Exchanges involve many sellers to many buyers. Supply chain improvements and collaborative commerce refers to
activities, other than buying or selling, among business partners, such as supply chain improvements, communication,
collaboration, and information sharing for joint design and planning.
Dif: 1
Type: ES
Page Ref: 181-182
AACSB:
Objective:
82.
List fve major benefts of B2B for buyers or sellers or both.
Answer:
Major benefts of B2B for buyers, sellers, or both include (1) creating new sales or purchase opportunities; (2) eliminating
paper and reducing administrative costs; (3) expediting processing and reducing cycle time; (4) lowering search costs and
time for buyers to fnd products and vendors; (5) increasing productivity of employees dealing with buying and/or
selling; (6) reducing errors and improving quality of services; (7) making product confguration easier; (8) reducing
marketing and sales costs for sellers; (9) reducing inventory levels and costs; (10) enabling customized online catalogs with
diferent prices for diferent customers; (11) increasing production fexibility, permitting just-in-time delivery; (12)
reducing procurement costs for buyers; (13) facilitating customization via confguration; (14) providing for efcient
customer service; and (15) increasing opportunities for collaboration.
Dif: 2
Type: ES
Page Ref: 187
AACSB:
Objective:
83.
Identify fve of the seven types of e-procurement.
Answer:
E-sourcing, e-tendering, e-reverse auctioning, e-informing, web-based ERP, e-market sites, and e-MRO are seven types of
e-procurement.
Dif: 2
Type: ES
Page Ref: 199-200
AACSB:
Objective:
84.
What are the three major functions of exchanges?
Answer:
The three major functions of exchanges are matching buyers and sellers, facilitating transactions, and maintaining
exchange policies and infrastructure.
Dif: 1
Type: ES
Page Ref: 207
AACSB:
Objective:
85.
List fve generic types of portals.
Answer:
The fve generic types of portals are portals for suppliers and other partners, customer portals, employee portals, executive
and supervisor portals, and mobile portals.
Dif: 1
Type: ES
Page Ref: 212-213
AACSB:
Objective:
1.
FALSE
2.
TRUE
3.
FALSE
4.
FALSE
5.
FALSE
6.
TRUE
7.
FALSE
8.
TRUE
9.
TRUE
10.
FALSE
11.
TRUE
12.
TRUE
13.
FALSE
14.
TRUE
15.
TRUE
16.
FALSE
17.
TRUE
18.
TRUE
19.
TRUE
20.
TRUE
21.
FALSE
22.
TRUE
23.
FALSE
24.
TRUE
25.
TRUE
26.
FALSE
27.
TRUE
28.
FALSE
29.
TRUE
30.
FALSE
31.
TRUE
32.
FALSE
33.
TRUE
34.
FALSE
35.
TRUE
36.
B
37.
A
38.
D
39.
A
40.
C
41.
C
42.
B
43.
C
44.
C
45.
D
46.
D
47.
B
48.
D
49.
D
50.
D
51.
A
52.
D
53.
B
54.
C
55.
C
56.
C
57.
C
58.
D
59.
A
60.
C
61.
A
62.
D
63.
B
64.
B
65.
D
66.
A
67.
D
68.
B
69.
C
70.
D
71.
A
72.
D
73.
B
74.
B
75.
D
76.
B
77.
C
78.
B
79.
D
80.
A
81.
The four basic types of B2B transactions and activities are sell-side, buy-side, exchanges, and supply chain improvements
and collaborative commerce. While sell-side refers to one seller to many buyers, buy-side refers to one buyer from many
sellers. Exchanges involve many sellers to many buyers. Supply chain improvements and collaborative commerce refers to
activities, other than buying or selling, among business partners, such as supply chain improvements, communication,
collaboration, and information sharing for joint design and planning.
82.
Major benefts of B2B for buyers, sellers, or both include (1) creating new sales or purchase opportunities; (2) eliminating
paper and reducing administrative costs; (3) expediting processing and reducing cycle time; (4) lowering search costs and
time for buyers to fnd products and vendors; (5) increasing productivity of employees dealing with buying and/or
selling; (6) reducing errors and improving quality of services; (7) making product confguration easier; (8) reducing
marketing and sales costs for sellers; (9) reducing inventory levels and costs; (10) enabling customized online catalogs with
diferent prices for diferent customers; (11) increasing production fexibility, permitting just-in-time delivery; (12)
reducing procurement costs for buyers; (13) facilitating customization via confguration; (14) providing for efcient
customer service; and (15) increasing opportunities for collaboration.
83.
E-sourcing, e-tendering, e-reverse auctioning, e-informing, web-based ERP, e-market sites, and e-MRO are seven types of
e-procurement.
84.
The three major functions of exchanges are matching buyers and sellers, facilitating transactions, and maintaining
exchange policies and infrastructure.
85.
The fve generic types of portals are portals for suppliers and other partners, customer portals, employee portals, executive
and supervisor portals, and mobile portals.
También podría gustarte
- E Business Chapter 4 TurbanDocumento15 páginasE Business Chapter 4 TurbanAbdulla75% (4)
- CH 6 Qaf 04Documento8 páginasCH 6 Qaf 04MahmoudTahboubAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 5 B2B Electronic Commerce True/FalseDocumento7 páginasChapter 5 B2B Electronic Commerce True/FalseNabilah Musri98Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 03Documento40 páginasTif 9780273761389 03Anh NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 01Documento52 páginasTif 9780273761389 01Anh NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 E-Marketplaces: Mechanisms, Tools, and Impacts of E-CommerceDocumento15 páginasChapter 2 E-Marketplaces: Mechanisms, Tools, and Impacts of E-CommercehussamAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Introduction To Electronic Commerce 3E 3rd EditionDocumento13 páginasTest Bank For Introduction To Electronic Commerce 3E 3rd Editionfareedh_meeran100% (2)
- Tif 9780273761389 11Documento41 páginasTif 9780273761389 11Anh Nguyễn0% (1)
- Chapter 6 Business To Business B2B MarketingDocumento32 páginasChapter 6 Business To Business B2B MarketingWilliam ZhangAún no hay calificaciones
- Think Marketing Canadian 2Nd Edition Tuckwell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento36 páginasThink Marketing Canadian 2Nd Edition Tuckwell Test Bank Full Chapter PDFgeraldine.wells536100% (11)
- THINK Marketing Canadian 2nd Edition Tuckwell Test Bank 1Documento28 páginasTHINK Marketing Canadian 2nd Edition Tuckwell Test Bank 1Marcos Ecklund100% (42)
- ch6,7,8 Check Your UnderstandingDocumento5 páginasch6,7,8 Check Your UnderstandingPaul CostaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1623 CLC Testbank Chapter2Documento17 páginas1623 CLC Testbank Chapter2Wolf's RainAún no hay calificaciones
- MKTGChapter 6 Business To Business B2B MarketingDocumento90 páginasMKTGChapter 6 Business To Business B2B MarketingGeorge BushAún no hay calificaciones
- E - Commerce Chapter 1 Test BankDocumento16 páginasE - Commerce Chapter 1 Test BankElenaStuffed71% (7)
- Multiple Choice Questions: Tybms Sem Vi Retail ManagementDocumento8 páginasMultiple Choice Questions: Tybms Sem Vi Retail ManagementprashantAún no hay calificaciones
- Testbank Chapter 3 7.edition With AnswerDocumento26 páginasTestbank Chapter 3 7.edition With Answerqwerty1234qwer88% (8)
- E Commerce Section - Sheet 2 - AnswerDocumento6 páginasE Commerce Section - Sheet 2 - AnswerAsmaa AbdelhakeemAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2Documento5 páginasChapter 2Lee ConanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 07Documento51 páginasTif 9780273761389 07Anh NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing Management 1St Edition Marshall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento67 páginasMarketing Management 1St Edition Marshall Test Bank Full Chapter PDFfarleyphedral0p100% (13)
- Practice QuizDocumento9 páginasPractice Quizyoussef888 tharwatAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch9test Banks 202236710107 Isaay Witness EmmanuelDocumento8 páginasCh9test Banks 202236710107 Isaay Witness EmmanuelWitney EmmanuelAún no hay calificaciones
- B2B MarketingDocumento4 páginasB2B Marketingmms a19Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pomtest 6Documento12 páginasPomtest 6Ali KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- E - Business Chapter 4Documento6 páginasE - Business Chapter 4James MorganAún no hay calificaciones
- TBChap 09Documento20 páginasTBChap 09Alishba KaiserAún no hay calificaciones
- Mis 6th Edition Bidgoli Test BankDocumento24 páginasMis 6th Edition Bidgoli Test Bankphedrajoshuan28yjy100% (31)
- Mis 6Th Edition Bidgoli Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento45 páginasMis 6Th Edition Bidgoli Test Bank Full Chapter PDFvictoredanajdnk9100% (10)
- 616e6c7785408Documento94 páginas616e6c7785408Jesin John LMC19MCA003Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ebusiness TestbanksDocumento951 páginasEbusiness Testbanksjou20220354Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 10Documento16 páginasCH 10Chris Fox100% (1)
- 1623 CLC Testbank Chapter1Documento16 páginas1623 CLC Testbank Chapter1Wolf's RainAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise B2C AnswerDocumento5 páginasExercise B2C AnswerNabilah Musri98Aún no hay calificaciones
- Final Exam - Chapter 1 - The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocumento4 páginasFinal Exam - Chapter 1 - The Revolution Is Just BeginningABCAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap12 GM6e TIFDocumento21 páginasChap12 GM6e TIFradislamyAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Study GuideDocumento11 páginasChapter 2 Study GuideLoretta Lynn AltmayerAún no hay calificaciones
- Rev View Qu Estions::: UreecalldDocumento11 páginasRev View Qu Estions::: UreecalldAhmad N. AlawiAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Banks 7Documento51 páginasTest Banks 7OsamaAún no hay calificaciones
- B2B NotesDocumento17 páginasB2B Notesrashmeenkohli_6427700% (1)
- Chapter 12 Marketing Channels Delivering Customer Value 14ed NewDocumento21 páginasChapter 12 Marketing Channels Delivering Customer Value 14ed NewMohammed KhouliAún no hay calificaciones
- MIS10E Testbank CH10Documento16 páginasMIS10E Testbank CH10Kristi Herrera0% (1)
- MisDocumento17 páginasMisMIJANUR RAHMAN Summer 21Aún no hay calificaciones
- ch4 EcommerceDocumento24 páginasch4 EcommerceZiqi PzqAún no hay calificaciones
- Armstrong Mai08 Tif 14Documento31 páginasArmstrong Mai08 Tif 14Ruslan ZhussipbayevAún no hay calificaciones
- E-Commerce: A B2B GuideDocumento4 páginasE-Commerce: A B2B Guideaseem_activeAún no hay calificaciones
- Yambot ECommerceLAB4 PDFDocumento6 páginasYambot ECommerceLAB4 PDFYan YanAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Introduction To Electronic Commerce 3EDocumento13 páginasTest Bank For Introduction To Electronic Commerce 3EAbdullaAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 2: UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER DIFFERENCES ch02Documento7 páginasCHAPTER 2: UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER DIFFERENCES ch02DemianAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 1 QuizzsDocumento7 páginasCH 1 QuizzsKhant Hein WaiAún no hay calificaciones
- MSIT - 4A Web Commerce Assignment-Ta 10X5 50 Answer ALL QuestionsDocumento6 páginasMSIT - 4A Web Commerce Assignment-Ta 10X5 50 Answer ALL QuestionsSeshadri KrishnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic 1-Overview of Business To Business MarketingDocumento11 páginasTopic 1-Overview of Business To Business MarketinggregAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Overview of Electronic CommerceDocumento15 páginasChapter 1 Overview of Electronic CommercehussamAún no hay calificaciones
- 1because e Commerce Is Ubiquitous It Reduces A Marketspace B Transaction Costs C Dynamic Pricing D Price Discrimination 2 The Ability of Consumers To Use The Internet To Discover PDFDocumento10 páginas1because e Commerce Is Ubiquitous It Reduces A Marketspace B Transaction Costs C Dynamic Pricing D Price Discrimination 2 The Ability of Consumers To Use The Internet To Discover PDFAbul HosainAún no hay calificaciones
- In Terms of Market GeographyDocumento17 páginasIn Terms of Market GeographyAnu MathewsAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Models in E-Commerce: Presented By, Sandhya C, Assistant Professor, SNGCEDocumento98 páginasBusiness Models in E-Commerce: Presented By, Sandhya C, Assistant Professor, SNGCEAkhil Mathew PhilipAún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 14Documento50 páginasTif 9780273761389 14Anh NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 11Documento41 páginasTif 9780273761389 11Anh Nguyễn0% (1)
- Tif 9780273761389 10Documento52 páginasTif 9780273761389 10Anh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Tif 9780273761389 07Documento51 páginasTif 9780273761389 07Anh NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Tif 9780273761389 09Documento38 páginasTif 9780273761389 09Anh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Lab Manual Exp 3 - Gas Temperature Process ControlDocumento8 páginasLab Manual Exp 3 - Gas Temperature Process ControlAhmad DanialAún no hay calificaciones
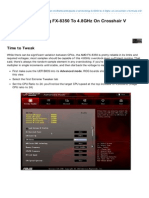
- Guide: Overclocking FX-8350 To 4.8GHz On Crosshair V Formula-ZDocumento7 páginasGuide: Overclocking FX-8350 To 4.8GHz On Crosshair V Formula-ZBobapatatasAún no hay calificaciones
- HP-PreFab - Butterfly-DCDocumento9 páginasHP-PreFab - Butterfly-DCanbanandAún no hay calificaciones
- Byjusbusinesscanvasmodel 190201155441Documento5 páginasByjusbusinesscanvasmodel 190201155441Aarsh SoniAún no hay calificaciones
- Cain and Banks Utility Scale Wind Presentation 2015 SEAOC ConventionDocumento24 páginasCain and Banks Utility Scale Wind Presentation 2015 SEAOC ConventionTrầmLãngAún no hay calificaciones
- Samsung Ue40f5500 TrainingDocumento49 páginasSamsung Ue40f5500 TrainingLuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Python Class ConceptsDocumento16 páginasPython Class ConceptsPhoenix Liebe JeffAún no hay calificaciones
- Weigh Bridge Truck Out Finding ReportDocumento6 páginasWeigh Bridge Truck Out Finding Reportbee398Aún no hay calificaciones
- Agnes CVDocumento3 páginasAgnes CVMaziwa ProAún no hay calificaciones
- Paragon Hard Disk Manager Pro 2009 Portable Rar PDFDocumento4 páginasParagon Hard Disk Manager Pro 2009 Portable Rar PDFDanAún no hay calificaciones
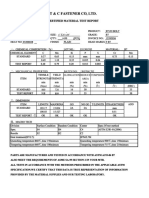
- T & C Fastener Co, LTD.: Certified Material Test ReportDocumento1 páginaT & C Fastener Co, LTD.: Certified Material Test Reportlady romeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Mastering Sap S4hana 1709Documento617 páginasMastering Sap S4hana 1709yakar55592% (38)
- TM 11-5820-498-34P - Radio - Sets - AN - VRC-53 - 64 - 125 - 160 - 1976 PDFDocumento42 páginasTM 11-5820-498-34P - Radio - Sets - AN - VRC-53 - 64 - 125 - 160 - 1976 PDFWurzel1946Aún no hay calificaciones
- CRM in Russia and U.S. - Case Study From American Financial Service IndustryDocumento40 páginasCRM in Russia and U.S. - Case Study From American Financial Service IndustryebabjiAún no hay calificaciones
- A Line Follower Robot-ICCAE 2010Documento6 páginasA Line Follower Robot-ICCAE 2010Ioan DorofteiAún no hay calificaciones
- Bosch p7100 Injection Pump Service Manual PDFDocumento2 páginasBosch p7100 Injection Pump Service Manual PDFAdam Johnson7% (14)
- Pcan-Usb Userman EngDocumento29 páginasPcan-Usb Userman EngantidoteunrealAún no hay calificaciones
- ATM200 Actuators PDFDocumento8 páginasATM200 Actuators PDFMiguel ComprésAún no hay calificaciones
- Amber Heard - Twitter BotScores Machine Learning Analysis ReportDocumento7 páginasAmber Heard - Twitter BotScores Machine Learning Analysis ReportC TaftAún no hay calificaciones
- GK500 ManualDocumento14 páginasGK500 ManualDox BachmidAún no hay calificaciones
- ZTE ZXSDR R8882 Product DescriptionDocumento23 páginasZTE ZXSDR R8882 Product Descriptionrdmiguel_198360% (1)
- Advanced Database Management System Course Code: 3340701Documento5 páginasAdvanced Database Management System Course Code: 3340701Madhav KotechaAún no hay calificaciones
- Reference Manual (0.8.0) (2022.04.16) : OpencoreDocumento111 páginasReference Manual (0.8.0) (2022.04.16) : OpencorevalakiakinemtevagyAún no hay calificaciones
- 31.33.00010 31-JAN-2023 31-JAN-2023 Closed A318, A319, A320, A321, A330, ... 23-71, 31-33, 31-36, ... External QAR 3TU/2TV Installation/removalDocumento107 páginas31.33.00010 31-JAN-2023 31-JAN-2023 Closed A318, A319, A320, A321, A330, ... 23-71, 31-33, 31-36, ... External QAR 3TU/2TV Installation/removalNaixAún no hay calificaciones
- Drive Range - Emergency Fifth Gear (Automatic Transmission - Transaxle) - ALLDATA RepairDocumento3 páginasDrive Range - Emergency Fifth Gear (Automatic Transmission - Transaxle) - ALLDATA RepairgabotoyoAún no hay calificaciones
- Event Management System1Documento24 páginasEvent Management System1Suchi UshaAún no hay calificaciones
- ASR9000xr Understanding SNMP and TroubleshootingDocumento56 páginasASR9000xr Understanding SNMP and TroubleshootingDharmendraAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 4 VBox User-Manual EngDocumento12 páginas5 4 VBox User-Manual Engmax2smith-70% (1)
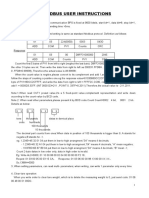
- LH86 ModbusDocumento2 páginasLH86 ModbusMarcos Luiz AlvesAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 05: Joining Tables: JoinsDocumento4 páginasLab 05: Joining Tables: JoinsNida FiazAún no hay calificaciones