Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
CH 9
Cargado por
api-37052600 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
83 vistas45 páginasChapter 9 Resonant Converters Hard Switching Waveforms the output current can be positive or negative Copyright (c) 2003 by John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Descripción original:
Título original
Ch9
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoChapter 9 Resonant Converters Hard Switching Waveforms the output current can be positive or negative Copyright (c) 2003 by John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
83 vistas45 páginasCH 9
Cargado por
api-3705260Chapter 9 Resonant Converters Hard Switching Waveforms the output current can be positive or negative Copyright (c) 2003 by John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 45
Chapter 9
Zero-Voltage or Zero-Current Switchings
• converters for soft switching
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-1
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
One Inverter Leg
• The output current can be positive or negative
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-2
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Hard Switching Waveforms
• The output current can be positive or negative
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-3
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Turn-on and Turn-off Snubbers
• Turn-off snubbers are used
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-4
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Switching Trajectories
• Comparison of Hard versus soft switching
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-5
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Undamped Series-Resonant Circuit
• The waveforms shown include initial conditions
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-6
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Series-Resonant Circuit with
Capacitor-Parallel Load
• The waveforms shown include initial conditions
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-7
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Impedance of a Series-Resonant Circuit
• The impedance is capacitive below the
resonance frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-8
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Undamped Parallel-Resonant Circuit
• Excited by a current source
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-9
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Impedance of a Parallel-Resonant Circuit
• The impedance is inductive at below the
resonant frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-10
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Series Load Resonant (SLR) Converter
• The transformer is ignored in this equivalent
circuit
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-11
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SLR Converter Waveforms
• The operating frequency is below one-half the
resonance frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-12
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SLR Converter Waveforms
• The operating frequency is in between one-half the
resonance frequency and the resonance frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-13
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SLR Converter Waveforms
• The operating frequency is above the resonance
frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-14
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Lossless Snubbers in SLR Converters
• The operating frequency is above the resonance
frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-15
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SLR Converter Characteristics
• Output Current as a function of operating
frequency for various values of the output voltage
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-16
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
SLR Converter Control
• The operating frequency is varied to regulate the
output voltage
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-17
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Parallel Load Resonant (PLR) Converter
• The transformer is ignored in this equivalent
circuit
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-18
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
PLR Converter Waveforms
• The current is in a discontinuous conduction
mode
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-19
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
PLR Converter Waveforms
• The operating frequency is below the resonance
frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-20
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
PLR Converter Waveforms
• The operating frequency is above the resonance
frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-21
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
PLR Converter Characteristics
• Output voltage as a function of operating
frequency for various values of the output current
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-22
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Hybrid-Resonant DC-DC Converter
• Combination of series and parallel resonance
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-23
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Parallel-Resonant Current-Source Converter
• Basic circuit to illustrate the operating principle
at the fundamental frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-24
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Parallel-Resonant Current-Source Converter
• Using thyristors; for induction heating
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-25
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Class-E Converters
Optimum mode
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-26
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Class-E Converters
Non-Optimum
mode
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-27
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Resonant Switch Converters
Classifications
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-28
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZCS Resonant-Switch Converter
• One possible implementation
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-29
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZCS Resonant-Switch Converter
• Waveforms; voltage is regulated by varying the
switching frequency
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-30
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZCS Resonant-Switch Converter
• A practical circuit
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-31
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS Resonant-Switch Converter
• Serious limitations
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-32
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS Resonant-Switch Converter
• Waveforms
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-33
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
MOSFET Internal Capacitances
• These capacitances affect the MOSFET switching
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-34
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS-CV DC-DC Converter
• The inductor current must reverse direction
during each switching cycle
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-35
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS-CV DC-DC Converter
• One transition is shown
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-36
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS-CV Principle Applied to DC-AC Inverters
• Very large ripple in the output current
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-37
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Three-Phase ZVS-CV DC-AC Inverter
• Very large ripple in the output current
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-38
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Output Regulation by Voltage Control
• Each pole operates at nearly 50% duty-ratio
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-39
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ZVS-CV with Voltage Cancellation
• Commonly used
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-40
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Resonant DC-Link Inverter
• The dc-link voltage
is made to oscillate
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-41
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Three-Phase Resonant DC-Link Inverter
• Modifications have been proposed
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-42
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
High-Frequency-Link Inverter
• Basic principle for selecting integral half-cycles of the
high-frequency ac input
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-43
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
High-Frequency-Link Inverter
• Low-frequency ac output is synthesized by selecting
integral half-cycles of the high-frequency ac input
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-44
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
High-Frequency-Link Inverter
• Shows how to implement such an inverter
Copyright © 2003 Chapter 9 Resonant Converters 9-45
by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
También podría gustarte
- DC AcDocumento41 páginasDC AcDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorAún no hay calificaciones
- 1LN InvertersDocumento49 páginas1LN Invertersankit.chandra.eee21Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 10Documento38 páginasCH 10anasAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 8 Mohan (Laminas) PDFDocumento41 páginasChap 8 Mohan (Laminas) PDFfer6669993Aún no hay calificaciones
- DC DCDocumento34 páginasDC DCDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorAún no hay calificaciones
- SMPSDocumento59 páginasSMPSDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch17 PDFDocumento18 páginasCh17 PDFjoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch6 PDFDocumento39 páginasCh6 PDFanasAún no hay calificaciones
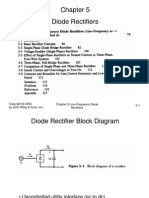
- Diode Rectifiers: 5-1 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 5 Line-Frequency Diode RectifiersDocumento40 páginasDiode Rectifiers: 5-1 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 5 Line-Frequency Diode RectifiersKaren HerreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersDocumento34 páginasCh7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersjimyaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Inverters: Inverters Take DC From A Battery (Etc) and Convert It Electronically To Ac PowerDocumento13 páginasInverters: Inverters Take DC From A Battery (Etc) and Convert It Electronically To Ac PowerAbu-Abdullah SameerAún no hay calificaciones
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureDocumento54 páginasELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: EctureJohn Paul JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Power Electronic Systems: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 1 Introduction 1-1Documento12 páginasChapter 1 Power Electronic Systems: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 1 Introduction 1-1eserimAún no hay calificaciones
- Ned Mohan Power Electronics CH5 SlidesDocumento40 páginasNed Mohan Power Electronics CH5 SlidesTayyab Hussain100% (1)
- DC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDocumento34 páginasDC-DC Converters For Switch-Mode DC Power Supplies and Dc-Motor DrivesDina GaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer: S. Kar Chowdhury Substations DepartmentDocumento48 páginasTransformer: S. Kar Chowdhury Substations DepartmentSupervisor CCCAún no hay calificaciones
- Earthing Transformers For Power SystemsDocumento12 páginasEarthing Transformers For Power SystemsSreekanth Reddy100% (1)
- Three Phase Full Bridge RectifierDocumento10 páginasThree Phase Full Bridge RectifierAmit BaroiAún no hay calificaciones
- Ferroresonance 2011Documento35 páginasFerroresonance 2011Andrew MitchellAún no hay calificaciones
- Push Pull ConvertersDocumento44 páginasPush Pull ConvertersRaminAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 TransformerDocumento33 páginas7 TransformerMd. Sojib KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Types of Inverters and Their ApplicationsDocumento18 páginasTypes of Inverters and Their Applicationsaa bbAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-3 May 25 McIver Tertiary WdgsDocumento24 páginas2-3 May 25 McIver Tertiary WdgsGaurav KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch13 PDFDocumento20 páginasCh13 PDFanasAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer RepairDocumento20 páginasTransformer Repairpankajmadhu50% (2)
- Earthing Transformers Design and FunctionDocumento12 páginasEarthing Transformers Design and Functionjitendrakmr593Aún no hay calificaciones
- DC Motor DrivesDocumento20 páginasDC Motor DrivesashiqnafasAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformers, General, Part 1Documento17 páginasTransformers, General, Part 1parvezblogAún no hay calificaciones
- Earthing Transformers For Power SystemsDocumento12 páginasEarthing Transformers For Power SystemsArunabh BhattacharyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulas and Conversion Factors: Section OutlineDocumento8 páginasFormulas and Conversion Factors: Section OutlineHarsh ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer 1Documento42 páginasTransformer 1Sayed NagyAún no hay calificaciones
- Vp Electronics Winter Training - Inverters Basics, Types, Applications & PWM TechnologyDocumento25 páginasVp Electronics Winter Training - Inverters Basics, Types, Applications & PWM TechnologyLenowahira DillemanowaryAún no hay calificaciones
- Delta Feroresonance EffectsDocumento17 páginasDelta Feroresonance EffectsReynante T. BitasAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Electronics Converters, Applications, and DesignDocumento736 páginasPower Electronics Converters, Applications, and Designaaaravin100% (7)
- Ieee Transactions On Industrial Electron PDFDocumento12 páginasIeee Transactions On Industrial Electron PDF李漢祥Aún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation On: Power Transformer BY BhelDocumento23 páginasPresentation On: Power Transformer BY BhelYe Min OoAún no hay calificaciones
- Single phase Transformers: Key ConceptsDocumento33 páginasSingle phase Transformers: Key ConceptsMaster ChiefAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear TransformerDocumento44 páginasLinear TransformerRonmark AbinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer dimensions MATLAB codeDocumento30 páginasTransformer dimensions MATLAB codesenthilkumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ac To AcDocumento32 páginasAc To AcAbenezer ZenebeAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer Modelling:-1.) Application of TransformersDocumento17 páginasTransformer Modelling:-1.) Application of TransformersVasudevan KunjithapathamAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer Coupled Class A Amplifier: BY - V.Surya Prakash Reddy VTU - 9597 B-Tech (Ece) 2 YearDocumento23 páginasTransformer Coupled Class A Amplifier: BY - V.Surya Prakash Reddy VTU - 9597 B-Tech (Ece) 2 YearSuryaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3Documento9 páginasChapter 3api-293198287Aún no hay calificaciones
- EfficiencyDocumento21 páginasEfficiency4zfq8g84rkAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer Voltage Regulation GuideDocumento21 páginasTransformer Voltage Regulation GuideAbdelilahaliAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Documento20 páginasDC Drives: by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Chapter 2 Power Semiconductor Switches: An Overview 2-1 2-1Engr Umar AshrafAún no hay calificaciones
- Pulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Power ConvertersDe EverandPulse-Width Modulated DC-DC Power ConvertersAún no hay calificaciones
- Radio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsDe EverandRadio Frequency Transistors: Principles and Practical ApplicationsCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (2)
- Practical Switching Power Supply DesignDe EverandPractical Switching Power Supply DesignCalificación: 2 de 5 estrellas2/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Calificación: 2.5 de 5 estrellas2.5/5 (3)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDe Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDe EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2)
- Electronics And Circuit Design Made EasyDe EverandElectronics And Circuit Design Made EasyCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (9)
- CH 21Documento27 páginasCH 21api-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Review of Basic Semiconductor PhysicsDocumento17 páginasReview of Basic Semiconductor Physicsapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 20Documento27 páginasCH 20avi013Aún no hay calificaciones
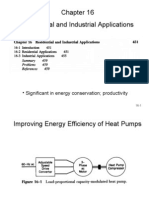
- Residential and Industrial Applications: - Significant in Energy Conservation ProductivityDocumento11 páginasResidential and Industrial Applications: - Significant in Energy Conservation Productivityapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
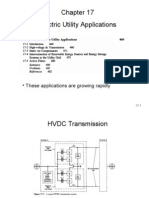
- Electric Utility Applications: - These Applications Are Growing RapidlyDocumento18 páginasElectric Utility Applications: - These Applications Are Growing Rapidlyapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Utility Interface: - Power Quality Has Become An Important IssueDocumento20 páginasUtility Interface: - Power Quality Has Become An Important Issueapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Synchronous Motor Drives: - A Large Variety of Applications - Higher EfficiencyDocumento10 páginasSynchronous Motor Drives: - A Large Variety of Applications - Higher Efficiencyapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
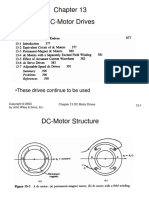
- DC-Motor Drives: - These Drives Continue To Be UsedDocumento20 páginasDC-Motor Drives: - These Drives Continue To Be Usedapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 8Documento41 páginasCH 8api-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Motor Drives: - Motor Drives Are One of The Most Important Applications of Power ElectronicsDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To Motor Drives: - Motor Drives Are One of The Most Important Applications of Power Electronicsapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Induction Motor DrivesDocumento31 páginasInduction Motor DrivesjohnbardenAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersDocumento34 páginasCh7 DC-DC Switch Mode ConvertersjimyaoAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 10Documento38 páginasCH 10api-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- CH 11Documento15 páginasCH 11api-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- SRAC 282webDocumento4 páginasSRAC 282webapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- 281 FsDocumento4 páginas281 Fsapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Grants Tilapia Ti La Pia ReportDocumento49 páginasGrants Tilapia Ti La Pia Reportapi-3705260100% (1)
- G17 Managing Systemsfor Tilapia CultureDocumento5 páginasG17 Managing Systemsfor Tilapia Cultureapi-3705260100% (1)
- 280 FsDocumento4 páginas280 Fsapi-3705260Aún no hay calificaciones
- Monarch Industrial Products (I) Pvt. Ltd. Decorative Floor Toppings Supply Order Price ListDocumento1 páginaMonarch Industrial Products (I) Pvt. Ltd. Decorative Floor Toppings Supply Order Price ListgangadevimgmAún no hay calificaciones
- Geotech Civ150 CompressDocumento4 páginasGeotech Civ150 CompressismaeelAún no hay calificaciones
- LaptopDocumento20 páginasLaptopNeeraj SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Profiles For Cylindrical Vault Roofing SystemsDocumento24 páginasMultiple Stiffened Cold-Formed Steel Profiles For Cylindrical Vault Roofing SystemsTiago LopesAún no hay calificaciones
- Panasonic Model TG6511FXDocumento82 páginasPanasonic Model TG6511FXLakiLakicAún no hay calificaciones
- Math TaskDocumento2 páginasMath TaskAsher MananganAún no hay calificaciones
- Database transactions, recovery, and concurrencyDocumento30 páginasDatabase transactions, recovery, and concurrencyIvan Jan AvigueteroAún no hay calificaciones
- Face Recognization and Detection System For Attendance.Documento39 páginasFace Recognization and Detection System For Attendance.Deepanshu Sharma33% (3)
- Heat 4e Chap02 LectureDocumento48 páginasHeat 4e Chap02 LectureAbdul MohsinAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT 1 PPT Satellite CommunicationDocumento34 páginasUNIT 1 PPT Satellite Communicationselvi100% (1)
- White Paper c11 737101Documento13 páginasWhite Paper c11 737101Aleksandar PopovicAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermocouple & PRT Cable Selection GuideDocumento15 páginasThermocouple & PRT Cable Selection Guidetees220510Aún no hay calificaciones
- Banyule Standard DrawingsDocumento103 páginasBanyule Standard DrawingsTarek AbulailAún no hay calificaciones
- JT85 Vertical to Horizontal Drive Shaft Gearbox, 90 Deg Bevel Gear Box, 4 to 1 Gearbox, 2-Way Gearbox, Right Angle Gearbox Speed Increaser,Speed Increaser Gearbox Micro, 90 Degree Power Transfer 1 to 1 RatioDocumento7 páginasJT85 Vertical to Horizontal Drive Shaft Gearbox, 90 Deg Bevel Gear Box, 4 to 1 Gearbox, 2-Way Gearbox, Right Angle Gearbox Speed Increaser,Speed Increaser Gearbox Micro, 90 Degree Power Transfer 1 to 1 RatioWarren LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- PNG382 FT en 11Documento2 páginasPNG382 FT en 11Misu1983Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hallite Metric Fluid Power CatalogDocumento342 páginasHallite Metric Fluid Power CatalogOscar Acevedo Miranda100% (1)
- Create Custom Pane Programmatically For Panels in Drupal 7Documento2 páginasCreate Custom Pane Programmatically For Panels in Drupal 7CoklatAún no hay calificaciones
- E1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesDocumento84 páginasE1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesSatyanarayana Gurram100% (1)
- DF PDFDocumento8 páginasDF PDFAtif JaveadAún no hay calificaciones
- System 1: Bently NevadaDocumento4 páginasSystem 1: Bently Nevadanabil160874Aún no hay calificaciones
- Beginning Android DevelopmentDocumento721 páginasBeginning Android DevelopmentNikola Johnny Popadic67% (3)
- Unit 2 - EDDocumento42 páginasUnit 2 - EDMohit L.E. 008Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics 110A: Electromagnetism: 1 Introduction and OverviewDocumento4 páginasPhysics 110A: Electromagnetism: 1 Introduction and OverviewJoshua LinAún no hay calificaciones
- LDRDocumento4 páginasLDRRaymond ValdezAún no hay calificaciones
- Irf 744 PBFDocumento8 páginasIrf 744 PBFPosada Burgueño CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- CAD (ME2155) Lab ManualDocumento18 páginasCAD (ME2155) Lab Manualharishj93Aún no hay calificaciones
- Damping FactorDocumento2 páginasDamping FactorAngel Morales MartínezAún no hay calificaciones
- SemaphoreDocumento29 páginasSemaphoreSaranya ThangarajAún no hay calificaciones
- Vastu Tips For CareerDocumento2 páginasVastu Tips For CareerBeyond ThoughtsAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit One: Wind LoadsDocumento67 páginasUnit One: Wind Loadsabdu yimerAún no hay calificaciones