Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Terbutaline Sulfate
Cargado por
Ivanne Hisoler100%(2)100% encontró este documento útil (2 votos)
9K vistas1 páginaDrug Study
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoDrug Study
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOC, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
100%(2)100% encontró este documento útil (2 votos)
9K vistas1 páginaTerbutaline Sulfate
Cargado por
Ivanne HisolerDrug Study
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOC, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
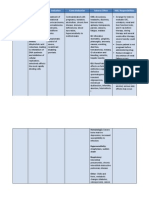
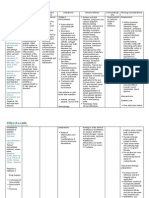
Drug Data Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibilities
Generic Name Pharmacologic General Indications Concentrations CNS: Restlessness, Before
Terbutaline Class In low doses, acts relatively - Prophylaxis and - Hypersensitivity to apprehension, anxiety, fear, - Observe 15 rights of drug
sulfate Beta2-selective selectively at beta2-adrenergic treatment of bronchial terbutaline CNS stimulation, hyperkinesia, administration.
adrenergic receptors to cause asthma and reversible - Tachyarrhythmias, insomnia, tremor, drowsiness, - Reduce dosage with hepatic or
Trade Name antagonist bronchodilation and relax the bronchospasm that tachycardia caused irritability, weakness, vertigo, renal failure.
Brethine pregnant uterus; may occur with by digitalis headache, seizures - Assess for hypersensitivity to drug.
Therapeutic At higher doses, beta2 bronchitis and intoxication - Assess for any contraindications to
Minimum Dose Class selectively is lost and the drug emphysema, in - General anesthesia CV: Cardiac arrhythmias, the drug.
5 mg at 6-hr Antasthmatic, acts at beta1 receptors to cause patients 12 yr and with halogenated palpitations, angina pain, - Educate about side effects of
intervals tid Bronchodilator, typical sympathomimetic older hydrocarbons or changes in BP and ECG drug.
Sympathomimetic cardiac effects. - Unlabeled use: cyclopropane
Maximum Dose , Tocolytic drug Tocolytic to prevent - Unstable vasomotor GI: Nausea, vomiting, During
15 mg/day Pharmacokinetics preterm labor system disorders heartburn, unusual or bad taste - Use minimal doses for minimal
Pregnancy Risk - Labor and delivery in mouth periods of time, drug tolerance
Contents Factor D: May cross placenta; enters - Lactation can occur with prolonged use.
Terbutaline B breast milk Respiratory: Respiratory - Keep a beta-blocker, such as
Precaution atenolol, readily available in
su M: Tissue difficulties, pulmonary edema,
- Diabetes, Coronary case cardiac dysrhythmias
lf E: Urine coughing, bronchospasm
insufficiency, CAD, occur.
at
History of CVA, COPD - For oral forms, administer with
e Rout Onset Peak Duratio Other: Sweating, pallor,
e n patient, water to facilitate swallowing.
flushing, muscle cramps,
Oral 30 2-3 hr 4-8 hr Hyperthyroidism, - For parenteral forms, avoid
Availability and elevated LFTs
min History of seizure contact with the needle.
color SubQ 5-15 30-60 1.5-4 hr disorder, - Stay with patient throughout
- Tablets: 2.5, 5 min min
Psychoneurotic
mg whole duration of
individuals, administration.
- Injection: 1 Drug Half Life
Hypertension
mg/mL 2-4 hr
After
Drug interaction - Monitor client for at least 30
Routes of > Drug to drug
administration minutes.
- Increased likelihood - Arrange for regular follow-up,
Oral of cardiac
Subcutaneous including blood tests, to
arrhythmias with evaluate effects.
halogenated - Instruct to report chest pain,
hydrocarbon dizziness, insomnia, weakness,
anesthetics tremor or irregular heartbeat,
- Risk of failure to respond to usual
bronchospasms if dosage.
combined with - Instruct to take medication as
diuretics directed for the full course of
- Increased risk of therapy, even if feeling better.
hypokalemia and - Do not double dose.
ECG changes with - Do proper documentation.
MAOIs and TCAs
> Drug to food
- none reported
Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source: Source:
Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Karch, Amy: 2009 Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing Karch, Amy: 2009 Lippincott’s Nursing
Lippincott’s Nursing Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1125-1126 Nursing Drug Guide, pp. 1126 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Drug Guide, pp. 1126 Drug Guide, pp. 1127
Drug Guide, pp. 1125- Drug Guide, pp. 1125 Guide, pp. 1126
1126
También podría gustarte
- Promethazine HCLDocumento2 páginasPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Ceftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinDocumento4 páginasCeftriaxone, Misoprostol, OxytocinKrizia Bonilla100% (1)
- HydralazineDocumento2 páginasHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study MgSO4Documento1 páginaDrug Study MgSO4Brigette Quirante100% (1)
- HydralazineDocumento1 páginaHydralazineIvanne Hisoler75% (8)
- Drug Study of Magnesium SulfateDocumento2 páginasDrug Study of Magnesium SulfateEm Hernandez Arana83% (6)
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDocumento5 páginasDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Terbutaline BricanylDocumento1 páginaTerbutaline BricanylB PAún no hay calificaciones
- Clomid Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study HydralazineDocumento10 páginasDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaAún no hay calificaciones
- DS HydralazineDocumento3 páginasDS HydralazineGe LoAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocumento3 páginasClinical Medications Worksheets: (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsEAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study - NifedipineDocumento2 páginasDrug Study - NifedipineSharlene Agcanas100% (10)
- Terbutaline SulfateDocumento2 páginasTerbutaline SulfateRhoellet VenzonAún no hay calificaciones
- Methergine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasMethergine Drug StudycuakialyannaAún no hay calificaciones
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento1 páginaGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonAún no hay calificaciones
- HYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)Documento1 páginaHYDRALAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE - (Apresoline)wen_pilAún no hay calificaciones
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaMethyldopa Drug Studychinchin ramosAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMaan Molinyawe81% (16)
- Folic AcidDocumento3 páginasFolic Acidapi-37979410% (1)
- Diclofenac SodiumDocumento3 páginasDiclofenac SodiumRichard Mendeja0% (1)
- OxytocinDocumento1 páginaOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263Documento2 páginasMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263AkiraMamo100% (1)
- Drug Study Form OxyDocumento3 páginasDrug Study Form OxyRyan OdioAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnesium SulfateDocumento2 páginasMagnesium SulfateCecilia Cenas Bendol100% (2)
- Methotrexate )Documento2 páginasMethotrexate )Angela Tenorio100% (2)
- Drug Study CytotecDocumento2 páginasDrug Study CytotecLuige Avila60% (10)
- TerbutalineDocumento1 páginaTerbutalineRyan Paul BalotAún no hay calificaciones
- Delivery Room Drug StudyDocumento11 páginasDelivery Room Drug StudyChinimansiAún no hay calificaciones
- Methergine Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasMethergine Drug StudyJj Delacruz0% (1)
- Drug Study OxytocinDocumento1 páginaDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanAún no hay calificaciones
- Nitric oxide inhalation gas for pulmonary hypertensionDocumento3 páginasNitric oxide inhalation gas for pulmonary hypertensionJinky Nacar DomingoAún no hay calificaciones
- OxytocinDocumento1 páginaOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocumento9 páginasOxytocin Drug StudyAyessah Mapa100% (1)
- Carboprost Drug Study for Postpartum Bleeding and AbortionDocumento4 páginasCarboprost Drug Study for Postpartum Bleeding and Abortionshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Drug Study - Nifedipine PODocumento1 páginaDrug Study - Nifedipine POJet BautistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocumento7 páginasDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoAún no hay calificaciones
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocumento3 páginas11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- Drug Study - KetoprofenDocumento3 páginasDrug Study - KetoprofenThalia UyAún no hay calificaciones
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Documento2 páginasDrug Study-Nifedipine-BALLON, Karlo C.Melinda Cariño Ballon100% (1)
- Hydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsDocumento1 páginaHydralazine hydrochloride: Antihypertensive drug generic name, brand name, indications, adverse effectsSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocumento2 páginasAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- Drug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and GastrointestinalDocumento64 páginasDrug Study Number 3 Repro.,respi and Gastrointestinaljamaica cabrigaAún no hay calificaciones
- Verapamil HCL Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasVerapamil HCL Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocumento2 páginasDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMonica Lyka BancaleAún no hay calificaciones
- Betamethasone (Drug Study)Documento4 páginasBetamethasone (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Generic Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)Documento3 páginasGeneric Name (Brand Name) Methergine (Methylergonovine Maleate)jennix_030883% (6)
- RitodrineDocumento4 páginasRitodrineMariquita BuenafeAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study PethidineDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Pethidinerica sebabillonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasMethyldopa Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (1)
- Drug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, SimvastatinDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Atenolol, Cefuroxime, Simvastatinpaupaulala100% (4)
- Metoprolol Drug StudyDocumento4 páginasMetoprolol Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaAún no hay calificaciones
- CARDIOVASCULARDocumento2 páginasCARDIOVASCULARAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study SalbutamolDocumento2 páginasDrug Study Salbutamolliza sian100% (2)
- Albuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Documento1 páginaAlbuterol (Ventolin, Salbutamol)Jocelyn Rivera100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento8 páginasDrug StudyApril Sarol67% (3)
- Ms Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CDocumento19 páginasMs Task Gomez Ellyza Syrelle CSyrelle GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Doctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityDocumento2 páginasDoctor's Circumcision Procedure Damages Child's Urethra Leading to Civil LiabilityIvanne Hisoler100% (1)
- LTD Finals Cases Batch 1Documento29 páginasLTD Finals Cases Batch 1Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- LTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Documento18 páginasLTD Cases Batch 2 (6.24.14)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Procedural Due Process Case DigestsDocumento8 páginasProcedural Due Process Case DigestsIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Digests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Documento1 páginaDigests (Canons 21-22 of CPR)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Documento31 páginasLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Land Titles Cases (6.21.14)Documento31 páginasLand Titles Cases (6.21.14)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Digests For Canons 10-13Documento6 páginasCase Digests For Canons 10-13Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- CONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Documento18 páginasCONTRACTS (Pre Finals)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Daily Assignment PlanDocumento2 páginasDaily Assignment PlanIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- The Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodDocumento17 páginasThe Decriminalization of Vagrancy by Christian MonsodIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Freedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsDocumento22 páginasFreedom of Expression, Assembly and Petition Case DigestsIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Contract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Documento3 páginasContract of Lease (Motor Vehicle)Ivanne Hisoler67% (6)
- Legal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Documento34 páginasLegal Ethics Codals (Rules 135-143)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Affidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Documento1 páginaAffidavit of Loss - (SSS ID)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Penicillin G BenzathineDocumento1 páginaPenicillin G BenzathineIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Case Digest (QC v. Ericta)Documento1 páginaCase Digest (QC v. Ericta)Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Constitutional Law I NotesDocumento59 páginasConstitutional Law I NotesIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Cases 1 15Documento11 páginasCases 1 15Ivanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Eminent Domain Case DigestsDocumento18 páginasEminent Domain Case DigestsIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Persons - Midterms NotesDocumento23 páginasPersons - Midterms NotesEvina Michaela LupangoAún no hay calificaciones
- Republic vs. Castellvi DigestDocumento1 páginaRepublic vs. Castellvi DigestIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Persons - Notes For MidtermsDocumento10 páginasPersons - Notes For MidtermsIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- Affidavit of Loss - CabrerosDocumento1 páginaAffidavit of Loss - CabrerosIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- OxytocinDocumento1 páginaOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Rgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchDocumento40 páginasRgaleon Consti1 - Cases 3rd BatchIvanne HisolerAún no hay calificaciones
- MetoclopramideDocumento1 páginaMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- MethotrexateDocumento2 páginasMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- RC Infant Flow LP NCPAP System Workbook UG enDocumento60 páginasRC Infant Flow LP NCPAP System Workbook UG enWandi PrasadhaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Project On CopdDocumento43 páginasA Project On CopdEric KhailahAún no hay calificaciones
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Uses, Types & Side EffectsDocumento5 páginasCalcium Channel Blockers: Uses, Types & Side EffectsOpio IsaacAún no hay calificaciones
- BM Sakharkar - Principles of Hospital Administration and Planning, 2nd Edition PDFDocumento394 páginasBM Sakharkar - Principles of Hospital Administration and Planning, 2nd Edition PDFNaMak89% (28)
- Cleft Lip and PalateDocumento91 páginasCleft Lip and PalatedrgreeshmahariniAún no hay calificaciones
- Facemask treatment of Class III malocclusionDocumento31 páginasFacemask treatment of Class III malocclusionNada EmadAún no hay calificaciones
- Pcrs Handbook For Dentists HSEDocumento58 páginasPcrs Handbook For Dentists HSESimona BudauAún no hay calificaciones
- Leptin and ObesityDocumento28 páginasLeptin and ObesityБаттөр ОтгонбатAún no hay calificaciones
- Retrieval of Unerupted Teeth in PedodonticsDocumento12 páginasRetrieval of Unerupted Teeth in PedodonticsMICO JAYAún no hay calificaciones
- MVU ReportDocumento33 páginasMVU Reportdash.prashanta86Aún no hay calificaciones
- Do Attention Span and Doodling Relate To Ability To Learn Content PDFDocumento4 páginasDo Attention Span and Doodling Relate To Ability To Learn Content PDFAiaa Wanas100% (1)
- A Power Point Presentation On Plant DiseaseDocumento19 páginasA Power Point Presentation On Plant DiseaseMurali Sambhu100% (1)
- Diabetic FootDocumento13 páginasDiabetic FootSafoora RafeeqAún no hay calificaciones
- POINT TrialDocumento27 páginasPOINT TrialRutaAún no hay calificaciones
- Anemia ChartDocumento1 páginaAnemia ChartBetsy Brown ByersmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiology An Illustrated Textbook (Jaypee) (PDF) (Tahir99) VRGDocumento2136 páginasCardiology An Illustrated Textbook (Jaypee) (PDF) (Tahir99) VRGGoglea Theodor94% (17)
- 12th English Book-2 S.QsDocumento33 páginas12th English Book-2 S.QsJawad Ahmed KhawajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Trauma and Its Impact Activity PacketDocumento38 páginasUnderstanding Trauma and Its Impact Activity PacketDeepika BhandariAún no hay calificaciones
- Healing Architecture Final ReportDocumento35 páginasHealing Architecture Final ReportAlisha PradhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Iv PediaDocumento2 páginasIv PediaDuane LilocAún no hay calificaciones
- Antisocial Personality Disorder ExplainedDocumento16 páginasAntisocial Personality Disorder ExplainedSiti Musliha100% (1)
- Laboratory Safety ProceduresDocumento72 páginasLaboratory Safety ProceduresRollin Navora PamintuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryDocumento34 páginasCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitati On (CPR) : 2.1 HistoryGurudas SwainAún no hay calificaciones
- PublishedmilkfeverDocumento22 páginasPublishedmilkfeverdarisAún no hay calificaciones
- The ABCDE Approach To Difficult Weaning From Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane OxygenationDocumento11 páginasThe ABCDE Approach To Difficult Weaning From Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenationjose luis iribarrenAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurnal Resesi Gingiva 6Documento6 páginasJurnal Resesi Gingiva 6Muhammad KholisAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Paper 4 Theory Samuel Sierra 11CDocumento22 páginasBiology Paper 4 Theory Samuel Sierra 11CGabriela TrujilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Anaesthesia For Non Cardiac Surgery in Children With Congenital Heart DiseaseDocumento12 páginasAnaesthesia For Non Cardiac Surgery in Children With Congenital Heart Diseasekadek gunadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurnal Skripsi Anestesi 4Documento8 páginasJurnal Skripsi Anestesi 4Tiara Anggun NurartoAún no hay calificaciones
- Resettlement and Rehabilitation of People: Its Problems and ConcernsDocumento3 páginasResettlement and Rehabilitation of People: Its Problems and ConcernsGourabAún no hay calificaciones