Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
CH 21 Gloss
Cargado por
api-91979209Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
CH 21 Gloss
Cargado por
api-91979209Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Page 1 of 2
2
0
0
8
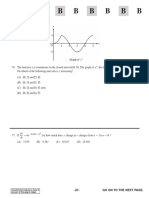
B
J
U
P
r
e
s
s
.
U
n
a
u
t
h
o
r
i
z
e
d
r
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
p
r
o
h
i
b
i
t
e
d
.
Glossary
Chapter 21Acids, Bases, and Salts
hydronium ion (p. 513) The cation formed by the self-ionization of water;
H3O
+
.
hydroxide ion (p. 513) The anion formed by the self-ionization of water;
OH
.
dynamic equilibrium (p. 513) The state of any two-way process in which the
concentration of particles remains relatively constant but the identity of the
individual particles constantly changes.
acid (p. 514) Any substance that donates hydrogen ions (protons, or H
+
),
according to the Brnsted-Lowry model; any substance that produces
hydronium ions (H3O
+
) in an aqueous solution, according to the Arrhenius
model. Other definitions of acids exist.
base (p. 515) Any substance that accepts hydrogen ions (protons, or H
+
),
according to the Brnsted-Lowry model; any substance that produces
hydroxide ions (OH
) in an aqueous solution, according to the Arrhenius
model. Other definitions of bases exist.
Arrhenius model (p. 515) One of the first useful models of acids and bases in
which acid compounds form hydronium ions (H3O
+
) in aqueous solutions
and bases form hydroxide ions (OH
) in aqueous solutions.
Brnsted-Lowry model (p. 515) A model of acids and bases (more complete
than the Arrhenius model) that defines acidity and alkalinity based on
hydrogen ion transfer. Acids donate hydrogen ions (H
+
, or protons), and
bases accept hydrogen ions.
monoprotic acid (p. 516) An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion.
polyprotic acid (p. 517) An acid that can donate two or more hydrogen ions.
conjugate base (p. 517) The proton acceptor produced after a Brnsted-
Lowry acid donates a proton.
conjugate acid (p. 518) The proton donor produced after a Brnsted-Lowry
base accepts a proton.
salt (p. 520) Any ionic compound that could be produced by the
combination of a base cation and an acid anion in a neutralization reaction.
neutralization reaction (p. 520) A reaction between an acid and a base. In
aqueous solutions, the products are a salt and water.
Chapter 21 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Page 2 of 2
2
0
0
8
B
J
U
P
r
e
s
s
.
U
n
a
u
t
h
o
r
i
z
e
d
r
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
o
n
p
r
o
h
i
b
i
t
e
d
.
pH scale (p. 525) A scale that indicates the acidity or alkalinity of a solution
based on the logarithm (an exponent of 10) of the hydronium ion
concentration in moles per liter. A pH of 7 is neutral, a pH of 0 is extremely
acidic, and a pH of 14 is extremely basic.
acidic (p. 525) Having a pH value less than 7.
alkaline (p. 525) Having a pH value greater than 7. Also called basic.
pH indicator (p. 526) Any substance, but often an organic compound, that
turns a specific color in a solution with a particular pH and that may be used
to determine the pH of a solution when used with other indicators.
pH meter (p. 527) An instrument designed to measure the pH of a solution,
using the electrical potential of the hydronium ions in the solution.
También podría gustarte
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- B.Tech Ist Year Syllabus PDFDocumento6 páginasB.Tech Ist Year Syllabus PDFsushil.vgiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Smoke SensorsDocumento15 páginasSmoke SensorsSatish HSAún no hay calificaciones
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Lecture 1-2 PDFDocumento49 páginasLecture 1-2 PDFASHISH MEENAAún no hay calificaciones
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- 4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - StuDocumento62 páginas4 - Rate Laws and Stoichiometry - StuTiệp MatícAún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Atomic Physics Solved Examples - AskIITiansDocumento3 páginasAtomic Physics Solved Examples - AskIITiansthiripura sundariAún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- 신소재과학 시험문제모음Documento9 páginas신소재과학 시험문제모음Hanjin SeoAún no hay calificaciones
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Electron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3Documento63 páginasElectron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3younessinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Rotameter Overview PDFDocumento8 páginasRotameter Overview PDFSteve Goke AyeniAún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- Me6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDocumento8 páginasMe6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionMohanraj SubramaniAún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- 11CD108 Plasticity and Metal Forming - First Series Test PART-A (9 X 2 18 Marks) Answer ALL QuestionsDocumento1 página11CD108 Plasticity and Metal Forming - First Series Test PART-A (9 X 2 18 Marks) Answer ALL Questionsselva_raj215414Aún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Hadron ColliderDocumento121 páginasHadron ColliderDeepak VermaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- NS 6145 Laser and LightDocumento69 páginasNS 6145 Laser and LightMeesixAún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- BC YES Calculator MCDocumento10 páginasBC YES Calculator MCbingfang wuAún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocumento7 páginasElectromagnetic WavesPerfectly Hacked100% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (345)
- Electrician Mostly Asked MCQ For RRB ALP PDFDocumento32 páginasElectrician Mostly Asked MCQ For RRB ALP PDFSajid Faniband100% (1)
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 2C - 3 Principal Axes and Principal Moments of InertiaDocumento3 páginasAerial Robotics Lecture 2C - 3 Principal Axes and Principal Moments of InertiaIain McCullochAún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Uce Physics Paper Two 3Documento7 páginasUce Physics Paper Two 3Okiror GeorgeAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Proceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeDocumento9 páginasProceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeTanzil ZaidiAún no hay calificaciones
- SEAM-Maths1-1.2 SD-Trigonometric Functions 28-8-19 SPCEDocumento13 páginasSEAM-Maths1-1.2 SD-Trigonometric Functions 28-8-19 SPCESatish BarotAún no hay calificaciones
- Compressor MaterialsDocumento4 páginasCompressor MaterialsAhmed HassanAún no hay calificaciones
- Higgs Lecture NotesDocumento48 páginasHiggs Lecture Noteszcapg17Aún no hay calificaciones
- HTLS Conductors - Mechanical CalculationDocumento25 páginasHTLS Conductors - Mechanical CalculationJorge Pinto RochaAún no hay calificaciones
- PHSC2112 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Remedial Exam WEWO!Documento10 páginasPHSC2112 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Remedial Exam WEWO!Christian PaulAún no hay calificaciones
- (C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)Documento459 páginas(C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)gog100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Year 10 Physics Holiday PackDocumento10 páginasYear 10 Physics Holiday Packivan micoAún no hay calificaciones
- Drying Introduction, DefinationDocumento15 páginasDrying Introduction, DefinationChintan ModiAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopDocumento30 páginasPharmaceutical Chemistry Answer Key Blue PacopJeannie UyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)