Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Intermolecular Force
Cargado por
swanderfeildDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Intermolecular Force
Cargado por
swanderfeildCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
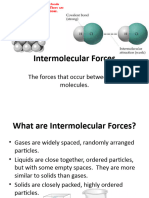
Intermolecular Forces
London forces
Exist between all atoms Size of force is relative to size of electron cloud Susceptible to distortion and electron density shifts (induced instantaneous dipoles)
Permanent Dipole
Polar molecules have permanent dipole.
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen must be bonded to Nitrogen, Florien, Oxygen atom to have hydrogen boning. There is 180 angle between two molecules. H bonds are the strongest intermolecular forces and give molecules unusually high melting and boiling points
Physical Properties in relation to intermolecular forces - Carbon chain length increases means boiling temperature increase because there are more London forces which requires more energy to break - Branching increases means boiling temp decreases as less overlap between chains so less London forces - Hydrogen bonds reduce volatility of molecules such as alcohols compared to alkanes, they are much stronger than London dispersion forces
Experiments into solubility by mixing various solvents together Ionic compounds are soluble in water as dipoles on water bond with the oppositely charged ions Alcohols are also soluble in water due to the ability to Hydrogen bond although increase in Carbon chain length, decrease in solubility Polar and non-polar solvents are immiscible as forces present before mixing do not equal the potential for new forces. Compounds are only soluble in solvents which have similar intermolecular forces
También podría gustarte
- 15chy1001c C PDFDocumento32 páginas15chy1001c C PDFhrAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 5 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocumento12 páginasLesson 5 Intermolecular Forces of AttractionJames BagsikAún no hay calificaciones
- Thermochemistry 1 (Intermolecular Forces) - 2022Documento16 páginasThermochemistry 1 (Intermolecular Forces) - 2022GloryAún no hay calificaciones
- Semester 2 Chem NotesDocumento10 páginasSemester 2 Chem NotesClayton FengAún no hay calificaciones
- Water Notes: Syllabus Dot Point Notes/InformationDocumento9 páginasWater Notes: Syllabus Dot Point Notes/InformationClayton FengAún no hay calificaciones
- Covalent Compound PropertiesDocumento31 páginasCovalent Compound PropertiesApril Mae BaldozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrogen Bonding: Yoshita - O Level CandidateDocumento31 páginasHydrogen Bonding: Yoshita - O Level CandidateYoshitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento28 páginasIntermolecular ForceskarjackerAún no hay calificaciones
- London Dispersion ForcesDocumento4 páginasLondon Dispersion Forceskimdaniel2006Aún no hay calificaciones
- F332 Notes (Polymer Revolution)Documento7 páginasF332 Notes (Polymer Revolution)Becky Tenney67% (3)
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocumento19 páginasIntermolecular Forces of AttractionNickolai AntoineAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is Hydrogen BondingDocumento6 páginasWhat Is Hydrogen BondingKate MagpayoAún no hay calificaciones
- Self-Check 1.1Documento12 páginasSelf-Check 1.1Justine AmarantoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Bonding IIDocumento7 páginasChemical Bonding IIdanielmahsaAún no hay calificaciones
- Boiling Point NotesDocumento7 páginasBoiling Point NotesJozelle GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.4 Intermolecular Forces: Topic 4: Chemical Bonding & StructureDocumento42 páginas4.4 Intermolecular Forces: Topic 4: Chemical Bonding & StructurePatrick AbidraAún no hay calificaciones
- Summary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.5 Intermolecular BondingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Chemistry Textbook - Section 2.5 Intermolecular BondingRachel JeffresonAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.4 Intermolecular Forces: Topic 4: Chemical Bonding & StructureDocumento41 páginas4.4 Intermolecular Forces: Topic 4: Chemical Bonding & Structureapi-546066323Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Unit 2 Part 2 ReallyacademicsDocumento26 páginasChemistry Unit 2 Part 2 ReallyacademicsWill Andy100% (1)
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento24 páginasIntermolecular ForcesEvangelene Esquillo SanaAún no hay calificaciones
- States of Matter - 1211 (Download)Documento20 páginasStates of Matter - 1211 (Download)Mahlodi LamolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - Online NotesDocumento9 páginasChapter 2 - Online NotesJasleen KaurAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento16 páginasIntermolecular Forcesmaricon pocheAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento14 páginasIntermolecular ForcesNisidini JasingheAún no hay calificaciones
- Finals ReviewerDocumento5 páginasFinals ReviewerARIAR, Jyllianne Kyla C.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Module 1Documento10 páginasModule 1Aira Bauzon ValerioAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.7 Intermolecular ForcesDocumento5 páginas4.7 Intermolecular ForcesrachpAún no hay calificaciones
- Gen Chem 2 M1bDocumento7 páginasGen Chem 2 M1bJohndee Mozart Dela CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento4 páginasIntermolecular ForcesAgathaAún no hay calificaciones
- IMF's of Attraction Solid, Liquid and GasesDocumento18 páginasIMF's of Attraction Solid, Liquid and GasesMark John GuardamanoAún no hay calificaciones
- General Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saDocumento25 páginasGeneral Chemistry: Dr. Rabih O. Al-Kaysi Ext: 47247 Email: Kaysir@ksau-Hs - Edu.saapi-1982440650% (2)
- ChemDocumento5 páginasChemkerwin OligarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Inorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsDocumento40 páginasInorganic Biological Molecules - Water 0 MineralsjonAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento4 páginasIntermolecular ForcesKineticsAún no hay calificaciones
- WWPWPWDocumento30 páginasWWPWPWRaven LampaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Chemistry Unit 4Documento31 páginas1 - Chemistry Unit 4shirley wang100% (1)
- Intermolecular Forces: Chemistry Mrs. CoyleDocumento17 páginasIntermolecular Forces: Chemistry Mrs. CoyleTiqa AbdullahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2Documento6 páginasChapter 2Idk UlitAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocumento10 páginasIntermolecular Forces of AttractionRaisa TayagAún no hay calificaciones
- SCH 4U - Bonds Properties of Organic CompoundsDocumento31 páginasSCH 4U - Bonds Properties of Organic CompoundsDajour CollinsAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Intermolecular ForcesDocumento17 páginas7 Intermolecular ForcesfathmathfaiherAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.1 Bio400Documento15 páginas2.1 Bio400Siti Asyura Aina Saiful AzharAún no hay calificaciones
- Alcohols: The Physical Properties of AlcoholsDocumento6 páginasAlcohols: The Physical Properties of AlcoholsKimberly A. S. SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Notes q2Documento8 páginasScience Notes q2itohtomoka017Aún no hay calificaciones
- CHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceDocumento20 páginasCHM02 - CO1 - LESSON2 - Intermolecular ForceMeg IglianeAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento17 páginasIntermolecular ForcesNursherina AsanjiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Water As Universal Solvent and CoolentDocumento10 páginas2 Water As Universal Solvent and CoolentZaifi KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular ForcesDocumento57 páginasIntermolecular ForcesCherilou ConchaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter #4 Chapter #4 Chapter #4: Liquids and Solids Liquids and Solids Liquids and SolidsDocumento34 páginasChapter #4 Chapter #4 Chapter #4: Liquids and Solids Liquids and Solids Liquids and SolidsStatus LandAún no hay calificaciones
- Liquids and Water Properties: Material Science & Chemistry Week Seven LectureDocumento21 páginasLiquids and Water Properties: Material Science & Chemistry Week Seven LectureIbrahim AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Weak ForcesDocumento17 páginasWeak Forcesbiri.melisa.105Aún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and SolidsDocumento47 páginasIntermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solidsapi-683027695Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Sections 11.1 - 11.3Documento82 páginasChapter 11 Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids: Sections 11.1 - 11.3Michael MaglaqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESDocumento2 páginasLesson 3. INTERMOLECULAR FORCESmariaisabelmatala22Aún no hay calificaciones
- Properties of WaterDocumento5 páginasProperties of Wateraeriel23Aún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento8 páginasUntitledWaggle The GreatAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormDocumento2 páginasCarbon Is of Immense Significance To Us in Both Its Elemental Form and in The Combined FormkalloliAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 4 - 18.11.2022Documento18 páginasLecture 4 - 18.11.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.5 Physical Properties: Syllabus StatementsDocumento1 página4.5 Physical Properties: Syllabus StatementsBreeSchuchAún no hay calificaciones
- We Are All Managers Now... NotesDocumento4 páginasWe Are All Managers Now... NotesswanderfeildAún no hay calificaciones
- Edexcel GCE: Wednesday 19 January 2005 Morning Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocumento6 páginasEdexcel GCE: Wednesday 19 January 2005 Morning Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesswanderfeildAún no hay calificaciones
- Absorption of Beta Radiation: ApparatusDocumento1 páginaAbsorption of Beta Radiation: ApparatusswanderfeildAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.4, 4.5 TestDocumento9 páginas4.4, 4.5 TestezajihaAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsDocumento9 páginas4.4, 4.5 Exam Questions MsswanderfeildAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.6, 4.7 Exam QuestionsDocumento32 páginas4.6, 4.7 Exam QuestionsswanderfeildAún no hay calificaciones
- Edexcel GCE Core 1 Mathematics C1 May 2005 6663/01 Question PaperDocumento24 páginasEdexcel GCE Core 1 Mathematics C1 May 2005 6663/01 Question Paperrainman875Aún no hay calificaciones