Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Problem Based
Cargado por
api-189549713Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Problem Based
Cargado por
api-189549713Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
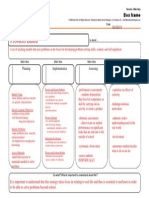
Hierarchic: 4 Main Ideas
Side ideas
Makes Sense Strategies
2008 Edwin Ellis, All Rights Reserved Published by Makes Sense Strategies, LUC, Notthport, AL www.MakesSenseStrategies.com
Name: Charity Smoot
Date: February 21, 2013
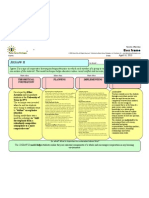
PROBLEM-BASED LEARNING MODEL
Is about...
Problem-Based Learning is an instructional method that challenges students to "learn to learn". It consists of carefully selected and designed problems that demands from the learner, an acquisition of critical knowledge, problem-solving proficiency, self-directed learning strategies, and team participation skills.
THEORITICAL FOUNDATION
Developed by Howard Barrows and his colleagues at AAcMaster University (medical school) in the late 1960's Barrows defined Problem-Based Learning as, "the learning that results from the process of working towards the understanding of a resolution of a problem". A.K.A="ACTIVE LEARNING" Student-centered
PLANNING
A
-Identify Topic-Teachers should choose a topic that is more "complex and abstract" because these topics don't have specific characteristics -Specify Learning Objectives=AAust have (2) types of objectives for your students. 1) The goal that you are trying to get the students to reach and 2) The experiences that promote their development/problem-solving skills...In order for this to work, students must encounter mistakes and struggle to find the answer. -Identify Problems=Aftake sure the students have some type of connection to the problem so that they can effectively design a strategy for solving it. Providing your students with any random problem will not ensure that they will become successful problem-solvers so therefore, teachers need to assign problems that are student-related. -Access Materials=Students must have access to the materials needed to solve the problem; Group collaboration is encouraged just in case there are not enough materials available for every student. (<Make sure all students are participating)
IMPLEMENTING
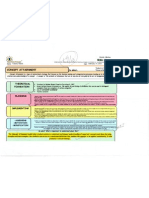
-Review and Present Problem^ The teacher reviews the prior knowledge needed to solve the problem and presents the students with a specific, concrete problem to solve/Problems can be "well-defined" or "ill-defined" depending on the teacher's choiceVForm Heterogeneous groups -Devise a Strategy=Students develop a strategy for solving the problem (Teacher must be sure to provide enough guidance so that the students don't waste time) -Implement the Strategy=5tudents carry out their strategies to solve the problem (Teacher provides instructional support that helps the students complete tasks that they were unable to complete on their own). -Discuss and Evaluate Results= Teacher asks students to access the validity of their solutions while she/he guides a discussion of the students' efforts and the results that they find
-ASSESSING -MOTIVATION MODIFICATION
Teachers can assess the students by performance assessments (measures knowledge and skill), systematic observations (assess students' strengths and weaknesses), checklists ("checks off the desired goal when it is met), and rating scales (measures the degree of success). Students are motivated by curiosity, challenge, real world examples, student involvement, and the ability to be independent. Teachers can modify the skill with younger children by presenting problems that are clear, concrete, and personalized while providing them with the guidance needed to successfully solve the problem. Also, make sure that the students have enough background information before beginning the lesson.
_L
So what? What is important to understand about this?
The Problem-Based Learning model helps students develop flexible knowledge, effective problem-solving skills, self-directed learning, effective collaboration skills, and intrinsic motivation which all encourage Students to become independent workers, critical thinkers, and lifelong learners.
También podría gustarte
- Human Growth and Development Mar2016 Answer KeyDocumento11 páginasHuman Growth and Development Mar2016 Answer KeyZen Dalina Daza100% (2)
- The Growth Mindset Classroom-Ready Resource Book: A Teacher's Toolkit for For Encouraging Grit and Resilience in All StudentsDe EverandThe Growth Mindset Classroom-Ready Resource Book: A Teacher's Toolkit for For Encouraging Grit and Resilience in All StudentsAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Plan On PBLDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan On PBLramtenki sreelekha100% (1)
- Savery y Duffy (1996) Problem Based Learning An Instructional Model and Its Constructivist FrameworkDocumento16 páginasSavery y Duffy (1996) Problem Based Learning An Instructional Model and Its Constructivist FrameworkjuanamaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem-Based ModelDocumento1 páginaProblem-Based Modelapi-225717058Aún no hay calificaciones
- Caitlin Magee Problem-Based Learning MatrixDocumento1 páginaCaitlin Magee Problem-Based Learning Matrixapi-241421790Aún no hay calificaciones
- Instructional PlanningDocumento7 páginasInstructional PlanningErica JambonganaAún no hay calificaciones
- P Based LearningDocumento8 páginasP Based LearningPdianghunAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Solving MethodDocumento21 páginasProblem Solving MethodBhaskar TupteAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Based MatrixDocumento1 páginaProblem Based Matrixapi-225990873Aún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 6 - Introduction To Principles and Strategies of TeachingDocumento7 páginasCHAPTER 6 - Introduction To Principles and Strategies of TeachingApenton MimiAún no hay calificaciones
- Teaching Learning ProcessDocumento17 páginasTeaching Learning ProcessJyoti Verma Jv100% (1)
- Other Teaching Strategies and Supplementary Methods Math 7 10Documento14 páginasOther Teaching Strategies and Supplementary Methods Math 7 10Nelmida, Henriane P.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Robby Problem-BasedDocumento1 páginaRobby Problem-Basedapi-240269666Aún no hay calificaciones
- StadDocumento1 páginaStadapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hand OutDocumento11 páginasHand OutGlensky Nadz NumbarAún no hay calificaciones
- TTL Group 2 Beed 3DDocumento50 páginasTTL Group 2 Beed 3DÇhřiśtïán Đąvə Łaýuğ IIAún no hay calificaciones
- Role of Teacher in Teaching Problem-Solving SkillsDocumento7 páginasRole of Teacher in Teaching Problem-Solving SkillsAnonymous CwJeBCAXpAún no hay calificaciones
- Educ 108Documento38 páginasEduc 108Jhomela MarcellanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 4 Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingDocumento5 páginasLesson 4 Critical Thinking and Problem SolvingrohanZorbaAún no hay calificaciones
- Educators File Year 2003Documento4 páginasEducators File Year 2003sszmaAún no hay calificaciones
- AssessmentDocumento3 páginasAssessmentKrisel TadtadAún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Guided Discovery MatrixDocumento1 páginaRevised Guided Discovery Matrixapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Teaching Strategies - For TeachersDocumento28 páginasTeaching Strategies - For TeachersNicole Powys100% (2)
- Guided DiscoveryDocumento1 páginaGuided Discoveryapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Crafting The Curriculum REVIEWDocumento21 páginasCrafting The Curriculum REVIEWBernard Vincent Guitan MineroAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem SolvingDocumento8 páginasProblem SolvingJils SureshAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment WednesdayDocumento1 páginaAssignment WednesdayKaren OfalsaAún no hay calificaciones
- Beyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTDocumento24 páginasBeyond Behavioral ObjectivesREPORTeugene louie ibarraAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem-Based ModelDocumento1 páginaProblem-Based Modelapi-239390438Aún no hay calificaciones
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocumento36 páginasStudent Directed Learning Strategiesyhanne100% (17)
- Problem Solving MethodDocumento17 páginasProblem Solving MethodATHIRA MOHAN50% (2)
- Madeline Hunter Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasMadeline Hunter Lesson PlanJade EranaAún no hay calificaciones
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocumento36 páginasStudent Directed Learning StrategiesSenthil Kumar100% (1)
- Strategies in Teaching TLEDocumento13 páginasStrategies in Teaching TLELara Ortaleza100% (1)
- Attitudes Towards Profession, Teaching Strategies, Teacher Indirectness and Classroom PerformanceDocumento24 páginasAttitudes Towards Profession, Teaching Strategies, Teacher Indirectness and Classroom PerformanceJoann Jacob100% (1)
- Questioning and Feedback: Method, But It Is Concerned in A More General Sense With The Way inDocumento11 páginasQuestioning and Feedback: Method, But It Is Concerned in A More General Sense With The Way inVildana NeslanovićAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrative ReviewerDocumento16 páginasIntegrative ReviewerSheila Mae CaballaAún no hay calificaciones
- Learner-Centered Instructional Strategies Group4 SoftDocumento7 páginasLearner-Centered Instructional Strategies Group4 SoftMa. Angelika Mejia100% (2)
- Approaches To Teaching and Learning (Part 1Documento17 páginasApproaches To Teaching and Learning (Part 1Kai BrightAún no hay calificaciones
- GD RevisedDocumento1 páginaGD Revisedapi-256532643Aún no hay calificaciones
- Habits of MindDocumento1 páginaHabits of Mindapi-548756435Aún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Based Learning: I. DefinitionDocumento6 páginasProblem Based Learning: I. DefinitionsadiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 11 MSC 1a4Documento27 páginasChapter 11 MSC 1a4Ram PalacioAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem SolvingDocumento6 páginasProblem SolvingTINJU123456Aún no hay calificaciones
- Group 3 Tegr 113Documento42 páginasGroup 3 Tegr 113Nicole Kate AsisAún no hay calificaciones
- Motivation As Expectancy × Value Reasoning, Often Within A Social ContextDocumento8 páginasMotivation As Expectancy × Value Reasoning, Often Within A Social ContextFajar MartaAún no hay calificaciones
- Educ 8 Lesson 2Documento5 páginasEduc 8 Lesson 2Jamira Inoc SoboAún no hay calificaciones
- Direct InstructionDocumento1 páginaDirect Instructionapi-300935840Aún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Based LearningDocumento1 páginaProblem Based Learningapi-300977721Aún no hay calificaciones
- Teaching MethodsDocumento45 páginasTeaching MethodsRyry Lee0% (1)
- Curriculum and Instruction (6503) : ANS Instructional MethodsDocumento11 páginasCurriculum and Instruction (6503) : ANS Instructional Methodskabeer anjumAún no hay calificaciones
- Guided Discovery ModelDocumento1 páginaGuided Discovery Modelapi-239390438Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wa0002.Documento14 páginasWa0002.pritidinda3070Aún no hay calificaciones
- SDM Institute of Nursingsciences Sattur, DharwadDocumento42 páginasSDM Institute of Nursingsciences Sattur, DharwadSavita HanamsagarAún no hay calificaciones
- Teacher Self-Assessment of Current Practices in Math ClassDocumento2 páginasTeacher Self-Assessment of Current Practices in Math ClassCristina Gabriela BrănoaeaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nature of Problem Based and Project Based TTL Maam Princes - 010249Documento24 páginasNature of Problem Based and Project Based TTL Maam Princes - 010249Princes Gado LuarcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Approachestocurriculumdesign 140614015628 Phpapp02Documento8 páginasApproachestocurriculumdesign 140614015628 Phpapp02ROSANA OBLIGARAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Solving MethodDocumento5 páginasProblem Solving MethodArash ErshadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Inquiry Based Learning and Its NatureDocumento6 páginasInquiry Based Learning and Its NatureOniel FajardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Sheeba Javed Roll Number: CB567532 Subject Name: Curriculum and Instruction Course Code: 6503 Date: 7 Semester Terminal ExamDocumento9 páginasName: Sheeba Javed Roll Number: CB567532 Subject Name: Curriculum and Instruction Course Code: 6503 Date: 7 Semester Terminal ExamNauman JavedAún no hay calificaciones
- Learning & Study Guide for Adult StudentsDe EverandLearning & Study Guide for Adult StudentsAún no hay calificaciones
- Student Teaching-Autism Lesson PlansDocumento11 páginasStudent Teaching-Autism Lesson Plansapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- DR Seussunitlessonplans (Final)Documento18 páginasDR Seussunitlessonplans (Final)api-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Guided Discovery MatrixDocumento1 páginaRevised Guided Discovery Matrixapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- "I Am Somebody" Black History Unit Lesson Plans Week(s) of February 2 and February 9 (2015) Charity A.C. SmootDocumento21 páginas"I Am Somebody" Black History Unit Lesson Plans Week(s) of February 2 and February 9 (2015) Charity A.C. Smootapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Permission Slip For Videos and PicturesDocumento1 páginaPermission Slip For Videos and Picturesapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Charity Smoot ResumeDocumento2 páginasCharity Smoot Resumeapi-189549713100% (1)
- DR Seussweek-LettertoparentsDocumento1 páginaDR Seussweek-Lettertoparentsapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Concept Attainment MatrixDocumento1 páginaRevised Concept Attainment Matrixapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Charity Smoot-Electronic Notebook Reflection PaperDocumento3 páginasCharity Smoot-Electronic Notebook Reflection Paperapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-Direct InstructionDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Direct Instructionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Discussion MatrixDocumento1 páginaRevised Discussion Matrixapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-Lecture DiscussionDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Lecture Discussionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Jigsaw MatrixDocumento1 páginaRevised Jigsaw Matrixapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-Problem-BasedDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Problem-Basedapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-JigsawDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Jigsawapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-InquiryDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Inquiryapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-IntegrativeDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Integrativeapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-Concept AttainmentDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Concept Attainmentapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- InquiryDocumento1 páginaInquiryapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-Guided DiscoveryDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Guided Discoveryapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-DiscussionDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Discussionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture DiscussionDocumento1 páginaLecture Discussionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- What I Like-StadDocumento1 páginaWhat I Like-Stadapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Direct InstructionDocumento1 páginaDirect Instructionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Concept AttainmentDocumento1 páginaConcept Attainmentapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- DiscussionDocumento1 páginaDiscussionapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- IntegrativeDocumento1 páginaIntegrativeapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guided DiscoveryDocumento1 páginaGuided Discoveryapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- StadDocumento1 páginaStadapi-189549713Aún no hay calificaciones
- HDPS 1303 - 930425105424Documento6 páginasHDPS 1303 - 930425105424Cheryl LimAún no hay calificaciones
- Artificial IntelligenceDocumento11 páginasArtificial IntelligenceInma Polo Tengoganasdefiesta100% (1)
- Fundamental Interpersonal Relations Orientation-Behaviour (FIRO-B)Documento7 páginasFundamental Interpersonal Relations Orientation-Behaviour (FIRO-B)VishnuChaithanyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Authors:: Wali Zahid & Leadership Readiness Class (2006) MBA / MS - SZABIST, KarachiDocumento38 páginasAuthors:: Wali Zahid & Leadership Readiness Class (2006) MBA / MS - SZABIST, Karachimaharajsaini4229Aún no hay calificaciones
- Systems Theory - Critique PaperDocumento6 páginasSystems Theory - Critique PaperJFSAún no hay calificaciones
- Models of Curriculum: Mrutyunjaya Mishra Lecturer, H.IDocumento51 páginasModels of Curriculum: Mrutyunjaya Mishra Lecturer, H.IBea Alyssa Galzote Bautista100% (1)
- Adoption TheoriesDocumento31 páginasAdoption TheoriesAnup KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- The Roles and Functions of A Nurse: Estigoy, Allain B. 02/21/11 BSN-4B NCM-105 Quiz 3 FinalsDocumento3 páginasThe Roles and Functions of A Nurse: Estigoy, Allain B. 02/21/11 BSN-4B NCM-105 Quiz 3 FinalsAnthony MarkAún no hay calificaciones
- Leadership and Management: Section 1 Group 11Documento19 páginasLeadership and Management: Section 1 Group 11Prachi GargAún no hay calificaciones
- Braidotti The Posthuman-LibreDocumento4 páginasBraidotti The Posthuman-LibreAnaMateusAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To CommunicationDocumento88 páginasIntroduction To CommunicationDiana Burns50% (2)
- A Me Culture Paper 2002Documento15 páginasA Me Culture Paper 2002Youssef AlyAún no hay calificaciones
- Watson Theory PaperDocumento9 páginasWatson Theory Paperapi-285171922Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gilbert Ryle Gilbert RyleDocumento2 páginasGilbert Ryle Gilbert RyleHannahAún no hay calificaciones
- Barriers To Communication and Principles For Effective CommunicationDocumento12 páginasBarriers To Communication and Principles For Effective Communicationpoojadixit9010Aún no hay calificaciones
- Psychoanalytic Therapy - Group 1Documento2 páginasPsychoanalytic Therapy - Group 1Ivy BarrionAún no hay calificaciones
- Person Centered TherapyDocumento4 páginasPerson Centered Therapysusanwhitten100% (2)
- SEO Jun Won - SeoulDocumento12 páginasSEO Jun Won - SeoulKatherine ElviraAún no hay calificaciones
- Path Goal TheoryDocumento1 páginaPath Goal TheoryMegat PngAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment in Secondary Social Studies: Michael P. ValeDocumento22 páginasAssessment in Secondary Social Studies: Michael P. ValeMaJoy Dela CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study On What Makes The Employee Unhappy at The WorkplaceDocumento2 páginasCase Study On What Makes The Employee Unhappy at The WorkplaceBhavitha MurthyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cognitive Bias ModifedDocumento3 páginasCognitive Bias ModifedShahid KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Nestle - ZakaDocumento34 páginasNestle - ZakazakavisionAún no hay calificaciones
- Gestalt PsychologyDocumento2 páginasGestalt PsychologyEzekiel D. Rodriguez100% (2)
- David AusubelDocumento18 páginasDavid AusubelViviana P. Sanchez100% (1)
- Behavior & AttitudesDocumento28 páginasBehavior & AttitudesWafiy Akmal100% (1)
- Inter SubjectivityDocumento24 páginasInter SubjectivityJayson Dela Torre Cortes63% (16)
- Leaders Are MadeDocumento2 páginasLeaders Are Made11458Aún no hay calificaciones